C#集合-列举(Enumeration)
在计算机这个范畴内存在许多种类的集合,从简单的数据结构比如数组、链表,到复杂的数据结构比如红黑树,哈希表。尽管这些数据结构的内部实现和外部特征大相径庭,但是遍历集合的内容确是一个共同的需求。.NET Framework通过IEnumerable和IEnumerator接口实现遍历集合功能。
| Non-Generic | Generic | 备注 |
| IEnumerator | IEnumerator<T> | |
| IEnumerable | IEnumerable<T> | 仅可遍历 |
| ICollection | ICollection<T> | 遍历,可统计集合元素 |
| IDictionary IList |
IDictionary<TKey,TValue> IList<T> |
拥有更过的功能 |
IEnumerable与IEnumerator
IEnumerator接口定义了遍历协议--在这个协议中,集合中的元素使用向前的方式进行遍历。它的声明如下:
public interface IEnumerator
{
bool MoveNext(); Object Current { get; } void Reset();
}
MoveNext将当前元素或指针移动到下一个位置,如果下一个位置没有元素那么返回false。Current返回在当前值位置的元素。在获取集合的第一个元素之前,必须调用MoveNext方法--这对于空集合同样适用。Reset方法,这移动到初始位置,从而允许集合可以再次遍历。Reset更过多是为COM互操作而设计:应该尽量直接避免调用此方法,因为它并没有得到普遍的支持(直接调用此方法是不必要的,因为创建一个新的列举实例更容易)。
集合一般都不实现列举器,相反,它们通过IEnurable接口提供列举器
public interface IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
通过定义一个单一返回列举器的方法,IEnumerable接口提供了更多的灵活性,从而各个实现类的遍历集合的逻辑可以各部相同。这也就意味着每个集合的使用者都可以创建自己的方法遍历集合而不会相互影响。IEnumerable可以被视作IEnumeratorProvider,它是所有集合类都必须实现的一个接口。
下面的代码演示了如何使用IEnumerable和IEnumerator:
string s = "Hello"; // IEnumerator
IEnumerator rator = s.GetEnumerator();
while (rator.MoveNext())
Console.Write(rator.Current + "."); Console.WriteLine(); // IEnumerable
foreach (char c in s)
Console.Write(c + ".");
一般地,很少调用GetEnumerator方法得到IEnumerator接口,这是由于C#提供了foreach语法(foreach语法编译后,会自动调用GetEnumerator从而遍历集合),这使得代码变得更简洁。
IEnumerable<T>与IEnumerator<T>
IEnumerator和IEnumerable对应的Generic接口定义如下:
public interface IEnumerator<out T> : IDisposable, IEnumerator
{
new T Current {
get;
}
}
public interface IEnumerable<out T> : IEnumerable
{
new IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator();
}
Generic的Current和GetEnumerator,增加了接口IEnumerable<T>与IEnumerator<T>的类型安全性,避免了对值类型进行装箱操作,对于集合的使用者更加便利。请注意,数字类型默认实现了IEnumerable<T>接口。
正是由于实现了类型安全的接口,方法Test2(arr)在编译时就会报错:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
char[] arr = new char[] { '1', '2', '3' };
Test1(arr); // ok
Test2(arr); // complie-error: cannot convert from char[] to IEnumerable[] Console.ReadLine();
} static void Test1(IEnumerable numbers)
{
foreach (object i in numbers)
Console.Write(i + ",");
} static void Test2(IEnumerable<int> numbers)
{
foreach (object i in numbers)
Console.Write(i + ",");
}
请注意,Array默认实现了IEnumerable<T>接口,那么它同时必然实现了IEnumerable接口。虽然char[]不能转换成IEnumrable<int>,但是却可以转换成IEnumeable,所以Test1可以通过编译,而Test2不能通过编译(类型转化失败错误)
对于集合类,对外暴露IEnumerable<T>是标准做法;并需要显示地实现IEnumerable接口,从而隐藏非Generic的IEnumerable。此时,你再调用GetEnumerator,将得到IEnumerator<T>。但有时候,为了兼容非Generic的集合,我们可以不遵守这个规则。最好的例子就是数组集合,数组必须返回非generic的IEnumerator以避免与早期的代码冲突。在这种情况下,为了获取IEnumerator<T>,就必须先把数组显示地转化为Generic接口,然后再获取:
char[] arr = new char[] { '1', '2', '3' };
var rator = ((IEnumerable<char>)arr).GetEnumerator();
幸运的是,你很少需要编写这样的代码,这就要归功于foreach语句。
IEnumerable<T>和IDisposable
IEnumerator<T>继承了IDisposable。这就允许列举器可以拥有资源的引用比如数据库连接,从而确保在遍历完成后释放这些资源。foreach会语句会识别这个特性,比如,下面的foreach语句
IList<char> chars =new List<char>(){'a', 'b', 'c'};
foreach (char c in chars)
Console.Write(c);
编译后的代码为:
.method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
{
......
