Linux C 数据结构 ->单向链表
之前看到一篇单向链表的博文,代码也看着很舒服,于是乎记录下来,留给自己~,循序渐进,慢慢
延伸到真正的内核链表~(敢问路在何方?路在脚下~)
1. 简介
链表是Linux 内核中最简单,最普通的数据结构。链表是一种存放和操作可变数量元素(常称为节点)
的数据结构,链表和静态数组的不同之处在于,它所包含的元素都是动态创建并插入链表的,在编译
时不必知道具体需要创建多少个元素,另外也因为链表中每个元素的创建时间各不相同,所以它们在
内存中无须占用连续内存区。正是因为元素不连续的存放,所以各个元素需要通过某种方式被链接在
一起,于是每个元素都包含一个指向下一个元素的指针,当有元素加入链表或从链表中删除元素时,
简单调整一下节点的指针就可以了。
根据它的特性,链表可分为:单链表,双链表,单向循环链表和双向循环链表,今天总结记录的就是
最简单的单链表,
1.1 节点类型描述
1 typedef struct node_t {
2 data_t data; /* 节点数据域 */
3 struct node_t *next; /* 节点的后继指针域 */
4 }linknode_t, *linklist_t;
另一种写法
1 struct node_t {
2 data_t data;
3 struct node_t *next;
4 }
5 typedef struct node_t linknode_t;
6 typedef struct node_t* linklist_t;
细看说明:
* linknode_t A;
* linklist_t p = &A;
*
* 结构变量A为所描述的节点,而指针变量p为指向此类型节点的指针(p值为节点的地址)
* 这样看来 linknode_t 和 linklist_t 的作用是一样的,那么为什么我们要定义两个数据类
* 型(同一种)呢? 答曰:主要为了代码的可读性,我们要求标识符要望文识义,便于理解
*
* linknode_t *pnode 指向一个节点
* linklist_t list 指向一个整体
1.2 头节点 head (~黄河之水天上来~)
在顺序存储线性表,如何表达一个空表{ },是通过list->last = -1来表现的,所谓的空表就是
数据域为NULL,而链表有数据域和指针域,我们如何表现空链表呢?这时,就引入了头结点
的概念,头结点和其他节点数据类型一样,只是数据域为NULL,head->next = NULL,下面
我们看一个创建空链表的函数,如何利用头结点来创建一个空链表,只要头节点在,链表就还在~
1 // 创建一个空链表
2 linklist_t
3 CreateEmptyLinklist()
4 {
5 linklist_t list;
6 list = (linklist_t)malloc(sizeof(linknode_t));
7
8 if(NULL != list) {
9 list->next = NULL;
10 }
11
12 return list;
13 }
2. 链表基本运算的相关"算法"操作 or 操刀(~烹羊宰牛且为乐,会须一饮三百杯~)
链表的运算除了上面的创建空链表,还有数据的插入,删除,查找等函数,链表的运算有各种实现方
法,如何写出一个高效的,封装性较好的函数是我们要考虑的,比如数据插入函数,我们就要尽可能
考虑所有能出现的结果,比如:1)如果需插入数据的链表是个空表;2)所插入的位置超过了链表的
长度;如果我们的函数能包含所有能出现的情况,不仅能大大提高我们的开发效率,也会减少代码的
错误率。下面看一个可用性较强的链表插入操作的函数实现~
int
InsertLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x)
{
linknode_t * node_prev, * node_at, * node_new;
int pos_at;
int found = 0;
if (NULL == list) return -1;
/* at must >= 0 */
if (at < 0) return -1;
/*第一步、新节点分配空间*/
node_new = (linklist_t)malloc(sizeof(linknode_t));
if (NULL == node_new) {
return -1;
}
node_new->data = x; /* assigned value */
/*
*节点如果插入超过链表长度的位置,会接到尾节点后面,
*这样,node_new成了尾节点,node_new->next = NULL
*/
node_new->next = NULL;
/*第二步、定位*/
node_prev = list; //跟随指针,帮助我们更好的定位
node_at = list->next; //遍历指针
pos_at = 0;
while(NULL != node_at) {
if(pos_at == at){
found = 1; //找到正确的位置,跳出循环
break;
}
/* move to the next pos_at */
node_prev = node_at; //跟随指针先跳到遍历指针的位置
node_at = node_at->next; //遍历指针跳到下一个节点的位置
pos_at++;
}
/*第三步、插入*/
if(found) {
/* found = 1,找到正确的位置,插入 */
node_new->next = node_at; //插入的节点next指向node_at
node_prev->next = node_new; //插入节点的前一个节点
}
else {
/*若是没找到正确的位置,即所插入位置超越了链表的长度,
*则接到尾节点的后面,同样,这样适用于{ }即空链表,这样
*我们可以建立一个空链表,利用这个函数,实现链表的初始化
*/
node_prev->next = node_new;
}
return 0;
}
3. 正文开始 Demo(~与君歌一曲,请君为我倾耳听~)
listlink.h
1 #ifndef _LIST_LINK_H_
2 #define _LIST_LINK_H_
3
4 typedef int data_t;
5
6 typedef struct node_t {
7 data_t data; /* 节点数据域 */
8 struct node_t * next; /* 节点的后继指针域 */
9 }linknode_t, * linklist_t;
10
11
12
13 /* 链表操作函数*/
14
15 // 创建一个空链表
