[C#]MemoryStream.Dispose之后,为什么仍可以ToArray()?
目录
概述
事件起因,一哥们在群里面贴出了类似下面这样的一段代码:
class Program
{
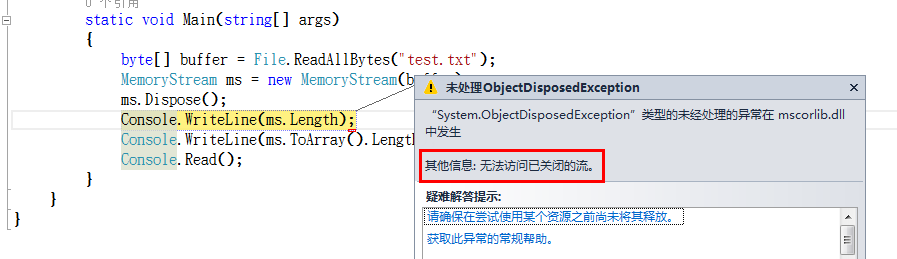
static void Main(string[] args)
{
byte[] buffer = File.ReadAllBytes("test.txt");
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(buffer);
ms.Dispose();
Console.WriteLine(ms.ToArray().Length);
Console.Read();
}
}
先不去考究这段代码到底有没有什么意义,就代码而言,内存流释放之后,再去使用ms会有问题么?
运行结果:
在印象中非托管资源Dispose之后,应该会出现“无法访问已释放的资源”之类的异常吧,但是你真正的运行的时候,你会发现并没有错。真的怪了,没办法,出于好奇也就研究了一下。
那我们如果访问ms对象的其他的属性(ms.Length)会怎么样呢?
访问其它的方法它也会出现上面的异常。
这问题出来了,难道内存流的Dispose方法是选择性的释放?
在看MemoryStream分析之前,回顾一下托管与非托管资源的概念。
托管资源
一般是指被CLR控制的内存资源,这些资源的管理可以由CLR来控制,例如程序中分配(new)的对象,作用域内的变量等。
非托管资源
是CLR不能控制或者管理的部分,这些资源有很多,比如文件流,数据库的连接,系统的窗口句柄(Window内核对象(句柄))、字体、刷子、dc打印机资源等等……这些资源一般情况下不存在于Heap(内存中用于存储对象实例的地方)中。
C#的垃圾回收器:
CLR为程序员提供的内存管理机制,使得程序员在编写代码时不需要显式的去释放自己使用的内存资源(这些在先前C和C++中是需要程序员自己去显式的释放的)。这种管理机制称为GC(garbage collection)。GC的作用是很明显的,当系统内存资源匮乏时,它就会被激发,然后自动的去释放那些没有被使用的托管资源(也就是程序员没有显式释放的对象)。对于那些非托管资源虽然垃圾回收器可以跟踪封装非托管资源的对象的生存期,但它不了解具体如何清理这些资源。还好.net提供了Finalize()方法,它允许在垃圾回收器回收该类资源时,适当的清理非托管资源。但是Finalize()会产生很多副作用。释放非托管资源
资源的释放一般是通过"垃圾回收器"自动完成的,但具体来说,仍有些需要注意的地方:
1、值类型和引用类型的引用其实是不需要什么"垃圾回收器"来释放内存的,因为当它们出了作用域后会自动释放所占内存,因为它们都保存在栈(Stack)中;
2、只有引用类型的引用所指向的对象实例才保存在堆(Heap)中,而堆因为是一个自由存储空间,所以它并没有像"栈"那样有生存期("栈"的元素弹出后就代表生存期结束,也就代表释放了内存),并且要注意的是,"垃圾回收器"只对这块区域起作用。
然而,有些情况下,当需要释放非托管资源时,就必须通过写代码的方式来解决。非托管资源的释放
当我们在类中封装了对非托管资源的操作时,我们就需要显式释放(Dispose),或隐式释放(Finalize)的释放这些资源。
Finalize一般情况下用于基类不带close方法或者不带Dispose显式方法的类,也就是说,在Finalize过程中我们需要隐式的去实现非托管资源的释放,然后系统会在Finalize过程完成后,自己的去释放托管资源。如果要实现Dispose方法,可以通过实现IDisposable接口,这样用户在使用这个类的同时就可以显示的执行Dispose方法,释放资源。(详细的内容可参考:http://blog.csdn.net/xiven/article/details/4951099)
MemoryStream分析
对于这个问题,吃饭的时候一直很纠结,所以就查了一些这方面的资料,也试图反编译MemoryStream类,看看Dispose方法是如何实现。
参考:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4274590/memorystream-close-or-memorystream-dispose
github上MemoryStream中的代码:
//
// System.IO.MemoryStream.cs
//
// Authors: Marcin Szczepanski (marcins@zipworld.com.au)
// Patrik Torstensson
// Gonzalo Paniagua Javier (gonzalo@ximian.com)
// Marek Safar (marek.safar@gmail.com)
//
// (c) 2001,2002 Marcin Szczepanski, Patrik Torstensson
// (c) 2003 Ximian, Inc. (http://www.ximian.com)
// Copyright (C) 2004 Novell, Inc (http://www.novell.com)
// Copyright 2011 Xamarin, Inc (http://www.xamarin.com)
//
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining
// a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
// "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
// without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
// distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to
// permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to
// the following conditions:
//
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
// included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
// EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
// MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
// NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE
// LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION
// OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION
// WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
// using System.Globalization;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Threading;
#if NET_4_5
using System.Threading.Tasks;
#endif namespace System.IO
{
[Serializable]
[ComVisible (true)]
[MonoLimitation ("Serialization format not compatible with .NET")]
public class MemoryStream : Stream
{
bool canWrite;
bool allowGetBuffer;
int capacity;
int length;
byte [] internalBuffer;
int initialIndex;
bool expandable;
bool streamClosed;
