Thrift 基础(C++ rpc )
一、thrift简介
thrift是Facebook开源的一套rpc框架,目前被许多公司使用
我理解的特点
- 使用IDL语言生成多语言的实现代码,程序员只需要实现自己的业务逻辑
- 支持序列化和反序列化操作,底层封装协议,传输模块
- 以同步rpc调用为主,使用libevent evhttp支持http形式的异步调用
- rpc服务端线程安全,客户端大多数非线程安全
- 相比protocol buffer效率差些,protocol buffer不支持rpc,需要自己实现rpc扩展,目前有grpc可以使用
由于thrift支持序列化和反序列化,并且支持rpc调用,其代码风格较好并且使用方便,对效率要求不算太高的业务,以及需要rpc的场景,可以选择thrift作为基础库
层次图:
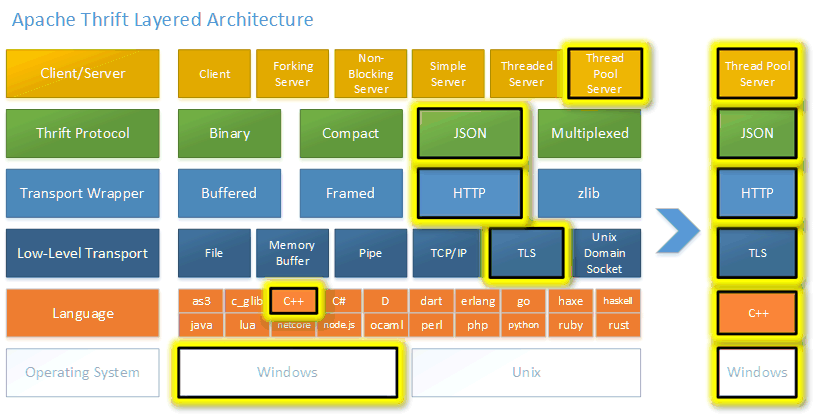
二、编译(thrift for c++ && centos7)
1、官网获取源码包 thrift-0.11.0.tar.gz 解压
tar zxvf thrift-0.11.0.tar.gz
2、安装依赖
yum -y install automake libtool flex bison pkgconfig gcc-c++ boost-devel libevent-devel zlib-devel python-devel ruby-devel openssl-devel
3、编译boost
使用boost_1_63_0.tar.gz
./bootstrap.sh
./b2
4、编译thrift
源码根目录运行
./configure && make
sudo make install
5、验证安装
thrift -version
显示 Thrift version 0.11.0
三、编写使用IDL编写.thrift文件
这里给出一个thrift的IDL基本语法列表,详细用法可以去官网查找
namespace cpp thrift.Test
//typedef 用法
typedef i32 MyInt32;
typedef string MyString;
typedef i32 UserId;
//struct 结构定义
struct TypedefTestStruct
{
1: MyInt32 field_MyInt32;
2: MyString field_MyString;
3: i32 field_Int32;
4: string filed_string;
}
//enum 枚举定义
enum Numberz
{
ONE = 1,
TWO,
THREE,
FIVE = 5,
SIX,
EIGHT = 8
}
//const 用法
const Numberz myNumberz = Numberz.ONE;
struct Bonk
{
1: string message,
2: i32 type
}
//类型嵌套
struct Xtruct
{
1: string string_thing,
2: i8 byte_thing,
3: i32 i32_thing,
4: i64 i64_thing
}
struct Xtruct2
{
1: i8 byte_thing,
2: Xtruct struct_thing,
3: i32 i32_thing
}
//支持map list set类型分别对应C++中的 map = stl::map list = stl::vector set = stl::set
typedef map<string, Bonk> MapType
struct Insanity
{
1: map<Numberz, UserId> userMap;
2: list<Xtruct> xtructs;
}
struct CrazyNesting
{
1: string string_field,
2: optional set<Insanity> set_field;
3: required list<map<set<i32>, map<i32,set<list<map<Insanity,string>>>>>> list_field,
4: binary binary_field
}
//union用法
union SomeUnion
{
1: map<NumberZ, UserId> map_thing,
2: string string_thing,
3: i32 i32_thing,
4: Xtruct3 xtruct_thing,
5: Insanity insanity_thing
}
//exception 异常
exception Xception
{
1: i32 errorCode,
2: string message
}
exception Xception2
{
1: i32 errorCode,
2: Xtruct struct_thing
}
// empty struct
struct EmptyStruct{}
struct OneField
{
1: EmptyStruct field;
}
//service 定义的一组rpc服务,一般是抽象出来的接口调用
service ThriftTest
{
void testVoid(),
string testString(1: string thing),
bool testBool(1: bool thing),
i8 testByte(1: i8 thing),
i32 testI32(1: i32 thing),
i64 testI64(1: i64 thing),
Xtruct testStruct(1: Xtruct thing),
Xtruct2 testNest(1: Xtruct2 thing),
map<string, string> testStringMap(1: map<string, string> thing),
set<i32> testSet(1: set<i32> thing),
list<i32> testList(1: list<i32> thing),
Numberz testEnum(1: Numberz thing),
map<i32, map<i32,i32>> testMapMap(1: i32 hello),
map<UserId, map<Numberz,Insanity>> testInsanity(1: Insanity argument),
Xtruct testMulti(1: i8 arg0, 2: i32 arg1, 3: i64 arg2, 4: map<i16, string> arg3, 5: Numberz arg4, 6: UserId arg5),
void testException(1: string arg) throws(1: Xception err1),
Xtruct testMultiException(1: string arg0, 2: string arg1) throws(1: Xception err1, 2: Xception2 err2),
oneway void testOneway(1:i32 secondsToSleep)
}
四、使用thrift文件生成C++代码
1、生成同步调用的C++代码
thrift -r --gen cpp xxx.thrift
2、生成异步调用的C++代码(同时同步调用的代码也被生成)
thrift --gen cpp:cob_style xxx.thrift
五、thrfit同步调用
1、StressTest.thrift文件
namespace cpp test.stress
service Service {
void echoVoid(),
i8 echoByte(1: i8 arg),
i32 echoI32(1: i32 arg),
i64 echoI64(1: i64 arg),
string echoString(1: string arg),
list<i8> echoList(1: list<i8> arg),
set<i8> echoSet(1: set<i8> arg),
map<i8, i8> echoMap(1: map<i8, i8> arg),
}
2、使用thrift -r --gen cpp StressTest.thrift 生成代码
gen-cpp目录有
StressTest_types.h StressTest_types.cpp StressTest_constants.h StressTest_constants.cpp Service.h Service.cpp Service_server.skeleton.cpp
生成
StressTest_types.h StressTest_constants.h 为相关类型定义文件
Service_server.skeleton为服务端需要的实现文件
3、代码实现
服务端:
