【JAVA基础】08 面向对象3
1. 多态
多态polymorhic概述
- 事物存在的多种形态。
- 多态前提
- 要有继承关系
- 要有方法重写
- 要有父类引用指向子类对象
- 案例演示
- 代码体现多态
- class Demo1_Polymorphic{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Cat c = new Cat();
- c.eat();
- Animal a = new Cat(); // 父类引用指向子类对象
- a.eat(); // 输出“猫吃鱼”
- }
- }
- class Animal {
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("动物吃饭");
- }
- }
- class Cat extends Animal {
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
- }
- }
- class Demo1_Polymorphic{
- 多态中的成员访问特点
- 成员变量
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)
- Father f = new Son();
- class Demo2_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Father f = new Son();
- System.out.println(f.num); //输出10
- }
- }
- class Father {
- int num = 10;
- }
- class Son extends Father {
- int num = 20;
- }

如果再上面例子的基础上,再生成一个Son类对象,则
- class Demo2_Polymorphic {
- class Demo2_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Father f = new Son();
- System.out.println(f.num); //输出10
- Son s = new Son();
- System.out.println(s.num); //输出20
- }
- }
- class Father {
- int num = 10;
- }
- class Son extends Father {
- int num = 20;
- }

- class Demo2_Polymorphic {
- 成员方法
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看右边(子类)——又称“动态绑定”
- Father f = new Son();
- 编译时,看父类中有没有该成员方法,有则编译成功;运行则动态绑定到子类的成员方法上,运行子类的成员方法。
- class Demo3_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Father f = new Son();
- f.print();// 输出son
- }
- }
- class Father {
- int num = 10;
- public void print() {
- System.out.println("father");
- }
- }
- class Son extends Father {
- int num = 20;
- public void print() {
- System.out.println("son");
- }
- }

- class Demo3_Polymorphic {
- 静态方法
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)
- 静态和类相关,算不上重写,所以,访问还是左边的
- class Demo4_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Father f = new Son();
- f.method(); //输出"father static method";
- // 相当于是Father.method(); 调用父类的方法
- }
- }
- class Father {
- int num = 10;
- public void print() {
- System.out.println("father");
- }
- public static void method(){
- System.out.println("father static method");
- }
- }
- class Son extends Father {
- int num = 20;
- public void print() {
- System.out.println("son");
- }
- public static void method(){
- System.out.println("son static method");
- }
- }
- class Demo4_Polymorphic {
- 总结:
- 只有非静态的成员方法,编译看左边(父类),运行看右边(子类)
- 其他都是编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)
- 成员变量
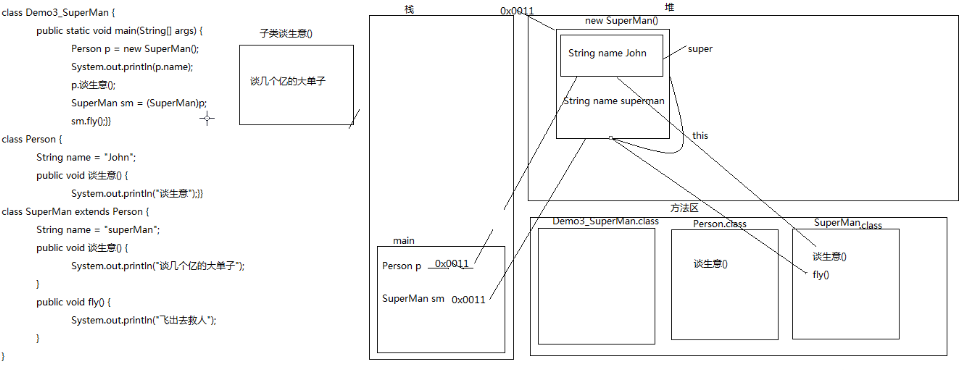
- 案例:超人的故事
- 通过该案例帮助理解多态的现象。
- class Demo5_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Person p = new SuperMan(); // 父类引用指向子类对象,超人提升为人
- System.out.println(p.name);// 输出“John”
- p.谈生意(); // 输出"谈几个亿的大单子"
- //p.fly(); //编译出错
- }
- }
- class Person {
- String name = "John";
- public void 谈生意() {
- System.out.println("谈生意");