int position;
int dirty_bytes;
#if NET_4_5
[NonSerialized]
Task<int> read_task;
#endif public MemoryStream () : this ()
{
} public MemoryStream (int capacity)
{
if (capacity < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("capacity"); canWrite = true; this.capacity = capacity;
internalBuffer = new byte [capacity]; expandable = true;
allowGetBuffer = true;
} public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); InternalConstructor (buffer, , buffer.Length, true, false);
} public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, bool writable)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); InternalConstructor (buffer, , buffer.Length, writable, false);
} public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, int index, int count)
{
InternalConstructor (buffer, index, count, true, false);
} public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, int index, int count, bool writable)
{
InternalConstructor (buffer, index, count, writable, false);
} public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, int index, int count, bool writable, bool publiclyVisible)
{
InternalConstructor (buffer, index, count, writable, publiclyVisible);
} void InternalConstructor (byte [] buffer, int index, int count, bool writable, bool publicallyVisible)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); if (index < || count < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("index or count is less than 0."); if (buffer.Length - index < count)
throw new ArgumentException ("index+count",
"The size of the buffer is less than index + count."); canWrite = writable; internalBuffer = buffer;
capacity = count + index;
length = capacity;
position = index;
initialIndex = index; allowGetBuffer = publicallyVisible;
expandable = false;
} void CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ()
{
if (streamClosed)
throw new ObjectDisposedException ("MemoryStream");
} public override bool CanRead {
get { return !streamClosed; }
} public override bool CanSeek {
get { return !streamClosed; }
} public override bool CanWrite {
get { return (!streamClosed && canWrite); }
} public virtual int Capacity {
get {
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
return capacity - initialIndex;
} set {
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); if (!expandable)
throw new NotSupportedException ("Cannot expand this MemoryStream"); if (value < || value < length)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("value",
"New capacity cannot be negative or less than the current capacity " + value + " " + capacity); if (internalBuffer != null && value == internalBuffer.Length)
return; byte [] newBuffer = null;
if (value != ) {
newBuffer = new byte [value];
if (internalBuffer != null)
Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, , newBuffer, , length);
} dirty_bytes = ; // discard any dirty area beyond previous length
internalBuffer = newBuffer; // It's null when capacity is set to 0
capacity = value;
}
} public override long Length {
get {
// LAMESPEC: The spec says to throw an IOException if the
// stream is closed and an ObjectDisposedException if
// "methods were called after the stream was closed". What
// is the difference? CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); // This is ok for MemoryStreamTest.ConstructorFive
return length - initialIndex;
}
} public override long Position {
get {
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
return position - initialIndex;
} set {
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
if (value < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("value",