IL_0026: callvirt instance class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator`1<!0> class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable`1<char>::GetEnumerator()
IL_002b: stloc.3
.try
{
.......
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator`1<char>::get_Current()
......
IL_0036: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::Write(char)
......
IL_003d: callvirt instance bool [mscorlib]System.Collections.IEnumerator::MoveNext()
......
} // end .try
finally
{
......
IL_0055: callvirt instance void [mscorlib]System.IDisposable::Dispose()
......
} // end handler
......
} // end of method Program::Main
因此,如果实现了IEnumable<T>接口,执行foreach时,会转化成调用GetEnumerator<T>, 在遍历完成之后,释放IEnumerator<T>。
实现列举接口
当满足下面的一个或多个条件时,需要实现IEnumerable或IEnumerable<T>
- 为了支持foreach语句
- 为了实现除了标准集合之外的集合都是可互操作的
- 为了满足一个复杂集合接口
- 为了支持集合初始化
而实现IEnumerable/IEnumerable<T>,你必须提供一个列举器,你可以通过下面三种方式实现
- 如果类包含了另外集合,那么需要返回所包含集合的列举器
- 在迭遍历内部使用yield return
- 实例化IEnumerator/IEnumerator<T>的实现
1)实例IEnumerator/IEnumerator<T>
返回另外一个集合的列举器就是调用内部集合的GetEnumerator。但是,这只发生在简单的场景中,在这样的场景中,内部集合中的元素已经满足需要。另外一种更为灵活的方式是通过yield return语句生成一个迭代器。迭代器(iteraotr)是C#语言特性,该特性用于辅助生产集合,同样地foreach可与用于iterator以遍历集合。一个迭代器自动处理IEnumerable和IEnumerator的实现。下面是一个简单的例子
internal class MyCollection : IEnumerable
{
int[] data ={ 1, 2, 3 }; public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
foreach (int i in data)
yield return i;
}
}
请注意,GetEnumerator根本就没有返回一个列举器。依赖于解析yield return后的语句,编译器编写了一个隐藏的内嵌列举器类,然后重构 GetEnumerator实现实例化,最后返回该类。迭代不仅功能强大而且简单。
通过IL代码,我们可以看到确实生产了一个内嵌的列举器类
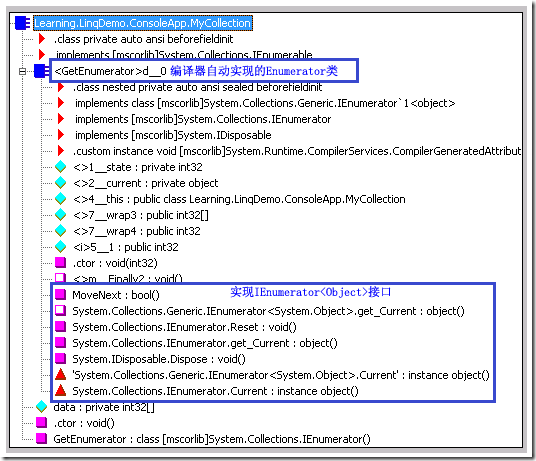
我们在上面代码的基础上,对MyCollecton做些许修改,使其不仅仅实现IEnumerable,还实现IEnumerable<T>
internal class MyCollection : IEnumerable<int>
{
int[] data ={ 1, 2, 3 }; public IEnumerator<int> GetEnumerator()
{
foreach (int i in data)
yield return i;
} IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return GetEnumerator();
}
}
因为IEnumerable<T>继承了IEnumerable,因此我们必须实现generic的GetEnumerator和非generic的GetEnumerator。按照标准的做法,我们已经实现了Generic的GetEnumerator。因此对于非Generic的GetEnumerator,我们直接调用Generic的GetEnumerator即可,这是因为IEnumerable<T>继承了IEnumerbale。
对应的IL代码如下:(请注意编译器实现的IEnumerator<Int32>接口,而不再是IEnumerator<Object>接口)

2)在使用yield return返回IEnumerable<T>