- }
- }
- class SuperMan extends Person {
- String name = "Super man";
- public void 谈生意() {
- System.out.println("谈几个亿的大单子");
- }
- public void fly() {
- System.out.println("飞出去救人");
- }
- }
- class Demo5_Polymorphic {
超人作为人类身份的属性信息对外展示,Person类和SuperMan类中重写的方法,实际执行的是超人身份的方法;
在这个例子中,父类中没有fly方法,故编译失败,也无法执行。针对这个,要考虑下面的 向上转型和向下转型 的问题。
- 多态中 向上转型和向下转型
- 向上转型
- Person p = new SuperMan();
- 父类引用指向子类对象,就是向上转型
- 向下转型
- SuperMan sm = (SuperMan)p;
- class Demo5_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Person p = new SuperMan(); // 父类引用指向子类对象,超人提升为人
- System.out.println(p.name);// 输出“John”
- p.谈生意(); // 输出"谈几个亿的大单子"
- //p.fly(); //编译出错
- SuperMan sm = (SuperMan)p; // 向下转型
- sm.fly();
- }
- }
- class Person {
- String name = "John";
- public void 谈生意() {
- System.out.println("谈生意");
- }
- }
- class SuperMan extends Person {
- String name = "Super man";
- public void 谈生意() {
- System.out.println("谈几个亿的大单子");
- }
- public void fly() {
- System.out.println("飞出去救人");
- }
- }
- class Demo5_Polymorphic {
- 向上转型
补充参考:基本数据类型:
- 自动类型提升
- 强制类型转换
- class Demo1_Polymorphic{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int i = 10;
- byte b = 20;
- i = b; // 自动类型转换
- b = (byte)i; // 强制类型转换
- }
- }
- class Demo1_Polymorphic{
- 多态的好处和弊端
- 多态的好处
- 提高了代码的维护性(继承保证)
- 提高了代码的扩展性(由多态保证)
- 可以当做形式参数
- 可以接收任意子类对象
- 多态的弊端
- 不能使用子类的特有属性和行为
- 案例演示
- method(Animal a) 方便Animal的所有子类的 重写的方法调用
- method(Cat c) 这种直接调用子类,出现并行子类,调用父类方法,需要些新的method方法,传入不同的类作为实参。
- class Demo6_Polymorphic {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- method(new Cat());
- method(new Dog());
- /*
- Animal a = new Cat();
- Animal a = new Dog();
- 开发的时候很少在创建对象的时候用父类引用指向子类对象,
- 直接创建子类对象更方便,可以使用子类中的特有属性和方法
- */
- }
- /*
- public static void method(Cat c) {
- c.eat();
- }
- public static void method(Dog d) {
- d.eat();
- }*/
- public static void method(Animal a) { // 当做参数的时候,用多态最好,扩展性强
- //关键字 instanceof 判断前边的引用是否是后边的数据类型
- if (a instanceof Cat) {
- Cat c = (Cat)a;
- c.eat();
- c.catchMouse();
- }else if (a instanceof Dog) {
- Dog d = (Dog)a;
- d.eat();
- d.lookHome();
- }else {
- a.eat();
- }
- /*
- // 如果把Dog强转成Cat,就会出现类型转换异常,ClassCastException
- Cat c = (Cat)a;
- c.eat();
- c.catchMouse();*/
- }
- }
- class Animal {
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("动物吃饭");
- }
- }
- class Cat extends Animal {
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
- }
- public void catchMouse() {
- System.out.println("抓老鼠");
- }
- }
- class Dog extends Animal {
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("狗吃肉");
- }
- public void lookHome() {
- System.out.println("看家");
- }
- }
- class Demo6_Polymorphic {
- 多态的好处
2. 抽象类
- 抽象类概述
- 抽象就是看不懂的
- 抽象类的特点
- 抽象类和抽象方法必须用abstract关键字修饰
- abstract class 类名 ()
- public abstract void eat();
- 抽象类不一定有抽象方法,有抽象方法的类一定是抽象类或者接口
- 抽象类不能实例化,那么,抽象类如何实例化呢?
