java小知识点简单回顾
1.java的数据类型分为两种:简单类型和引用类型(数组、类以及接口)。注意,java没有指针的说法,只有引用。简单类型的变量被声明时,存储空间也同时被分配;而引用类型声明变量(对象)时,仅仅为其分配了一个引用类型的内存,类似于c++里面的指针类型。要使用new来为此对象分配实际需要的内存,即实例化。
Eg:
(1):数组:int a[][];a=new int[1][2];一般常常把int a[][]写为int[][] a.
需要注意的是:数组还可以直接用数据列表来初始化,省去new操作:int[] s={1,2}等价于int[] s=new int[2];s[0]=1;s[1]=2.
另外,数组(不论为全局变量还是局部变量),一旦实例化,就会自动初始化为0.而c++里面局部变量数组里不会初始化为0,而为随机值(全局变量数组自动初始化为0)。
每一个数组都有一个length属性,eg:int a[][]=new int[4][5]; a.length=4; a[0].length=5; a[1].legnth=5…
(2):类:class a; a a1;a1=new a();然后才可以操作其中的成员。
2.println()比print多带了换行功能。
3.java里null为小写,而c++里为大写。
4.java里char为2字节,没有unsigned修饰符,所有数据都是有符号数。
5.java和c++里,八进制都是数字前加0,十六进制数前面加0x.
Eg:0453,0x234ac.
6.java里布尔型为boolean.且不允许其他类型与boolean型转换。而c++里为bool型,可以与整型转换。
7.java里,小范围数据转换为大范围数据(比如整型转换为浮点型),可以自动转换;而大范围转换为小范围,则必须强制转换,因为不安全。
8.final修饰符修饰变量,则当做常量来使用。修饰方法,使其不能被子类覆盖;修饰类,使其不能被继承。
9.java里,类的成员变量定义时,允许变量名与方法(函数)名相同,可以人为在类中直接对成员变量初始化,当然JVM会自动为所有成员变量初始化,简单类型赋值为0,字符类型赋值为’\0000’,布尔赋值为false,引用类型赋值为null。而c++不允许成员变量与方法名相同,不能在类中初始化,只能在对象创建完后通过构造函数或其他方式初始化。Java和c++的对象不一个东西。
10.java里,引用类型其实本质是对数据那块内存的引用。在方法传参时,简单类型的形参就是一个数据副本,不影响实参;而引用类型的形参是数据内存空间的引用的副本,即地址名副本,会影响实参。举个例子:java里的方法形参如果是类类型,产生一个引用副本,指向原来的类内存,对其操作会影响实参;而c++则不会,产生的是一个类副本,位于堆栈里新开辟的一块内存处。
11.方法过载:多个成员方法同名,区别在于他们的参数数量或类型不同。
12.static:java里,声明static成员变量和c++一样,都在类内,只是c++要求在类外定义,而java不是,是在方法中定义,不论是static方法还是一般方法,也可以通过类名访问进行赋值。Static方法都可以访问static成员变量,对于一般成员变量,需要通过在方法里新建一个对象来访问。
13.java没有全局变量。类中的方法只能在类中定义,不能放在类外,而且其声明和定义不能分开。
14.java的JVM会自动回收不再被对象引用的实例存储空间。
15.this:c++里this为自身的一个指针,用操作符->;而java里为自身的一个引用,用操作符.。
16.Object类存放于java.lang包中,是java语言里所有类的直接或间接超类。
17.super:为当前对象的超类的引用。
使用有三种情况:
(1)访问被隐藏的超类成员变量。Eg:super.var;
(2)调用超类中被覆盖的方法。
(3)调用超类中的构造方法。在子类构造函数的函数体中,必须调用super([paramList])。
18.java里没有虚函数,对于成员方法的调用都是在运行中动态确定,即可以用对不同子类的引用实行多态。
19.abstract:可以用来修饰类和方法,形成抽象类和抽象方法。含有抽象方法的类一定是抽象类,抽象类也可以没有抽象方法。抽象类可以产生对象,但是不能实例化,其对象可以被非抽象子类实例所引用。抽象方法只需声明,不需实现,即abstract修饰符+方法声明。有三种方法不能作为抽象方法:构造方法、类方法以及私有方法。
20.Object类是所有类的超类,其方法适用于所有类。
它提供的常用方法:
(1).clone()方法:生成一个类的实例的拷贝,返回这个拷贝的实例。
Eg:point p=new point(20,30); point pcopy=p.clone();
P与pcopy引用的是两个不同的实例,但其内容完全相同。
(2).equals()方法:比较两个对象类是否相同,返回true(相同)或false(不相同)。注意这里比较的是两个对象的具体内容是否相同,比如类成员、方法等等。
Eg:a和b都是point类的实例,a.equals(b).
