利用python+graphviz绘制数据结构关系图和指定目录下头文件包含关系图
作为一名linux系统下的C语言开发,日常工作中经常遇到两个问题:
一是分析代码过程中,各种数据结构互相关联,只通过代码很难理清系统中所有结构体的整体架构,影响代码消化的效率;
二是多层头文件嵌套包含,在新增需要被多处引用的结构体或者函数接口时,难以找到合适的地方放置结构体和函数接口的定义。
为解决这两个问题,用python分别写了两个脚本:
第一个脚本用于绘制关键数据结构的关联关系图,协助快速理解组织架构,加速理解代码逻辑;
第二个脚本用于分析指定目录下的头文件包含关系,协助新增结构体或者函数接口时快速找到合适的放置位置;
两个脚本绘图效果分别见下图1,图2。
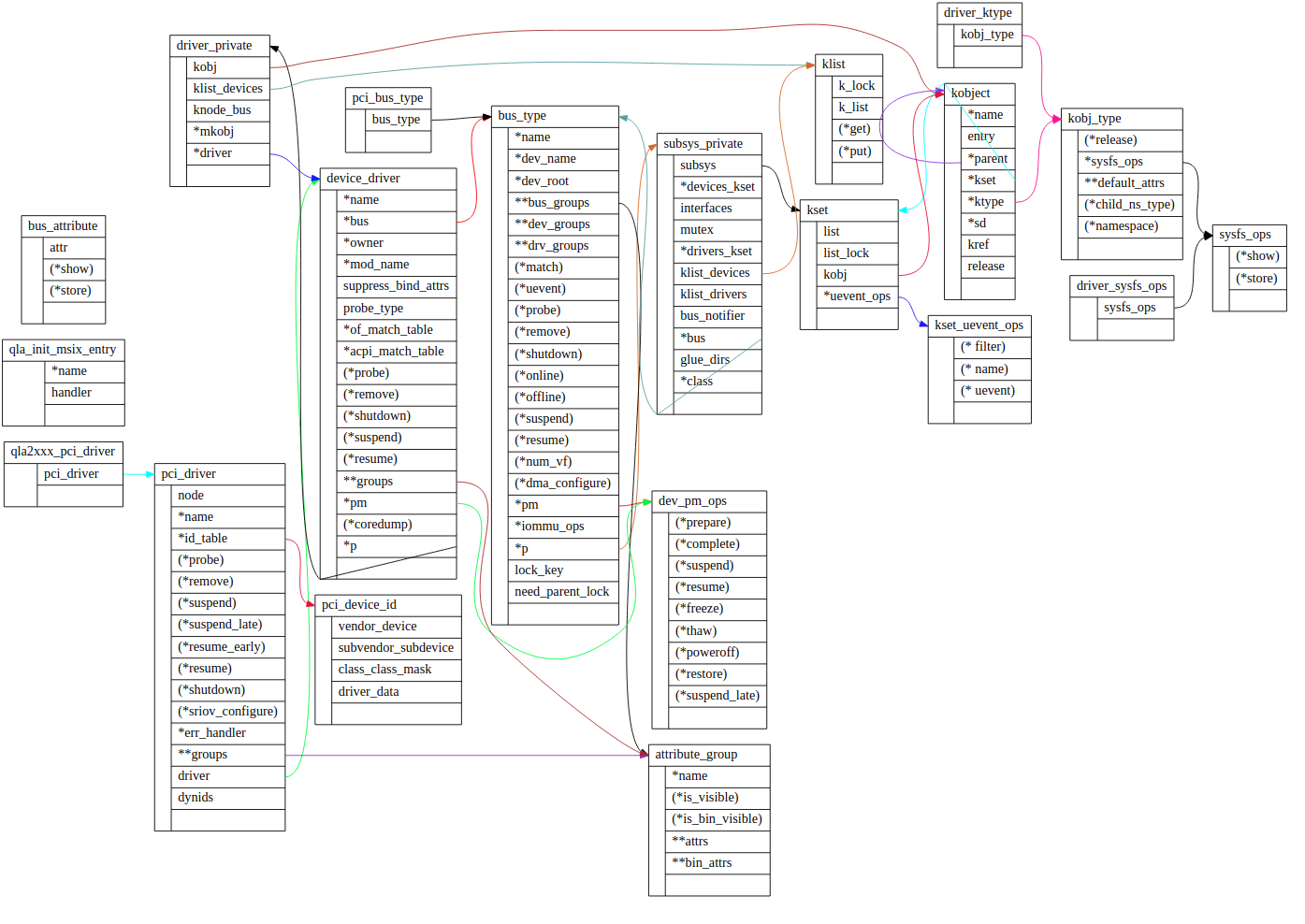
图1.数据结构关联关系图
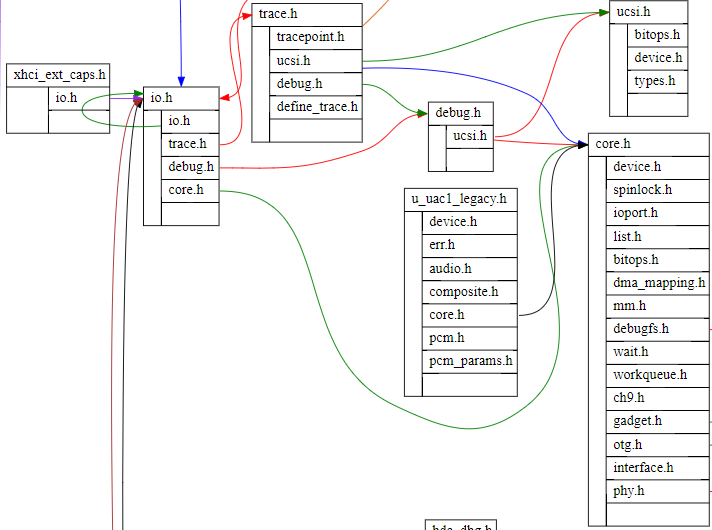
图2.头文件包含关系图(截取部分)
以下代码是用于分析结构体关联关系的python脚本(analysis_data_struct.py),使用方法如下:
1.在电脑上安装python和graphviz绘图工具(自行搜索,安装方法略);
2.把需要绘制关系图的关键数据结构复制粘贴到一个文本文件中;
3.把脚本中的保存数据结构文件路径(G:\git_repository\libreofficedraw\linux_4.18\plfc_struct )替换为自己的保存数据结构的文件路径(可自行修改脚本,通过参数传入文件路径);
4.执行命令 python analysis_data_struct.py >tmpfile; dot -Tsvg tmpfile -o xxxx.svg; 其中第一条命令使用python分析数据结构并生成用于绘图的dot语言,第二条命令利用graphviz根据tmpfile中的dot语言描述绘图。图形保存到xxxx.svg文件中;可以使用浏览器打开。
- #!/usr/bin/python3
- import os,re
- prefix = '''digraph spdk {
- graph [
- rankdir = "LR"
- //splines=polyline
- //overlap=false
- ];
- node [
- fontsize = "16"
- shape = "ellipse"\r
- ];
- edge [
- ];
- '''
- middle_str = ''
- edge_list = []
- edge_string = ''
- cur_indentation_level = 0
- space4 = ' '
- space8 = space4 + space4
- space12 = space4 + space8
- space16 = space4 + space12
- node_database = {}
- node_database['created'] = []
- color_arrary = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'black','blueviolet','brown', 'cadetblue','chocolate','crimson','cyan','darkgrey','deeppink','darkred']
- with open(r'G:\git_repository\libreofficedraw\linux_4.18\plfc_struct', 'r') as file_input:
- tmpline = file_input.readline()
- while(tmpline):
- tmpline = re.sub(r'([^a-zA-Z0-9]const )', ' ', tmpline)
- #for match :struct device {
- if re.search(r'struct\s*([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*\{', tmpline):
- m = re.search(r'struct\s*([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*\{', tmpline)
- cur_indentation_level += 1
- if (cur_indentation_level == 1):
- node_name = m.group(1)
- node_str = space4 + '\"' + node_name + '\" [\n' + space8 + 'label = \"<head> '+ node_name +'\l|\n' + space12 + '{|{\n'
- node_database['created'].append(node_name)
- try:
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] = node_str
- except:
- node_database[node_name] = {}
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] = node_str
- #for match :struct device *parent;
- elif re.search(r'struct\s*([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*(\**)(\s*)([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*;', tmpline) and cur_indentation_level > 0:
- m = re.search(r'struct\s*([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*(\**)(\s*)([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*;', tmpline)
- member_type = m.group(1)
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] += space16 + '<'+ member_type + '> ' + m.group(2) + m.group(3) + m.group(4) + '\l|\n'
- try:
- node_database[member_type]['included_by'].append(node_name)
- except:
- try:
- node_database[member_type]['included_by'] = []
- node_database[member_type]['included_by'].append(node_name)