- 按照多态的方式,由具体的子类实例化。其实这也是多态的一种,抽象类多态。
- 抽象类的子类
- 要么是抽象类
- 要么重写抽象类中的所有抽象方法
- 案例演示
- class Demo1_Abstract {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Animal a = new Cat();
- a.eat();
- print(a);
- }
- public static void print(Animal a) {
- a.eat();
- }
- }
- abstract class Animal { // 抽象类
- public abstract void eat(); // 抽象方法
- }
- class Cat extends Animal {
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
- }
- }
- class Demo1_Abstract {
- class Demo1_Abstract {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
- public static void print(Animal a) {
- a.eat();
- }
- }
- abstract class Animal { // 抽象类
- public abstract void eat(); // 抽象方法
- }
- class Cat extends Animal {
- //错误: Cat不是抽象的, 并且未覆盖Animal中的抽象方法eat()
- }
- class Demo1_Abstract {
- 抽象类联系(猫狗,抽象类为动物)
具体事物:猫,狗
共性:姓名,年龄,吃饭
猫的特性:抓老鼠
狗的特性:看家- class Test1_Animal {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Cat c = new Cat("加菲",8);
- System.out.println(c.getName() + "..." + c.getAge());
- c.eat();
- c.catchMouse();
- Dog d = new Dog("八公",30);
- System.out.println(d.getName() + "..." + d.getAge());
- d.eat();
- d.lookHome();
- }
- }
- /*
- 案例演示:
- 具体事物:猫,狗
- 共性:姓名,年龄,吃饭
- 猫的特性:抓老鼠
- 狗的特性:看家
- */
- abstract class Animal {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- public Animal(){}
- public Animal(String name,int age) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public void setName(String name) { // 设置姓名
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getName() { // 获取姓名
- return name;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) { // 设置年龄
- this.age = age;
- }
- public int getAge() { // 获取年龄
- return age;
- }
- public abstract void eat(); // 抽象方法:吃饭
- }
- class Cat extends Animal {
- public Cat(){}
- public Cat(String name,int age) {
- super(name,age);
- }
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
- }
- public void catchMouse() {
- System.out.println("抓老鼠");
- }
- }
- class Dog extends Animal {
- public Dog(){}
- public Dog(String name,int age) {
- super(name,age);
- }
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("狗吃肉");
- }
- public void lookHome() {
- System.out.println("抓老鼠");
- }
- }
- class Test1_Animal {
- class Test2_Teacher {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Teacher t = new BaseTeacher();
- print(t);
- print(new EmpTeacher());
- }
- public static void print(Teacher t) {
- t.teach();
- }
- }
- /*
- 具体事物:基础班老师,就业班老师
- 共性:姓名、年龄、讲课
- */
- abstract class Teacher {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- public abstract void teach();
- public Teacher() {}
- public Teacher(String name, int age) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- }
- class BaseTeacher extends Teacher {
- public BaseTeacher() {}
- public BaseTeacher(String name, int age) {
- super(name, age);
- }
- public void teach() {
- System.out.println("基础班老师 讲课");
- }
- }
- class EmpTeacher extends Teacher {
- public EmpTeacher() {}
- public EmpTeacher(String name, int age) {
- super(name, age);
- }
- public void teach() {
- System.out.println("就业班老师 讲课");
- }
- }
老师抽象类
- class Test2_Teacher {
- class Test3_Student {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- state(new BaseStudent());
- state(new EmpStudent());
- }
- public static void state(Student s) {
- s.study();
- }
- }
- /*
- 具体事物:基础班学生,就业班学生
- 共性:姓名,年龄,学习
- */
- abstract class Student {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- public abstract void study();
- public Student() {}
- public Student(String name, int age) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getNamge() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- }
- class BaseStudent extends Student {
- public BaseStudent() {}
- public BaseStudent(String name, int age) {
- super(name,age);
- }
- public void study() {
- System.out.println("基础班学生在学习");
- }
- }
- class EmpStudent extends Student {
- public EmpStudent() {}
- public EmpStudent(String name, int age) {
- super(name,age);
- }
- public void study() {
- System.out.println("就业班学生在学习");
- }
- }
学生抽象类
- class Test3_Student {
- class Test4_Employee {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Coder c = new Coder("John", "001", 10000.00);
- c.work();
- Manager m = new Manager("Ann", "033", 40000.00, 10000);
- m.work();
- }
- }
- /*
- 假如我们在开发一个系统时,需要对程序员类进行设计。
- 程序员包含3个属性:
- 姓名
- 工号
- 工资
- 经理:出了含有程序员的属性外,还有一个奖金属性
- 用继承的思想设计出程序员类和经理类。
- 要求类中提供必要的方法进行属性访问。
- */
- abstract class Employee {
- private String name;
- private String code;
- private double salary;
- public Employee() {}
- public Employee(String name, String code, double salary) {
- this.name = name;
- this.code = code;
- this.salary = salary;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getName(){
- return name;
- }
- public void setCode(String code) {
- this.code = code;
- }
- public String getCode(){
- return code;
- }
- public void setSalary(double salary) {
- this.salary = salary;
- }
- public double getSalary(){
- return salary;
- }
- public abstract void work();
- }
- class Manager extends Employee {
- private int bonus;
- public Manager() {}
- public Manager(String name, String code, double salary, int bonus) {
- super(name,code,salary);
- this.bonus = bonus;
- }
- public void setBonus(int bonus) {
- this.bonus = bonus;
- }
- public int getBonus(){
- return bonus;
- }
- public void work() {
- System.out.println("项目经理" + this.getName() + "在工作");
- System.out.println("奖金是" + this.getBonus());
- }
- }
- class Coder extends Employee {
- public Coder() {}
- public Coder(String name, String code, double salary) {
- super(name,code,salary);
- }
- public void work() {
- System.out.println("程序员" + this.getName() + "在工作");
- }
- }
雇员:程序员,项目经理
- class Test4_Employee {
- 抽象类和抽象方法必须用abstract关键字修饰
- 抽象类的注意问题
- 一个抽象类如果没有抽象方法,可不可以定义为抽象类?如果可以,有什么意义?
