mysql-表完整性约束
阅读目录
一 介绍
约束条件与数据类型的宽度一样,都是可选参数
作用:用于保证数据的完整性和一致性
主要分为:
PRIMARY KEY (PK) 标识该字段为该表的主键,可以唯一的标识记录
FOREIGN KEY (FK) 标识该字段为该表的外键
NOT NULL 标识该字段不能为空
UNIQUE KEY (UK) 标识该字段的值是唯一的
AUTO_INCREMENT 标识该字段的值自动增长(整数类型,而且为主键)
DEFAULT 为该字段设置默认值 UNSIGNED 无符号
ZEROFILL 使用0填充
说明:
1. 是否允许为空,默认NULL,可设置NOT NULL,字段不允许为空,必须赋值
2. 字段是否有默认值,缺省的默认值是NULL,如果插入记录时不给字段赋值,此字段使用默认值
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male'
age int unsigned NOT NULL default 20 必须为正值(无符号) 不允许为空 默认是20
3. 是否是key
主键 primary key
外键 foreign key
索引 (index,unique...)
二 not null与default
是否可空,null表示空,非字符串
not null - 不可空
null - 可空
默认值,创建列时可以指定默认值,当插入数据时如果未主动设置,则自动添加默认值
create table tb1(
nid int not null defalut 2,
num int not null)
==================not null====================
mysql> create table t1(id int); #id字段默认可以插入空
mysql> desc t1;
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
mysql> insert into t1 values(); #可以插入空 mysql> create table t2(id int not null); #设置字段id不为空
mysql> desc t2;
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
mysql> insert into t2 values(); #不能插入空
ERROR 1364 (HY000): Field 'id' doesn't have a default value ==================default====================
#设置id字段有默认值后,则无论id字段是null还是not null,都可以插入空,插入空默认填入default指定的默认值
mysql> create table t3(id int default 1);
mysql> alter table t3 modify id int not null default 1; ==================综合练习====================
mysql> create table student(
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> age int(3) unsigned not null default 18,
-> sex enum('male','female') default 'male',
-> hobby set('play','study','read','music') default 'play,music'
-> );
mysql> desc student;
+-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+------------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+------------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | int(3) unsigned | NO | | 18 | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | male | |
| hobby | set('play','study','read','music') | YES | | play,music | |
+-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+------------+-------+
mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon');
mysql> select * from student;
+------+-----+------+------------+
| name | age | sex | hobby |
+------+-----+------+------------+
| egon | 18 | male | play,music |
+------+-----+------+------------+
验证
三 unique
============设置唯一约束 UNIQUE===============
方法一:
create table department1(
id int,
name varchar(20) unique,
comment varchar(100)
); 方法二:
create table department2(
id int,
name varchar(20),
comment varchar(100),
constraint uk_name unique(name)
); mysql> insert into department1 values(1,'IT','技术');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into department1 values(1,'IT','技术');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry 'IT' for key 'name'
mysql> create table t1(id int not null unique);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> desc t1;
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
row in set (0.00 sec)
not null+unique的化学反应
create table service(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
host varchar(15) not null,
port int not null,
unique(host,port) #联合唯一
); mysql> insert into service values
-> (1,'nginx','192.168.0.10',80),
-> (2,'haproxy','192.168.0.20',80),
-> (3,'mysql','192.168.0.30',3306)
-> ;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> insert into service(name,host,port) values('nginx','192.168.0.10',80);
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '192.168.0.10-80' for key 'host'
联合唯一
四 primary key
primary key字段的值不为空且唯一
一个表中可以:
单列做主键
多列做主键(复合主键)
但一个表内只能有一个主键primary key
============单列做主键===============
#方法一:not null+unique
create table department1(
id int not null unique, #主键
name varchar(20) not null unique,
comment varchar(100)
); mysql> desc department1;
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | UNI | NULL | |
| comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