- except:
- node_database[member_type] = {}
- node_database[member_type]['included_by'] = []
- node_database[member_type]['included_by'].append(node_name)
- #print('%s included by %s'%(member_type, node_database[member_type]['included_by']))
- if(member_type in node_database['created']):
- tmp_edge_str = space4 + node_name + ':' + member_type + ' -> ' + member_type + ':' + 'head'
- if not tmp_edge_str in edge_list:
- edge_list.append(tmp_edge_str)
- #for match : void *driver_data;
- elif re.search(r'\s*[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+\s*(\**[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*;', tmpline) and cur_indentation_level > 0:
- m = re.search(r'\s*[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+\s*(\**[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*;', tmpline)
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] += space16 + '<'+ m.group(1) + '> ' + m.group(1) + '\l|\n'
- #for match:const char *init_name;
- elif re.search(r'(.*)\s+(\**)(\s*)([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+\s*);', tmpline) and cur_indentation_level > 0:
- m = re.search(r'(.*)\s+(\**)(\s*)([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+\s*);', tmpline)
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] += space16 + '<'+ m.group(2) + '> ' + m.group(2) + m.group(3) + m.group(4) + '\l|\n'
- #for match:int *(*runtime_idle)(struct device *dev);
- elif re.search(r'\s*[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+\s*\**\s*\(\s*(\**\s*[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*\)\s*\([^\)]*\)\s*;', tmpline) and cur_indentation_level > 0:
- m = re.search(r'\s*[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+\s*\**\s*\(\s*(\**\s*[0-9a-zA-Z_\-]+)\s*\)\s*\([^\)]*\)\s*;', tmpline)
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] += space16 + '<'+ m.group(1) + '> (' + m.group(1) + ')\l|\n'
- #for match: };
- elif re.search(r'\s*\}\s*;', tmpline):
- if(cur_indentation_level >= 1):
- cur_indentation_level -= 1
- if (cur_indentation_level == 0):
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] += space12 + '}}\"\n'
- node_database[node_name]['node_str'] += space8 + 'shape = \"record\"\n' + space4 + '];\n'
- if 'included_by' in node_database[node_name]:
- for parent_node in node_database[node_name]['included_by']:
- if parent_node in node_database['created']:
- tmp_edge_str = space4 + parent_node + ':' + node_name + ' -> ' + node_name + ':' + 'head'
- if not tmp_edge_str in edge_list:
- edge_list.append(tmp_edge_str)
- tmpline = file_input.readline()
- for tmpnode in node_database['created']:
- middle_str = middle_str + node_database[tmpnode]['node_str']
- for i, tmpstr in enumerate(edge_list):
- edge_string += tmpstr + '[color="' + color_arrary[i%len(color_arrary)] + '"]\n'
- print(prefix + middle_str + '\n' + edge_string + '}')
以下为记录数据结构的文本文件(plfc_struct),用于测试。
- struct bus_type {
- const char *name;
- const char *dev_name;
- struct device *dev_root;
- const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;
- const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