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/PlatformThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/Thread.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/server/TNonblockingServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TNonblockingServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TNonblockingServerTransport.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include "Service.h"
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::test::stress;
class ServiceHandler : virtual public ServiceIf {
public:
ServiceHandler() {
}
void echoVoid() {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("echoVoid\n");
}
int8_t echoByte(const int8_t arg) {
printf("echoByte %c\n", arg);
return arg;
}
int32_t echoI32(const int32_t arg) {
printf("echoI32\n");
return arg;
}
int64_t echoI64(const int64_t arg) {
printf("echoI64\n");
return arg;
}
void echoString(std::string& _return, const std::string& arg) {
printf("echoString\n");
}
void echoList(std::vector<int8_t> & _return, const std::vector<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoList\n");
}
void echoSet(std::set<int8_t> & _return, const std::set<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoSet\n");
}
void echoMap(std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & _return, const std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoMap\n");
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
stdcxx::shared_ptr<ServiceHandler> handler(new ServiceHandler());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new ServiceProcessor(handler));
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TNonblockingServerTransport> serverTransport(new TNonblockingServerSocket(port));
stdcxx::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory> threadFactory = std::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory>(new PlatformThreadFactory());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<ThreadManager> threadManager = ThreadManager::newSimpleThreadManager(10);
threadManager->threadFactory(threadFactory);
threadManager->start();
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TNonblockingServer> server(new TNonblockingServer(processor, protocolFactory, serverTransport, threadManager));
server->serve();
return 0;
}
我们需要实现ServiceHandler继承ServiceIf的相关接口,ServiceHandler是负责相关rpc调用业务的功能实现,
thrift服务器模型基本模型有四种、SimpleServer ThreadedServer ThreadPoolServer NoBlockingServer
SimpleServer 简单的单线程模型
ThreadedServer 一个线程一个连接
ThreadPoolServer 线程池
NoBlockingServer 基于libevent的IO复用模型 libevent在linux平台是基于epoll的reactor模型
还有一个异步Server模型TEvhttpServer 基于libevent的evhttp
这里服务端使用了非阻塞epoll实现的thrift服务端模型
客户端:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include "Service.h"
using namespace ::test::stress;
using namespace apache::thrift;
using namespace apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace apache::thrift::transport;
int main()
{
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TSocket> socket(new TSocket("localhost", 9090));
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TFramedTransport(socket));
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
ServiceClient client(protocol);
transport->open();
std::cout << "client echoByte byte=" << client.echoByte('A') << std::endl;
std::cout << "send_echoByte('B')" << std::endl;
client.send_echoByte('B');
std::cout << "send_echoByte('C')" << std::endl;
client.send_echoByte('C');
std::cout << "recv_echoByte()" << client.recv_echoByte() << std::endl;
std::cout << "recv_echoByte()" << client.recv_echoByte() << std::endl;
transport->close();
return 0;
}
客户端使用则比较简单,Service.h定义了相关接口,ServiceClient则是rpc客户类
TTransport new TFramedTransport(socket) 这里创建基于socket的传输层
TProtocol 协议层,序列化后的数据存储方式,这里以TBinaryProtocol 二进制存储
六、thrift异步调用
1、thrift文件同同步调用一致
2、使用thrift --gen cpp:cob_style StressTest.thrift 生成代码
StressTest_types.h StressTest_types.cpp StressTest_constants.h StressTest_constants.cpp Service.h Service.cpp Service_server.skeleton.cpp Service_async_server.skeleton.cpp
Service_server.skeleton.cpp 同步代码用不到
