Subsets I&&II——经典题
Subsets I
Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets.
Note:
- Elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
For example,
If nums = [1,2,3], a solution is:
- [
- [3],
- [1],
- [2],
- [1,2,3],
- [1,3],
- [2,3],
- [1,2],
- []
- ]
思路一(http://www.cnblogs.com/felixfang/p/3775712.html)
可以用递推的思想,观察S=[], S =[1], S = [1, 2] 时解的变化。
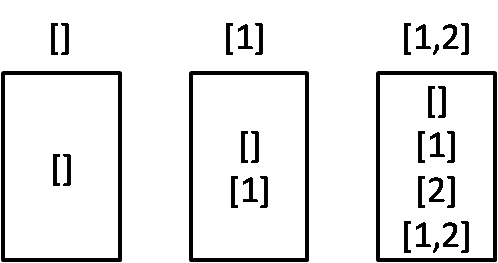
可以发现S=[1, 2] 的解就是 把S = [1]的所有解末尾添上2,然后再并上S = [1]里面的原有解。因此可以定义vector<vector<int> > 作为返回结果res, 开始时res里什么都没有,第一步放入一个空的vecotr<int>,然后这样迭代n次,每次更新res 内容,最后返回res。
代码:
- class Solution {
- public:
- vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
- vector<vector<int> > res;
- vector<int> emp;
- res.push_back(emp);
- sort(S.begin(), S.end());
- if(S.size() == ) return res;
- for(vector<int>::iterator ind = S.begin(); ind < S.end(); ++ind){
- int size = res.size();
- for(int i = ; i < size; ++i){
- vector<int> v;
- for(vector<int>::iterator j = res[i].begin(); j < res[i].end(); ++j){
- v.push_back(*j);
- }
- v.push_back(*ind);
- res.push_back(v);
- }
- }
- return res;
- }
- };
思路二
所谓子集,就是包含原集合中的一些元素,不包含另一些元素。如果单独看某一个元素,它都有两种选择:"被包含在子集中"和"不被包含在子集中",对于元素个数为n、且不含重复元素的S,子集总数是2n。因此我们可以遍历S的所有元素,然后用递归考虑每一个元素包含和不包含的两种情况。
代码,这种思路需要用到递归
(代码来自http://www.acmerblog.com/leetcode-solution-subsets-6227.html 这篇博客可以好好看看)
- // LeetCode, Subsets
- // 增量构造法,深搜,时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(n)
- class Solution {
- public:
- vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
- sort(S.begin(), S.end()); // 输出要求有序
- vector<vector<int> > result;
- vector<int> path;
- subsets(S, path, , result);
- return result;
- }
- private:
- static void subsets(const vector<int> &S, vector<int> &path, int step,
- vector<vector<int> > &result) {
- if (step == S.size()) {
- result.push_back(path);
- return;
- }
- // 不选S[step]
- subsets(S, path, step + , result);
- // 选S[step]
- path.push_back(S[step]);
- subsets(S, path, step + , result);
- path.pop_back();
- }
- };
思路同上,代码中可以采用位向量法,开一个位向量bool selected[n],每个元素可以选或者不选。
- // LeetCode, Subsets
- // 位向量法,深搜,时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(n)
- class Solution {
- public:
- vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
- sort(S.begin(), S.end()); // 输出要求有序
- vector<vector<int> > result;
- vector<bool> selected(S.size(), false);
- subsets(S, selected, , result);
- return result;
- }
- private:
- static void subsets(const vector<int> &S, vector<bool> &selected, int step,
- vector<vector<int> > &result) {
- if (step == S.size()) {
- vector<int> subset;
- for (int i = ; i < S.size(); i++) {
- if (selected[i]) subset.push_back(S[i]);
- }
- result.push_back(subset);
- return;
- }
- // 不选S[step]
- selected[step] = false;
- subsets(S, selected, step + , result);
- // 选S[step]
- selected[step] = true;
- subsets(S, selected, step + , result);
- }
- };
Subsets II
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets.
Note:
- Elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
For example,
If nums = [1,2,2], a solution is:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
思路一:
其实比较简单,就是每当遇到重复元素的时候我们就只把当前结果集的后半部分加上当前元素加入到结果集中,因为后半部分就是上一步中加入这个元素的所有子集,上一步这个元素已经加入过了,前半部分如果再加就会出现重复。所以算法上复杂度上没有提高,反而少了一些操作,就是遇到重复时少做一半,不过这里要对元素集合先排序,否则不好判断重复元素。同样的还是可以用递归和非递归来解,不过对于重复元素的处理是一样的。
我们以S=[1,2,2]为例:

可以发现从S=[1,2]变化到S=[1,2,2]时,多出来的有两个子集[2,2]和[1,2,2],这两个子集,其实就是 [2], [1,2]末尾都加上2 而产生。而[2], [1,2] 这两个子集实际上是 S=[1,2]的解到 S=[1]的解 新添加的部分。
因此,若S中有重复元素,可以先排序;遍历过程中如果发现当前元素S[i] 和 S[i-1] 相同,那么不同于原有思路中“将当前res中所有自己拷贝一份再在末尾添加S[i]”的做法,我们只将res中上一次添加进来的子集拷贝一份,末尾添加S[i]。
- class Solution {
- public:
- vector<vector<int> > subsetsWithDup(vector<int> &S) {
- vector<vector<int> > subsets;
- vector<int> v;
- subsets.push_back(v);
- if(S.empty()) return subsets;
- sort(S.begin(), S.end());
- int m = 0; //m 用来存储上一次加进来的子集们的起始index
- for(vector<int>::iterator i = S.begin(); i < S.end(); ++i){
- int start = ((i != S.begin() && *i == *(i-1)) ? m : 0); //如果S的当前元素和前一个元素相同,只拷贝上次加进来的子集
- int end = subsets.size();
