OLAP vs OLTP: what makes the difference
OLAP vs OLTP: what makes the difference
OLPT and OLAP are complementingtechnologies. You can't live without OLTP: it runs your business dayby day. So, using getting strategic information from OLTP is usuallyfirst “quick and dirty” approach, but can become limiting later.
This post explores keydifferences between two technologies.
OLTPstands for On LineTransaction Processing and is a datamodeling approach typically used to facilitate and manage usual business applications.
Most of applications you see and use areOLTP based.
OLAPstands for On LineAnalytic Processing and is an approach to answer multi-dimensional queries. OLAP was conceived forManagement Information Systems and Decision
Support Systems but isstillwidely underused: every day I see too much people makingout business intelligence from OLTP data!
With the constant growth of dataanalysis and business intelligence applications (now even in smallbusiness) understanding OLAP nuances and benefits is a must if youwant provide valid and useful analytics to management.
The following table summarized maindifferences between OLPT and OLAP:
|
OLTP |
OLAP |
|
|
Application |
Operational: ERP, CRM, legacy apps, ... |
Management Information System, Decision Support System |
|
Typical users |
Staff |
Managers, Executives |
|
Horizon |
Weeks, Months |
Years |
|
Refresh |
Immediate |
Periodic |
|
Data model |
Entity-relationship |
Multi-dimensional |
|
Schema |
Normalized |
Star |
|
Emphasis |
Update |
Retrieval |
Let's go straight to each key points.
Horizon
OLTP databases store “live”operational information. An invoice, for example, once paid, ispossibly moved to some sort of backup store, maybe upon period closing. On the other side5-10 strategic analysis are usual to identify trends. Extending
life of operational data, would not be enough (in addition to possibly impacting performance).
Even keeping that data indexedand online for years, you would surely face compatibility problems.It is quite improbable that your current invoice fields andreferences are the same of 10 years ago!
But neither performance norcompatibility are the biggest concern under large horizon. Realproblem is business dynamics. Today business constantly change andthe traditional entity-relationship approach is too vulnerable tochanges. I will better explore this
point in next post with apractical example.
Refresh
OLPT requires instant update. When youcash some money from an ATM you balance shall be immediately updated.OLAP has not such requirement. Nobody needs instant information tomake strategic business decision.
This allows OLAP data to be refresheddaily. This means extra timing and resources for cleansing andaccruing data. If, for example, an invoice was canceled, we wouldn'tlike to see its value first inflating sales figures and later reverted.
More time and more resources would alsoallow better indexing to address huge tables covering the extendedhorizon.
Data Model & Schema
This is possibly the most evidentdifference between two approaches. OLTP perfectly fits traditionalentity-relationship or object-oriented models. We usually refer toinformation as attributes related to entities, objects or classes,like product price, invoice
amount or client name. Mapping can bewith a simple, one argument function:
product » price
invoice » amount
client » name
Such functions can be implementedthough classic tables, one row per instance, whereeach attribute ismapped to one column.
Now, if you listen to typical businessquestions you perceive a different requirement:
What is gross margin by product category in Europe and Asia?
What's our current inventory by product and warehouse?
Which was the evolution of return rate of different products acquired by different suppliers?
Are mapped as functions of multiplearguments (left side):
Product category × Region » Grossmargin
Product × Warehouse » Inventory
Supplier × Time × Product » Returnrate
Mapping attributes to columns do not work any more in this case: a multi-dimensionalapproach is required.
Tables do not naturally support multi-dimensional approachbut relational databases are still the most widely used, proven andreliable approach today available. Reliability and performance is amust if we think in storing terabytes of data along years.
The solution is use an hybridapproach based sitting on conventional relational technology. Thismodel employs so calledstar-schema instead of traditionalnormalization.
Emphasis
OLPT emphasis is on update. Transactionlevel isolation assures that database is always in a consistentstate. This can imply in some overhead to coordinate concurrentupdates but is necessary even in small applications.
On the other side OLAP can be updatedby periodic (daily) processes that work in standalone mode thusconsistency can be assured through update process.
But OLAP faces another challenge:retrieval. Suppose a telecom executive asking how much was billedlast year in communications from USA to Japan. Can you figure howmuch time would it take to go ever each individual call to get theresult?
OLTP emphasis is on retrieval andit organizes data to return result of ad hoc inquiries in a reasonableamount of time.
Two worlds, two obstacles
So, in practice you need two differentdatabases, one for OLAP and another one for OLTP. The second one isusually called a Data Warehouse and is a must if you want to makeserious business intelligence.
But, if this is best solution why itisn't widely adopted? Why so many people are still trying to use BItools on traditional OLTP database? These are the most common reasons I have seen in practice:
Doctrine. For years data modelers have been educated to normalize data and for years they have been told that data redundancy is first deadly sin.Habit is worst enemy of OLAP approach. Even when a star schema was officially
adopted for BI applications, I have seen an irresistible attraction tosnowflaking (I'll explain this term in next posts).
Ingenuity. “Let's buy a good tool that will do the magic with little effort!”. This seems quite a better alternative to creating and feeding a second database. It doesn't work, still can be a valid solution if, as IT manager, you
have just opened your second envelope. In next post I will illustrate with practical example what will probably go wrong.
Building a relational data warehouse isactually not so difficult, neither exclusively applicable tomulti-billion corporations or terabytes of data and, infuture
posts,I pretend to show a pragmatic and agile approach.
For further detail on OLAP technology Isuggest to read: OlapSolutions - 2nded.
By Erik Tomsen, also available at Amazon.
