Android 系统启动过程详解
android 使用 linux 内核,一般运行在 ARM 体系架构上,android 设备启动的过程,应用层之下基本等同于linux, 从应用层第一个程序init开始有所区别,下面开始介绍。
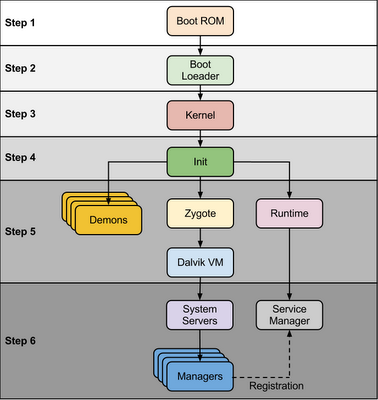
step1, boot rom 主要作用是加载 boot loader 进入内存并执行,boot rom 一般固化在芯片上,设备启动加电自检后从固定的地址开始执行
step2,boot loader 分2步执行,boot rom只加载了第一部分bootloader代码进入内存,这部分代码随即加载第二部分bootloader代码,第二部分是核心,它完成了必要的环境准备后,开始加载内核.
Bootloader is small program which runs before Android operating system running. Bootloader is first program to run so It is specific for board and processor. Device manufacturer either use popular bootloaders like redboot,uboot, qi bootloader or they develop own bootloaders, It’s not part of Android Operating System. bootloader is the place where OEMs and Carriers put there locks and restrictions. Bootloader perform execution in two stages, first stage It to detect external RAM and load program which helps in second stage, In second stage bootloader setup network, memory, etc. which requires to run kernel, bootloader is able to provide configuration parameters or inputs to the kernel for specific purpose. Android bootloader can be found at <Android Source>\bootable\bootloader\legacy\usbloaderlegacy loader contain two important files that need to address here. 1. init.s - Initializes stacks, zeros the BSS segments, call _main() in main.c
2. main.c - Initializes hardware (clocks, board, keypad, console), creates Linux tags Refer this link to know more about Android bootloader :
https://motorola-global-portal.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/86208/~/bootloader-frequently-asked-questions
step3, android 内核启动过程与标准linux类似,完成内存子系统、保护模式、任务调度系统、驱动子系统、设备系统、文件系统等的初始化,最后运行第一个应用程序init. 与标准系统有所不同的是,android的内核增加了部分驱动及补丁,
What is the difference between the linux and android kernels?, here's a list of changes/addons that the Android Project made to the Linux kernel:
Binder: It is an Android specific interprocess communication mechanism and remote method invocation system.
ashmem: "Android Shared Memory". It is a new shared memory allocator, similar to POSIX SHM but with a different behavior and sporting a simpler file-based API.
pmem: "Process memory allocator": It is used to manage large (-+ MB) physically contigous regions of memory shared between userspace and kernel drivers.
logger: This is the kernel support for the logcat command.
wakelocks: It is used for power management files. It holds the machine awake on a per-event basis until wakelock is released.
oom handling: It kills processes as available memory becomes low.
alarm manager: It lets user space tell the kernel when it would like to wake up.
RAM_CONSOLE: Allows to save kernel printk messages to a buffer in RAM, so that after a kernel panic they can be viewed in the next kernel invocation.
USB gadget driver for ADB
yaffs2 flash filesystem
step4, init 进程,从这一步开始,android的启动跟其他linux发行版(如redhat,gentoo,ubuntu)就不一样了,init程序的实现、init.rc文件的格式,都是不一样的。init 进程主要功能是挂载磁盘分区,然后根据init.rc的配置解析并执行
Init is the very first process, we can say it is a root process, or the grandfather of all processes. The init process has two responsibilities.
- Mounts directories like /sys , /dev or /proc
- Runs init.rc script
- The init process can be found at /init :: <android source>/system/core/init
- Init.rc file can be found at :: <android source>/system/core/rootdir/
Android has specific format and rules for init.rc files. More information about this rules can be found in: What is inside the init.rc and what is it used for.
At this stage, you can finally see the Android logo in your screen.
init.rc主要配置项如下:
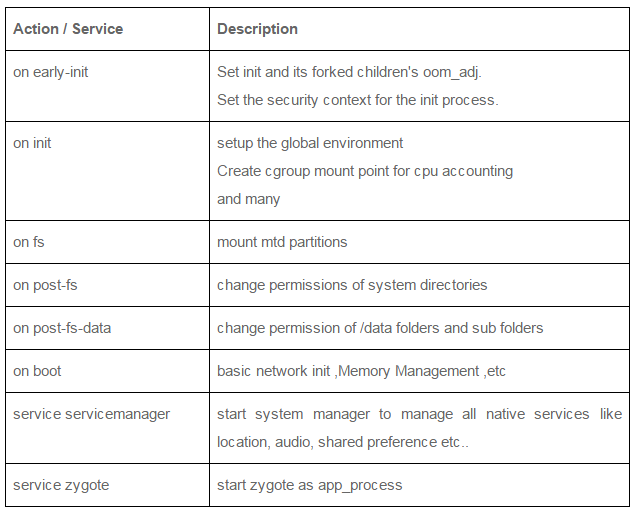
/system/bin/logd/sbin/adbd/system/bin/usbd/system/bin/debuggerd/system/bin/rild/system/bin/runtime/system/bin/dbus-daemonsystem_server- zygote
这些进程都是 init 进程 fork+execve 出来的子进程
After the above steps are completed, Zygote launches the system services. The Zygote forks a new process to launch the system services.