- const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;
- int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
- int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
- int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
- int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
- void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
- int (*online)(struct device *dev);
- int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
- int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
- int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
- int (*num_vf)(struct device *dev);
- int (*dma_configure)(struct device *dev);
- const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
- const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
- struct subsys_private *p;
- struct lock_class_key lock_key;
- bool need_parent_lock;
- };
- struct pci_driver {
- struct list_head node;
- const char *name;
- const struct pci_device_id *id_table; /* Must be non-NULL for probe to be called */
- int (*probe)(struct pci_dev *dev, const struct pci_device_id *id); /* New device inserted */
- void (*remove)(struct pci_dev *dev); /* Device removed (NULL if not a hot-plug capable driver) */
- int (*suspend)(struct pci_dev *dev, pm_message_t state); /* Device suspended */
- int (*suspend_late)(struct pci_dev *dev, pm_message_t state);
- int (*resume_early)(struct pci_dev *dev);
- int (*resume) (struct pci_dev *dev); /* Device woken up */
- void (*shutdown) (struct pci_dev *dev);
- int (*sriov_configure) (struct pci_dev *dev, int num_vfs); /* On PF */
- const struct pci_error_handlers *err_handler;
- const struct attribute_group **groups;
- struct device_driver driver;
- struct pci_dynids dynids;
- };
- struct device_driver {
- const char *name;
- struct bus_type *bus;
- struct module *owner;
- const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
- bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
- enum probe_type probe_type;
- const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
- const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
- int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
- int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
- void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
- int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
- int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
- const struct attribute_group **groups;
- const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
- void (*coredump) (struct device *dev);
- struct driver_private *p;
- };
- struct driver_private {
- struct kobject kobj;
- struct klist klist_devices;
- struct klist_node knode_bus;
- struct module_kobject *mkobj;
- struct device_driver *driver;
- };
- struct kobject {
- const char *name;
- struct list_head entry;
- struct kobject *parent;
- struct kset *kset;
- struct kobj_type *ktype;
- struct kernfs_node *sd; /* sysfs directory entry */
- struct kref kref;
- #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_KOBJECT_RELEASE
- struct delayed_work release;
- #endif
- unsigned int state_initialized:;