16 linklist_t CreateEmptyLinklist();
17
18 // 销毁链表
19 void DestroyLinklist(linklist_t list);
20
21 // 清空链表
22 void ClearLinklist(linklist_t list);
23
24 // 是否为空链表
25 int IsEmptyLinklist(linklist_t list);
26
27 // 链表长度
28 int LengthLinklist(linklist_t list);
29
30 // 获去链表节点数据
31 int GetLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t * x);
32
33 // 设置链表节点数据
34 int SetLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x);
35
36 // 插入节点
37 int InsertLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x);
38
39 // 删除节点
40 int DeleteLinklist(linklist_t list, int at);
41
42 // 链表转置
43 linklist_t ReverseLinklist(linklist_t list);
44
45 // 打印链表
46 int Display(linklist_t list);
47
48
49 #endif // _LIST_LINK_H_
listlink.c
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include "listlink.h"
4
5 // 创建一个空链表
6 linklist_t
7 CreateEmptyLinklist()
8 {
9 linklist_t list;
10 list = (linklist_t)malloc(sizeof(linknode_t));
11
12 if(NULL != list) {
13 list->next = NULL;
14 }
15
16 return list;
17 }
18
19 // 销毁链表
20 void
21 DestroyLinklist(linklist_t list)
22 {
23 if(NULL != list) {
24 ClearLinklist(list);
25 free(list);
26 }
27 }
28
29 // 清空链表
30 void
31 ClearLinklist(linklist_t list)
32 {
33 linknode_t * node; /* pointer to the node to be remove */
34 if(NULL == list) return;
35
36 while(NULL != list->next) {
37 node = list->next;
38 list->next = node->next; //此时node->next是第二node节点元素依次往后
39 free(node);
40 }
41 return;
42 }
43
44 // 是否为空链表
45 int
46 IsEmptyLinklist(linklist_t list)
47 {
48 if(NULL != list) {
49 if(NULL == list->next) // 只有头节点
50 return 1; // 返回1,是个空链表
51 else
52 return 0; // 返回0,链表非空
53
54 } else
55 return -1; // 返回-1, 错误的类型
56 }
57
58 // 链表长度
59 int
60 LengthLinklist(linklist_t list)
61 {
62 int len = 0;
63 linknode_t * node; // 遍历指针
64
65 if(NULL == list) return -1;
66
67 node = list->next; // node指针指向第一个节点
68 while(NULL != node) {
69 len++;
70 node = node->next;
71 }
72
73 return len;
74 }
75
76 // 获去一个链表指定节点数据域的数据值
77 int
78 GetLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t * x)
79 {
80 linknode_t *node; // 遍历节点的指针
81 int pos; // 用于遍历比较
82
83 if(NULL == list) return -1;
84 /*at 必须要 >= 0*/
85 if(at < 0) return -1;
86
87 /* 从第一个元素开始 */
88 node = list->next; // node指针指向一个元素
89 pos = 0;
90 while(NULL != node) {
91 if(at == pos) {
92 if(NULL != x)
93 *x = node->data;
94 return 0;
95 }
96 // 下一个元素
97 node = node->next;
98 pos++;
99 }
100 return -1;
101 }
102
103 // 设置一个指定链表节点的数据域值
104 int
105 SetLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x)
106 {
107 linknode_t * node; // 遍历链表
108 int pos;
109 int found = 0;
110
111 if(!list) return -1;
112 /*at 必须 >= 0*/
113 if(at < 0) return -1;
114
115 /* node指针指向第一个元素 */
116 node = list->next;
117 pos = 0;
118 while(NULL != node) {
119 if(at == pos) {
120 found = 1; // 找到了位置
121 node->data = x;
122 break;
123 }
124 /*往后移动元素*/
125 node = node->next;
126 pos++;
127 }
128 if(1 == found)