我们创建的类MyCollection可以做为复杂集合类的基本实现。但是,如果你不需要实现IEnumerable<T>,那么应可以通过yield return语句实现一个IEnumerable<T>,而不是编写MyCollection这样的类。也就是说你可以把迭代逻辑迁移到一个返回IEnumerable<T>的方法中,然后让编译器来为你完成剩余的事情。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{ foreach(int i in GetSomeIntegers())
Console.WriteLine(i); Console.ReadLine();
} static IEnumerable<int> GetSomeIntegers()
{
int[] data = { 1, 2, 3 };
foreach (int i in data)
yield return i;
}
}
与之对应的IL代码
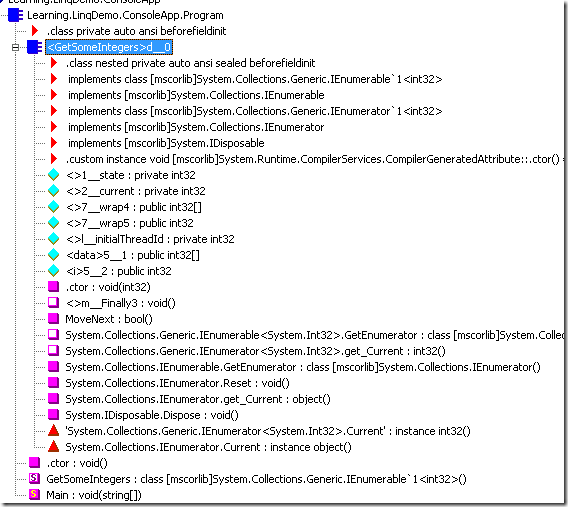
从IL代码中,我们可以看到,编译器同样生产了一个内部的类,该类实现了IEnumerator<Int32>接口。
3)如果类包含了另外集合,那么需要返回所包含集合的列举器
最后一种实现方式将就是编写一个类直接实现IEnumerator接口。其实这也就是编译器之前做的事情。在实际中,你不需要这么做。
首先我们来实现非Generic的IEnumerator
internal class MyCollection : IEnumerable
{
int[] data ={ 1, 2, 3 }; public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
return new Enumerator(this);
} private class Enumerator : IEnumerator
{
MyCollection collection;
int index; public Enumerator(MyCollection collection)
{
this.collection = collection;
index = -1;
} public object Current
{
get { return collection.data[index]; }
} public bool MoveNext()
{
if (index < collection.data.Length-1)
{
index++;
return true;
} return false;
} public void Reset()
{
index = -1;
}
}
}
然后,我们在上述代码的基础上,实现Generic的IEnumerator
internal class MyCollection : IEnumerable<Int32>
{
int[] data = { 1, 2, 3 }; // implement IEnumerable<T>
public IEnumerator<Int32> GetEnumerator()
{
return new Enumerator(this);
}
// implement IEnumerable
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return GetEnumerator();
} private class Enumerator : IEnumerator<Int32>
{
MyCollection collection;
int index; public Enumerator(MyCollection collection)
{
this.collection = collection;
index = -1;
} #region implement IEnumerator<T>
public int Current
{
get { return collection.data[index]; }
} public void Dispose()
{
} public bool MoveNext()
{
if (index < collection.data.Length - 1)
{
index++;
return true;
} return false;
} public void Reset()
{
index = -1;
}
#endregion // implement IEnumerator
object IEnumerator.Current
{
get { return Current; }
}
}
}
Generic版本的IEnumerator比非Generic的IEnumberator效率高一些,因为不需要把int转化成object,从而减少了装箱的开销。我们多看一眼此时对应的IL代码:

显然地,我们可以看到我们手动创建Enumerator与编译器生成的Enumerator是一样的
此外,当我们使用第二种方式的时候,如果我们有多个IEnumerable<T>的方法,那么编译器会产生多个实现了IEnumerator<T>的类
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{ foreach (int i in GetSomeIntegers())
Console.WriteLine(i); foreach (int i in GetSomeOdds())
