Django REST framework —— 权限组件源码分析
在上一篇文章中我们已经分析了认证组件源码,我们再来看看权限组件的源码,权限组件相对容易,因为只需要返回True 和False即可
代码
class ShoppingCarView(ViewSetMixin, APIView):
permission_classes = [MyPermission, ]
def list(self,request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
查看购物车信息
:param args:
:param kwargs:
:return:
"""
try:
ret = BaseResponse()
pay_course_list = []
# key = 'shoppingcar_%s_%s' % (USERID, '*')
key = settings.SHOPCAR_FORMAT.format( request.user.id, "*")
user_key_list = COON.keys(pattern=key) # 取到这个用户对应的所有课程字典 对应的键
for key in user_key_list:
# 对应的每个键值 去取每个课程对应的信息 和价格列表
temp = {
'id': COON.hget(key, 'id').decode('utf8'),
'name': COON.hget(key, 'name').decode('utf8'),
'img': COON.hget(key, 'img').decode('utf8'),
'default': COON.hget(key, 'default').decode('utf8'),
'price_dict': json.loads(COON.hget(key, 'price_dict').decode('utf8')),
}
pay_course_list.append(temp)
ret.data = pay_course_list
except Exception as e:
ret.data = '查看失败'
ret.code = 00000
return Response(ret.dict) 视图类
视图类
class MyPermission(BasePermission):
message = 'VIP用户才能访问' def has_permission(self, request, view):
"""
自定义权限只有VIP用户才能访问
"""
# 因为在进行权限判断之前已经做了认证判断,所以这里可以直接拿到request.user
if request.user and request.user.type == 2: # 如果是VIP用户
return True
else:
return False
自定义权限类
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^payment/$', payment.PaymentView.as_view({'post': 'create','put': 'update','get':'list'})),
]
路由
跟上一篇一样,来看代码是如何走到我自定义的权限类中的。
1.首先从url中分析
1.先来到视图类中的as.view()方法

而我们的自定义的方法中没有as.view()方法,那就要去父类ViewSetMixin和APIView中去找,好看源码
2.分析源码
1.先看ViewSetMixin类中
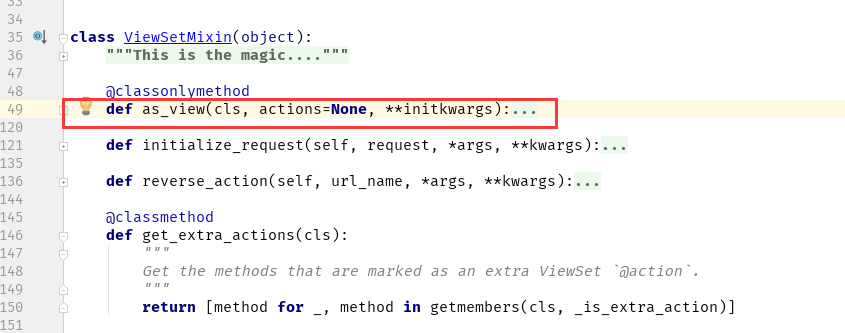

class ViewSetMixin(object):
"""
This is the magic. Overrides `.as_view()` so that it takes an `actions` keyword that performs
the binding of HTTP methods to actions on the Resource. For example, to create a concrete view binding the 'GET' and 'POST' methods
to the 'list' and 'create' actions... view = MyViewSet.as_view({'get': 'list', 'post': 'create'})
""" @classonlymethod
def as_view(cls, actions=None, **initkwargs):
"""
Because of the way class based views create a closure around the
instantiated view, we need to totally reimplement `.as_view`,
and slightly modify the view function that is created and returned.
"""
# The suffix initkwarg is reserved for displaying the viewset type.
# eg. 'List' or 'Instance'.
cls.suffix = None # The detail initkwarg is reserved for introspecting the viewset type.
cls.detail = None # Setting a basename allows a view to reverse its action urls. This
# value is provided by the router through the initkwargs.
cls.basename = None # actions must not be empty
if not actions:
raise TypeError("The `actions` argument must be provided when "
"calling `.as_view()` on a ViewSet. For example "
"`.as_view({'get': 'list'})`") # sanitize keyword arguments
for key in initkwargs:
if key in cls.http_method_names:
raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a "
"keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that."
% (key, cls.__name__))
if not hasattr(cls, key):
raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r" % (
cls.__name__, key)) def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
self = cls(**initkwargs)
# We also store the mapping of request methods to actions,
# so that we can later set the action attribute.
# eg. `self.action = 'list'` on an incoming GET request.
self.action_map = actions # Bind methods to actions
# This is the bit that's different to a standard view
for method, action in actions.items():
handler = getattr(self, action)
setattr(self, method, handler) if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'):
self.head = self.get self.request = request
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs # And continue as usual
# 前面都是在对传参做判断和重新赋值,重要的是下面这一步,最后return 调用了dispatch方法
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)