rows in set (0.01 sec) #方法二:在某一个字段后用primary key
create table department2(
id int primary key, #主键
name varchar(20),
comment varchar(100)
); mysql> desc department2;
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) #方法三:在所有字段后单独定义primary key
create table department3(
id int,
name varchar(20),
comment varchar(100),
constraint pk_name primary key(id); #创建主键并为其命名pk_name mysql> desc department3;
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
rows in set (0.01 sec)
单列主键
==================多列做主键================
create table service(
ip varchar(15),
port char(5),
service_name varchar(10) not null,
primary key(ip,port)
); mysql> desc service;
+--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| ip | varchar(15) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| port | char(5) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| service_name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
+--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into service values
-> ('172.16.45.10','','mysqld'),
-> ('172.16.45.11','','mariadb')
-> ;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> insert into service values ('172.16.45.10','','nginx');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '172.16.45.10-3306' for key 'PRIMARY'
多列主键
五 auto_increment
约束字段为自动增长,被约束的字段必须同时被key约束
#不指定id,则自动增长
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
); mysql> desc student;
+-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | male | |
+-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
mysql> insert into student(name) values
-> ('egon'),
-> ('alex')
-> ; mysql> select * from student;
+----+------+------+
| id | name | sex |
+----+------+------+
| 1 | egon | male |
| 2 | alex | male |
+----+------+------+ #也可以指定id
mysql> insert into student values(4,'asb','female');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into student values(7,'wsb','female');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student;
+----+------+--------+
| id | name | sex |
+----+------+--------+
| 1 | egon | male |
| 2 | alex | male |
| 4 | asb | female |
| 7 | wsb | female |
+----+------+--------+ #对于自增的字段,在用delete删除后,再插入值,该字段仍按照删除前的位置继续增长
mysql> delete from student;
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student;
Empty set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into student(name) values('ysb');
mysql> select * from student;
+----+------+------+
| id | name | sex |
+----+------+------+
| 8 | ysb | male |
+----+------+------+ #应该用truncate清空表,比起delete一条一条地删除记录,truncate是直接清空表,在删除大表时用它
mysql> truncate student;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from student;
+----+------+------+
| id | name | sex |
+----+------+------+
| 1 | egon | male |
+----+------+------+
row in set (0.00 sec)
#在创建完表后,修改自增字段的起始值
mysql> create table student(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20),
-> sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
-> ); mysql> alter table student auto_increment=3; mysql> show create table student;
.......
ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from student;
+----+------+------+
| id | name | sex |
+----+------+------+
| 3 | egon | male |
+----+------+------+
row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show create table student;
.......
ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 #也可以创建表时指定auto_increment的初始值,注意初始值的设置为表选项,应该放到括号外
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
)auto_increment=3; #设置步长
sqlserver:自增步长
基于表级别
create table t1(
id int。。。
)engine=innodb,auto_increment=2 步长=2 default charset=utf8 mysql自增的步长:
show session variables like 'auto_inc%'; #基于会话级别
set session auth_increment_increment=2 #修改会话级别的步长 #基于全局级别的
set global auth_increment_increment=2 #修改全局级别的步长(所有会话都生效) #!!!注意了注意了注意了!!!
If the value of auto_increment_offset is greater than that of auto_increment_increment, the value of auto_increment_offset is ignored.
