苏浪浪 201771010120 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第七章学习总结
第七周
1、实验目的与要求
(1)进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;
(2)掌握Object类的常用API用法;
(3)掌握ArrayList类用法与常用API;
(4)掌握枚举类使用方法;
(5)结合本章知识,理解继承与多态性两个面向对象程序设计特征,并体会其优点;
(6)熟练掌握Java语言中基于类、继承技术构造程序的语法知识(ch1-ch5);
(7)利用已掌握Java语言程序设计知识,学习设计开发含有1个主类、2个以上用户自定义类的应用程序。
2、实验内容和步骤
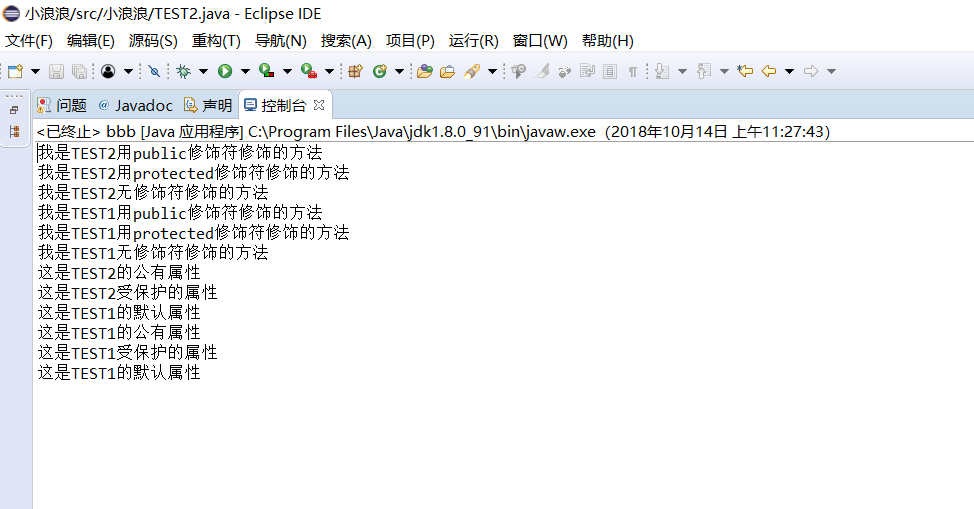
实验1 补充以下程序中主类内main方法体,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
|
public class TEST1 { private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; private void tese1() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void tese2() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void tese3() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void tese4() { System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class TEST2 extends TEST1{ private String e1 = "这是TEST2的私有属性"; public String e2 = "这是TEST2的公有属性"; protected String e3 = "这是TEST2受保护的属性"; String e4 = "这是TEST2的默认属性"; public void demo1() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void demo2() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void demo3() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void demo4() { System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { TEST2 test2 = new TEST2(); /*以下设计代码分别调用 demo1 demo2 demo3 demo4 test1 test2 test3 test4方法和t1 t2 t3 t3 e1 e2 e3 e4属性,结合程序运行结果理解继承和权限修饰符的用法与区别*/ } } |
package 小浪浪;
public class bbb {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TEST2 test2 = new TEST2();
test2.demo1();
test2.demo3();
test2.demo4();
test2.test2();
test2.test3();
test2.test4();
String e2=test2.e2;
String e3=test2.e3;
String e4=test2.e4;
System.out.println(e2);
System.out.println(e3);
System.out.println(e4);
System.out.println(test2.t2);
System.out.println(test2.t3);
System.out.println(test2.t4);
}
}
package 小浪浪;
public class TEST1 {
private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性";
public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性";
protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性";
String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性";
private void test1() {
System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
public void test2() {
System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void test3() {
System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void test4() {
System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
package 小浪浪;
public class TEST2 extends TEST1{
private String e1 = "这是TEST2的私有属性";
public String e2 = "这是TEST2的公有属性";
protected String e3 = "这是TEST2受保护的属性";
String e4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性";
public void demo1() {
System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
private void demo2() {
System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void demo3() {
System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void demo4() {
System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
实验2 第五章测试程序反思,继承知识总结。
测试程序1:
编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10(教材174页-177页);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Object类的定义及用法;
package equals; import java.time.*;
import java.util.Objects; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
// 快速测试,看看这些对象是否相同
if (this == otherObject) return true;
// 如果显式参数为空,则必须返回false
if (otherObject == null) return false;
// 如果类不匹配,它们就不能相等
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;
// 现在我们知道otherObject是一个非空雇员
Employee other = (Employee) otherObject;
// 测试字段是否具有相同d的值
return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay);
} public int hashCode()
{
return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay);
} public String toString()
{
return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay
+ "]";
}
}
package equals; /**
* This program demonstrates the equals method.