"Position cannot be negative" ); if (value > Int32.MaxValue)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("value",
"Position must be non-negative and less than 2^31 - 1 - origin"); position = initialIndex + (int) value;
}
} protected override void Dispose (bool disposing)
{
streamClosed = true;
expandable = false;
} public override void Flush ()
{
// Do nothing
} public virtual byte [] GetBuffer ()
{
if (!allowGetBuffer)
throw new UnauthorizedAccessException (); return internalBuffer;
} public override int Read ([In,Out] byte [] buffer, int offset, int count)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); if (offset < || count < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("offset or count less than zero."); if (buffer.Length - offset < count )
throw new ArgumentException ("offset+count",
"The size of the buffer is less than offset + count."); CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); if (position >= length || count == )
return ; if (position > length - count)
count = length - position; Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, position, buffer, offset, count);
position += count;
return count;
} public override int ReadByte ()
{
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
if (position >= length)
return -; return internalBuffer [position++];
} public override long Seek (long offset, SeekOrigin loc)
{
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); // It's funny that they don't throw this exception for < Int32.MinValue
if (offset > (long) Int32.MaxValue)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("Offset out of range. " + offset); int refPoint;
switch (loc) {
case SeekOrigin.Begin:
if (offset < )
throw new IOException ("Attempted to seek before start of MemoryStream.");
refPoint = initialIndex;
break;
case SeekOrigin.Current:
refPoint = position;
break;
case SeekOrigin.End:
refPoint = length;
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentException ("loc", "Invalid SeekOrigin");
} // LAMESPEC: My goodness, how may LAMESPECs are there in this
// class! :) In the spec for the Position property it's stated
// "The position must not be more than one byte beyond the end of the stream."
// In the spec for seek it says "Seeking to any location beyond the length of the
// stream is supported." That's a contradiction i'd say.
// I guess seek can go anywhere but if you use position it may get moved back. refPoint += (int) offset;
if (refPoint < initialIndex)
throw new IOException ("Attempted to seek before start of MemoryStream."); position = refPoint;
return position;
} int CalculateNewCapacity (int minimum)
{
if (minimum < )
minimum = ; // See GetBufferTwo test if (minimum < capacity * )
minimum = capacity * ; return minimum;
} void Expand (int newSize)
{
// We don't need to take into account the dirty bytes when incrementing the
// Capacity, as changing it will only preserve the valid clear region.
if (newSize > capacity)
Capacity = CalculateNewCapacity (newSize);
else if (dirty_bytes > ) {
Array.Clear (internalBuffer, length, dirty_bytes);
dirty_bytes = ;
}
} public override void SetLength (long value)
{
if (!expandable && value > capacity)
throw new NotSupportedException ("Expanding this MemoryStream is not supported"); CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); if (!canWrite) {
throw new NotSupportedException (Locale.GetText
("Cannot write to this MemoryStream"));
} // LAMESPEC: AGAIN! It says to throw this exception if value is
// greater than "the maximum length of the MemoryStream". I haven't
// seen anywhere mention what the maximum length of a MemoryStream is and
// since we're this far this memory stream is expandable.