- 可以。
目的只有一个,就是不让其他类创建本类对象,交给子类完成
- 可以。
abstract不能和哪些关键字共存?
abstract 和 static
被abstract修饰的方法没有方法体;
被static修饰的可以用 类名.调用,但是类名.调用 抽象方法是没有意义的。abstract 和 final
被abstract修饰的方法强制子类重写;
被final修饰的方法,不让子类重写。这两个修饰词是矛盾的。abstract 和 private
被abstract修饰的是为了让子类看到并强制重写
被private修饰的不让子类访问,所以他两是矛盾的。- class Demo4_Abstract {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("Hello World!");
- }
- }
- /*
- 面试题1:
- 一个抽象类如果没有抽象方法,可不可以定义为抽象类?如果可以,有什么意义?
- 答:
- 可以。
- 目的只有一个,就是不让其他类创建本类对象,交给子类完成
- 面试题2:
- abstract不能和哪些关键字共存?
- 答:
- abstract 和 static
- 被abstract修饰的方法没有方法体;
- 被static修饰的可以用 类名.调用,但是类名.调用 抽象方法是没有意义的。
- abstract 和 final
- 被abstract修饰的方法强制子类重写;
- 被final修饰的方法,不让子类重写。这两个修饰词是矛盾的。
- abstract 和 private
- 被abstract修饰的是为了让子类看到并强制重写
- 被private修饰的不让子类访问,所以他两是矛盾的。
- */
- abstract class Demo {
- // public static abstract void print();
- // Demo4_Abstract.java:21: 错误: 非法的修饰符组合: abstract和static
- // public final abstract void print();
- // Demo4_Abstract.java:29: 错误: 非法的修饰符组合: abstract和final
- // private abstract void print();\
- // Demo4_Abstract.java:36: 错误: 非法的修饰符组合: abstract和private
- }
- class Demo4_Abstract {
- 一个抽象类如果没有抽象方法,可不可以定义为抽象类?如果可以,有什么意义?
3. 接口
- 接口概述
- 从狭义的角度讲,就是指java中的interface
- 从广义的角度讲,就是对外提供规则的都是接口
- 接口特点
- 接口关键字interface表示
- interface 接口名 {}
- 类实现接口用 implements表示
- class 类名 implements 接口名 {}
- 接口不能实例化
- 那么,接口如何实例化呢?
- 按照多态的方式来实例化
- 接口的子类
- 可以是抽象类,但是意义不大。
- 可以使具体类,要重写接口中的所有抽象方法(推荐方案)
- 接口关键字interface表示
- 案例演示:接口特点
- class Demo1_Interface {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //Inter i = new Inter(); // 接口不能被实例化,因为调用抽象方法没有意义
- Inter i = new Demo();
- i.print();
- }
- }
- interface Inter {
- public abstract void print(); // 接口中的方法都是抽象的
- }
- class Demo implements Inter {
- public void print() {
- System.out.println("print");
- }
- }
接口类-子类是具体类,重写接口的 抽象方法(推荐)
- class Demo1_Interface {
- class Demo1_Interface {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
- }
- interface Inter {
- public abstract void print(); // 接口中的方法都是抽象的
- }
- abstract class Demo implements Inter {
- }
接口-子类是抽象类(不推荐)
- class Demo1_Interface {
接口的成员特点:
成员变量
- 只能是常量,并且是静态的,并公共的。
- 默认修饰符:public static final(即使不手写,也会默认添加)
- 建议:自己手动给出
构造方法
- 接口没有构造方法
成员方法
- 只能是抽象方法
- 默认修饰符:public abstract
- 建议:自己手动给出
- 只能是抽象方法
- 案例演示
- class Demo1_Interface {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Demo d = new Demo();
- d.print();
- System.out.println(Inter.num);
- }
- }
- interface Inter {
- public static final int num = 10; // 系统会默认添加public static final,建议手动写出
- // 这三个关键词没有顺序区别
- // public Inter(){} 报错,接口中没有构造方法
- // public void print() {} // 接口中不能定义非抽象方法
- void print(); // 前面默认添加了public abstract修饰词
- public abstract void print2();
- }
- class Demo /* extends Object */ implements Inter { // 一个类不写继承任何一个类,默认继承Object类
- public void print() {
- System.out.println(num);
- }
- public void print2() {}
- }
- class Demo1_Interface {
- class Test1_Aniaml {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Cat c = new Cat("加菲",8);
- c.eat();
- c.sleep();
- JumpCat jc = new JumpCat("跳高猫",3);
- jc.eat();
- jc.sleep();
- jc.jump();
- }
- }
- /*
- 动物类:姓名,年龄,吃饭,睡觉
- 猫和狗
- 动物培训接口:跳高
- */
- abstract class Animal {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- public Animal(){}
- public Animal(String name,int age){
