C++ 双链表基本操作
上一篇博客主要总结了单向链表,这次再总结一下双向链表.
1.概念
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。
结构图如下所示:
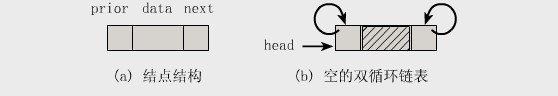
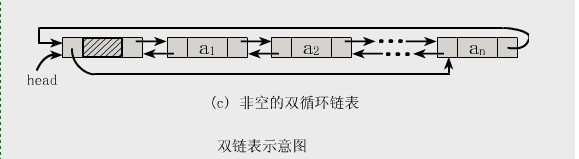
2.基本操作实例
DoubleList.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "DoubleList.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
DoubleList::DoubleList()
{
pDoubleListNode pDouList = NULL;
// 创建双链表
CreateDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 打印逆序链表
PrintDouReverseList(pDouList);
// 节点后插入节点
InsertNodeAfter(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 节点前插入节点
InsertNodeBefore(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除节点
DeleteNode(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除链表
DeleteDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
system("PAUSE");
}
DoubleList::~DoubleList()
{
}
//创建双向链表
void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
char x; // 定义成char型是用于输入'q'时可以退出,其实定义成int也能退出
pDoubleListNode p, s;
head = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
head->next = NULL;
head->prior = NULL; // 构造头结点p
p = head;
printf("\n输入双向链表的元素,每输入一个元素后按回车,输入q表示结束.\n");
fflush(stdin); //清空输入缓冲区
x = getchar();
while (x != 'q')
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = x - ''; // 得到的是输入字符的ASCII码,减去30H就变成想要的数字
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
p = s;
fflush(stdin);
x = getchar();
}
if (x == 'q')
{
printf("双向链表构造完毕!\n");
}
}
//打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf("\n打印出双向链表数据为:\n");
if (!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while (p)
{
printf("%d\n", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
}
//逆序打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf("\n打印出逆序双向链表数据为:\n");
if (!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while (p->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
while (p->prior)
{
printf("%d \n", p->data);
p = p->prior;
}
}
}
//求链表长度
int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int length = ;
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p = head->next;
while (p)
{
length++;
p = p->next;
}
}
return length;
}
//判断链表是否为空
bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
return true;
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!\n");
return true;
} return false;
}
//把双向链表置空
void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p, q;
p = q = head->next; //是p、q指向第一个元素
head->next = NULL;
while (p) //逐个释放元素所占内存
{
p = p->next;
free(q);
q = p;
}
}
}
// 删除双向链表
void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
printf("\n删除双向链表\n");
ClearDouList(head);
free(head);
head = NULL;
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int i = ;
printf("\n在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素\n");
printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n");
scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, );
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n");
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + )
{
printf("插入位置错误!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == GetDouListLength(head)) //如果在最后一个元素后面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = s;
p->next = s;
s->prior = p;
}
}
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int i = ;
printf("\n在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素\n");
printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n");
scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, );
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n");
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + )
{
printf("插入位置错误!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == ) // 如果在第一个元素前面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
s->prior = head; // 新结点的前结点指向头结点
s->next = p; // 新结点的后结点指向原head的后结点
p->prior = s ; // 原第一个结点的前结点指向新结点
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = p->prior;
s->next = p;
p->prior->next = s;
p->prior = s;
}
}
}
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int pos;
int i = ;
pDoubleListNode p = head;
printf("\n在双向链表中删除第i个位置的元素\n");
printf("请输入要删除的位置:");
scanf_s("%d", &pos, ); if (IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
return;
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head))
{
printf("删除的位置不存在!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == GetDouListLength(head))
{
p->prior->next = NULL;
free(p);
}
else
{
p->prior->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = p->prior;
free(p);
}
}
}
DoubleList.h
#pragma once
typedef struct DoubleListNode
{
int data; //数据
struct DoubleListNode *prior; //前驱
struct DoubleListNode *next; //后继
}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;
class DoubleList
{
public:
DoubleList();
~DoubleList();
//初始化双向链表
void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//逆序打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//求链表长度
int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head);
//判断链表是否为空
bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head);
//把双向链表置空
void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表
void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素m
void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head);
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head);
};
3.对链表插入节点的理解
例如在节点i前插入一个新的节点(即上面代码中的InsertNodeBefore函数):
链表结构体为:
假设该链表由五个节点构成,分别为A,B,C,D,E
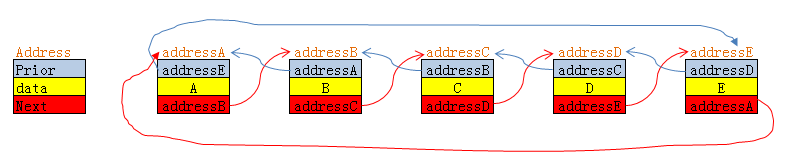
图中假设了A,B,C,D,E的地址分别为:addressA,addressB,addressC,addressD,addressE。
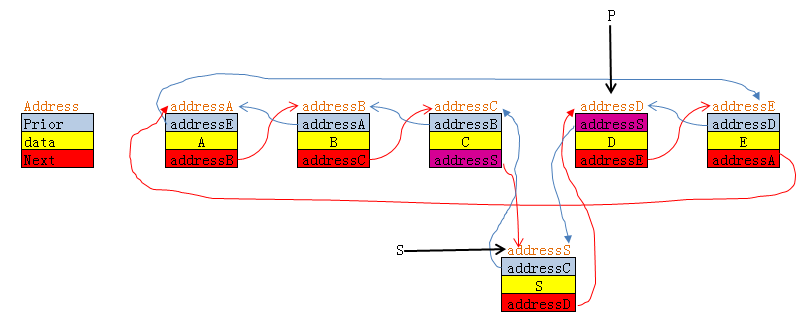
下面将分析链表的前插的例子:
双链表的前插,下面这是在节点"D"前插入一个新的节点"S"的代码和分析
C++ 双链表基本操作的更多相关文章
- c语言实现双链表的基本操作—增删改查
//初始化 Node*InitList() { Node*head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if(NULL==head) { printf("内存分配失败! ...
