Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN
Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN
Xiao Wang 2016.05.02
Triplet Loss Layer could be a trick for further improving the accuracy of CNN. Today, I will introduce the whole process, and display the code for you. This tutorial mainly from the blog:
http://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/46812153
http://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/46788025
and the paper: <FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering>.
First, Let's talk about how to add the layer into caffe and make test this layer to check whether it works or not. And then, we will discuss the paper and introduce the process of how the triplet loss come from. In the new version of caffe framework, it mainly consists of these steps for add a new layer i.e.
step 1. add the paprameter message in the corresponding layer, which located in ./src/caffe/proto/caffe.proto ;
step 2. add the declaration information of the layer in ./include/caffe/***layers.hpp ;
step 3. add the corresponding .cpp and .cu files in ./src/caffe/layers/, realize the function of the new added layer;
step 4. add test code of new added layers in ./src/caffe/gtest/, test its foreward and back propagation and its computation speed.
Let's do it step by step.
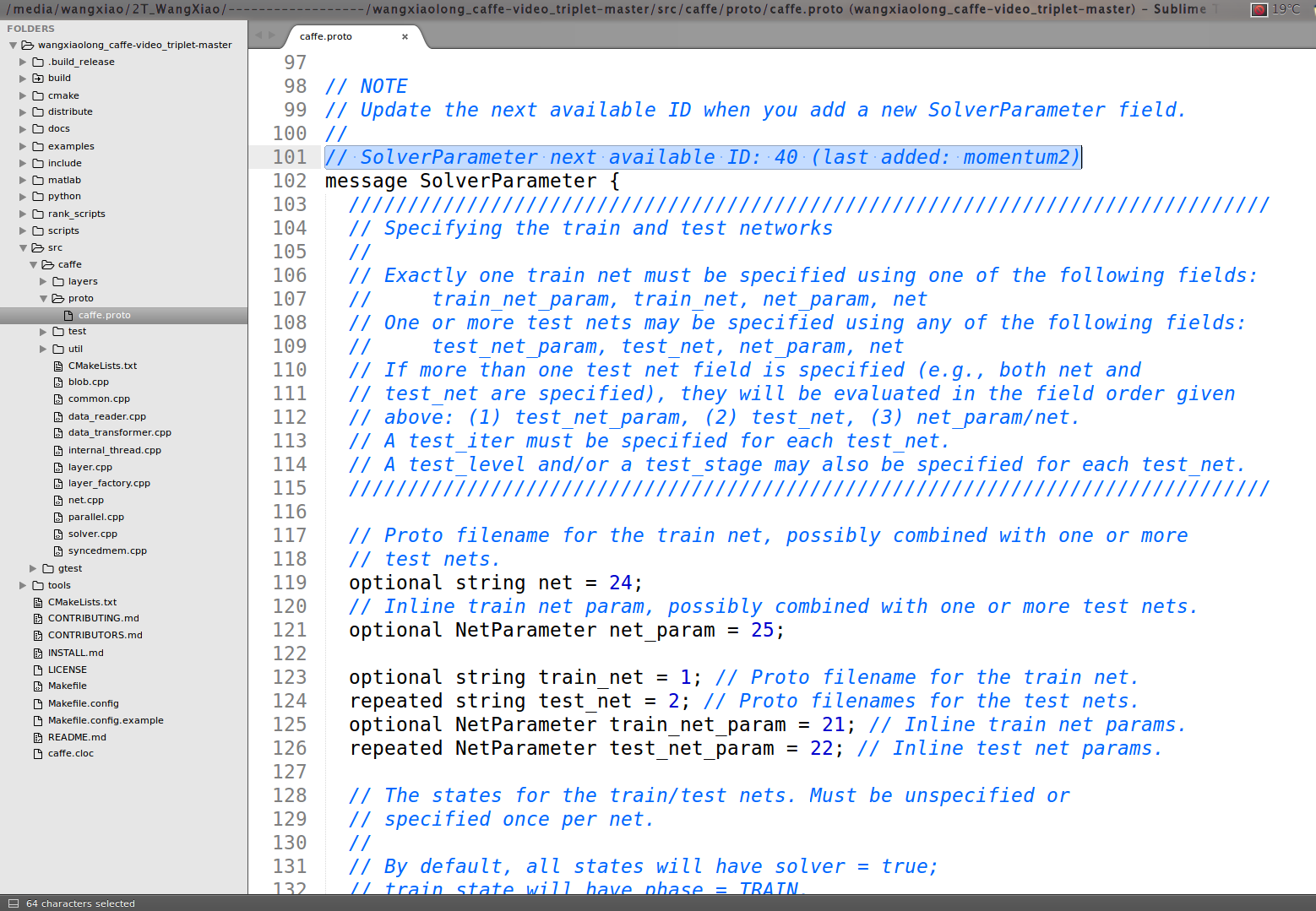
First, we add triplet loss layer in caffe.proto file:
we could found that in line 101, it said: SolverParameter next available ID: 40 (last added: momentum2), thus we add the ID: 40 as the new added information :
message RankParameter {
optional uint32 neg_num = 1 [default = 1];
optional uint32 pair_size = 2 [default = 1];
optional float hard_ratio = 3;
optional float rand_ratio = 4;