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public void setName(String name){
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getName(){
- return name;
- }
- public void setAge(int age){
- this.age = age;
- }
- public int getAge(){
- return age;
- }
- public abstract void eat();
- public abstract void sleep();
- }
- interface Jumping {
- public void jump();
- }
- class Cat extends Animal {
- public Cat(){}
- public Cat(String name,int age){
- super(name,age);
- }
- public void eat() {
- System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
- }
- public void sleep() {
- System.out.println("侧着睡");
- }
- }
- class JumpCat extends Cat implements Jumping {
- public JumpCat(){}
- public JumpCat(String name,int age){
- super(name,age);
- }
- public void jump() {
- System.out.println("猫跳高");
- }
- }
动物:猫类,跳高的接口
- class Test1_Aniaml {
3. 各种类,接口之间的关系
3.1 类与类,类与接口,接口与接口的关系
- 类与类
- 继承关系
- 只能单继承,可以多层继承
- 继承关系
- 类与接口
- 实现关系,可以单实现,也可以多实现
- 并且还可以在继承一个类的同时实现多个接口
- class Demo1_Interface {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
- }
- interface InterA {
- public abstract void printA();
- }
- interface InterB {
- public abstract void printB();
- }
- class Demo implements InterA,InterB {
- public void printA() {
- System.out.println("printA");
- }
- public void printB() {
- System.out.println("printB");
- }
- }
- class Demo1_Interface {
- 接口与接口
- 继承关系
- 可以单继承,也可以多继承。
- class Demo1_Interface {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
- }
- interface InterA {
- public abstract void printA();
- }
- interface InterB {
- public abstract void printB();
- }
- interface InterC extends InterA,InterB {
- }
- class Demo1_Interface {
- 继承关系
3.2 抽象类和接口的区别
- 成员区别
- 抽象类
- 成员变量:可以变量,也可以常量
- 构造方法:有
- 成员方法:可以抽象,也可以非抽象
- 接口
- 成员变量:只可以常量
- 成员方法:只可以抽象
- 抽象类
- 关系区别
- 类与类
- 继承,单继承
- 类与接口
- 实现,单实现,多实现
- 接口与接口
- 继承,单继承,多继承
- 类与类
- 设计理念区别
- 抽象类
- 被继承体现的是“is a”的关系。
- 抽象类中定义的是该继承体系的共性功能
- 接口
- 被实现体现的是“like a”的关系。
- 接口中定义的是该继承体系的扩展功能
4. 包package
- 为什么要有包
- 将字节码(.class)进行分类存放
- 包其实就是文件夹
- 包的概述
- 举例:
- 需求:
- 学生:增加、删除、修改、查询
- 老师:增加、删除、修改、查询
- 方案1:按照功能分
- com.heima.add
- AddStudent
- AddTeacher
- com.heima.delete
- DeleteStudent
- DeleteTeacher
- com.heima.update
- UpdateStudent
- UpdateTeacher
- com.heima.find
- FindStudent
- FindTeacher
- com.heima.add
- 方案2:按照模块分
- com.heima.teacher
- AddTeacher
- DeleteTeacher
- UpdateTeacher
- FindTeacher
- com.heima.student
- AddStudent
- DeleteStudent
- UpdateStudent
- FindStudent
- com.heima.teacher
- 需求:
- 举例:
- 包的定义
- 格式
- package 包名;
- 多级包用“.” 分开即可
- 注意事项
- package语句必须是程序的第一条可执行的代码
- package语句在一个java文件中只能有一个
- 如果没有package,默认表示无包名
- 案例演示
- package com.heima;
- // package语句必须是程序的第一条可执行的代码
- // 一个文件内只能有一个package语句
- class Demo1_Package {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
- }
- package com.heima;
- 格式
- 如何编译运行带包的类
- 案例演示
- javac编译时加上-d即可
- javac -d . HelloWorld.java
- 通过java命令执行
- java 包名.HelloWorld
- java com.heima.Demo1_Package
- javac编译时加上-d即可
- 案例演示
- 不同包下类之间的访问
- 案例演示
- package com.heima;
- // package语句必须是程序的第一条可执行的代码
- // 一个文件内只能有一个package语句
- import com.baidu.Person;
- import com.xxx.Student;
- //import java.util.Scanner; //在开发中我们用的都是导入具体的类
- import java.util.*; //*代表通配符,他会到该包下挨个匹配,匹配上就导入