翻译:如果auto_increment_offset的值大于auto_increment_increment的值,则auto_increment_offset的值会被忽略
比如:设置auto_increment_offset=3,auto_increment_increment=2 mysql> set global auto_increment_increment=5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> set global auto_increment_offset=3;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show variables like 'auto_incre%'; #需要退出重新登录
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-------+
| auto_increment_increment | 1 |
| auto_increment_offset | 1 |
+--------------------------+-------+ create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
); mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon1'),('egon2'),('egon3');
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-------+------+
| id | name | sex |
+----+-------+------+
| 3 | egon1 | male |
| 8 | egon2 | male |
| 13 | egon3 | male |
+----+-------+------+
步长increment与起始偏移量offset:auto_increment_increment,auto_increment_offset
六 foreign key
员工信息表有三个字段:工号 姓名 部门
公司有3个部门,但是有1个亿的员工,那意味着部门这个字段需要重复存储,部门名字越长,越浪费
解决方法:
我们完全可以定义一个部门表
然后让员工信息表关联该表,如何关联,即foreign key
#表类型必须是innodb存储引擎,且被关联的字段,即references指定的另外一个表的字段,必须是主键
create table department(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null
)engine=innodb; #dpt_id外键,关联父表(department主键id),同步更新,同步删除
create table employee(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
dpt_id int,
constraint fk_name foreign key(dpt_id)
references department(id)
on delete cascade
on update cascade
)engine=innodb; #先往父表department中插入记录
insert into department values
(1,'欧德博爱技术有限事业部'),
(2,'艾利克斯人力资源部'),
(3,'销售部'); #再往子表employee中插入记录
insert into employee values
(1,'egon',1),
(2,'alex1',2),
(3,'alex2',2),
(4,'alex3',2),
(5,'李坦克',3),
(6,'刘飞机',3),
(7,'张火箭',3),
(8,'林子弹',3),
(9,'加特林',3)
; #删父表department,子表employee中对应的记录跟着删
mysql> delete from department where id=3;
mysql> select * from employee;
+----+-------+--------+
| id | name | dpt_id |
+----+-------+--------+
| 1 | egon | 1 |
| 2 | alex1 | 2 |
| 3 | alex2 | 2 |
| 4 | alex3 | 2 |
+----+-------+--------+ #更新父表department,子表employee中对应的记录跟着改
mysql> update department set id=22222 where id=2;
mysql> select * from employee;
+----+-------+--------+
| id | name | dpt_id |
+----+-------+--------+
| 1 | egon | 1 |
| 3 | alex2 | 22222 |
| 4 | alex3 | 22222 |
| 5 | alex1 | 22222 |
+----+-------+--------+
示范
表1 foreign key 表2
则表1的多条记录对应表2的一条记录,即多对一 利用foreign key的原理我们可以制作两张表的多对多,一对一关系
多对多:
表1的多条记录可以对应表2的一条记录
表2的多条记录也可以对应表1的一条记录 一对一:
表1的一条记录唯一对应表2的一条记录,反之亦然 分析时,我们先从按照上面的基本原理去套,然后再翻译成真实的意义,就很好理解了 、、
辅助理解
三张表:出版社,作者信息,书
一对多(或多对一):一个出版社可以出版多本书
关联方式:foreign key
=====================多对一=====================
create table press(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
); create table book(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
press_id int not null,
foreign key(press_id) references press(id)
on delete cascade
on update cascade
); insert into press(name) values
('北京工业地雷出版社'),
('人民音乐不好听出版社'),
('知识产权没有用出版社')
; insert into book(name,press_id) values
('九阳神功',1),
('九阴真经',2),
('九阴白骨爪',2),
('独孤九剑',3),
('降龙十巴掌',2),
('葵花宝典',3)
;
多对多:一个作者可以写多本书,一本书也可以有多个作者,双向的一对多,即多对多
关联方式:foreign key+一张新的表
=====================多对多=====================
create table author(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
); #这张表就存放作者表与书表的关系,即查询二者的关系查这表就可以了
create table author2book(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
author_id int not null,
book_id int not null,