129 return 0;
130 else
131 return -1;
132 }
133
134 // 插入节点
135 int
136 InsertLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x)
137 {
138 /*
139 * node_at and pos_at are used to locate the position of node_at.
140 * node_prev follows the node_at and always points to previous node
141 * of node_at.
142 * node_new is used to point to the new node to be inserted.
143 */
144 linknode_t * node_prev, * node_at, * node_new;
145 int pos_at;
146 int found = 0;
147
148 if(NULL == list) return -1;
149
150 /* at 必须 >= 0 */
151 if(at < 0) return -1;
152
153 node_new = malloc(sizeof(linknode_t));
154 if(NULL == node_new)
155 return -1;
156 node_new->data = x; // assigned value
157 node_new->next = NULL;
158
159 node_prev = list; // head
160 node_at = list->next; //node_at指针指向第一元素
161 pos_at = 0;
162 while(NULL != node_at) {
163 if(pos_at == at) {
164 found = 1; // found the node ‘at'
165 break;
166 }
167 /* move to the next pos_at */
168 node_prev = node_at;
169 node_at = node_at->next;
170 pos_at++;
171 }
172
173 if(found) {
174 /* insert */
175 node_new->next = node_at;
176 node_prev->next = node_new;
177 } else{
178 /*
179 * If not found,means the provided 'at'
180 * exceeds the upper limit of the list, just
181 * append the new node to the end of the list
182 */
183 node_prev->next = node_new;
184 }
185
186 return 0;
187 }
188
189 // 删除节点
190 int
191 DeleteLinklist(linklist_t list, int at)
192 {
193 /*
194 * node_at and pos_at are used to locate the position of node_at.
195 * node_prev follows the node_at and always points to previous node
196 * of node_at.
197 */
198 linknode_t * node_prev, * node_at;
199 int pos_at;
200 int found = 0;
201
202 if(!list) return -1;
203 if(at < 0) return -1;
204
205 node_prev = list; // node_prev指针指向链表头
206 node_at = list->next; // node_at指针指向第一元素
207 pos_at = 0;
208
209 while(NULL != node_at) {
210 if(pos_at == at) {
211 // found the node 'at'
212 found = 1;
213 break;
214 }
215 // move to the next pos_at
216 node_prev = node_at;
217 node_at = node_at->next;
218 pos_at++;
219 }
220 if(found) {
221 // remove
222 node_prev->next = node_at->next;
223 free(node_at);
224 return 0;
225 }else
226 return -1;
227 }
228
229 // 链表转置
230 linklist_t
231 ReverseLinklist(linklist_t list)
232 {
233 linknode_t * node; // iterator
234 linknode_t * node_prev; // previous node of iterator
235 linknode_t * node_next; /* next node of iterator
236 * used to backup next of iterator
237 */
238 if(NULL == list) return NULL;
239 node_prev = NULL;
240 node = list->next; // node指针指向第一个元素
241 while(NULL != node) {
242 /*
243 * step1: backup node->next
244 * due to the next of iterator will be
245 * modified in step2
246 */
247 node_next = node->next;
248 /*
249 * when iterator reaches the last node
250 * of original list, make the list head
251 * point to the last node, so the original
252 * last one becomes the first one.