Service_async_server.skeleton.cpp则为http的异步实现
服务端:
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/async/TAsyncProtocolProcessor.h>
#include <thrift/async/TEvhttpServer.h>
#include <event.h>
#include <evhttp.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "Service.h"
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::async;
using namespace ::test::stress;
class ServiceHandler : virtual public ServiceIf {
public:
ServiceHandler() {
}
void echoVoid() {
printf("echoVoid\n");
}
int8_t echoByte(const int8_t arg) {
printf("echoByte %c\n", arg);
return arg;
}
int32_t echoI32(const int32_t arg) {
printf("echoI32\n");
return arg;
}
int64_t echoI64(const int64_t arg) {
printf("echoI64\n");
return arg;
}
void echoString(std::string& _return, const std::string& arg) {
printf("echoString %s\n", arg.c_str());
_return = arg;
}
void echoList(std::vector<int8_t> & _return, const std::vector<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoList\n");
}
void echoSet(std::set<int8_t> & _return, const std::set<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoSet\n");
}
void echoMap(std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & _return, const std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoMap\n");
}
};
class ServiceAsyncHandler : public ServiceCobSvIf {
public:
ServiceAsyncHandler() {
syncHandler_ = std::auto_ptr<ServiceHandler>(new ServiceHandler);
// Your initialization goes here
}
virtual ~ServiceAsyncHandler(){}
void echoVoid(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void()> cob) {
syncHandler_->echoVoid();
return cob();
}
void echoByte(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(int8_t const& _return)> cob, const int8_t arg) {
int8_t _return = 0;
_return = syncHandler_->echoByte(arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoI32(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(int32_t const& _return)> cob, const int32_t arg) {
int32_t _return = 0;
_return = syncHandler_->echoI32(arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoI64(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(int64_t const& _return)> cob, const int64_t arg) {
int64_t _return = 0;
_return = syncHandler_->echoI64(arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoString(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::string const& _return)> cob, const std::string& arg) {
std::string _return;
syncHandler_->echoString(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoList(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::vector<int8_t> const& _return)> cob, const std::vector<int8_t> & arg) {
std::vector<int8_t> _return;
syncHandler_->echoList(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoSet(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::set<int8_t> const& _return)> cob, const std::set<int8_t> & arg) {
std::set<int8_t> _return;
syncHandler_->echoSet(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoMap(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::map<int8_t, int8_t> const& _return)> cob, const std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & arg) {
std::map<int8_t, int8_t> _return;
syncHandler_->echoMap(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
protected:
std::auto_ptr<ServiceHandler> syncHandler_;
};
int main()
{
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<ServiceAsyncProcessor> asynProcessor(new ServiceAsyncProcessor(
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<ServiceCobSvIf>(new ServiceAsyncHandler())));
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncProtocolProcessor> asynProtocolProcessor(new TAsyncProtocolProcessor(asynProcessor,
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory>(new TBinaryProtocolFactory())));
TEvhttpServer server(asynProtocolProcessor, 9999);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
这里实现ServiceHandler的相关业务接口即可实现rpc服务端的相关功能
客户端:
#include "Service.h"