optional float margin = 5 [default = 0.5];
}
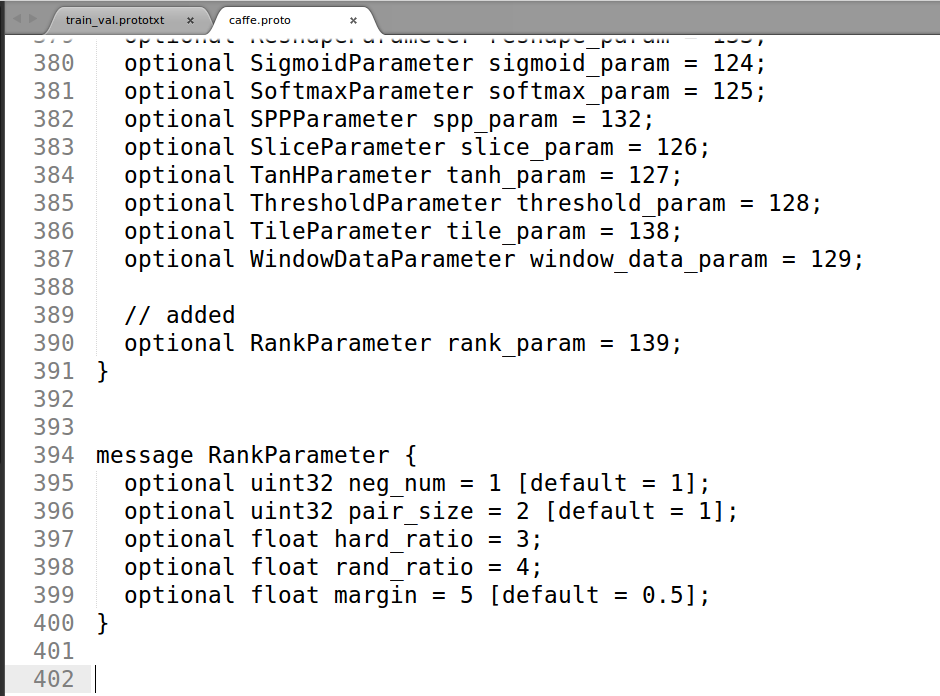
Second, we add the declearation information about triplet loss layer in ./include/caffe/TripletLoss_layers.hpp
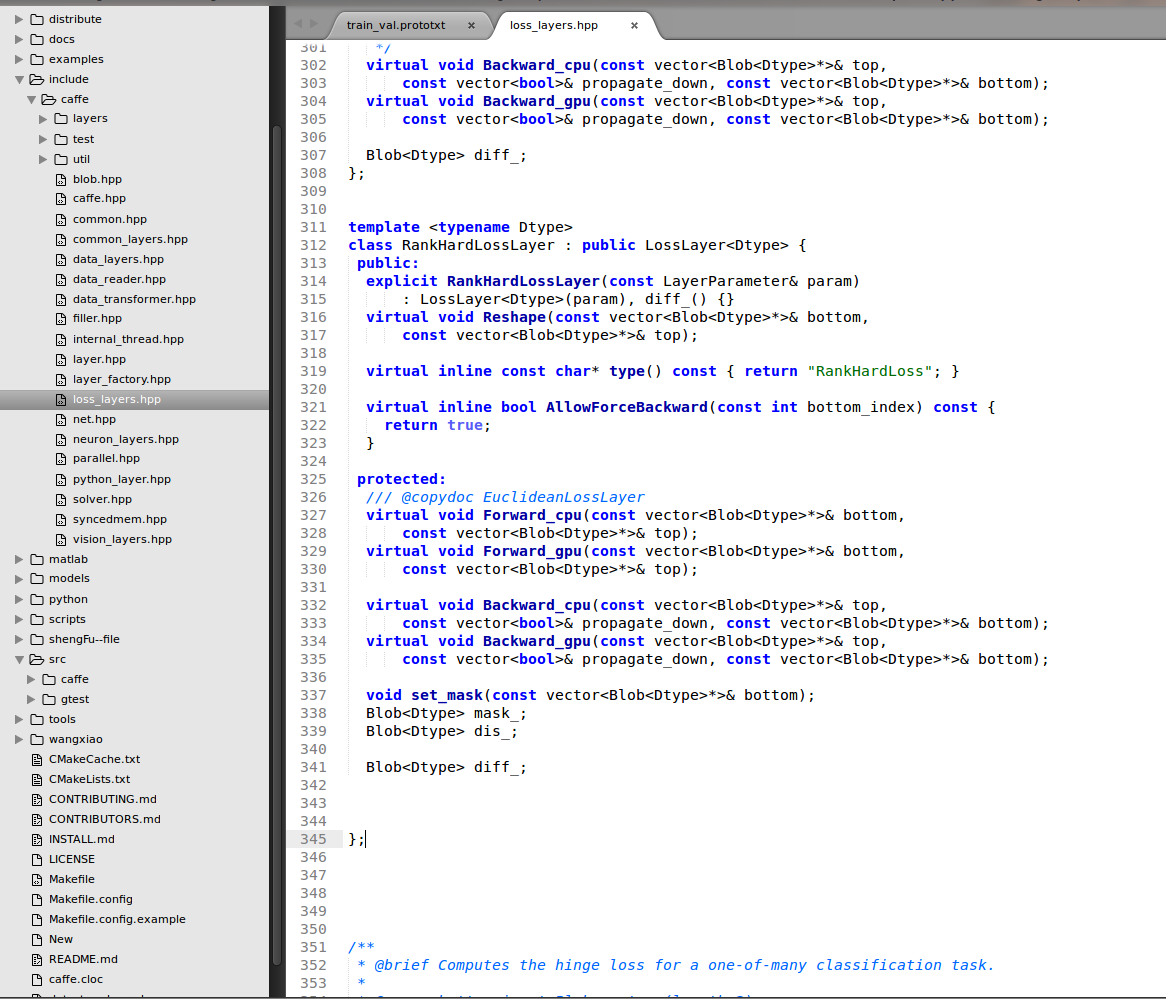
Third, We compile the triplet loss layer of .cpp and .cu file
First of all is the .cpp file
#include <vector> #include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cfloat> #include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/io.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
#include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp" using std::max;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv; namespace caffe { int myrandom (int i) { return caffe_rng_rand()%i;} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top); diff_.ReshapeLike(*bottom[]);
dis_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->num(), , );
mask_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->num(), , );
} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::set_mask(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom)
{ RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num();
int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size();
float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
float margin = rank_param.margin(); int hard_num = neg_num * hard_ratio;
int rand_num = neg_num * rand_ratio; const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[]->cpu_data();
int count = bottom[]->count();
int num = bottom[]->num();
int dim = bottom[]->count() / bottom[]->num();
Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data(); for(int i = ; i < num * num; i ++)
{
dis_data[i] = ;
mask_data[i] = ;
} // calculate distance
for(int i = ; i < num; i ++)
{