* @version 1.12 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EqualsTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);
Employee alice2 = alice1;
Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);
Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15);
Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15);
boss.setBonus(5000);
System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss);
System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss));
System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode());
System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode());
System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode());
System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode());
}
}
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = 0;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double bonus)
{
this.bonus = bonus;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
Manager other = (Manager) otherObject;
// super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same class
return bonus == other.bonus;
} public int hashCode()
{
return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus);
} public String toString()
{
return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]";
}
}
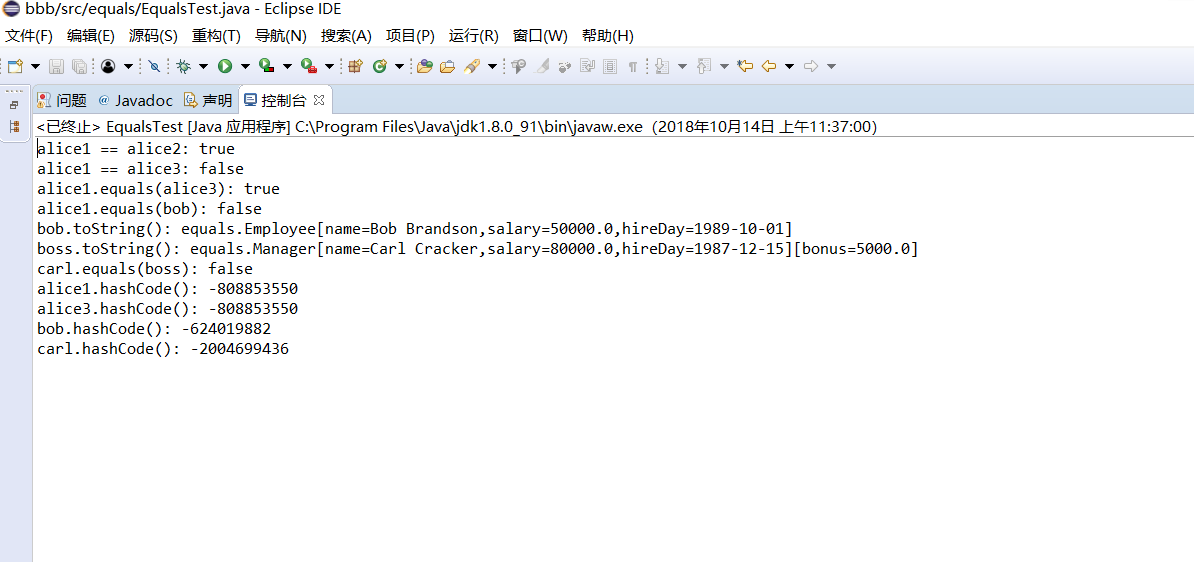
测试程序2:
编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-11(教材182页);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates the ArrayList class.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ArrayListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array list with three Employee objects
ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15));
staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1));
staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15)); // raise everyone's salary by 5%
for (Employee e : staff)
e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
+ e.getHireDay());
}
}
package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
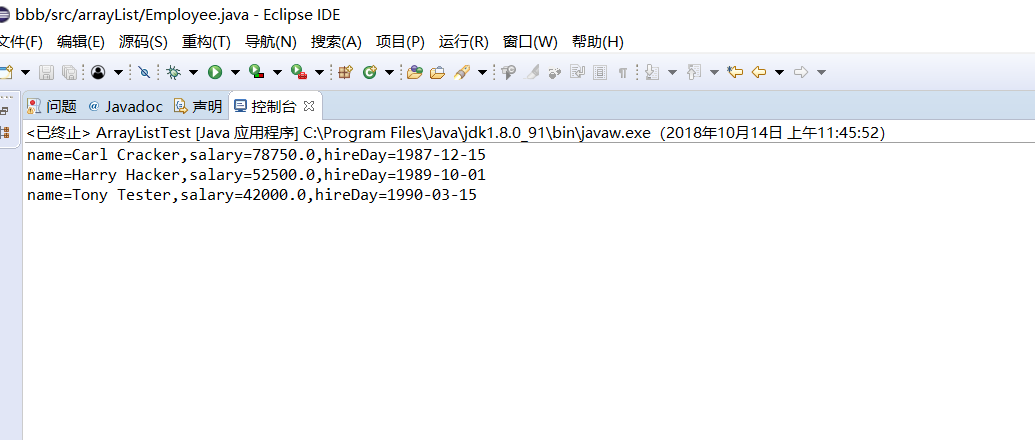
测试程序3:
编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页);
结合运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
package enums; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates enumerated types.