注意:如果直接比较a==b的话,比较的是是否引用同一个实例,并非是其内容。
(3).getClass()方法:返回Class类的一个对象,这个对象的内容是调用者的类的信息,包括类名、接口等等。通过调用这个方法,可以获得自己本身的类的全面可用信息。
Eg:point p = new point (20 ,30); System .out .println (“对象p的类名是:”+p .getClass().getName());
其中,getName()是类Class的成员方法,返回其对象保存的类名。上例中返回的是“point”。
(4).toString()方法:以字符串形式返回当前对象的有关信息。
Eg:Integer a=new Integer(10); System .out .println(a.toString()); 输出的是“10”。
21.访问控制权限表
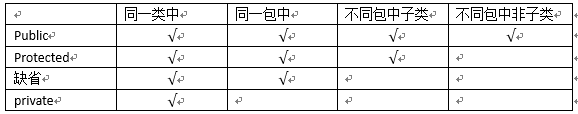
22.接口是方法声明(与抽象方法唯一的区别是没有abstract修饰)和常量的集合。Java没有类多继承,但接口可以多继承。接口与类类似,也有相同的访问权限,继承时用extends,超接口用逗号隔开。接口里的方法都具有public、abstract属性,成员变量都具有public、final和static属性,修饰符省略不写。
Eg:interface College{
Int MAX_NUM=100;
Void add(Object oo);
Int current();
}
接口实现的关键字是implements,一个非抽象类可以实现多个接口,用逗号分隔,可以访问接口中所有成员变量,而且必须实现接口中所有成员方法,方法实现时必须加上public修饰符。
Eg:class fifo implements College{
Public void add(Object oo){
}
Public int current(){
}
}
23.接口可以作为一个引用类型来使用。可以用接口类型的变量来引用所有实现该接口的类实例,动态访问这些类实现的方法。
Eg:College cv=new fifo(); Object obj=new Object(); cv.add(obj);
24.java源程序构成:
(1)最多一条package语句,放在最前头;
(2)可以有任意条import语句;
(3)如果没有类时至少要有一个接口的定义,接口可以任意个。
(4)在Application编程中,包含main()方法的类声明为public。
(5)在一个源程序中,只能有一个类被声明为public。
(6)用public声明的类名作为源程序的文件名且以.java作为后缀。如果源程序没有类定义,则取接口名作为文件名。
(7)在一个源程序中定义的所有类和接口,在成功编译后都将生成一个对应的字节码文件,这些文件的名是类名或接口名,并以.class作为扩展名。
25.多线程简单小结:
(1)线程由.start()启动,从run()方法开始执行。Run()相当于单线程程序里main()。
(2)两种创建多线程的方法:
<1>生成Thread类:
生成Thread类的子类;
在子类中覆盖run()方法;
生成子类的对象,并且调用start()方法启动新线程。
eg:
/*
* To change this template, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package pkg1_11_1; /**
*
* @author jiu
*/
public class Main {
public Main(){
FirstThread first = new FirstThread();
SecondThread second = new SecondThread();
first.start();
second.start();
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main();
}
}
class FirstThread extends Thread {
public void run(){
try{
System.out.println("First thread starts running.");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("First"+i);
sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("First thread finishes running.");
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
class SecondThread extends Thread {
public void run(){
try{
System.out.println("\tSecond thread starts running.");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("\tSecond"+i);
sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("\tSecond thread finishes running.");
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
结果截图:

<2>生成一个类,声明实现Runnable接口:
程序中某个类声明实现Runnable接口,并且在这个类中实现run()方法;
生成这个类的对象;
用Thread(Runnable target)构造器生成Thread对象,其中,target是声明实现了Runnable接口的对象,并且用start()方法启动线程。
eg:
/*
* To change this template, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package pkg1_11_1; /**
*
* @author jiu
*/
public class Main {
public Main(){
FirstThread first = new FirstThread();
SecondThread second = new SecondThread();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(first);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(second);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main();
}
}
class FirstThread implements Runnable {
public void run(){
try{
System.out.println("First thread starts running.");
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.println("First"+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("First thread finishes running.");