253 */
254 if(NULL == node_next)
255 list->next = node;
256 /*
257 * step2: reverse the linkage between nodes
258 * make the node pointer to the previous node,
259 * not the next node
260 */
261 node->next = node_prev;
262 /*
263 * step3: move forward
264 */
265 node_prev = node;
266 node = node_next;
267 }
268
269 return list;
270 }
271
272 // 打印链表
273 int
274 Display(linklist_t list)
275 {
276 linknode_t * node;
277
278 if(NULL == list) return -1;
279
280 node = list->next;
281 while(node != NULL) {
282 printf(" %d ", node->data);
283 node = node->next;
284 }
285 printf("\n");
286
287 return 0;
288 }
289
290
291 int main(int argc, char * argv[])
292 {
293 int i;
294 data_t x;
295 linklist_t p;
296
297 /*创建链表*/
298 p = CreateEmptyLinklist();
299 Display(p);
300 data_t a[10] = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19};
301
302 for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
303 /*插入链表*/
304 InsertLinklist(p, i, a[i]);
305 }
306 Display(p);
307
308 /*链表转置*/
309 ReverseLinklist(p);
310 /*链表长度*/
311 printf("The length of the list is [%d]\n", LengthLinklist(p));
312 Display(p);
313
314 /*获取特定节点值*/
315 GetLinklist(p, 4, &x);
316 printf("The No.4 of this list is [%d]\n", x);
317
318 /*设置特定节点的值*/
319 SetLinklist(p, 4, 100);
320 GetLinklist(p, 4, &x);
321 printf("After updating! The No.4 of this list is [%d]\n", x);
322 Display(p);
323
324 /*删除节点*/
325 DeleteLinklist(p,5);
326 printf("After delete!The length of list is [%d]\n", LengthLinklist(p));
327 Display(p);
328
329 /*清空链表*/
330 ClearLinklist(p);
331 if(IsEmptyLinklist(p))
332 printf("This list is empty!\n");
333 /*销毁链表*/
334 DestroyLinklist(p);
335 printf("This list is destroyed!\n");
336
337
338 return 0;
339
340 }
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include "listlink.h"
4
5 // 创建一个空链表
6 linklist_t
7 CreateEmptyLinklist()
8 {
9 linklist_t list;
10 list = (linklist_t)malloc(sizeof(linknode_t));
11
12 if(NULL != list) {
13 list->next = NULL;
14 }
15
16 return list;
17 }
18
19 // 销毁链表
20 void
21 DestroyLinklist(linklist_t list)
22 {
23 if(NULL != list) {
24 ClearLinklist(list);
25 free(list);
26 }
27 }
28
29 // 清空链表
30 void
31 ClearLinklist(linklist_t list)
32 {
33 linknode_t * node; /* pointer to the node to be remove */
34 if(NULL == list) return;
35
36 while(NULL != list->next) {
37 node = list->next;
38 list->next = node->next; //此时node->next是第二node节点元素依次往后
39 free(node);
40 }
41 return;
42 }
43
44 // 是否为空链表
45 int
46 IsEmptyLinklist(linklist_t list)
47 {
48 if(NULL != list) {
49 if(NULL == list->next) // 只有头节点
50 return 1; // 返回1,是个空链表
51 else
52 return 0; // 返回0,链表非空
53
54 } else
55 return -1; // 返回-1, 错误的类型
56 }
57
58 // 链表长度
59 int
60 LengthLinklist(linklist_t list)
61 {
62 int len = 0;
63 linknode_t * node; // 遍历指针
64
65 if(NULL == list) return -1;
66
67 node = list->next; // node指针指向第一个节点
68 while(NULL != node) {
69 len++;
70 node = node->next;
71 }
72
73 return len;
74 }
75
76 // 获去一个链表指定节点数据域的数据值
77 int
78 GetLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t * x)
79 {
80 linknode_t *node; // 遍历节点的指针
81 int pos; // 用于遍历比较
82
83 if(NULL == list) return -1;
84 /*at 必须要 >= 0*/
85 if(at < 0) return -1;
86
87 /* 从第一个元素开始 */
88 node = list->next; // node指针指向一个元素
89 pos = 0;
90 while(NULL != node) {
91 if(at == pos) {
92 if(NULL != x)
93 *x = node->data;
94 return 0;
95 }
96 // 下一个元素
97 node = node->next;
98 pos++;