2.找dispatch方法在哪里,答案肯定是在APIView中

def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
## request = Request(.....)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers try:
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response

所有的关键点都在dispatch方法里面:
(1) request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)

def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the initial request object.
"""
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), #[BasicAuthentication(),],把对象封装到request里面了
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), parser_context=parser_context )
(2) self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
self.perform_authentication(request) 认证
self.check_permissions(request) 权限
self.check_throttles(request)
(3)self.check_permissions(request)
def check_permissions(self, request):
"""
Check if the request should be permitted.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is not permitted.
"""
for permission in self.get_permissions():
if not permission.has_permission(request, self):
self.permission_denied(
request, message=getattr(permission, 'message', None)
)
(4)self.get_permissions():
def get_permissions(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of permissions that this view requires.
"""
return [permission() for permission in self.permission_classes] 列表生成式,把自定义的权限类的对象,放在一个对象中
(5)self.permission_classes

这里默认去settings全局中去找,如果局部配置了静态变量,就直接去找局部的静态变量
(6)在看看我们继承的BasePermission
class BasePermission(object):
"""
A base class from which all permission classes should inherit.
""" def has_permission(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
"""
return True def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
"""
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
"""
return True
默认是没有任何逻辑判断的,所以我们在自定义权限类的时候,得自己写这两个方法。
另外说明一下下面这个犯法的作用
def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
"""
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
"""
return True
对当前登录用户做些判断
def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
"""
判断当前评论用户的作者是不是你当前的用户
只有评论的作者才能删除自己的评论
"""
print('这是在自定义权限类中的has_object_permission')
print(obj.id)
if request.method in ['PUT', 'DELETE']:
if obj.user == request.user:
# 当前要删除的评论的作者就是当前登陆的用户
return True
else:
return False
else:
return True
总结:
(1)使用
- 自己写的权限类:1.必须继承BasePermission类; 2.必须实现:has_permission方法
(2)返回值
- True 有权访问
- False 无权访问
(3)局部
- permission_classes = [MyPremission,]
(4)全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
#权限
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":['API.utils.permission.SVIPPremission'],