- unsigned int state_in_sysfs:;
- unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:;
- unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:;
- unsigned int uevent_suppress:;
- };
- struct subsys_private {
- struct kset subsys;
- struct kset *devices_kset;
- struct list_head interfaces;
- struct mutex mutex;
- struct kset *drivers_kset;
- struct klist klist_devices;
- struct klist klist_drivers;
- struct blocking_notifier_head bus_notifier;
- unsigned int drivers_autoprobe:;
- struct bus_type *bus;
- struct kset glue_dirs;
- struct class *class;
- };
- struct kset {
- struct list_head list;
- spinlock_t list_lock;
- struct kobject kobj;
- const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
- };
- struct kobj_type {
- void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj);
- const struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops;
- struct attribute **default_attrs;
- const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *(*child_ns_type)(struct kobject *kobj);
- const void *(*namespace)(struct kobject *kobj);
- };
- struct sysfs_ops {
- ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *, char *);
- ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *, const char *, size_t);
- };
- struct dev_pm_ops {
- int (*prepare)(struct device *dev);
- void (*complete)(struct device *dev);
- int (*suspend)(struct device *dev);
- int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
- int (*freeze)(struct device *dev);
- int (*thaw)(struct device *dev);
- int (*poweroff)(struct device *dev);
- int (*restore)(struct device *dev);
- int (*suspend_late)(struct device *dev);
- };
- struct kset_uevent_ops {
- int (* const filter)(xxxxxxx);
- const char *(* const name)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj);
- int (* const uevent)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
- };
- struct qla_init_msix_entry {
- const char *name;
- irq_handler_t handler;
- };
- struct attribute_group {
- const char *name;
- umode_t (*is_visible)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *, int);
- umode_t (*is_bin_visible)(struct kobject *,struct bin_attribute *, int);
- struct attribute **attrs;
- struct bin_attribute **bin_attrs;
- };
- struct bus_attribute {
- struct attribute attr;
- ssize_t (*show)(struct bus_type *bus, char *buf);
- ssize_t (*store)(struct bus_type *bus, const char *buf, size_t count);
- };
- struct klist {
- spinlock_t k_lock;
- struct list_head k_list;
- void (*get)(struct klist_node *);
- void (*put)(struct klist_node *);
- } ;
- struct pci_device_id {
- __u32 vendor_device; /* Vendor and device ID or PCI_ANY_ID*/
- __u32 subvendor_subdevice; /* Subsystem ID's or PCI_ANY_ID */
- __u32 class_class_mask; /* (class,subclass,prog-if) triplet */
- kernel_ulong_t driver_data; /* Data private to the driver */
- };
- struct device {
- struct device *parent;
- struct device_private *p;
- struct kobject kobj;
- const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */
- const struct device_type *type;
- struct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to
- * its driver.