- for(int j = start; j < end; ++j){
- vector<int> vt;
- for(vector<int>::iterator k = subsets[j].begin(); k < subsets[j].end(); ++k){
- vt.push_back(*k);
- }
- vt.push_back(*i);
- subsets.push_back(vt);
- }
- m = end;
- }
- return subsets;
- }
- };
思路二:
对于含有重复元素的S,可以先排序,然后考虑去重:我们可以发现如果所遍历的当前元素S[i] 和 目前的子集的末尾元素相同,那么就不再需要考虑"不包含当前元素到子集中"的情况,只需要考虑"包含当前元素到子集中一种情况"。举个例子:对于S=[1,2,2],如果遍历到第二个"2",当前子集v是[1, 2],这个时候如果考虑"不把2包含进子集的情况",即维持子集=[1,2]不动,遍历下一个元素;这样其结果会出现重复。因为考虑另一个递归调用,其当前子集v是[1],也遍历到了S的第二个"2",它将这个"2"元素放入当前子集,虽然继续遍历下一个元素。这两个递归调用的结果是重复的。因此,若当前递归调用所遍历到的元素和当前子集v的末尾元素相同,只考虑"把当前元素添加到子集末尾"的情况。
- // LeetCode, Subsets II
- // 增量构造法,版本1,时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(n)
- class Solution {
- public:
- vector<vector<int> > subsetsWithDup(vector<int> &S) {
- sort(S.begin(), S.end()); // 必须排序
- vector<vector<int> > result;
- vector<int> path;
- dfs(S, S.begin(), path, result);
- return result;
- }
- private:
- static void dfs(const vector<int> &S, vector<int>::iterator start,
- vector<int> &path, vector<vector<int> > &result) {
- result.push_back(path);
- for (auto i = start; i < S.end(); i++) {
- if (i != start && *i == *(i-)) continue;
- path.push_back(*i);
- dfs(S, i + , path, result);
- path.pop_back();
- }
- }
- };
Subsets I&&II——经典题的更多相关文章
- zoj 1081:Points Within(计算几何,判断点是否在多边形内,经典题)
Points Within Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB Statement of the Problem Several dra ...
- poj 1611:The Suspects(并查集,经典题)
The Suspects Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 20000K Total Submissions: 21472 Accepted: 10393 De ...
- Hihicoder 题目1 : Trie树(字典树,经典题)
题目1 : Trie树 时间限制:10000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 小Hi和小Ho是一对好朋友,出生在信息化社会的他们对编程产生了莫大的兴趣,他们约定好互相帮助,在编 ...
- poj 3264:Balanced Lineup(线段树,经典题)
Balanced Lineup Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 32820 Accepted: 15447 ...
- poj 2503:Babelfish(字典树,经典题,字典翻译)
Babelfish Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 30816 Accepted: 13283 Descr ...
- poj 2001:Shortest Prefixes(字典树,经典题,求最短唯一前缀)
Shortest Prefixes Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Submissions: 12731 Accepted: 544 ...
- hdu 1247:Hat’s Words(字典树,经典题)
Hat’s Words Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- hdu 1075:What Are You Talking About(字典树,经典题,字典翻译)
What Are You Talking About Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 102400/204800 K ...
- hdu 1251:统计难题(字典树,经典题)
统计难题 Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131070/65535 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
随机推荐
- bzoj1263: [SCOI2006]整数划分(高精度+构造)
第一次写压位高精度只好抄黄学长的 代码最后一段想了好久一看评论区才知道黄学长写错了= =很气 自己最后改对了T^T 这题最优是一直划分3出来直到<=4 #include<iostream& ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 031 B - Reversi(DP)
B - Reversi 题目链接:https://atcoder.jp/contests/agc031/tasks/agc031_b 题意: 给出n个数,然后现在你可以对一段区间修改成相同的值,前提是 ...
- BZOJ1880: [Sdoi2009]Elaxia的路线(最短路)
1880: [Sdoi2009]Elaxia的路线 Time Limit: 4 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MBSubmit: 2049 Solved: 805 题目链接:https ...
- ACM3790迪杰斯特拉算法运用
最短路径问题 Problem Description 给你n个点,m条无向边,每条边都有长度d和花费p,给你起点s终点t,要求输出起点到终点的最短距离及其花费,如果最短距离有多条路线,则输出花费最少的 ...
- sgu 131 状压DP
棋盘覆盖(二) 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 描述 The banquet hall of Computer Scientists' Palace has a ...
- Spring Boot 打包部署
一.打包成jar并部署 1.工程--右键选择运行配置: 在Goals中输入: org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-jar-plugin:.RELEASE:repackage ...
- 【设计模式】 模式PK:命令模式VS策略模式
1.概述 命令模式和策略模式的类图确实很相似,只是命令模式多了一个接收者(Receiver)角色.它们虽然同为行为类模式,但是两者的区别还是很明显的.策略模式的意图是封装算法,它认为“算法”已经是一个 ...
- 【poj2947】高斯消元求解同模方程组【没有AC,存代码】
题意: p start enda1,a2......ap (1<=ai<=n)第一行表示从星期start 到星期end 一共生产了p 件装饰物(工作的天数为end-start+1+7*x, ...
- 【BZOJ4104】解密运算 [暴力]
解密运算 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MB[Submit][Status][Discuss] Description 对于一个长度为N的字符串,我们在字 ...
- UOJ#31 【UR #2】猪猪侠再战括号序列
传送门http://uoj.ac/problem/31 大家好我是来自百度贴吧的_叫我猪猪侠,英文名叫_CallMeGGBond. 我不曾上过大学,但这不影响我对离散数学.复杂性分析等领域的兴趣:尤其 ...