constraint fk_author foreign key(author_id) references author(id)
on delete cascade
on update cascade,
constraint fk_book foreign key(book_id) references book(id)
on delete cascade
on update cascade,
primary key(author_id,book_id)
); #插入四个作者,id依次排开
insert into author(name) values('egon'),('alex'),('yuanhao'),('wpq'); #每个作者与自己的代表作如下
egon:
九阳神功
九阴真经
九阴白骨爪
独孤九剑
降龙十巴掌
葵花宝典
alex:
九阳神功
葵花宝典
yuanhao:
独孤九剑
降龙十巴掌
葵花宝典
wpq:
九阳神功 insert into author2book(author_id,book_id) values
(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(1,4),
(1,5),
(1,6),
(2,1),
(2,6),
(3,4),
(3,5),
(3,6),
(4,1)
;
#两张表:学生表和客户表
一对一:一个学生是一个客户,一个客户有可能变成一个学校,即一对一的关系
关联方式:foreign key+unique
#一定是student来foreign key表customer,这样就保证了:
#1 学生一定是一个客户,
#2 客户不一定是学生,但有可能成为一个学生 create table customer(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null
); create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
class_name varchar(20) not null default 'python自动化',
level int default 1,
customer_id int unique, #该字段一定要是唯一的
foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) #外键的字段一定要保证unique
on delete cascade
on update cascade
); #增加客户
insert into customer(name) values
('李飞机'),
('王大炮'),
('守榴弹'),
('吴坦克'),
('赢火箭'),
('战地雷')
; #增加学生
insert into student(name,customer_id) values
('李飞机',1),
('王大炮',2)
;
练习:账号信息表,用户组,主机表,主机组
#用户表
create table user(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
username varchar(20) not null,
password varchar(50) not null,
primary key(username,password)
); insert into user(username,password) values
('root',''),
('egon',''),
('alex','alex3714')
; #用户组表
create table usergroup(
id int primary key auto_increment,
groupname varchar(20) not null unique
); insert into usergroup(groupname) values
('IT'),
('Sale'),
('Finance'),
('boss')
; #主机表
create table host(
id int primary key auto_increment,
ip char(15) not null unique default '127.0.0.1'
); insert into host(ip) values
('172.16.45.2'),
('172.16.31.10'),
('172.16.45.3'),
('172.16.31.11'),
('172.10.45.3'),
('172.10.45.4'),
('172.10.45.5'),
('192.168.1.20'),
('192.168.1.21'),
('192.168.1.22'),
('192.168.2.23'),
('192.168.2.223'),
('192.168.2.24'),
('192.168.3.22'),
('192.168.3.23'),
('192.168.3.24')
; #业务线表
create table business(
id int primary key auto_increment,
business varchar(20) not null unique
);
insert into business(business) values
('轻松贷'),
('随便花'),
('大富翁'),
('穷一生')
; #建关系:user与usergroup create table user2usergroup(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
user_id int not null,
group_id int not null,
primary key(user_id,group_id),
foreign key(user_id) references user(id),
foreign key(group_id) references usergroup(id)
); insert into user2usergroup(user_id,group_id) values
(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(1,4),
(2,3),
(2,4),
(3,4)
; #建关系:host与business create table host2business(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
host_id int not null,
business_id int not null,
primary key(host_id,business_id),
foreign key(host_id) references host(id),
foreign key(business_id) references business(id)
); insert into host2business(host_id,business_id) values
(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(2,2),
(2,3),
(3,4)
; #建关系:user与host create table user2host(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
user_id int not null,
host_id int not null,
primary key(user_id,host_id),
foreign key(user_id) references user(id),
foreign key(host_id) references host(id)