- */
- struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */
- struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated this
- device */
- void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, device
- core doesn't touch it */
- void *driver_data; /* Driver data, set and get with
- dev_set/get_drvdata */
- struct dev_links_info links;
- const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */
- void (*release)(struct device *dev);
- struct iommu_group *iommu_group;
- struct iommu_fwspec *iommu_fwspec;
- };
- struct dev_links_info {
- struct list_head suppliers;
- struct list_head consumers;
- enum dl_dev_state status;
- };
- struct pci_dynids {
- spinlock_t lock; /* Protects list, index */
- struct list_head list; /* For IDs added at runtime */
- };
- ////////////////////以下结构体名称为全局变量,结构体成员为全局变量的类型,用于绘图时关联全局变量及其类型///////////////////////
- struct qla2xxx_pci_driver {
- struct pci_driver pci_driver;
- };
- struct pci_bus_type {
- struct bus_type bus_type;
- };
- struct driver_ktype {
- struct kobj_type kobj_type;
- };
- struct driver_sysfs_ops {
- struct sysfs_ops sysfs_ops;
- };
- struct qla2xxx_pci_tbl{
- struct pci_device_id pci_device_id;
- };
- struct bus_kset {
- struct kset kset;
- };
- struct bus_uevent_ops {
- struct kset_uevent_ops kset_uevent_ops;
- };
以下脚本(analysis_head_file.py)用于分析指定目录下头文件包含关系,使用方法如下:
1.在电脑上安装python和graphviz绘图工具(自行搜索,安装方法略);
2.把脚本中的代码路径(G:\git_repository\linux-stable\linux-4.18\drivers\net\wireless\broadcom)替换为需要分析的文件路径(可自行修改脚本,通过参数传入文件路径);
3.执行命令 python analysis_head_file.py >tmpfile; dot -Tsvg tmpfile -o xxxx.svg; 其中第一条命令使用python分析数据结构并生成用于绘图的dot语言,第二条命令利用graphviz根据tmpfile中的dot语言描述绘图。图形保存到xxxx.svg文件中;可以使用浏览器打开。
- #!/usr/bin/python3
- import os,re
- prefix = '''digraph spdk {
- graph [
- rankdir = "LR"
- //splines=polyline
- overlap=false
- ];
- node [
- fontsize = "16"
- shape = "ellipse"\r
- ];
- edge [
- ];
- '''
- def get_head_file_list(path_file):
- head_file_list = []
- with open(path_file, 'r') as file_input:
- tmpline = file_input.readline()
- while (tmpline):
- #to match #include < XXX/YYY.h >
- m = re.search(r'#include\s*[<\"]\s*(.*/)([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]*)\.[Hh]\s*[>\"]', tmpline)
- if m:
- head_file_list.append(re.sub(r'\-', '_', m.group(2)))
- #to match #include < XXX.h >
- elif re.search(r'#include\s*[<\"]\s*([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]*)\.[Hh]\s*[>\"]', tmpline):
- m = re.search(r'#include\s*[<\"]\s*([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]*)\.[Hh]\s*[>\"]', tmpline)
- head_file_list.append(re.sub(r'\-', '_', m.group(1)))
- tmpline = file_input.readline()
- return head_file_list
- def build_node_from_file(file_path, file_name, edges, included_by):
- i = 0
- space4 = ' '
