Python菜鸟之路:Python基础(三)
一、编码
推荐阅读《字符编码的前世今生》:http://tgideas.qq.com/webplat/info/news_version3/804/808/811/m579/201307/218730.shtml
1. 常见编码介绍
- GB2312编码:适用于汉字处理、汉字通信等系统之间的信息交换
- GBK编码:是汉字编码标准之一,是在 GB2312-80 标准基础上的内码扩展规范,使用了双字节编码,即每个汉子占2byte。
- ASCII编码:是对英语字符和二进制之间的关系做的统一规定
- Unicode编码:这是一种世界上所有字符的编码。当然了它没有规定的存储方式。
- UTF-8编码:是 Unicode Transformation Format - 8 bit 的缩写, UTF-8 是 Unicode 的一种实现方式。它是可变长的编码方式,可以使用 1~4 个字节表示一个字符,可根据不同的符号而变化字节长度。每个汉子占3byte。
2. 编码转换
Python内部的字符串一般都是 Unicode编码。代码中字符串的默认编码与代码文件本身的编码是一致的。所以要做一些编码转换通常是要以Unicode作为中间编码进行转换的,即先将其他编码的字符串解码(decode)成 Unicode,再从 Unicode编码(encode)成另一种编码。
- decode 的作用是将其他编码的字符串转换成 Unicode 编码,eg name.decode(“GB2312”),表示将GB2312编码的字符串name转换成Unicode编码
- encode 的作用是将Unicode编码转换成其他编码的字符串,eg name.encode(”GB2312“),表示将GB2312编码的字符串name转换成GB2312编码
所以在进行编码转换的时候必须先知道 name 是那种编码,然后 decode 成 Unicode 编码,最后才 encode 成需要编码的编码。当然了,如果 name 已经就是 Unicode 编码了,那么就不需要进行 decode 进行解码转换了,直接用 encode 就可以编码成你所需要的编码。值得注意的是:对 Unicode 进行编码和对 str 进行编码都是错误的。
要在同一个文本中进行两种编码的输出等操作就必须进行编码的转换,先用decode将文本原来的编码转换成Unicode,再用encode将编码转换成需要转换成的编码。
二、Set集合
Set集合是一个无序不重复的。源码中对他的诸多方法进行了说明
class set(object):
"""
set() -> new empty set object
set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
"""
def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present.
"""
pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements from this set. """
pass def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return a shallow copy of a set. """
pass def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.)
"""
pass def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements of another set from this set. """
pass def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing.
"""
pass def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in both sets.)
"""
pass def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. """
pass def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return True if two sets have a null intersection. """
pass def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Report whether another set contains this set. """
pass def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Report whether this set contains another set. """
pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove and return an arbitrary set element.
Raises KeyError if the set is empty.
"""
pass def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError.
"""
pass def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.)
"""
pass def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. """
pass def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the union of sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in either set.)
"""
pass def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the union of itself and others. """
pass def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self&value. """
pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x. """
pass def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self==value. """
pass def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
pass def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>=value. """
pass def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>value. """
pass def __iand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self&=value. """
pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of set.__init__
"""
set() -> new empty set object
set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __ior__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self|=value. """
pass def __isub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self-=value. """
pass def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement iter(self). """