- class Demo1_Package {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Person p = new Person("张三",23);
- System.out.println(p.getName() + "..." + p.getAge());
- //p.print(); //在不同包下的无关类,不允许访问,因为是protected修饰的
- /*Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- int x = sc.nextInt();
- System.out.println(x);*/
- Student s = new Student("李四",24);
- System.out.println(s.getName() + "..." + s.getAge());
- s.method();
- }
- }
- package com.heima;
import关键字的概述和使用
为什么要有import
其实就是让有包的类对调用者可见,不用写全类名了
导包格式
import 包名;
注意:
这种方式导入是到类的名称。
虽然可以最后写*,但是不建议。
- package,import,class有没有顺序关系
- 有。
- package 第一行,只能一个文件一句
- import 中间,可以有多句
- class 放在这两个下面
5. 修饰符
- 四种权限修饰符
- private 本类;
- 默认 本类;同一个包下(子类和无关类)
- protected 本类;同一个包下(子类和无关类);不同包下(子类)
- public 本类;同一个包下(子类和无关类);不同包下(子类);不同包下(无关类)
- 修饰符
- 权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
- 状态修饰符:static,final
- 抽象修饰符:abstract
- 类
- 权限修饰符:默认修饰符,public
- 状态修饰符:final
- 抽象修饰符:abstract
- 用的最多的就是:public
成员变量:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
状态修饰符:static,final
用的最多的就是:private
构造方法:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
用的最多的就是:public
成员方法:
权限修饰符:private,默认的,protected,public
状态修饰符:static,final
抽象修饰符:abstract
用的最多的就是:public
除此以外的组合规则:
成员变量:public static final
成员方法:
public static
public abstract
public final
6. 内部类
内部类概述
- 在类中定义类,叫做内部类
内部类访问特点
内部类可以直接访问外部类的成员,包括私有。
外部类要访问内部类的成员,必须创建对象。
外部类名.内部类名 对象名 = 外部类对象.内部类对象;
案例演示
- class Demo1_InnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //Inner i = new Inner();
- //i.method();
- //外部类名.内部类名 = 外部类对象.内部类对象
- Outer.Inner oi = new Outer().new Inner(); //创建内部类对象
- oi.method();
- }
- }
- class Outer { // 外部类
- private int num = 10;
- class Inner { // 内部类
- public void method() {
- System.out.println(num);
- }
- }
- }
- class Demo1_InnerClass {
- 内部类分类
- 成员内部类
- 成员内部类私有使用
- class Demo2_InnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //Outer.Inner oi = new Outer().new Inner(); //内部类私有,无法调用
- //oi.method();
- Outer o = new Outer();
- o.print();
- }
- }
- class Outer {
- private int num = 10;
- private class Inner { //内部类私有
- public void method() {
- System.out.println(num);
- }
- }
- public void print() {
- Inner i = new Inner(); // 外部类,提供内部类实例化方法
- i.method();
- }
- }
内部类私有
- class Demo2_InnerClass {
- class Test1_InnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Outer.Inner oi = new Outer().new Inner();
- oi.show();
- }
- }
- //要求:使用已知的变量,在控制台输出30,20,10。
- //内部类之所以能获取到外部类的成员,是因为他能获取到外部类的引用外部类名.this
- class Outer {
- public int num = 10;
- class Inner {
- public int num = 20;
- public void show() {
- int num = 30;
- System.out.println(num);
- System.out.println(this.num);
- System.out.println(Outer.this.num);
- }
- }
- }
成员内部类面试题:获取成员变量
- class Test1_InnerClass {
- 成员内部类私有使用
- 静态成员内部类
- class Demo1_InnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //外部类名.内部类名 对象名 = 外部类名.内部类对象;
- Outer.Inner oi = new Outer.Inner();
- oi.method();
- Outer.Inner2.print();
- }
- }
- class Outer {
- static class Inner { // 静态成员内部类
- public void method() {
- System.out.println("method");
- }
- }
- static class Inner2 {
- public static void print() {
- System.out.println("print");
- }
- }
- }
静态内部类
- class Demo1_InnerClass {
- 局部内部类
- 局部内部类,只能在其所在的方法中访问
- 局部内部类访问局部变量的问题
- 局部内部类访问局部变量必须用final修饰
局部内部类在访问他所在方法中的局部变量必须用final修饰,为什么?