for(int j = i + ; j < num; j ++)
{
const Dtype* fea1 = bottom_data + i * dim;
const Dtype* fea2 = bottom_data + j * dim;
Dtype ts = ;
for(int k = ; k < dim; k ++)
{
ts += (fea1[k] * fea2[k]) ;
}
dis_data[i * num + j] = -ts;
dis_data[j * num + i] = -ts;
}
} //select samples vector<pair<float, int> >negpairs;
vector<int> sid1;
vector<int> sid2; for(int i = ; i < num; i += pair_size)
{
negpairs.clear();
sid1.clear();
sid2.clear();
for(int j = ; j < num; j ++)
{
if(label[j] == label[i])
continue;
Dtype tloss = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
if(tloss == ) continue; negpairs.push_back(make_pair(dis_data[i * num + j], j));
}
if(negpairs.size() <= neg_num)
{
for(int j = ; j < negpairs.size(); j ++)
{
int id = negpairs[j].second;
mask_data[i * num + id] = ;
}
continue;
}
sort(negpairs.begin(), negpairs.end()); for(int j = ; j < neg_num; j ++)
{
sid1.push_back(negpairs[j].second);
}
for(int j = neg_num; j < negpairs.size(); j ++)
{
sid2.push_back(negpairs[j].second);
}
std::random_shuffle(sid1.begin(), sid1.end(), myrandom);
for(int j = ; j < min(hard_num, (int)(sid1.size()) ); j ++)
{
mask_data[i * num + sid1[j]] = ;
}
for(int j = hard_num; j < sid1.size(); j++)
{
sid2.push_back(sid1[j]);
}
std::random_shuffle(sid2.begin(), sid2.end(), myrandom);
for(int j = ; j < min( rand_num, (int)(sid2.size()) ); j ++)
{
mask_data[i * num + sid2[j]] = ;
} } } template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[]->cpu_data();
int count = bottom[]->count();
int num = bottom[]->num();
int dim = bottom[]->count() / bottom[]->num(); RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num(); //
int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size(); //
float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