99 }
100 return -1;
101 }
102
103 // 设置一个指定链表节点的数据域值
104 int
105 SetLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x)
106 {
107 linknode_t * node; // 遍历链表
108 int pos;
109 int found = 0;
110
111 if(!list) return -1;
112 /*at 必须 >= 0*/
113 if(at < 0) return -1;
114
115 /* node指针指向第一个元素 */
116 node = list->next;
117 pos = 0;
118 while(NULL != node) {
119 if(at == pos) {
120 found = 1; // 找到了位置
121 node->data = x;
122 break;
123 }
124 /*往后移动元素*/
125 node = node->next;
126 pos++;
127 }
128 if(1 == found)
129 return 0;
130 else
131 return -1;
132 }
133
134 // 插入节点
135 int
136 InsertLinklist(linklist_t list, int at, data_t x)
137 {
138 /*
139 * node_at and pos_at are used to locate the position of node_at.
140 * node_prev follows the node_at and always points to previous node
141 * of node_at.
142 * node_new is used to point to the new node to be inserted.
143 */
144 linknode_t * node_prev, * node_at, * node_new;
145 int pos_at;
146 int found = 0;
147
148 if(NULL == list) return -1;
149
150 /* at 必须 >= 0 */
151 if(at < 0) return -1;
152
153 node_new = malloc(sizeof(linknode_t));
154 if(NULL == node_new)
155 return -1;
156 node_new->data = x; // assigned value
157 node_new->next = NULL;
158
159 node_prev = list; // head
160 node_at = list->next; //node_at指针指向第一元素
161 pos_at = 0;
162 while(NULL != node_at) {
163 if(pos_at == at) {
164 found = 1; // found the node ‘at'
165 break;
166 }
167 /* move to the next pos_at */
168 node_prev = node_at;
169 node_at = node_at->next;
170 pos_at++;
171 }
172
173 if(found) {
174 /* insert */
175 node_new->next = node_at;
176 node_prev->next = node_new;
177 } else{
178 /*
179 * If not found,means the provided 'at'
180 * exceeds the upper limit of the list, just
181 * append the new node to the end of the list
182 */
183 node_prev->next = node_new;
184 }
185
186 return 0;
187 }
188
189 // 删除节点
190 int
191 DeleteLinklist(linklist_t list, int at)
192 {
193 /*
194 * node_at and pos_at are used to locate the position of node_at.
195 * node_prev follows the node_at and always points to previous node
196 * of node_at.
197 */
198 linknode_t * node_prev, * node_at;
199 int pos_at;
200 int found = 0;
201
202 if(!list) return -1;
203 if(at < 0) return -1;
204
205 node_prev = list; // node_prev指针指向链表头
206 node_at = list->next; // node_at指针指向第一元素
207 pos_at = 0;
208
209 while(NULL != node_at) {
210 if(pos_at == at) {
211 // found the node 'at'
212 found = 1;
213 break;
214 }
215 // move to the next pos_at
216 node_prev = node_at;
217 node_at = node_at->next;
218 pos_at++;
219 }
220 if(found) {
221 // remove
222 node_prev->next = node_at->next;
223 free(node_at);
224 return 0;
225 }else
226 return -1;
227 }
228
229 // 链表转置
230 linklist_t
231 ReverseLinklist(linklist_t list)
232 {
233 linknode_t * node; // iterator
234 linknode_t * node_prev; // previous node of iterator
235 linknode_t * node_next; /* next node of iterator
236 * used to backup next of iterator
237 */
238 if(NULL == list) return NULL;
239 node_prev = NULL;
240 node = list->next; // node指针指向第一个元素
241 while(NULL != node) {
242 /*
243 * step1: backup node->next
244 * due to the next of iterator will be
245 * modified in step2
246 */
247 node_next = node->next;
248 /*
249 * when iterator reaches the last node
250 * of original list, make the list head
251 * point to the last node, so the original
252 * last one becomes the first one.