因为当调用这个方法时,局部变量如果没有用final修饰,他的生命周期和方法的生命周期是一样的,当方法弹栈,这个局部变量也会消失。
那么如果局部内部类对象还没有马上消失想用这个局部变量,就没有了。
如果用final修饰会在类加载的时候进入常量池,即使方法弹栈,常量池的常量还在,也可以继续使用。
但是jdk1.8取消了这个事情,所以我认为这是个bug
- class Demo1_InnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Outer o = new Outer();
- o.method();
- }
- }
- //局部内部类
- class Outer {
- public void method() {
- final int num = 10;
- //int num = 10; 错误:从内部类中访问本地变量num;需要被声明为最终类型。final
- class Inner { // 局部内部类
- public void print() {
- System.out.println(num);
- }
- }
- Inner i = new Inner(); //只能在局部所在的方法中访问
- i.print();
- }
- /*public void run() {
- Inner i = new Inner(); //局部内部类,只能在其所在的方法中访问
- i.print();
- }*/
- }
局部内部类示例,final修饰符修饰变量
- class Demo1_InnerClass {
- 匿名内部类
- 就是内部类的简化写法。
- 前提:
- 存在一个类或者接口
- 这里的类可以是具体类也可以是抽象类。
- 格式
new 类名或者接口名() {
重写方法;
}
- 本质是什么呢?
- 是一个继承了该类或者实现了该接口的子类匿名对象。
- 案例演示
- class Demo1_NoNameInnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Outer o = new Outer();
- o.method();
- }
- }
- interface Inter {
- public void print();
- }
- class Outer {
- /*class Inner implements Inter { // 这是有名字的内部类,继承Inter接口
- public void print() {
- System.out.println("print");
- }
- }*/
- public void method(){
- //Inner i = new Inner();
- //i.print();
- //new Inner().print();
- //Inter i = new Inner(); //父类引用指向子类对象
- new Inter() { //实现Inter接口
- public void print() { //重写抽象方法
- System.out.println("print");
- }
- }.print(); //
- }
- }
匿名内部类:单个方法调用
- class Demo1_NoNameInnerClass {
- class Demo2_NoNameInnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Outer o = new Outer();
- o.method();
- }
- }
- interface Inter {
- public void show1();
- public void show2();
- }
- //匿名内部类只针对重写一个方法时候使用
- class Outer {
- public void method() {
- /*new Inter(){
- public void show1() {
- System.out.println("show1");
- }
- public void show2() {
- System.out.println("show2");
- }
- }.show1();
- new Inter(){
- public void show1() {
- System.out.println("show1");
- }
- public void show2() {
- System.out.println("show2");
- }
- }.show2();*/
- Inter i = new Inter(){
- public void show1() {
- System.out.println("show1");
- }
- public void show2() {
- System.out.println("show2");
- }
- /*public void show3() {
- System.out.println("show3");
- }*/
- };
- i.show1();
- i.show2();
- //i.show3(); //匿名内部类是不能向下转型的,因为没有子类类名
- }
- }
匿名内部类只针对重写一个方法时候使用
- class Demo2_NoNameInnerClass {
- 匿名内部类在开发中的应用
- class Test1_NoNameInnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //如何调用PersonDemo中的method方法呢?
- PersonDemo pd = new PersonDemo ();
- //pd.method(new Student());
- pd.method(new Person() {
- public void show() {
- System.out.println("show");
- }
- });
- }
- }
- //这里写抽象类,接口都行
- abstract class Person {
- public abstract void show();
- }
- class PersonDemo {
- //public void method(Person p) { //Person p = new Student(); //父类引用指向子类对象
- /*
- Person p = new Person(){
- public void show() {
- System.out.println("show");
- }
- };
- */
- public void method(Person p) {
- p.show();
- }
- }
- class Student extends Person {
- public void show() {
- System.out.println("show");
- }
- }
匿名内部类在开发中,当做参数传递(把匿名内部类当做一个对象)
- class Test1_NoNameInnerClass {
- class Test2_NoNameInnerClass {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //Outer.method().show(); //链式编程,每次调用方法后还能继续调用方法,证明调用方法返回的是对象
- Inter i = Outer.method();
- i.show();
- }
- }
- //按照要求,补齐代码
- interface Inter {
- void show();
- }
- class Outer {
- //补齐代码
- public static Inter method() {
- return new Inter() {
- public void show() {
- System.out.println("HelloWorld");
- }
- };
- }
- }
- //要求在控制台输出”HelloWorld”
根据主方法的调用方法,补齐代码
- class Test2_NoNameInnerClass {
- 成员内部类
【JAVA基础】08 面向对象3的更多相关文章
- Java基础-初识面向对象编程(Object-Oriented-Programming)
Java基础-初识面向对象编程(Object-Oriented-Programming) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. Java是一门面向对象的程序设计语言.那么什 ...