float margin = rank_param.margin();
Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data(); set_mask(bottom);
Dtype loss = ;
int cnt = neg_num * num / pair_size * ; for(int i = ; i < num; i += pair_size)
{
for(int j = ; j < num; j++)
{
if(mask_data[i * num + j] == )
continue;
Dtype tloss1 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
Dtype tloss2 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[(i + ) * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
loss += tloss1 + tloss2;
}
} loss = loss / cnt;
top[]->mutable_cpu_data()[] = loss;
} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) { const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[]->cpu_data();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[]->mutable_cpu_diff();
int count = bottom[]->count();
int num = bottom[]->num();
int dim = bottom[]->count() / bottom[]->num(); RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num();
int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size();
float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
float margin = rank_param.margin(); Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data(); for(int i = ; i < count; i ++ )
bottom_diff[i] = ; int cnt = neg_num * num / pair_size * ; for(int i = ; i < num; i += pair_size)
{
const Dtype* fori = bottom_data + i * dim;
const Dtype* fpos = bottom_data + (i + ) * dim; Dtype* fori_diff = bottom_diff + i * dim;
Dtype* fpos_diff = bottom_diff + (i + ) * dim;
for(int j = ; j < num; j ++)
{
if(mask_data[i * num + j] == ) continue;
Dtype tloss1 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
Dtype tloss2 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[(i + ) * num + j] + Dtype(margin)); const Dtype* fneg = bottom_data + j * dim;