原文地址:http://www.cbsolution.net/techniques/ontarget/olap_vs_oltp_what_makes
下图引自另外一个网页,点击图片跳转
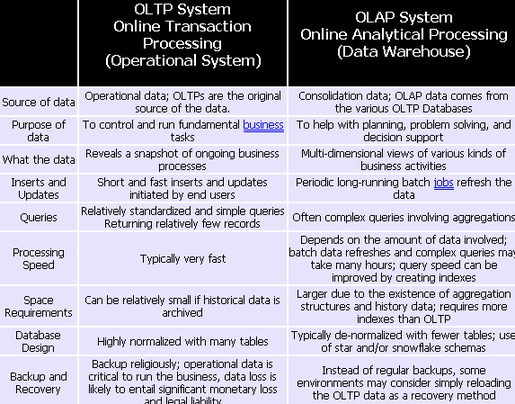
OLAP vs OLTP: what makes the difference的更多相关文章
- OLAP、OLTP的介绍和比较 via csdn
OLAP.OLTP的介绍和比较 数据处理大致可以分成两大类: OLTP(On-Line Transaction Processing)联机事务处理 也称为面向交易的处理系统,其基本特征是顾客的原始数据 ...
- OLAP和OLTP的区别(基础知识) 【转】
联机分析处理 (OLAP) 的概念最早是由关系数据库之父E.F.Codd于1993年提出的,他同时提出了关于OLAP的12条准则.OLAP的提出引起了很大的反响,OLAP作为一类产品同联机事务处理 ( ...
- OLAP和OLTP的区别
OLAP(On-Line Analytical Processing)联机分析处理,也称为面向交易的处理过程,其基本特征是前台接收的用户数据可以立即传送到计算中心进行处理,并在很短的时间内给出处理结果 ...
- day 59 MySQL之锁、事务、优化、OLAP、OLTP
MySQL之锁.事务.优化.OLAP.OLTP 本节目录 一 锁的分类及特性 二 表级锁定(MyISAM举例) 三 行级锁定 四 查看死锁.解除锁 五 事务 六 慢日志.执行计划.sql优化 七 ...
- olap和Oltp(转)
OLAP和OLTP的区别(基础知识) 联机分析处理 (OLAP) 的概念最早是由关系数据库之父E.F.Codd于1993年提出的,他同时提出了关于OLAP的12条准则.OLAP的提出引起了很大的反响, ...
- OLAP、OLTP的介绍和比较
OLTP与OLAP的介绍 数据处理大致可以分成两大类:联机事务处理OLTP(on-line transaction processing).联机分析处理OLAP(On-Line Analytical ...
- Oracle OLAP 与 OLTP 介绍
文章出处:http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/article/details/5794844 感谢原作者的分享. 数据处理大致可以分成两大类:联机事务处理OLTP( ...
- OLAP和OLTP基础知识
数据处理大致可以分成两大类:联机事务处理OLTP(on-line transaction processing).联机分析处理OLAP(On-Line Analytical Processing).O ...
- OLAP和OLTP的区别(基础知识)
联机分析处理 (OLAP) 的概念最早是由关系数据库之父E.F.Codd于1993年提出的,他同时提出了关于OLAP的12条准则.OLAP的提出引起了很大的反响,OLAP作为一类产品同联机事务处理 ( ...
随机推荐
- PL/SQL 听课笔记
PL/SQL: 知识回顾: SQL: 结构化查询语言: T-SQL: microsoft sql语言: PL/SQL: Oracle sql语言: 变量命名规则: 1.首字母必须是字母,可以包含字 ...
- iOS - VIPER 架构模式
1.VIPER 从字面意思来理解,VIPER 即 View Interactor Presenter Entity Router(展示器(视图) 交互器 协调器 实体(数据) 路由器),迄今为止,划分 ...
- HDU4801·二阶魔方
题意:给定二阶魔方初始状态,问N(1 <= N <= 7)步旋转操作以内最多能使几个面相同. dfs搜索+剪枝. 魔方的每个旋转操作即对应于一个置换操作.又因为相对运动,上层左旋一次和下层 ...
- linux rwxrwxrwt文件夹属性
/tmp 的permission是rwxrwxrwt chmod 0777 /abc rwxrwxrwx chmod 777 /abc rwxrwxrwx chmod 17 ...
- 详细地jsoncpp编译方法 和 vs2010中导入第三方库的方法
详细地jsoncpp编译方法 和 vs2010中导入第三方库的方法 一 编译链接 1 在相应官网下载jsoncpp 2 解压得到jsoncpp-src-0.5.0文件 3 打开jsoncpp-src- ...
- gO语言的安装和环境变量的配置
一.Go语言下载 go语言官方下载地址:https://golang.org/dl/ 找到适合你系统的版本下载,本人下载的是windows版本.也可以下载Source自己更深层次研究go语言. 二.G ...
- RAC 集群更换IP
RAC 集群更换 IP 主要分三步:停集群服务.配置服务器网络.修改集群配置.下面是同网段内更换 IP 示例.(r7.r8为服务器名称,orcl为ORACLE_SID,scanip为 scan 名称) ...
- JSON和JSONP区别和联系
由于Sencha Touch 2这种开发模式的特性,基本决定了它原生的数据交互行为几乎只能通过AJAX来实现. 当然了,通过调用强大的PhoneGap插件然后打包,你可以实现100%的Socket通讯 ...
- jquery 全选功能
1.直接全选(复选框名字要统一) <input type="CHECKBOX" id="cbSelectAll" onclick="$('inp ...
- Oracle session inactive状态临时表数据未清空问题
问题描述:Oracle数据库,java代码使用某数据库实例,获取connection并在使用结束关闭,而session未销毁,而是状态变为inactive从而导致临时表数据未清空. Oracle临时表 ...