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
class SecondThread implements Runnable {
public void run(){
try{
System.out.println("\tSecond thread starts running.");
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.println("\tSecond"+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("\tSecond thread finishes running.");
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
结果截图:

(3)同步锁:使一个方法或代码段不能同时被两个及以上的线程访问,用synchronized修饰。修饰方法时只需在方法前加上修饰符,eg:synchronized void dep(){};修饰代码段时,必须把代码段括起来,并且其前加上synchronized(对象名),eg:synchronized(this){…}。
(4)wait()方法可以使线程处于阻塞状态,等待其他的线程用notify()唤醒;notify()或notifyAll()方法唤醒其他一个或所有线程。
eg:
/*
* To change this template, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package pkg1_11_1;
import java.lang.Runnable;
import java.lang.Thread;
/**
*
* @author jiu
*/
/**
*
本例子实现两个线程,每个线程交换输出1到100的数字。
*/
public class Main implements Runnable {
public Main(){
TestThread test1 = new TestThread(this,"1");
TestThread test2 = new TestThread(this,"2");
test2.start();
test1.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main();
}
public void run() {
TestThread t = (TestThread)Thread.currentThread();
try{
if(!t.getName().equalsIgnoreCase("1")){
synchronized(this) {
wait();
}
}
while(true) {
System.out.println("@time in thread"+t.getName()+"="+t.increaseTime());
if(t.getTime()%10==0) {
synchronized(this) {
System.out.println("**********************************************");
notify();
if(t.getTime()==100) break;
wait();
}
}
}
}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
class TestThread extends Thread{
private int time = 0;
public TestThread(Runnable r,String name) {
super(r,name);
}
public int getTime() {
return time;
}
public int increaseTime() {
return ++time;
}
}
结果:
run:
@time in thread1=1
@time in thread1=2
@time in thread1=3
@time in thread1=4
@time in thread1=5
@time in thread1=6
@time in thread1=7
@time in thread1=8
@time in thread1=9
@time in thread1=10
**********************************************
@time in thread2=1
@time in thread2=2
@time in thread2=3
@time in thread2=4
@time in thread2=5
@time in thread2=6
@time in thread2=7
@time in thread2=8
@time in thread2=9
@time in thread2=10
**********************************************
@time in thread1=11
@time in thread1=12
@time in thread1=13
@time in thread1=14
@time in thread1=15
@time in thread1=16
@time in thread1=17
@time in thread1=18
@time in thread1=19
@time in thread1=20
**********************************************
。。。
。。。
**********************************************
@time in thread1=91
@time in thread1=92
@time in thread1=93
@time in thread1=94
@time in thread1=95
@time in thread1=96
@time in thread1=97
@time in thread1=98
@time in thread1=99
@time in thread1=100
**********************************************
@time in thread2=91
@time in thread2=92
@time in thread2=93
@time in thread2=94
@time in thread2=95
@time in thread2=96
@time in thread2=97
@time in thread2=98
@time in thread2=99
@time in thread2=100
**********************************************
java小知识点简单回顾的更多相关文章
- java编程IO简单回顾和学习
java编程IO操作必不可少的,很久不玩IO,回顾一下,写了几个小程序,记录一下,方便查阅和学习. 1.给出一个整数数组,将其写入一个文件,再从文件中读出,并按整数大小逆序打印. package co ...