Console.WriteLine(i); Console.ReadLine();
} static IEnumerable<Int32> GetSomeIntegers()
{
int[] collection = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
foreach (int i in collection)
yield return i;
} static IEnumerable<Int32> GetSomeOdds()
{
int[] collection = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
foreach (int i in collection)
if(i%2==1)
yield return i;
} }
对应的IL代码可以看到有两个内部IEnumerator<T>类
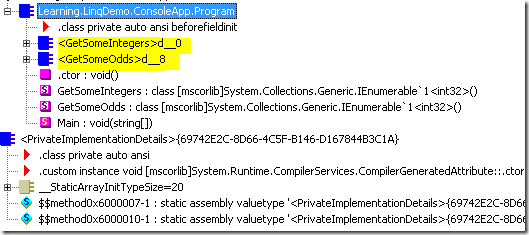
而下面的代码只会产生一个IEnumerator<T>类
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{ foreach (int i in GetSomeIntegers())
Console.WriteLine(i); foreach (int i in GetSomeOdds())
Console.WriteLine(i); Console.ReadLine();
} static IEnumerable<Int32> GetSomeIntegers()
{
return GetDetails();
} static IEnumerable<Int32> GetSomeOdds()
{
return GetDetails(true);
} private static IEnumerable<Int32> GetDetails(bool isOdd = false)
{
int[] collection = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int index = 0; foreach (int i in collection)
{
if (isOdd && i % 2 == 1)
yield return i;
if (!isOdd)
yield return collection[index]; index++;
}
}
}
同样地,下面的代码也只会产生一个IEnumerator<T>类
....
static IEnumerable<Int32> GetSomeIntegers()
{
foreach (int i in GetDetails())
yield return i;
} static IEnumerable<Int32> GetSomeOdds()
{
foreach (int i in GetDetails(true))
yield return i;
}
....
由此,我们可以发现,在实现IEnumerable时,特别是有多个实现时,需要注意尽量减少编译器生成IEnumerator的类的个数。我猜测在内部,编译器应该是根据真正不同的yield return对于的iterator来确定IEnumerator类的个数。在我的示例代码中,产出两个IEnumerator类时,GetSomeIntegers和GetSomeOdds的yield return的iterator是不同的;而在产生一个IEnumerator类时,它们都指向GetDetails的yield return对应的iterator。
最后,我们再来看看IEnumerator与Iterator
在网上,并没有关于两者的明确区分,或许是我把两个不该混淆的概念混淆了。下面是我自己的看法,如果不正确,欢迎指正:
1) 实现IEnumerator用于实现IEnumerable,与GetEnumerator方法关联在一起,从而可以使用foreach;而且一旦一个类中确定了遍历(MoveNext)的方式之后,那么就只有这一种方式去遍历集合了。.NET Framework中大多数集合的IEnumerator都默认向前只读的方式遍历集合。
2)Iterator用于遍历集合,可以有多个实现方式,唯一的要求是返回IEnumerator<T>,从某种意义上说,Iterator就是IEnumerator。两者的区别是,前者一旦确定,就只能使用这个方式遍历集合然后返回一个IEnumerator;而后者可以在多个方法中以多种方式遍历集合然后返回不同的IEnumerator。(我认为,两者的差别与IComparable和IComparer的差别类似)。
C#集合-列举(Enumeration)的更多相关文章
- Java 获取Enumeration类型的集合
学习到java的io流中关于序列流SequenceInputStream使用,其中把3个以上的流串联起来操作, 使用的参数是生成运行时类型为 InputStream 对象的 Enumeration 型 ...
- c#列举和迭代器
列举 - Enumeration 迭代器是一个值序列(集合)上的一个只读且只向前移动的游标.迭代器要么实现了IEnumerator接口,要么实现了IEnumerator<T>接口. 从技术 ...