Dtype* fneg_diff = bottom_diff + j * dim;
if(tloss1 > )
{
for(int k = ; k < dim; k ++)
{
fori_diff[k] += (fneg[k] - fpos[k]); // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fpos_diff[k] += -fori[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fneg_diff[k] += fori[k];
}
}
if(tloss2 > )
{
for(int k = ; k < dim; k ++)
{
fori_diff[k] += -fpos[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fpos_diff[k] += fneg[k]-fori[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fneg_diff[k] += fpos[k];
}
} }
} for (int i = ; i < count; i ++)
{
bottom_diff[i] = bottom_diff[i] / cnt;
} } #ifdef CPU_ONLY
STUB_GPU(RankHardLossLayer);
#endif INSTANTIATE_CLASS(RankHardLossLayer);
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(RankHardLoss); } // namespace caffe
and the .cu file
#include <vector> #include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/io.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
#include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp" namespace caffe { template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
Forward_cpu(bottom, top);
} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
Backward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
} INSTANTIATE_LAYER_GPU_FUNCS(RankHardLossLayer); } // namespace caffe
Finally, we make the caffe file and check whether have some mistakes about it.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
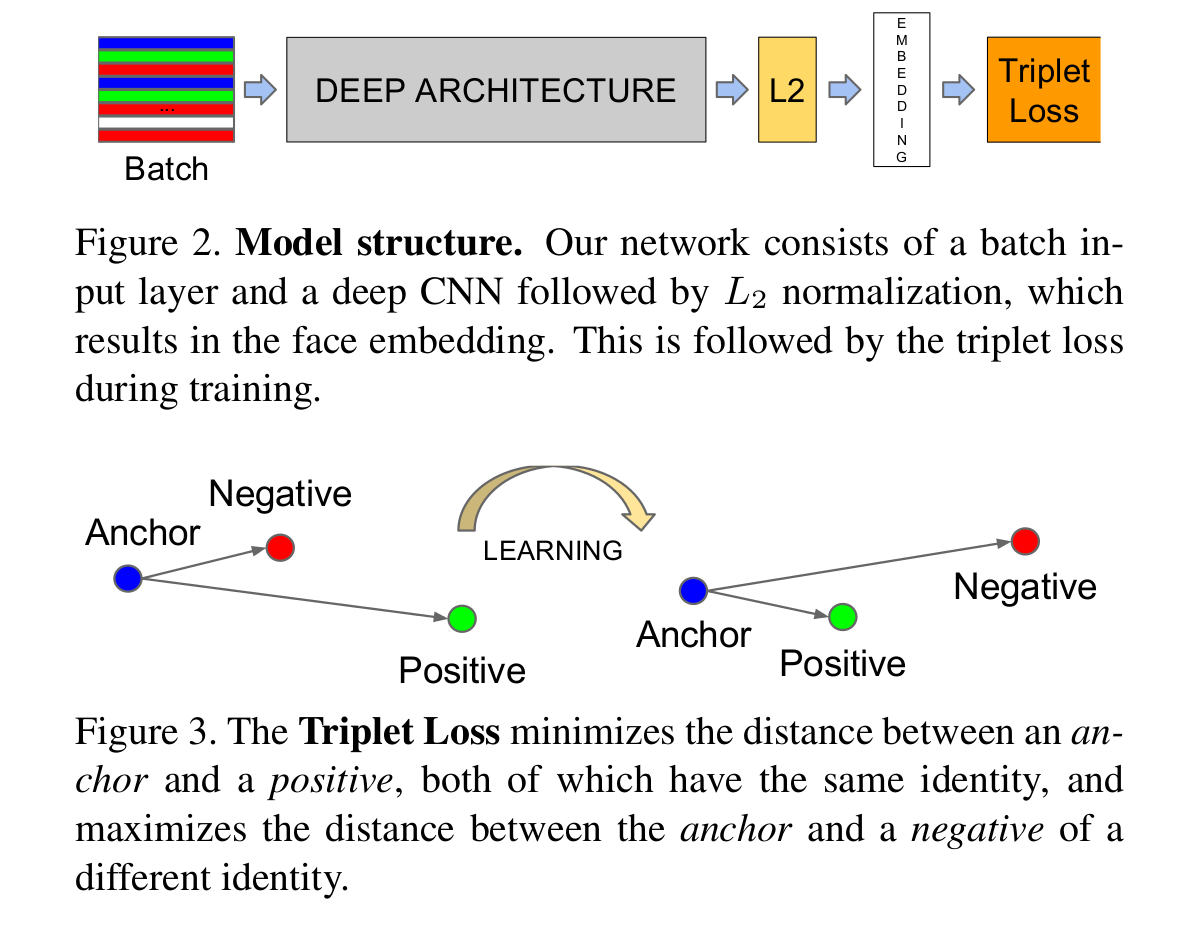
Let's continue to talk about the triplet loss:
Just like the above figure showns, the triplet loss usually have three components, i.e. the anchors, the positive, and the negative. What we are going to do is try to reduce the distance between the archor and the same, and push the different from the anchors.