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/PlatformThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/Thread.h>
#include <thrift/async/TAsyncChannel.h>
#include <thrift/async/TEvhttpClientChannel.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TProtocol.h>
#include <event.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::async;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::concurrency;
using namespace ::test::stress;
class MyClient : public ServiceCobClient
{
public:
MyClient(stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncChannel> channel, TProtocolFactory* protocolFactory)
: ServiceCobClient(channel, protocolFactory)
{
}
virtual ~MyClient(){}
virtual void completed__(bool success)
{
if (success)
{
std::cout << "completed" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "completed failed" << std::endl;
}
}
void my_send_byte()
{
std::cout << "begin my_send_byte" << std::endl;
stdcxx::function<void(ServiceCobClient*)> cob = stdcxx::bind(&MyClient::recv_byte_callback, this, stdcxx::placeholders::_1);
echoByte(cob, 'A');
std::cout << "end my_send_byte" << std::endl;
}
void my_send_string()
{
std::cout << "begin my_send_string" << std::endl;
stdcxx::function<void(ServiceCobClient*)> cob = stdcxx::bind(&MyClient::recv_string_callback, this, stdcxx::placeholders::_1);
echoString(cob, "test asynclient");
std::cout << "end my_send_string" << std::endl;
}
void recv_byte_callback(ServiceCobClient* client)
{
std::cout << "recv_byte_callback" << std::endl;
_res_byte = recv_echoByte();
std::cout << "_res_byte =" << _res_byte << std::endl;
}
void recv_string_callback(ServiceCobClient* client)
{
std::cout << "recv_string_callback" << std::endl;
recv_echoString(_res_string);
std::cout << "_res_string=" << _res_string << std::endl;
}
private:
char _res_byte;
std::string _res_string;
};
class ClientThread : public Runnable
{
public:
ClientThread(event_base* base, std::string & host, int port)
: _base(base), _host(host), _port(port)
{
}
virtual ~ClientThread(){}
virtual void run()
{
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncChannel> channel1(new TEvhttpClientChannel(_host, "/", _host.c_str(), _port, _base));
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncChannel> channel2(new TEvhttpClientChannel(_host, "/", _host.c_str(), _port, _base));
MyClient client1(channel1, new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
MyClient client2(channel2, new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
client1.my_send_byte();
client1.my_send_string();
client2.my_send_byte();
client2.my_send_string();
while (1)
{
client1.my_send_byte();
sleep(1);
}
}
protected:
private:
event_base* _base;
std::string _host;
int _port;
};
int main()
{
std::string host = "192.168.119.129";
int port = 9999;
event_base* base = event_base_new();
stdcxx::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory> threadFactory = std::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory>(new PlatformThreadFactory());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<ThreadManager> threadManager = ThreadManager::newSimpleThreadManager(10);
threadManager->threadFactory(threadFactory);
threadManager->start();
stdcxx::shared_ptr<Thread> thread = threadFactory->newThread(std::shared_ptr<ClientThread>(new ClientThread(base, host, port)));
thread->start();
event_base_dispatch(base);
event_base_free(base);
return 0;
}
客户端则实现了MyClient,MyClient继承公共的rpc服务接口,提供了异步回调的recv_byte_callback,recv_string_callback函数, ClientThread的线程函数的实现则对MyClient异步客户端进了测试
七、简单总结
通过这两天的学习,简单总结一下这个库
1、thrift的C++代码实现很漂亮,很规范,适合学习阅读
2、thrift可以满足很多基本的rpc调用场景
3、本文只是简单写了thrift的用法,想深入了解这个库的,其内部实现还是需要花时间好好研究
作者 [@karllen][3]
2018 年 09月 15日
QQ群: 347769318
Thrift 基础(C++ rpc )的更多相关文章
- thrift基础知识
1. 架构图 Thrift 包含一个完整的堆栈结构用于构建客户端和服务器端.下图描绘了 Thrift 的整体架构. 图 1. 架构图 如图所示,图中黄色部分是用户实现的业务逻辑,褐色部分是根据 Thr ...
- Thrift 个人实战--RPC服务的发布订阅实现(基于Zookeeper服务)
前言: Thrift作为Facebook开源的RPC框架, 通过IDL中间语言, 并借助代码生成引擎生成各种主流语言的rpc框架服务端/客户端代码. 不过Thrift的实现, 简单使用离实际生产环境还 ...