253 */
254 if(NULL == node_next)
255 list->next = node;
256 /*
257 * step2: reverse the linkage between nodes
258 * make the node pointer to the previous node,
259 * not the next node
260 */
261 node->next = node_prev;
262 /*
263 * step3: move forward
264 */
265 node_prev = node;
266 node = node_next;
267 }
268
269 return list;
270 }
271
272 // 打印链表
273 int
274 Display(linklist_t list)
275 {
276 linknode_t * node;
277
278 if(NULL == list) return -1;
279
280 node = list->next;
281 while(node != NULL) {
282 printf(" %d ", node->data);
283 node = node->next;
284 }
285 printf("\n");
286
287 return 0;
288 }
289
290
291 int main(int argc, char * argv[])
292 {
293 int i;
294 data_t x;
295 linklist_t p;
296
297 /*创建链表*/
298 p = CreateEmptyLinklist();
299 Display(p);
300 data_t a[10] = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19};
301
302 for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
303 /*插入链表*/
304 InsertLinklist(p, i, a[i]);
305 }
306 Display(p);
307
308 /*链表转置*/
309 ReverseLinklist(p);
310 /*链表长度*/
311 printf("The length of the list is [%d]\n", LengthLinklist(p));
312 Display(p);
313
314 /*获取特定节点值*/
315 GetLinklist(p, 4, &x);
316 printf("The No.4 of this list is [%d]\n", x);
317
318 /*设置特定节点的值*/
319 SetLinklist(p, 4, 100);
320 GetLinklist(p, 4, &x);
321 printf("After updating! The No.4 of this list is [%d]\n", x);
322 Display(p);
323
324 /*删除节点*/
325 DeleteLinklist(p,5);
326 printf("After delete!The length of list is [%d]\n", LengthLinklist(p));
327 Display(p);
328
329 /*清空链表*/
330 ClearLinklist(p);
331 if(IsEmptyLinklist(p))
332 printf("This list is empty!\n");
333 /*销毁链表*/
334 DestroyLinklist(p);
335 printf("This list is destroyed!\n");
336
337
338 return 0;
339
340 }
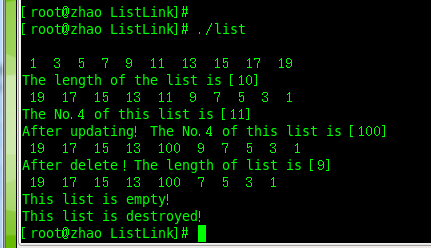
运行
视频学习资料
单链表
http://www.makeru.com.cn/live/5413_1924.html?s=45051
循环链表及线性表的应用
http://www.makeru.com.cn/course/details/1902?s=45051
学习交流资料下载群:830802928
Linux C 数据结构 ->单向链表的更多相关文章
- Linux C 数据结构 ->单向链表<-(~千金散尽还复来~)
之前看到一篇单向链表的博文,代码也看着很舒服,于是乎记录下来,留给自己~,循序渐进,慢慢 延伸到真正的内核链表~(敢问路在何方?路在脚下~) 1. 简介 链表是Linux 内核中最简单,最普通的数据结 ...
- linux内核数据结构之链表
linux内核数据结构之链表 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结构不一样,只有前驱和后继指针,而没有数据域.后来看代码注释发现该 ...
- linux内核数据结构之链表【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/3475643.html 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结 ...