- [C++11][数据结构]自己的双链表实现
这个双链表,是我模仿stl的list制作的,只实现了一些基本功能,像merge,transfer这些就没有实现,用户可以用基本操作来自己做外部实现. 我没有选用stl的[begin,end)迭代器模式 ...
- 双链表【参照redis链表结构】
参照了Redis里面的双链表结构,可以说是完全复制粘贴,redis的双链表还是写的很通俗易懂的,没有什么花里胡哨的东西,但是redis还有个iter迭代器的结构来遍历链表.我这里就没有实现了,只是实现 ...
- python-实现双链表
双链表和单链表进行比较的优点与不同 节点多了一个前驱指针域 在很多基本操作上,多了一种选择,因为双链表可以向前进行移动寻位 如果给每个节点添加一个对应的下标,那么在寻找节点时,我们可以使用二分发来进行 ...
- JAVA 链表操作:单链表和双链表
主要讲述几点: 一.链表的简介 二.链表实现原理和必要性 三.单链表示例 四.双链表示例 一.链表的简介 链表是一种比较常用的数据结构,链表虽然保存比较复杂,但是在查询时候比较便捷,在多种计算机语言都 ...
- java实现双链表(差点没写吐系列...)
刚才把单链表写完了,现在又把双链表写了,双链表和单链表的区别就是每个节点有prior和next两个指针,不同于单链表的一个next指针,而且,正是因为有这两个指针,所以双链表可以前后两个方向去移动指针 ...
- 数据结构图文解析之:数组、单链表、双链表介绍及C++模板实现
0. 数据结构图文解析系列 数据结构系列文章 数据结构图文解析之:数组.单链表.双链表介绍及C++模板实现 数据结构图文解析之:栈的简介及C++模板实现 数据结构图文解析之:队列详解与C++模板实现 ...
- C和指针 第十二章 使用结构和指针 双链表和语句提炼
双链表中每个节点包含指向当前和之后节点的指针,插入节点到双链表中需要考虑四种情况: 1.插入到链表头部 2.插入到链表尾部 3.插入到空链表中 4.插入到链表内部 #include <stdio ...
- C#双链表
单链表允许从一个结点直接访问它的后继结点,所以, 找直接后继结点的时间复杂度是 O(1).但是,要找某个结点的直接前驱结点,只能从表的头引用开始遍历各结点.如果某个结点的 Next 等于该结点,那么, ...
随机推荐
- 汉化Eclipse+配色方法(官方语言包)
一. 汉化方法: 1.Eclipse版本查询:安装目录readme,查版本号;参照查代号如下表: 代号 平台版本 项目 主要版本发行日期 SR1发行日期 SR2发行日期 N/A 3.0 [1] N/A ...
- Cocos2d-html5 笔记4: 粒子
今天看了cocos2d-html5里面的粒子系统相关的代码,首先看了代码中引用的两篇文章, 这两篇文章google上都可以搜到pdf的. The Ocean Spray in Your Face [j ...
- 关于javascript中的 执行上下文和对象变量
什么是执行上下文 当浏览器的解释器开始执行我们的js代码的时候,js代码运行所处的环境可以被认为是代码的执行上下文,执行上下文(简称-EC)是ECMA-262标准里的一个抽象概念,用于同可执行代码(e ...
- spring事务的传播特性
所谓事务传播行为就是多个事务方法相互调用时,事务如何在这些方法间传播.Spring 支持 7 种事务传播行为: PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在 ...
- cocos2dx-lua使用UIListView制作二级折叠菜单
折叠菜单,用过jquery accordion的同学都知道是啥玩艺儿~,图片效果就是介样: cocos2dx不带有此控件,因此我们动手来实现一个. 原理很简单,展开的时候往listview里inser ...
- [Tips]解决HG之waiting for lock on repository
# Symptom 在tortoiseHg中commit或者Sync change的时候,总是出现下面的错误: waiting for lock on repository ... # Solutio ...
- shadow fight 1.6.0 内购
shadow fight 之前的版本只需要安装LocallApstore即可内购. 1.6.0的版本中加了越狱检查. 所以LocallApstore 无法直接使用. 需要安装xcon避开越狱检查. 也 ...
- C# 之 读写文件
1.使用 FileStream 读写文件 添加命名空间引用: using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; us ...
- C语言中将字符串转换为数字的方法
C语言提供了几个标准库函数,可以将字符串转换为任意类型(整型.长整型.浮点型等)的数字.以下是用atoi()函数将字符串转换为整数的一个例子: # include <stdio. h># ...
- Play on Words 欧拉通路(回路)判断
Play on Words note: 判断一下连通性. #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring ...