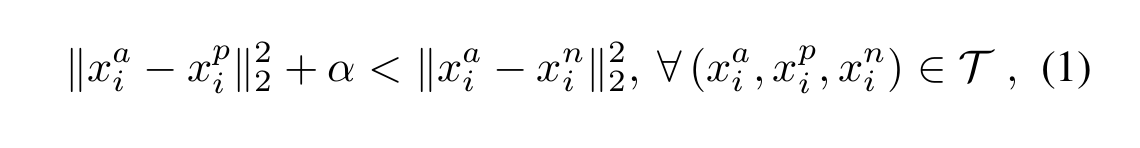
Thus, the whole loss could be described as following:
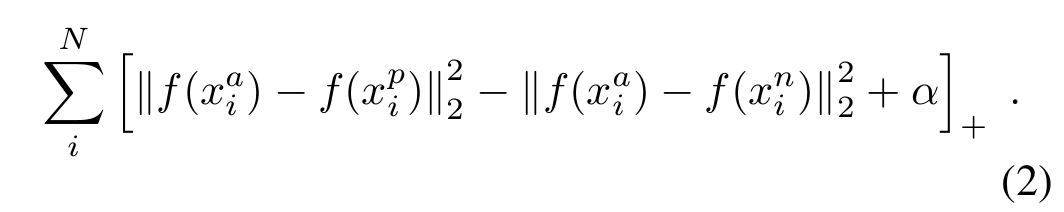
Only select triplets randomly may lead to slow converage of the network, and we need to find those hard triplets, that are active and can therefore contribute to improving the model. The following section will give you an explanination about the approach.
Triplet Selection:
There are two appproaches for generate triplets, i.e.
1. Generate triplets offline every n steps, using the most recent newwork checkpoint and computing the argmin and argmax on a subset of the data.
2. Generate the triplets online. This can be done by selecting the hard positive/negative exemplars form within a mini-batch.
This paper use all anchor-positive pairs in a mini-batch while still selecting the hard negatives. the all anchor-positive method was more stable and converaged slightly faster at the begining of training.
The code could refer the github page: https://github.com/wangxiao5791509/caffe-video_triplet
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "RankHardLoss"
rank_param{
neg_num: 4
pair_size: 2
hard_ratio: 0.5
rand_ratio: 0.5
margin: 1
}
bottom: "norml2"
bottom: "label"
}Triplet Loss Implementation using Pytorch:
the following document comes from: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#tripletmarginloss
Creates a criterion that measures the triplet loss given an input tensors x1, x2, x3 and a margin with a value greater than 0. This is used for measuring a relative similarity between samples. A triplet is composed by a, p and n: anchor, positive examples and negative example respectively. The shapes of all input tensors should be (N,D)(N,D).
The distance swap is described in detail in the paper Learning shallow convolutional feature descriptors with triplet losses by V. Balntas, E. Riba et al.
The loss function for each sample in the mini-batch is:
where d(xi,yi)=∥xi−yi∥pd(xi,yi)=‖xi−yi‖p.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
- Shape:
-
- Input: (N,D)(N,D) where D is the vector dimension.
- Output: scalar. If reduce is False, then (N).
>>> triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2)
>>> input1 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> input2 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> input3 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> output = triplet_loss(input1, input2, input3)
>>> output.backward()
Example:
import torch.nn as nn
triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.2, p=2)
# 计算特征向量
anchor = model.forward(data[0])
positive = model.forward(data[1])
negative = model.forward(data[2])
# 计算三元组loss
loss = triplet_loss.forward(anchor, positive, negative)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN的更多相关文章
- 怎样在caffe中添加layer以及caffe中triplet loss layer的实现
关于triplet loss的原理.目标函数和梯度推导在上一篇博客中已经讲过了.详细见:triplet loss原理以及梯度推导.这篇博文主要是讲caffe下实现triplet loss.编程菜鸟.假 ...