if (value < || (value + initialIndex) > (long) Int32.MaxValue)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException (); int newSize = (int) value + initialIndex; if (newSize > length)
Expand (newSize);
else if (newSize < length) // Postpone the call to Array.Clear till expand time
dirty_bytes += length - newSize; length = newSize;
if (position > length)
position = length;
} public virtual byte [] ToArray ()
{
int l = length - initialIndex;
byte[] outBuffer = new byte [l]; if (internalBuffer != null)
Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, initialIndex, outBuffer, , l);
return outBuffer;
} public override void Write (byte [] buffer, int offset, int count)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); if (offset < || count < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException (); if (buffer.Length - offset < count)
throw new ArgumentException ("offset+count",
"The size of the buffer is less than offset + count."); CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); if (!CanWrite)
throw new NotSupportedException ("Cannot write to this stream."); // reordered to avoid possible integer overflow
if (position > length - count)
Expand (position + count); Buffer.BlockCopy (buffer, offset, internalBuffer, position, count);
position += count;
if (position >= length)
length = position;
} public override void WriteByte (byte value)
{
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
if (!canWrite)
throw new NotSupportedException ("Cannot write to this stream."); if (position >= length) {
Expand (position + );
length = position + ;
} internalBuffer [position++] = value;
} public virtual void WriteTo (Stream stream)
{
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed (); if (stream == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("stream"); stream.Write (internalBuffer, initialIndex, length - initialIndex);
} #if NET_4_5 public override Task CopyToAsync (Stream destination, int bufferSize, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// TODO: Specialization but what for?
return base.CopyToAsync (destination, bufferSize, cancellationToken);
} public override Task FlushAsync (CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
return TaskConstants.Canceled; try {
Flush ();
return TaskConstants.Finished;
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Task<object>.FromException (ex);
}
} public override Task<int> ReadAsync (byte[] buffer, int offset, int count, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); if (offset < || count < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("offset or count less than zero."); if (buffer.Length - offset < count )
throw new ArgumentException ("offset+count",
"The size of the buffer is less than offset + count.");
if (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
return TaskConstants<int>.Canceled; try {
count = Read (buffer, offset, count); // Try not to allocate a new task for every buffer read
if (read_task == null || read_task.Result != count)
read_task = Task<int>.FromResult (count); return read_task;
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Task<int>.FromException (ex);
}
} public override Task WriteAsync (byte[] buffer, int offset, int count, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (buffer == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); if (offset < || count < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException (); if (buffer.Length - offset < count)
throw new ArgumentException ("offset+count",
"The size of the buffer is less than offset + count."); if (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
return TaskConstants.Canceled; try {
Write (buffer, offset, count);
return TaskConstants.Finished;
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Task<object>.FromException (ex);
}
}
#endif
}
}
通过上面的代码,你可以看出,很多方法和属性中都会有这样的一个方法的调用:
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
该方法的实现
void CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ()
{
if (streamClosed)
throw new ObjectDisposedException ("MemoryStream");
}
通过方法名可以清楚的知道该方法的作用:检查如果关闭了则抛出Dispose异常,通过方法体也可以清楚的知道该方法的作用。
你可以看一下ToArray方法
public virtual byte [] ToArray ()
{
int l = length - initialIndex;
byte[] outBuffer = new byte [l]; if (internalBuffer != null)
Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, initialIndex, outBuffer, , l);
return outBuffer;
}
从代码中,也可以看出该方法并没有对流是否关闭进行检查。
总结
虽然上面的代码能说明为什么出现异常的原因,但是为什么要这样设计?为什么其他的方法会检测是否释放而ToArray方法反而放过呢?
功底有限,也只能到这地步,如果哪个园友有更深入的解释,可以给个合理的解释,为什么这样设计?
选择性的释放,那会不会就不安全了呢?
[C#]MemoryStream.Dispose之后,为什么仍可以ToArray()?的更多相关文章
- C#导入导出数据你该知道的方法。
导入数据 using NPOI.HSSF.UserModel; using NPOI.SS.UserModel; using NPOI.XSSF.UserModel; using System; us ...
- 压缩文本、字节或者文件的压缩辅助类-GZipHelper
下面为大家介绍一.NET下辅助公共类GZipHelper,该工具类主要作用是对文本.字符.文件等进行压缩与解压.该类主要使用命名空间:System.IO.Compression下的GZipStream ...