* @version 1.0 2004-05-24
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EnumTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) ");
String input = in.next().toUpperCase();
Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input);
System.out.println("size=" + size);
System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation());
if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)
System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _.");
}
} enum Size
{
SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }
public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation;
}

实验3:采用个人账号登录https://pintia.cn/,完成《2018秋季西北师范大学面向对象程序设计(Java)(ch1-ch5)测试题2》,测试时间60分钟;
实验4: 课后完成实验3未完成的测试内容
实验总结:
在学长的指导之下进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;在老师的讲解以及实验测试下掌握了Object类的常用API用法、ArrayList类用法与常用API、枚举类使用方法;大概理解了继承与多态性两个面向对象程序设计特征,掌握了Java语言中基于类、继承技术构造程序的语法知识;
苏浪浪 201771010120 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第七章学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010118马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.接口 在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成.Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个 ...
随机推荐
- 怎么在java中创建一个自定义的collector
目录 简介 Collector介绍 自定义Collector 总结 怎么在java中创建一个自定义的collector 简介 在之前的java collectors文章里面,我们讲到了stream的c ...
- Android Studio快捷键动态演示
Android Studio出来很久了,大部分已经转过来了,相对于Eclipse又是毋庸置疑,更好的使用快捷键必定达到事半功倍的效果. 友情提示:某些电脑按F1-F12键需要先按住FN,比如我的Mac ...
- Muduo网络库实战(二):实现服务器与客户端的连接
1. 方案的确定 1)基本需求 用户1000+, IO压力不大: 多个客户端打开网站,输入查询字符串strclient,发送给服务器=>服务器接收客户端发过来的数据并处理,将结果返回给客户端: ...
- 1745 Divisibility
Divisibility Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 14084 Accepted: 4989 Descrip ...
- RocketMQ搭建全过程
RocketMQ下载地址:https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/rocketmq/4.3.0/rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-relea ...
- Linux之《荒岛余生》(一)准备篇
xin片之争,已经暴露了中国xin的问题,我等码农束手无策:而在操作系统方面,成果也是乏善可陈:现如今酷炫的Web监控工具,让很多研发丧失了真正处理问题的能力. 越接近底层,就越接近真相,在计算机的世 ...
- D - 小Z的加油店 线段树+差分+GCD
D - 小Z的加油店 HYSBZ - 5028 这个题目是一个线段树+差分+GCD 推荐一个差分的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/cjoierljl/p/8728110.ht ...
- neo4j在docker容器环境中无法启动的问题
回去过了个周末,neo4j就无法启动了 数据还没备份出来,着急啊.上周回去前刚刚在研究怎么把数据导出来,尝试了一些容器导出的方法,没有成功.周一回来就无法启动了... 表现为启动后过几十秒又变为sto ...
- jquery注册页面的判断及代码的优化
今天主要负责完成注册页面的jquery代码的写入与优化,基本代码和登录页面差不多,复制修改一下代码就行了,主要区别在于多了一个重复密码与密码是否一致的判断,刚开始写出来的代码导致每个框的后面都追加重复 ...
- python小游戏-pygame模块
一.tkinter模块的GUI 基本上使用tkinter来开发GUI应用需要以下5个步骤: 导入tkinter模块中我们需要的东西. 创建一个顶层窗口对象并用它来承载整个GUI应用. 在顶层窗口对象上 ...