Core services:
Starting power manager
Creating the Activity Manager
Starting telephony registry
Starting package manager
Set activity manager service as system process
Starting context manager
Starting system contact providers
Starting battery service
Starting alarm manager
Starting sensor service
Starting window manager
Starting Bluetooth service
Starting mount service Other services: Starting status bar service
Starting hardware service
Starting NetStat service
Starting connectivity service
Starting Notification Manager
Starting DeviceStorageMonitor service
Starting Location Manager
Starting Search Service
Starting Clipboard Service
Starting checkin service
Starting Wallpaper service
Starting Audio Service
Starting HeadsetObserver
Starting AdbSettingsObserver Now we have finally completed the booting process (system service are up and running in memory).
Android 系统启动过程详解的更多相关文章
- Android 核心分析 之八Android 启动过程详解
Android 启动过程详解 Android从Linux系统启动有4个步骤: (1) init进程启动 (2) Native服务启动 (3) System Server,Android服务启动 (4) ...
- Android编译过程详解(一)
Android编译过程详解(一) 注:本文转载自Android编译过程详解(一):http://www.cnblogs.com/mr-raptor/archive/2012/06/07/2540359 ...
- linux内核剖析(零)linux系统启动过程详解-开机加电后发生了什么
本文参考了如下文章 深入理解linux启动过程 mbr (主引导记录(Master Boot Record)) 电脑从开机加电到操作系统main函数之前执行的过程 详解linux系统的启动过程及系统初 ...
- Cocos2dx-3.0版本 从开发环境搭建(Win32)到项目移植Android平台过程详解
作为重量级的跨平台开发的游戏引擎,Cocos2d-x在现今的手游开发领域占有重要地位.那么问题来了,作为Cocos2dx的学习者,它的可移植特性我们就需要掌握,要不然总觉得少一门技能.然而这个时候各种 ...
- Ubuntu系统启动过程详解
作者:杨硕,华清远见嵌入式学院讲师. 一. Ubuntu的启动流程 ubuntu的启动流程和我们熟知的RedHat的启动方式有所区别. RedHat的启动过程如下图: 这是我们熟知的linux启动流程 ...
- Android编译过程详解(三)
前面两节讲解了自定义Android编译项和创建Product产品配置文件,除了编译和定义产品相关环境变量外,还需要定义Board相关环境变量. 1. build/core/config.mk 109 ...
- Android编译过程详解(二)
通过上篇文章,我们分析了编译android时source build/envsetup.sh和lunch命令,在执行完上述两个命令后, 我们就可以进行编译android了. 1. make 执行ma ...
- Linux系统启动过程详解
启动第一步--加载BIOS当你打开计算机电源,计算机会首先加载BIOS信息,BIOS信息是如此的重要,以至于计算机必须在最开始就找到它.这是因为BIOS中包含了CPU的相关信息.设备启动顺序信息.硬盘 ...
- Cordova 打包 Android release app 过程详解
Cordova 打包 Android release app 过程详解 时间 -- :: SegmentFault 原文 https://segmentfault.com/a/119000000517 ...
随机推荐
- 笔记-python lib-pymongo
笔记-python lib-pymongo 1. 开始 pymongo是python版的连接库,最新版为3.7.2. 文档地址:https://pypi.org/project/pymong ...
- python re模块实现计算器
def mul_div(exp): #计算乘除 while True: ret = re.search('[\d\.]+[\*\/]-?[\d\.]+', exp) if ret: atom_exp ...
- 我教你怎么玩转git
我教你怎么玩转git 1.想要练习解决冲突? 很好办.创建本地分支,a,b, a上面,这样改.b上面那样改. 然后你就解决冲突就可以了. 可以merge 或者cheerypick 2.想要玩一个不要历 ...
- windows下进程间通信(转)
摘 要 随着人们对应用程序的要求越来越高,单进程应用在许多场合已不能满足人们的要求.编写多进程/多线程程序成为现代程序设计的一个重要特点,在多进程程序设计中,进程间的通信是不可避免的.Microsof ...
- Maven学习 (三) 使用m2eclipse创建web项目
1.首先确认你的eclipse已经安装好m2eclipse的环境,可以参照上两篇Maven学习内容 2.新建一个maven的项目 3.下一步默认配置,使用默认的工作空间,或者你可以自己选择其他的空间 ...
- equals和toString
Object的equals方法默认比较地址值.所以当需要比较两个对象的内容时需要重写equals方法.
- c语言字符串内存分配小记
一.疑问 有这样一道题: #include "stdio.h" int main() { ]; ]; scanf("%s", word1); scanf(&qu ...
- 手把手教你写Windows 64位平台调试器
本文网页排版有些差,已上传了doc,可以下载阅读.本文中的所有代码已打包,下载地址在此. ------------------------------------------------------- ...
- dynamic基元类型与隐式类型的局部变量var
dynamic代码示例 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; na ...
- 2 25urllib.py
""" urllib.request.urlopen(url,data,timeout) """ # from urllib.request ...