- 面试题-Java基础-集合和数组
1.Java集合类框架的基本接口有哪些? 集合类接口指定了一组叫做元素的对象.集合类接口的每一种具体的实现类都可以选择以它自己的方式对元素进行保存和排序.有的集合类允许重复的键,有些不允许.Java集 ...
- Java面试准备之集合框架
集合框架 Collection:List列表,Set集 Map:Hashtable,HashMap,TreeMap Collection 是单列集合 List 元素是有序的(元素存取是有序).可重复 ...
- Java面试题:Java中的集合及其继承关系
关于集合的体系是每个人都应该烂熟于心的,尤其是对我们经常使用的List,Map的原理更该如此.这里我们看这张图即可: 1.List.Set.Map是否继承自Collection接口? List.Set ...
- Java面试专题-集合篇(2)
- [010] - JavaSE面试题(十):集合之Map
第一期:Java面试 - 100题,梳理各大网站优秀面试题.大家可以跟着我一起来刷刷Java理论知识 [010] - JavaSE面试题(十):集合之Map 第1问:HashMap和HashTable ...
- Java 集合系列11之 Hashtable详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
概要 前一章,我们学习了HashMap.这一章,我们对Hashtable进行学习.我们先对Hashtable有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会使用Hashtable.第1部分 Ha ...
- JavaEE基础(十七)/集合
1.集合框架(HashSet存储字符串并遍历) A:Set集合概述及特点 通过API查看即可 B:案例演示 HashSet存储字符串并遍历 HashSet<String> hs = new ...
随机推荐
- day5----正则
%a 本地(locale)简化星期名称 %A 本地完整星期名称 %b 本地简化月份名称 %B 本地完整月份名称 %c 本地相应的日期和时间 ...
- C/C++中static关键字详解
静态变量作用范围在一个文件内,程序开始时分配空间,结束时释放空间,默认初始化为0,使用时可以改变其值. 静态变量或静态函数只有本文件内的代码才能访问它,它的名字在其它文件中不可见.用法1:函数内部声明 ...
- line-height,vertical-align及图片居中对齐问题根源解析
关于图片居中对齐的问题,进入前端行业虽然有一段时间了,以为自己懂了,可是实际上还是一知半解,找了一些博客来看了一下,但是感觉讲的有点碎,看完还是一知半解. 查阅了一下<css权威指南>,结 ...
- c#中的static
1.C# 不支持静态局部变量(在方法范围内声明的变量). 2.static类一般用于与状态无关的类.那么,什么是与状态无关的类?我的理解是当一个类中没有属性,只有方法的的时候,就可以认为这个类是与状态 ...
- C#常用IO流与读写文件
.文件系统 ()文件系统类的介绍 文件操作类大都在System.IO命名空间里.FileSystemInfo类是任何文件系统类的基类:FileInfo与File表示文件系统中的文件:Directory ...
- VS下的Resharper插件报错“Can not resolve symbol”的解决办法
今天准备写代码的时候,发现代码中大片的红色,就像下面的图片一样.但是编译一下,也可以重新生成,运行也没有问题.于是就看了下svn上是不是有人改了哪里,发现也没有问题.于是又清理了下解决方案,再次生成, ...
- 3.SRS文档
1.功能需求 本程序的使用者为局域网用户.程序实现的主要功能是局域网的常见格式的文件的传 输.其用例图如图1.本程序可通过可视化操作界面实现一对多的文件传输. 1.1模块分析 为实现局域网文件传输, ...
- [C++] socket -7 [邮槽]
::利用邮槽实现windons进程通信 ::一般情况下CreateMailslot()常被使用在进程通信的服务器上,在客户端则是用函数CreateFile()打开指定的邮槽之后进行相关的操作. ::将 ...
- NodeJS系列~目录
回到占占推荐博客索引 Node.js官网对它的阐述 Node.js is a platform built on Chrome's JavaScript runtime for easily buil ...
- atitit.无线网卡 不能搜索到WiFi 无线路由信号的解决不能上网
atitit.无线网卡 不能搜索到WiFi 无线路由信号的解决不能上网 #---现象 pc机无线网卡不能搜索到无线路由信号.. 但是笔记本和手机是可以的... 不过pc机无线网卡能搜索到别的路由的信号 ...
