Codeforces Round #541 F. Asya And Kittens
题面:
题目描述:
题目分析:
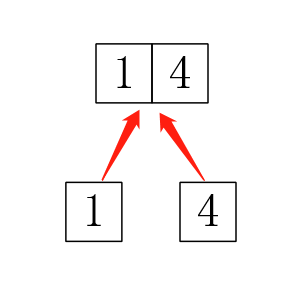
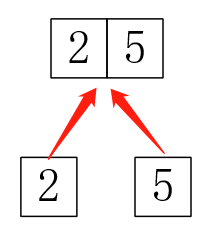
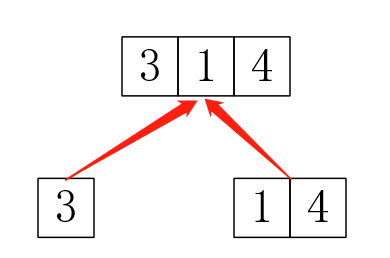
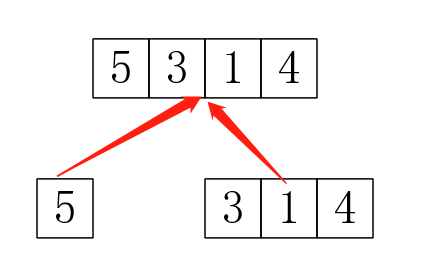
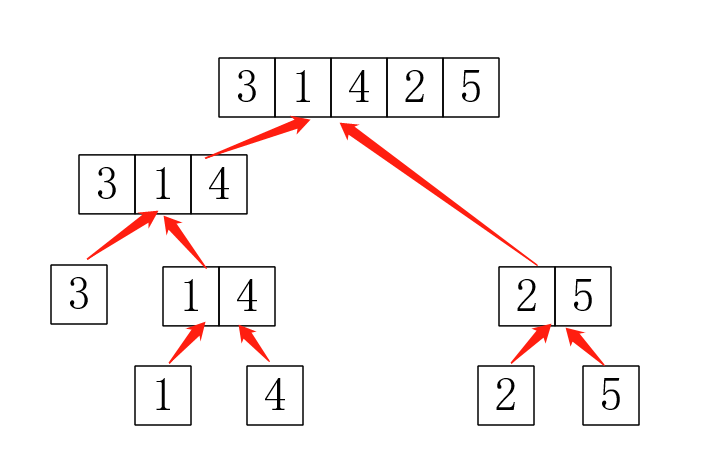
所以问题来了,第一:对于合并3,1我怎么知道是要合并3和1,4,而不是只合并3和1,把4抛弃?这时就要用到并查集,我们可以写一个并查集,查什么呢?当然是查在哪个隔间,然后把两个隔间合并。第二:这个好像只是模拟这个过程啊,怎样保存结果?其中一种做法就是给隔间分配额外的编号,把这个树(记得存树是存树的编号)存下来,然后用递归遍历一次就可以输出结果了(记得这时并查集查的是隔间的编号)。树:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> //万能头文件
2 using namespace std;
3 const int maxn = 150000 + 5;
4 int n;
5 int sets[2*maxn], L_node[2*maxn], R_node[2*maxn];
6
7 int F(int x){ //查
8 if(sets[x] == x || !sets[x]) return x;
9 return sets[x] = F(sets[x]);
10 }
11
12 void print(int x){ //输出答案
13 if(x <= n) printf("%d ", x);
14 else {
15 print(L_node[x]);
16 print(R_node[x]);
17 }
18 }
19
20 int main(){
21 cin >> n;
22 int id = n; //隔间编号
23 int x, y;
24 for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++){
25 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
26 x = F(x); //查
27 y = F(y);
28 sets[x] = sets[y] = ++id; //并
29 L_node[id] = x; //记录在哪个隔间
30 R_node[id] = y;
31 }
32 print(id);
33 return 0;
34 }
大佬的代码:(好像用数组模拟链表实现)
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> //万能头文件
2 using namespace std;
3 const int maxn = 150000 + 5;
4 int n;
5 int sets[maxn], G[maxn], last[maxn];
6
7 int F(int x){ //查
8 if(sets[x] == x) return x;
9 return sets[x] = F(sets[x]);
10 }
11
12 int main(){
13 cin >> n;
14 int x, y;
15
16 //初始化
17 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
18 sets[i] = i;
19 last[i] = i;
20 }
21
22 for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++){
23 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
24 x = F(x);
25 y = F(y);
26 G[last[x]] = y; //x的末尾一个元素接y
27 last[x] = last[y]; //x的末尾一个元素更新为y的末尾一个元素
28 sets[y] = x; //并, 且x为代表元
29 }
30
31 for(int i = F(1); i; i = G[i]){
32 scanf("%d ", i);
33 }
34 return 0;
35 }
Codeforces Round #541 F. Asya And Kittens的更多相关文章
- codeforces #541 F Asya And Kittens(并查集+输出路径)