- ASP.NET 导出gridview中的数据到Excel表中,并对指定单元格换行操作
1. 使用NPOI读取及生成excel表. (1)导出Click事件: 获取DataTable; 给文件加文件名: string xlsxName = "xxx_" + DateT ...
- 压缩文本、字节或者文件的压缩辅助类-GZipHelper 欢迎收藏
压缩文本.字节或者文件的压缩辅助类-GZipHelper 欢迎收藏 下面为大家介绍一.NET下辅助公共类GZipHelper,该工具类主要作用是对文本.字符.文件等进行压缩与解压.该类主要使用命名空间 ...
- C#、.NET网络请求总结(WebClient和WebRequest)
1.关于WebClient第三方的封装,支持多文件上传等 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; usin ...
- 一个对称加密、解密的方法C#工具类
封装了一个对称加解密的类,用私钥和密钥加解密 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using Syst ...
- .NET Core装饰模式和.NET Core的Stream
该文章综合了几本书的内容. 某咖啡店项目的解决方案 某咖啡店供应咖啡, 客户买咖啡的时候可以添加若干调味料, 最后要求算出总价钱. Beverage是所有咖啡饮料的抽象类, 里面的cost方法是抽象的 ...
- .NET Core/.NET之Stream简介
之前写了一篇C#装饰模式的文章提到了.NET Core的Stream, 所以这里尽量把Stream介绍全点. (都是书上的内容) .NET Core/.NET的Streams 首先需要知道, Syst ...
- .net MVC4一个登陆界面加验证
Model using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using Syst ...
随机推荐
- CSS中的 backgroundPosition 属性
body { background-image:url('bgimage.gif'); background-repeat:no-repeat; background-attachment:fixed ...
- Linux登录出现modle is unknow
一.问题描述 登录linux系统发现控制台无法登录,即使输入正确用户名和密码,也无法登录,回车看到有一个错误“module is unknow”. 但是,ssh可以正常登录. 二.解决办法 ssh登录 ...
- JMS介绍入门大白话版
以下内容转自: http://setting.iteye.com/blog/1097767 ------------------------------------------------------ ...
- 一个CentOS7的开发环境部署,包括防火墙|VPN|多IP多网关|HTTP代理服务器设置等
http://www.lenggirl.com/code/centos7.html layout: post title: "一个CentOS7的开发环境部署,包括防火墙|VPN|HTTP代 ...
- Dijkstra求最短路径
单源点的最短路径问题:给定带权有向图G和源点V,求从V到G中其余各顶点的最短路径 Dijkstra算法描述如下: (1)用带权的邻接矩阵arcs表示有向图,arcs[i][j]表示弧<vi,vj ...
- linux --备份oracle
1.exp\imp 导入导出命令使用exp username/pwd@sid file=path.dmp owner=user 不导出表数据:rows=n举例:exp iflashbuy/qwerwh ...
- Lua windows环境搭建
Lua语言的小巧和功能强大在朋友做的一个项目中得以验证,自己也尝试着了解一下,首先在window系统上搭建一个学习环境. 官网:https://www.lua.org/ 搭建运行环境提供2种方式,源码 ...
- Thread锁 Monitor类、Lock关键字和Mutex类
Monitor 类锁定一个对象 当多线程公用一个对象时,也会出现和公用代码类似的问题,这种问题就不应该使用lock关键字了,这里需要用到System.Threading中的一个类Monitor,我们可 ...
- 【转】【C#】C# 不常用关键字
1.__arglist 让我们先从__arglist开始. __arglist是用来给方法传送参数.通常我们是通过函数头部指定的参数列表给方法传递参数的.如果我们想要给方法传递一组新的参数,我们需要重 ...
- wireshark排查打印机问题
抓包工具排除故障 前言:上网慢,可能是内网堵了.装上wireshark,可抓到广播包,多播包,以及发给自己的包.如果想抓lan内其他人之间的通信包,那就要在sw上做端口镜像. 背景 调试打印机的人发现 ...