- 手把手教你基于Netty实现一个基础的RPC框架(通俗易懂)
阅读这篇文章之前,建议先阅读和这篇文章关联的内容. [1]详细剖析分布式微服务架构下网络通信的底层实现原理(图解) [2][年薪60W的技巧]工作了5年,你真的理解Netty以及为什么要用吗?(深度干 ...
- Thrift入门初探(2)--thrift基础知识详解
昨天总结了thrift的安装和入门实例,Thrift入门初探--thrift安装及java入门实例,今天开始总结一下thrift的相关基础知识. Thrift使用一种中间语言IDL,来进行接口的定义, ...
- 基于ZooKeeper和Thrift构建动态RPC调用
一.基本功能 实现服务端向ZooKeeper集群注册自己提供的服务,并且把自己的IP地址和服务端口创建到具体的服务目录下.客户端向ZooKeeper集群监听自己关注的RPC服务(例如:sayHello ...
- 【RPC】Thrift ICE 等 RPC 框架相关资料
RPC框架-Thrift-ICE Apache Thrift - Documentation Apache Thrift - Index of tutorial/ Apache Thrift - Ab ...
- J2EE分布式服务基础之RPC
一.RPC介绍 什么是RPC 远程过程调用(RPC)是一个协议,程序可以使用这个协议请求网络中另一台计算机上某程序的服务而不需知道网络细节. RPC模型 C/S模式 基于传输层协议 (例如 TCP/I ...
- Thrift 基础教程(一)安装篇
1.Thrift简单介绍 Thrift是一款由Fackbook开发的可伸缩.跨语言的服务开发框架,该框架已经开源而且增加的Apache项目.Thrift主要功能是:通过自己定义的Interface D ...
- Thrift使用入门---RPC服务
https://blog.csdn.net/zkp_java/article/details/81879577 RPC基本原理 大部分的RPC框架都遵循如下三个开发步骤: RPC通信过程如下图所示 通 ...
随机推荐
- UVa 11427 Expect the Expected (数学期望 + 概率DP)
题意:某个人每天晚上都玩游戏,如果第一次就䊨了就高兴的去睡觉了,否则就继续直到赢的局数的比例严格大于 p,并且他每局获胜的概率也是 p,但是你最玩 n 局,但是如果比例一直超不过 p 的话,你将不高兴 ...
- Mysql分析优化查询的方式
一:查询语句分析 1.通过create index idx_colunmsName on tableName(columns)为某个表的某些字段创建索引,注意主键和唯一键都会自动创建索引: 如为表st ...
- DDR中的一些知识点说明(ODT,ZQ校准,OCT,TDQS)
ODT ( On-DieTermination ,片内终结)ODT 也是 DDR2 相对于 DDR1 的关键技术突破,所谓的终结(端接),就是让信号被电路的终端吸 收掉,而不会在电路上形成反射, 造成 ...
- C#-ado.net学习笔记-会有更新
ado.net 通用类对象.在本地内存暂存数据 托管类对象.让本地通用类对象连接数据库,让本地通用类对象和数据库同步 连接数据库 new connection(connectstring) comma ...
- (记忆化搜索 )The Triangle--hdu --1163
http://poj.org/problem?id=1163 Description 73 88 1 02 7 4 44 5 2 6 5 (Figure 1) Figure 1 shows a ...
- CentOS 5.5 防火墙开启、关闭以及开放指定端口
之前有讲过公司新买的服务器使用的是CentOS5.5, 部署好Tomcat之后却发现输入114.80.*.*:8080(即ip:8080)却无法显示Tomcat默认的首页. 因为以前部署在Win Se ...
- android上的i-jetty (1)环境搭建
介绍下如果把android设备作为一个web服务器使用, 编译i-jetty 1. 将源码download下来,http://code.google.com/p/i-jetty/downloads/l ...
- ZUFE2483 DO IT YOURSELF 2017-05-31 14:41 40人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
2483: DO IT YOURSELF 时间限制: 2 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB 提交: 8 解决: 3 [提交][状态][讨论版] 题目描述 有四个字符串S,T,tmp,ans,一开始 ...
- OC语言-runtime
参考博客 IOS高级开发-Runtime(一) http://blog.csdn.net/lizhongfu2013/article/details/9496705 apple官方参考 Object- ...
- Dinic算法——重述
赛前赛后算是第三次接触Dinic算法了,每一次接触都能有种很好的感觉,直男的我没法描述~~ 已经比较懂得DInic的基本算法思想了 首先是bfs进行进行分层处理,然后dfs寻找分层后的最大流, ...