pass def __ixor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self^=value. """
pass def __len__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return len(self). """
pass def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<=value. """
pass def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<value. """
pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self!=value. """
pass def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self|value. """
pass def __rand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value&self. """
pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return state information for pickling. """
pass def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass def __ror__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value|self. """
pass def __rsub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value-self. """
pass def __rxor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value^self. """
pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
pass def __sub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self-value. """
pass def __xor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self^value. """
pass __hash__ = None
Set源码(3.5.1版本)
下边就几个常用的方法进行练习,方便加深理解
测试数据如下
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s2 = {2,4,6,7}
2.1 set的创建
set_1 = set() #创建一个空集合
set_2 = {123, ""} #集合中包含元素123,"456"
#将list转换为set
list_1 = [1,2,3,4,4]
set_3 = set(list_1)
# set_3 = [1,2,3,4]
2.2 set.difference和set.difference_update
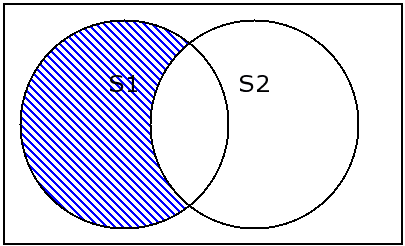
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s2 = {2,4,6,7}
s3 = a.difference(s2)
out: {1,3}
s1.difference_update(s2)
print(s1)
out: {1,3}
difference/difference_update
2.3 set.symmetric_difference和set.symmetric_difference_update 交集的补集
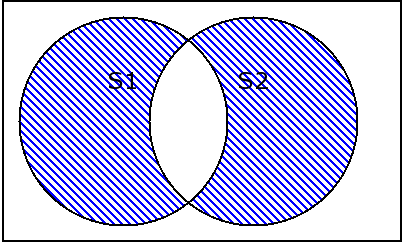
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s2 = {2,4,6,7}
s3 = s1.symmetric_difference(s2)
print(s3)
out: {1, 3, 6, 7}
s1.symmetric_difference_update(s2)
print(s1)
out: {1, 3, 6, 7}
symmetric_difference/symmetric_difference_update
2.4 set.intersection和set.intersection_update 交集
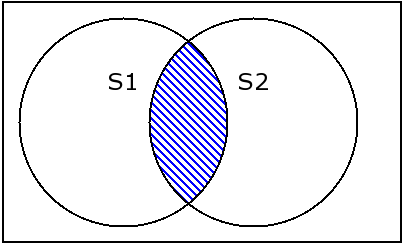
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s2 = {2,4,6,7}
s3 = s1.intersection(s2)
print(s3)
out: {2, 4}
s1.intersection_update(s2)
print(s1)
out: {2, 4}
intersection/intersection_update
2.5 union 全集
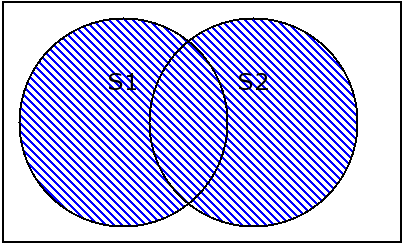
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s2 = {2,4,6,7}
s3 = s1.union(s2)
print(s3)
out: {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7}
union
2.6 discard 与 add
discard 移除集合中某个元素,如果元素不存在,do nothing,同remove相比,remove如果元素不存在,会报keyError错误
add 向集合中增加元素,如果元素存在,do nothing。
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s1.discard(1)
s1.discard(5)
print(s1)
out: {2, 3, 4}
discard
s1 = {1,2,3,4}
s1.add(2)
s1.add(5)
print(s1)
out: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
add
2.7 update
更新集合中的元素,已存在的更新,不存在的新增,更新对象可以是tuple 或者dict
Update a set with the union of itself and others.
2.8 其他(非set必备特性)
li=[1,2,3] # 会执行list的 __init__方法
li() # 会执行li的 __call__方法
list(tuple) 的原理:执行list.__init__ 构造函数,for循环tuple中的元素,然后添加到一个列表中
三、三元运算(或叫三目运算)
三元运算就是对简单的条件语句的缩写。
# 书写格式 result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2 # 如果条件成立,那么将 “值1” 赋值给result变量,否则,将“值2”赋值给result变量
Python菜鸟之路:Python基础(三)的更多相关文章
- python学习之路-day2-pyth基础2
一. 模块初识 Python的强大之处在于他有非常丰富和强大的标准库和第三方库,第三方库存放位置:site-packages sys模块简介 导入模块 import sys 3 sys模 ...
- Python菜鸟之路:Django 路由补充1:FBV和CBV - 补充2:url默认参数
一.FBV和CBV 在Python菜鸟之路:Django 路由.模板.Model(ORM)一节中,已经介绍了几种路由的写法及对应关系,那种写法可以称之为FBV: function base view ...
- Python全栈开发【基础三】
Python全栈开发[基础三] 本节内容: 函数(全局与局部变量) 递归 内置函数 函数 一.定义和使用 函数最重要的是减少代码的重用性和增强代码可读性 def 函数名(参数): ... 函数体 . ...