- 论文笔记之: Person Re-Identification by Multi-Channel Parts-Based CNN with Improved Triplet Loss Function
Person Re-Identification by Multi-Channel Parts-Based CNN with Improved Triplet Loss Function CVPR 2 ...
- Paper Reading: In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification
In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification 2017-07-02 14:04:20 This blog comes ...
- Re-ID with Triplet Loss
一篇讲Person Re-ID的论文,与人脸识别(认证)有非常多相通的地方. 文章链接: <In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identi ...
- triplet loss 在深度学习中主要应用在什么地方?有什么明显的优势?
作者:罗浩.ZJU链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/62486208/answer/199117070来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转 ...
- Facenet Triplet Loss
Triplet Loss 在人脸识别中,Triplet loss被用来进行人脸嵌入的训练.如果你对triplet loss很陌生,可以看一下吴恩达关于这一块的课程.Triplet loss实现起来并不 ...
- triplet loss
因为待遇低,因为工作不开心,已经严重影响了自己的工作积极性和工作效率,这几天发觉这样对自己实在是一种损失,决定提高工作效率,减少工作时间. 说说最近做的tracking, multi-object t ...
- Triplet Loss(转)
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013082989/article/details/83537370 作用:用于对差异较小的类别进行区分
- Caffe的loss layer(转)
英文可查:地址 1.SoftmaxWithLoss 对一对多的分类任务计算多项逻辑斯蒂损失,并通过softmax传递预测值,来获得各类的概率分布.该层可以分解为SoftmaxLayer+Multino ...
随机推荐
- 使用windows远程桌面连接Windows Azure中的Ubuntu虚拟机
1.创建ubuntu虚拟机,这里同样不再赘述,创建过程和创建Windows虚拟机基本一样,只是登录可以选择密钥注入或者用户名密码(为了方便我选择了用户名密码认证),创建完成后,查看虚拟机详情中的端口信 ...
- php 封装分页查询类
<?php /** file: page.class.php 完美分页类 Page */ class Page { private $total; //数据表中总记录数 private $lis ...
- 本周实验的PSP0过程文档
项目计划总结: 日期/任务 听课 编写程序 阅读相关书籍 日总计 周一 110 60 ...
- Java基础毕向东day04
1. 数组 2.选择排序.冒泡排序.折半查找.
- Linux下进程的建立
Linux下进程的建立 我们都知道,进程就是正在执行的程序.而在Linux中,可以使用一个进程来创建另外一个进程.这样的话,Linux的进程的组织结构其实有点像Linux目录树,是个层次结构的,可以使 ...
- ASP.NET中把xml转为dataset与xml字符串转为dataset及dataset转为xml的代码
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/_zjl/archive/2011/04/08/2009087.html XmlDatasetConvert.csusing System;usin ...
- [TOP10]十大渗透测试演练系统
本文总结了目前网络上比较流行的渗透测试演练系统,这些系统里面都提供了一些实际的安全漏洞,排名不分先后,各位安全测试人员可以亲身实践如何利用这个漏洞,同时也可以学习到漏洞的相关知识. DVWA (Dam ...
- 玩转渗透神器Kali:Kali Linux作为主系统使用的正确姿势TIPS
Kali Linux 前身是著名渗透测试系统BackTrack ,是一个基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版,包含很多安全和取证方面的相关工具. 本文假设你在新装好的kali linux环境下… ...
- Why am I getting an error converting a Foo** → const Foo**?
Because converting Foo** → const Foo** would be invalid and dangerous. C++ allows the (safe) convers ...
- (spring-第6回【IoC基础篇】)BeanDefinition——实例化Bean之前的第一大利器。
上节讲了Bean实例化的内部机制,这里再复述一遍: ResourceLoader从系统中加载XML配置信息,并由Resource来表示. BeanDefinitionReader从Resource中读 ...