F. Asya And Kittens Asya loves animals very much. Recently, she purchased nn kittens, enumerated the ...
- Codeforces #541 (Div2) - F. Asya And Kittens(并查集+链表)
Problem Codeforces #541 (Div2) - F. Asya And Kittens Time Limit: 2000 mSec Problem Description Inp ...
- Codeforces 1131 F. Asya And Kittens-双向链表(模拟或者STL list)+并查集(或者STL list的splice()函数)-对不起,我太菜了。。。 (Codeforces Round #541 (Div. 2))
F. Asya And Kittens time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #541 (Div. 2) D(并查集+拓扑排序) F (并查集)
D. Gourmet choice 链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/1131/problem/D 思路: = 的情况我们用并查集把他们扔到一个集合,然后根据 > ...
- Codeforces Round #541 (Div. 2) (A~F)
目录 Codeforces 1131 A.Sea Battle B.Draw! C.Birthday D.Gourmet choice(拓扑排序) E.String Multiplication(思路 ...
- Codeforces Round #541 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #541 (Div. 2) http://codeforces.com/contest/1131 A #include<bits/stdc++.h> us ...
- Codeforces Round #541
因为这次难得不在十点半(或是更晚),大家都在打,然后我又双叒叕垫底了=.= 自己对时间的分配,做题的方法和心态还是太蒻了,写的时候经常写一半推倒重来.还有也许不是自己写不出来,而是在开始写之前就觉得自 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 40 F. Runner's Problem
Educational Codeforces Round 40 F. Runner's Problem 题意: 给一个$ 3 * m \(的矩阵,问从\)(2,1)$ 出发 走到 \((2,m)\) ...
- F. Asya And Kittens并查集
F. Asya And Kittens time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
随机推荐
- hautoj 1268 小天使改名
1268: 小天使改名 时间限制: 2 秒 内存限制: 128 MB提交: 437 解决: 123提交 状态 题目描述 小天使的b站帐号被大家发现啦.于是小天使决定改名,将他原有ID中的两个不同位 ...
- element ui 渲染超过上百条数据时页面卡顿,更流畅的加载大量数据
问题:element ui table渲染上百条数据,页面渲染开始出现延时 解决方案:使用pl-table 注意:设置use-virtual并给定table高度
- Google Developer Profile
Google Developer Profile https://google.dev/u/me https://google.dev/u/109030792841960772125 Google D ...
- jest all in one
jest all in one ES Modules & TypeScript & React https://github.com/xgqfrms/FEAT/tree/master/ ...
- vue & vue router & match bug
vue & vue router & match bug match bugs solution name must be router https://stackoverflow.c ...
- react hooks & component will unmount & useEffect & clear up
react hooks & component will unmount & useEffect & clear up useEffect & return === u ...
- Flutter Navigator2.0
Example 1 import 'package:dart_printf/dart_printf.dart'; import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; cla ...
- 用Qt写了个将视频设置为壁纸的软件
软件功能很简单,使用时占用的资源和播放的视频有关: 依赖于FFplay,Github源码 效果图:
- Flutter 区分开发环境和生产环境
Uri _baseUrl; final isProd = const bool.fromEnvironment('dart.vm.product'); if (isProd) { _baseUrl = ...
- Laravel Queues 队列应用实战
队列,顾名思义,排着队等着做事情.在生活场景中,凡是排队的人,都是带有目的性的.要完成某件事情,才去排队的,要不没有谁会闲到排队玩儿.而在软件应用层面,队列是什么,队列有什么优点,我们什么时候需要用队 ...