- space8 = space4 + space4
- space12 = space4 + space8
- space16 = space4 + space12
- file_name_wo_h = re.search(r'([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]*)\.h', file_name).group(1)
- file_name_wo_h = re.sub(r'\-', '_',file_name_wo_h)
- #print(file_name_wo_h)
- node_str = space4 + '\"' + file_name_wo_h + '\" [\n' + space8 + 'label = \"<head> '+ file_name_wo_h +'.h\l|\n' + space12 + '{|{\n'
- headfilelist = ["aaa", "bbb"] #fake file list
- headfilelist2 = get_head_file_list(os.path.join(file_path, file_name))
- #print('headfilelist2:')
- #print(headfilelist2)
- for headfile in headfilelist2:
- i += 1
- try:
- included_by[headfile].append(file_name)
- except:
- included_by[headfile] = []
- included_by[headfile].append(file_name)
- node_str = node_str + space16 + '<'+ headfile + '> ' + headfile + '.h\l|\n'
- tmp_edge_str = space4 + file_name_wo_h + ':' + headfile + ' -> ' + headfile + ':' + 'head' #+ '[color="' + color_arrary[i%len(color_arrary)] + '"]\n'
- try:
- if not tmp_edge_str in edges[headfile]:
- edges[headfile].append(tmp_edge_str)
- except:
- edges[headfile] = []
- edges[headfile].append(tmp_edge_str)
- node_str = node_str + space12 + '}}\"\n'
- node_str = node_str + space8 + 'shape = \"record\"\n' + space4 + '];\n'
- #print(included_by)
- return {'node_str':node_str,'edges':edges}
- edges = {}
- included_by = {}
- node_created = []
- middle_str = ''
- edge_string = ''
- color_arrary = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'black','blueviolet','brown', 'cadetblue','chocolate','crimson','cyan','darkgrey','deeppink','darkred']
- for maindir, subdir, file_name_list in os.walk(r'G:\git_repository\linux-stable\linux-4.18\drivers\net\wireless\broadcom'):#('G:\git_repository\linux-stable\linux-4.18\drivers\usb'):
- for tmpfile in file_name_list:
- if re.match(r'.*\.h', tmpfile):
- result = build_node_from_file(maindir, tmpfile, edges, included_by)
- node_created.append(re.search(r'([0-9a-zA-Z_\-]*)\.h', tmpfile).group(1))
- middle_str = middle_str + '\n' + result['node_str']
- edges = result['edges']
- ##print(filelist2)
- for tmpfile in edges:
- if tmpfile in node_created:
- for i,tmpstr in enumerate(edges[tmpfile]):
- edge_string += tmpstr + '[color="' + color_arrary[i%len(color_arrary)] + '"]\n'
- print(prefix + middle_str + '\n' + edge_string + '}')
利用python+graphviz绘制数据结构关系图和指定目录下头文件包含关系图的更多相关文章
- 利用Graphviz绘制逻辑关系依赖图
说明:在很多情况下,需要将复杂且有些规律的代码整理成逻辑片段,这个时候就需要画图,很多时候图比代码更加直观 Graphviz是一个比较好的绘图工具,可以通过简单的代码绘制出复杂的逻辑图,且其代码就像平 ...
- c# 简易绘制C语言头文件包含关系图
最近在做一个项目的移植工作,项目很大,光c文件大约有1800多.由于某些需要,想要对某些代码文件引用的.h文件进行分析. 网上找了好久,暂无发现类似的工具. 正好,今天放假,就做了这么个工具. 好了, ...
- 利用Python快速绘制海报级别地图
1 简介 基于Python中诸如matplotlib等功能丰富.自由度极高的绘图库,我们可以完成各种极富艺术感的可视化作品,关于这一点我在系列文章在模仿中精进数据可视化中已经带大家学习过很多案例了. ...