- 数据结构-单向链表 C和C++的实现
数据结构,一堆数据的存放方式. 今天我们学习数据结构中的 链表: 链表的结构: 链表是一种特殊的数组,它的每个元素称为节点,每个节点包括两个部分: 数据域:存放数据,此部分与数组相同 指针域:存放了下 ...
- python数据结构——单向链表
链表 ( Linked List ) 定义:由许多相同数据类型的数据项按照特定顺序排列而成的线性表. 特点:各个数据在计算机中是随机存放且不连续. 优点:数据的增删改查都很方便,当有新的数据加入的时候 ...
- Python3玩转单链表——逆转单向链表pythonic版
[本文出自天外归云的博客园] 链表是由节点构成的,一个指针代表一个方向,如果一个构成链表的节点都只包含一个指针,那么这个链表就是单向链表. 单向链表中的节点不光有代表方向的指针变量,也有值变量.所以我 ...
- 玩转C线性表和单向链表之Linux双向链表优化
前言: 这次介绍基本数据结构的线性表和链表,并用C语言进行编写:建议最开始学数据结构时,用C语言:像栈和队列都可以用这两种数据结构来实现. 一.线性表基本介绍 1 概念: 线性表也就是关系户中最简单的 ...
- C# 单向链表数据结构 (一)
单向链表数据结构是有节点组成,每个节点包含两部分,第一部分为存储数据,第二部分为指向下一个节点的指针.注意,有两个特色的节点,分别为“头节点”和“尾节点”,头节点本身没有数据,只存储下一个节点的指针, ...
- 数据结构(1) 第一天 算法时间复杂度、线性表介绍、动态数组搭建(仿Vector)、单向链表搭建、企业链表思路
01 数据结构基本概念_大O表示法 无论n是多少都执行三个具体步骤 执行了12步 O(12)=>O(1) O(n) log 2 N = log c N / log c N (相当于两个对数进行了 ...
随机推荐
- [第七篇]——Docker Hello World之Spring Cloud直播商城 b2b2c电子商务技术总结
Docker Hello World Docker 允许你在容器内运行应用程序, 使用 docker run 命令来在容器内运行一个应用程序. 输出Hello world xxx@xxx:~$ do ...
- Xamarin UIProgressView自定义
Progress.ProgressImage = UIImage.FromFile ("progress.png"); Progress.TrackImage = UIImage. ...
- kubectl工具的windows\linux安装方法
kubectl 安装 下载kubectl二进制文件 curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.10.0 ...
- java.net.NoRouteToHostException: 无法指定被请求的地址
今天压力测试时, 刚开始出现了很多异常, 都是 java.net.NoRouteToHostException: Cannot assign requested address. 经网上查资料, 是 ...
- webpack learn4-1配置css单独分离打包
1 先安装extract-text-webpack-plugin npm i extract-text-webpack-plugin 2 配置webpack.config.js
- Mysql实现排序
排序 SELECT obj.user_id,obj.score,@rownum := @rownum + 1 AS rownum FROM ( SELECT ...
- 深入HTML5第二天
sub(subscripted下标标签)和sup(superscripted上标标签) 内联元素:inline element span(范围标签):内联元素inline element 特性:没有 ...
- vue.js 配置axios 用来ajax请求数据
* 用npm 安装 axios 切换到项目的根目录 npm install --save axios vue-axios * 在vue的入口文件./src/main.js 中引入axios, 添加2行 ...
- Zend Studio 配置SVN并导入SVN项目
php 开发过程中,一个项目比较大的话,就需要很多人共同来完成.那么怎样来管理之间的相互配合,分工等呢??那么SVN这个神器就有用处了.SVN:代码版本管理软件.更多svn详细信息请查阅相关文档,这里 ...
- cordova 打包 守护进程无法启动
方案 1 : 添加环境变量 _JAVA_OPTIONS = -Xmx512M 2: 在新建的 系统变量里 变量名 _JAVA_OPTIONS 变量值 -Djava.net.preferIPv4 ...