- 黑马程序员——【Java基础】——面向对象(二)异常机制、包(Package)
---------- android培训.java培训.期待与您交流! ---------- 一.异常机制 (一)异常概述 1.异常:就是程序在运行时出现不正常情况. 2.异常类:程序在运行时,出现的 ...
- Java基础之面向对象以及其他概念
一.基础知识:1.JVM.JRE和JDK的区别: JVM(Java Virtual Machine):java虚拟机,用于保证java的跨平台的特性. java语言是跨平台,jvm不是跨平台的. JR ...
- Java基础08 继承
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 继承(inheritance)是面向对象的重要概念.继承是除组合(composit ...
- Java基础08 继承(转载)
继承(inheritance)是面向对象的重要概念.继承是除组合(composition)之外,提高代码重复可用性(reusibility)的另一种重要方式.组合是重复调用对象的功能接口.继承可以重复 ...
- 【Java基础】面向对象下
面向对象下 这一章主要涉及其他关键字,包括 this.super.static.final.abstract.interface.package.import 等. static 在 Java 类中, ...
- 【java基础】面向对象的三大基本特征之-------继承
面向对象的三大特征:封装,继承,多态 java通过extends关键字来实现继承,而且是单继承,一个子类只可以有一个直接父类,但是父类还可以有父类... java.long.Object是所有类的父类 ...
- 黑马程序员——【Java基础】——面向对象(一)概述、类与对象、继承、抽象类、接口、多态、内部类
---------- android培训.java培训.期待与您交流! ---------- 一.面向对象概述 1.面向对象:是一个很抽象的概念,它相对面向过程而言,是一种程序设计的思想. 2.面向对 ...
- Python基础08 面向对象的基本概念
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 谢谢逆水寒龙,topmad和Liqing纠错 Python使用类(class)和对 ...
- 再探java基础——对面向对象的理解(1)
对象 对象是人们要进行研究的任何事物,从最简单的整数到复杂的飞机等均可看作对象,它不仅能表示具体的事物,还能表示抽象的规则.计划或事件.对象具有属性和行为,在程序设计中对象实现了数据和操作的结合,使数 ...
随机推荐
- 为什么scanf(" %c",&c)中%c前要空格?
空格确实不是必须的,但有了空格就可以忽略你输入的空格. ****例如:scanf(" %c" ,&c),你输入了' a'(a前面有个空格),a就能被c接受. 但控制符前如果 ...
- 浅谈头文件(.h)和源文件(.cpp)的区别
浅谈头文件(.h)和源文件(.cpp)的区别 本人原来在大一写C的时候,都是所有代码写在一个文件里一锅乱煮.经过自己开始写程序之后,发现一个工程只有一定是由多个不同功能.分门别类展开的文件构成的.一锅 ...
- 这些基本的 HTML5 标签你不能不知道
HTML5元素 HTML5是HTML最新的修订版本,2014年10月由万维网联盟(W3C)完成标准制定. HTML5是用来写网页的一门标记语言. 使用的时候需要在首行声明HTML,如:<!DOC ...
- django-rest-framework权限验证
django-rest-framework权限验证 在项目根目录下新建utils的文件 新建permissions.py from rest_framework.permissions import ...
- Java第二十天,Map集合(接口)
Map接口 一.定义 Map集合是双列集合,即一个元素包含两个值(一个key,一个value),Collection集合是单列集合. 定义格式: public interface Map<K,V ...
- Java入门第一阶段总结
前言 写了三周的模拟题,对原本就厌恶的模拟更加深恶痛绝.但是不得不说模拟题是对一门语言入门掌握其语法成效最快的一类题,轻松地从C入门到了Java.一直坚信各门语言都是想通的,一力破万法. 作业过程总结 ...
- shell http请求&处理返回值获取其中某个字段的值
并且第一个接口的返回值中部分参数得作为第二个接口的入参,所以做了如下shell验证 第一个接口返回的response body串: { "bizCode": "1&quo ...
- python3(三十六)StringIO BytesIO
""" StringIO和BytesIO """ __author__on__ = 'shaozhiqi 2019/9/23' # !/us ...
- hive常用函数四
字符串函数 1. 字符串长度函数:length 语法: length(string A) 返回值: int 说明:返回字符串A的长度 举例: hive> select length('abced ...
- AJ学IOS(54)多线程网络之NSOperation重要知识
AJ分享,必须精品 一:队列的类型与队列添加任务 1: 主队列 [NSOperationQueue mainQueue] 添加到”主队列”中的操作,都会放到主线程中执行. 2:非主队列 [[NSOpe ...