- 利用python实现dll依赖关系导出
#说明:遍历rootdir目录下所有dll,导出每个dll依赖的dll信息到dstdir目录下 # 配合NotePad++打开所有txt,搜索,可快速定位到某dll被依赖的所有dll文件 import ...
- c# 简易绘制C语言头文件包含关系图 v2.0
老规矩,先上图 节点样式说明: 1.粉色圆角,说明该节点下有循环引用 2.黄色菱形,说明该节点代表的文件在项目目录下未找到. 3.红色圆角,说明循环引用(从开始到最终,这种感情没变过,没有谁..... ...
- 利用File类过滤器列出目录下的指定目录或文件
需求:列出d盘下的全部txt文件 实现方法:利用File类的过滤器功能 package com.test.common.util; import java.io.File; import java.i ...
- python 实现统计ftp服务器指定目录下文件夹数目、文件数目及所有文件大小
本次主要为满足应用方核对上传到ftp服务器的文件是否缺漏. 主要要求:指定目录下,文件夹数目/文件数目/所有文件大小,类似Windows如下功能: 模块介绍: from ftplib import F ...
- Python批量重命名指定目录下文件的两种方法
#法一 import os path = "C://Python34//" for file in os.listdir(path): if os.path.isfile(os.p ...
- 《利用python进行数据分析》读书笔记 --第一、二章 准备与例子
http://www.cnblogs.com/batteryhp/p/4868348.html 第一章 准备工作 今天开始码这本书--<利用python进行数据分析>.R和python都得 ...
随机推荐
- jquery多级树形下拉菜单
效果图: 使用方法 (1)引入 jQuery 包,下载地址 (2)引入 zTree 包,下载地址 (3)引入 tree-select.js (4)$("#id").treeSele ...
- 16 (OC)* UIAnimation和CoreAnimation
目录 一 Core Animation 二 核心动画 2.1 基础动画 2.2 关键帧动画 2.3 动画组 2.4 转场动画 2.5 逐帧动画 三 UIView动画封装 3.1 基础动画 3.2 弹簧 ...
- iOS渠道追踪统计方法大全
说起 iOS 的渠道统计,不少人会想到苹果官方的 App 分析功能(iTunes Connect),但实际操作中我们会发现,这个服务的统计维度还不够全面,许多广告主和运营人员更关心的是各个推广渠道实际 ...
- oracle 11g 下载安装 使用记录
Oracle 11g 使用记录 1.下载oracle快捷安装版: (1)下载连接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ClC0hQepmTw2lSJ2ODtL7g 无提取码 (2)去 ...
- 实操:Could not autowire No beans of 'FastDFS Client' type found 的解决方法
前言: 今天接手了同事之前做的一个小项目,里面涉及到了 FastDFS 的使用.但是当我在本地运行项目的时候,却报了 Could not autowire No beans of 'FastDFS C ...
- [C++] C++中的常用库
转载自:C++常用库 C++ 资源大全 关于 C++ 框架.库和资源的一些汇总列表,内容包括:标准库.Web应用框架.人工智能.数据库.图片处理.机器学习.日志.代码分析等. 标准库 C++标准库,包 ...
- springboot项目启动报错 url' attribute is not specified and no embedded datasource could be configured
报错相关信息: 2019-07-22 17:12:48.971 ERROR 8312 --- [ main] o.s.b.d.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter : **** ...
- JQuery对于动态生成的标签绑定事件失效
JQuery对整个html文档进行dom操作后,我们要想动态绑定事件,有两种方法 1.在进行dom操作时,在标签中写上onclick="afun()" 2.利用document的操 ...
- 不fq安装 golang tools
go get -u -v github.com/golang/tools/go/buildutil ln -s $GOPATH/src/github.com/golang/tools $GOPATH/ ...
- OpenGL在ubuntu下的成功配置
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install build-essential sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-dev sudo a ...