}
Django REST framework —— 权限组件源码分析的更多相关文章
- Django REST framework —— 认证组件源码分析
我在前面的博客里已经讲过了,我们一般编写API的时候用的方式 class CoursesView(ViewSetMixin,APIView): pass 这种方式的有点是,灵活性比较大,可以根据自己的 ...
- Django rest framework 权限操作(源码分析)
知识回顾http://www.cnblogs.com/ctztake/p/8419059.html 这一篇是基于上一篇写的,上一篇谢了认证的具体流程,看懂了上一篇这一篇才能看懂, 当用户访问是 首先执 ...
- Django rest framework框架——APIview源码分析
一.什么是rest REST其实是一种组织Web服务的架构,而并不是我们想象的那样是实现Web服务的一种新的技术,更没有要求一定要使用HTTP.其目标是为了创建具有良好扩展性的分布式系统. 可用一句话 ...
- Django框架之DRF 认证组件源码分析、权限组件源码分析、频率组件源码分析
认证组件 权限组件 频率组件
- DRF框架(一)——restful接口规范、基于规范下使用原生django接口查询和增加、原生Django CBV请求生命周期源码分析、drf请求生命周期源码分析、请求模块request、渲染模块render
DRF框架 全称:django-rest framework 知识点 1.接口:什么是接口.restful接口规范 2.CBV生命周期源码 - 基于restful规范下的CBV接口 3.请求组件 ...
- Django-restframework 源码之认证组件源码分析
Django-restframework 源码之认证组件源码分析 一 前言 之前在 Django-restframework 的流程分析博客中,把最重要的关于认证.权限和频率的方法找到了.该方法是 A ...
- element-ui 组件源码分析整理笔记目录
element-ui button组件 radio组件源码分析整理笔记(一) element-ui switch组件源码分析整理笔记(二) element-ui inputNumber.Card .B ...
- Django的settings文件部分源码分析
Django的settings文件部分源码分析 在编写Django项目的过程中, 其中一个非常强大的功能就是我们可以在settings文件配置许多选项来完成我们预期的功能, 并且这些配置还必须大写, ...
- ceph-csi组件源码分析(1)-组件介绍与部署yaml分析
更多ceph-csi其他源码分析,请查看下面这篇博文:kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 ceph-csi组件源码分析(1)-组件介绍与部署yaml分析 基于tag v3.0.0 ht ...
随机推荐
- PHP防止sql语句注入终极解决方案(包含pdo各种操作使用实例)
PHP防止sql语句注入终极解决方案完美解决方案就是使用拥有Prepared Statement机制(预处理sql)的PDO //先做个实验 先不用预处理sql写法<pre><?ph ...
- linux iftop查看流量的方法
linux iftop查看流量的方法iftop 默认是查看eth0网卡的流量 这个是内网iftop -i eth1 检测eht1网卡的流量 eth1一般都是外网 具体可以iftop查看详细信息 < ...
- 腾讯物联网操作系统正式开源,最小体积仅1.8 KB
9月18日,腾讯宣布将开源自主研发的轻量级物联网实时操作系统TencentOS tiny.相比市场上其它系统,腾讯TencentOS tiny在资源占用.设备成本.功耗管理以及安全稳定等层面极具竞争力 ...
- vue脚手架(vue-cli)老版本(2.xx版)的使用
1. 在idea新建一个Static Web项目 2. 在新建的项目下打开cmd 3. 输入安装脚手架命令:npm install -g vue-cli 4. 查看安装的版本:vue -V (2. ...
- Jenkins 远程启动nodejs失败,使用pm2守护Nodejs
一.概述 使用Jenkins 远程ssh到linux,使用命令: ssh root@192.168.10.1 'cd /data/test;nohup npm start &' 发现linux ...
- Jenkins基于https的k8s配置
一.摘要 jenkins 连接低版本的k8s时,不需要验证.但是新版本的启用了https和角色管理 二.安装kubernetes插件 登录jenkins,点击 Manage Jenkins --> ...
- pytest_使用自定义标记mark
前言 pytest可以支持自定义标记,自定义标记可以把一个web项目划分多个模块,然后指定模块名称执行.app自动化的时候,如果想android和ios公用一套代码时,也可以使用标记功能,标明哪些是i ...
- NOI2019:Stay at Home
7.16 NOI D1 从同步赛开始更起好了 先看了一圈题目,发现T1非常可做,二次函数因为对称轴在\(x < 0\)的地方所以有跟一次函数类似的单调性,搞个单调队列维护一下似乎就可以了.大力码 ...
- go ---变量数据结构调试利器 go-spew
我们在使用Golang(Go语言)开发的过程中,会通过经常通过调试的方式查找问题的原因,解决问题,尤其是当遇到一个很棘手的问题的时候,就需要知道一段代码在执行的过程中,其上下文的变量对应的数据,以便进 ...
- 微信小程序与Django<一>
小程序开发的准备工作 1. 小程序开发者账号 a) 邮箱注册 b) 开发者配置与AppID c) https://mp.weixin.qq. ...