- Python学习之路-Day2-Python基础2
Python学习之路第二天 学习内容: 1.模块初识 2.pyc是什么 3.python数据类型 4.数据运算 5.bytes/str之别 6.列表 7.元组 8.字典 9.字符串常用操作 1.模块初 ...
- PYTHON学习之路_PYTHON基础(1)
学习内容: 1.Python介绍 2.Python程序初接触和变量 3.Python用户交互 4.Python数据类型 5.Python循环if...(elif)...else 6.Python循环w ...
- python学习之路-day1-python基础1
本节内容: Python介绍 发展史 Python 2 or 3? 安装 Hello World程序 变量 用户输入 模块初识 .pyc是个什么鬼? 数据类型初识 数据运算 表达式if ...else ...
- Python学习之路-Day2-Python基础3
Python学习之路第三天 学习内容: 1.文件操作 2.字符转编码操作 3.函数介绍 4.递归 5.函数式编程 1.文件操作 打印到屏幕 最简单的输出方法是用print语句,你可以给它传递零个或多个 ...
- Python学习之路-Day1-Python基础
学习python的过程: 在茫茫的编程语言中我选择了python,因为感觉python很强大,能用到很多领域.我自己也学过一些编程语言,比如:C,java,php,html,css等.但是我感觉自己都 ...
- Python学习之路1 - 基础入门
本文内容 Python介绍 安装Python解释器 输出 变量 输入 条件判断语句 循环语句 模块讲解 三元运算 字符串和二进制的相互转化 本系列文章使用的Python版本为3.6.2 使用开发工具为 ...
- PYTHON学习之路_PYTHON基础(4)
学习内容: 1.Python函数的基本语法 2.Python函数的返回值与变量 3.Python嵌套函数 4.Python递归函数及实例(二分查找) 5.Python匿名函数 6.Python内置方法 ...
随机推荐
- 【转】javascript 的类,原型,继承的理解
原文: https://www.cnblogs.com/codernie/p/9098184.html ------------------------------------------------ ...
- elasticsearch 安装和部署
jdk要用1.8以上(elasticsearch版本是1.7.3) 下载elasticsearch的tar包,解压开,更改其名称 mv elasticsearch-5.x.x elasticsear ...
- 文本文件打印类库(C#)
我写了一个打印文本文件的类库,功能包含:打印预览.打印.打印时能够选择打印机.能够指定页码范围. 调用方法很easy: TextFilePrinter p = new TextFilePrinter( ...
- AndroidStudio短信验证功能收不到验证码
http://mob.com/第三方接口获取地址: 登陆过后点我的后台即可上传,管理应用.需注意的是,即使验证不通过,只要整合了短信验证的Jar包,每天都有20条免费验证短信.现在的mob.com只支 ...
- java中数组的复制
数组复制使我们在编程过程中经常要使用到的,在java中数组复制我们大概能够分为两种,一种是引用复制,还有一种就是深度复制(复制后两个数组互不相干). 以下我们就通过測试的方法来具体看看什么是引用复制和 ...
- python 赋值 深浅拷贝
深浅拷贝 一.数字和字符串 对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值.浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 impor ...
- AI学习笔记
人人都是产品经理,继续设计课程啦啦啦啦 ADOBE: ps, ai, fl, dw, fw, ae, pr, id COREL: painter coreldraw autodesk: 三维: ...
- rk3288 LED上加入heartbeat功能
平台:瑞芯的rk3288 作者:fulinux *****本文同意转载.只是请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/fulinus**** 1.硬件环境 随意选取一个GPIO引脚作为he ...
- [转]Tomcat处理一个HTTP请求的过程
1.Tomcat Server的组成部分 1.1 - Server A Server element represents the entire Catalina servlet container. ...
- 公网通过代理访问阿里云vpc redis
前提条件 如果您需要从本地 PC 端访问 Redis 实例进行数据操作,可以通过在 ECS 上配置端口映射或者端口转发实现.但必须符合以下前提条件: 若 Redis 实例属于专有网络(VPC),ECS ...