- nginx知识点简单回顾
html { font-family: sans-serif } body { margin: 0 } article,aside,details,figcaption,figure,footer,h ...
- java 小知识点
1.转Java中Vector和ArrayList的区别 首先看这两类都实现List接口,而List接口一共有三个实现类,分别是ArrayList.Vector和LinkedList.List用于存 ...
- JAVA小知识点-Finally和Return的执行关系
如果Try和Catch中存在return语句的时候Finally内的语句是否会执行,执行的时候对结果又有什么影响呢?我写了个例子来试验这个问题: public static Map<String ...
- java小知识点汇总
1.ConcurrentHashMap使用segment来分段和管理锁,segment继承自ReentrantLock,因此ConcurrentHashMap使用ReentrantLock来保证线程安 ...
- Java小知识点总结
目录 配置 数据库配置文件 基础知识 Switch i++和++i 快捷打代码 输入数据 代码折叠 super关键字 instanceof 防止类型强制转换带来的错误 继承 第一个Java程序 Jav ...
- java小知识点 2015/10/6
java中length,length(),size()区别: 1 java中的length属性是针对数组说的,比如说你声明了一个数组,想知道这个数组的长度 2 java中的length()方法是针对字 ...
- java小知识点
1 判断是否为win系统 int version=System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase().indexOf("windows ...
- Java小知识点学习--------数组和位运算小知识点
位运算符: >>>无符号右移运算符,无符号右移的规则和右移的规则同样,仅仅是在填充时,无论原来是正数还是负数都用0来补充. 数组: arr1=arr2; 此时两个数组变量都会同一时 ...
随机推荐
- [UE4]Character,飞行模式。
Character 是pawn的子类,可以行走.跳跃.游泳.飞行的Pawn.
- Python中__init__和__new__的区别详解
__init__ 方法是什么? 使用Python写过面向对象的代码的同学,可能对 __init__ 方法已经非常熟悉了,__init__ 方法通常用在初始化一个类实例的时候.例如: # -*- cod ...
- 【Linux_Unix系统编程】chapter6 进程
chapter6 进程 重点关注进程虚拟内存的布局及内容.6.1 进程和程序 进程(process)是一个可执行程序(program)的实例. 程序是包含了一系列信息的文件,这些信息描述了如何在运行时 ...
- 本地管理表空间和字典管理表空间的特点,ASSM有什么特点
字典管理表空间(Dictionary-Managed Tablespace简称DMT),8i以前包括以后都还可以使用的一种表空间管理模式,通过数据字典管理表空间的空间使用. Oracle使用两个字典来 ...
- MySQL 创建数据库的两种方法
使用 mysqladmin 创建数据库 使用普通用户,你可能需要特定的权限来创建或者删除 MySQL 数据库. 所以我们这边使用root用户登录,root用户拥有最高权限,可以使用 mysql mys ...
- MAN 手册各章节功能介绍及快捷键键位整理
前言 Man 手册页(Manua pages ,缩写man page) 是在linux操作系统在线软件文档的一种普遍形式.内容包括计算机程序库和系统调用等命令的帮助手册. 手册页是用troff排版 ...
- php基础和数据库
服务器和客户端 客户端 程序: 通过浏览器直接运行 服务器 程序: 通过安装某种服务器软件 程序才可以运行 apache php文件 tom ...
- django框架预备知识
内容: 1.web预备知识 2.django介绍 3.web框架的本质及分类 4.django安装与基本设置 1.web预备知识 HTTP协议:https://www.cnblogs.com/wyb6 ...
- nginx支持pathinfo的方法,亲测有效的
修改配置文件,修改特点域名的配置文件 location ~ \.php { #去掉$ root H:/PHPServer/WWW; fastcgi_pass ; fastcgi_index index ...
- ajax调用json
//var data_str='({"detail":[{"html":"科技科技科技有限公司"},{"html":&q ...