); insert into user2host(user_id,host_id) values
(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(1,4),
(1,5),
(1,6),
(1,7),
(1,8),
(1,9),
(1,10),
(1,11),
(1,12),
(1,13),
(1,14),
(1,15),
(1,16),
(2,2),
(2,3),
(2,4),
(2,5),
(3,10),
(3,11),
(3,12)
;
作业:
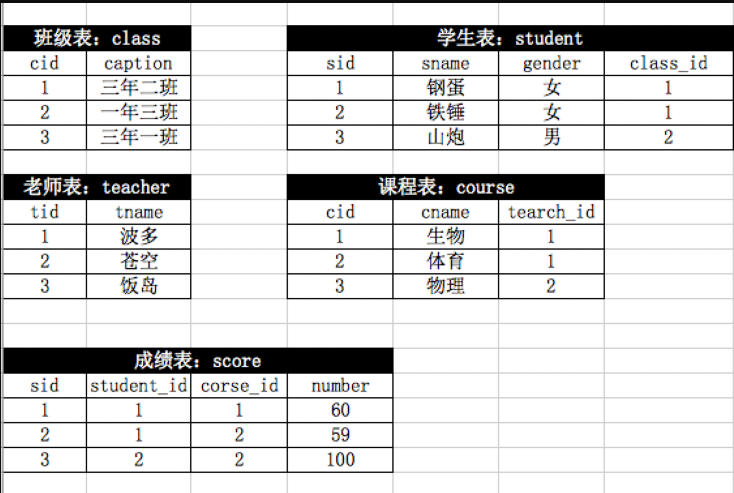
七、总结
1 not null 与default create table student2(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(5),
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'female'
); insert into student2(name) values('alex'); create table student3(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(5),
age int not null default 30
); insert into student3(name) values('alex'); 2 unique
#单列唯一
create table teacher(
id int not null unique,
name char(10)
);
insert into teacher values(1,'egon');
insert into teacher values(1,'alex'); #多列唯一
#255.255.255.255
create table services(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(10),
host char(15),
port int,
constraint host_port unique(host,port)
); insert into services values('ftp','192.168.20.17',8080);
insert into services values('httpd','192.168.20.17',8081); #auto_increment_offset:偏移量
create table dep(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(10)
);
insert into dep(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); create table dep1(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(10)
)auto_increment=10;
insert into dep1(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); #auto_increment_increment:步长
create table dep2(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(10)
);
set session auto_increment_increment=2; #会话级,只对当前会话有效
set global auto_increment_increment=2; #全局,对所有的会话都有效
insert into dep1(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); #auto_increment_offset:偏移量+auto_increment_increment:步长
注意:如果auto_increment_offset的值大于auto_increment_increment的值,则auto_increment_offset的值会被忽略
set session auto_increment_offset=2;
set session auto_increment_increment=3;
show variables like '%auto_in%'; create table dep3(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(10)
);
insert into dep3(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); #foreign key
#!!!先建被关联的表,并且被关联的字段必须唯一
create table dep(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50),
comment varchar(100)
); create table emp_info(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
dep_id int,
constraint fk_depid_id foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id)
on delete cascade
on update cascade
); #先给被关联的表初始化记录
insert into dep values
(1,'欧德博爱技术有限事业部','说的好...'),
(2,'艾利克斯人力资源部','招不到人'),
(3,'销售部','卖不出东西'); insert into emp_info values
(1,'egon',1),
(2,'alex1',2),
(3,'alex2',2),
(4,'alex3',2),
(5,'李坦克',3),
(6,'刘飞机',3),
(7,'张火箭',3),
(8,'林子弹',3),
(9,'加特林',3)
;
mysql-表完整性约束的更多相关文章
- MySQL表完整性约束
=======MySQL表完整性约束====== 目录: 一.介绍 二.not null 与 default 三.unique 四.primary key 五.auto_increment 六.for ...
- MySQL -表完整性约束(Day41)
阅读目录 一.介绍 二.not null 与 default 三.unique 四.primary key 五.auto_increment 六.foreign key 七. 总结 一 介绍 回到顶部 ...
- 三.mysql表的完整性约束
mysql表的完整性约束 什么是约束 not null 不能为空的 unique 唯一 = 不能重复 primary key 主键 = 不能为空 且 不能重复 foreign key ...
- MySQL表设计基础
MySQL表设计关于blog数据库中建立所有表的sql语句<一.>sql语句中 约束概念constraint concept1.1 实体完整性entity integrity(主键--唯一 ...
- SQL学习笔记三之MySQL表操作
阅读目录 一 存储引擎介绍 二 表介绍 三 创建表 四 查看表结构 五 数据类型 六 表完整性约束 七 修改表ALTER TABLE 八 复制表 九 删除表 一 存储引擎介绍 存储引擎即表类型,mys ...
- mysql数据库从删库到跑路之mysql表操作
表介绍 表相当于文件,表中的一条记录就相当于文件的一行内容,不同的是,表中的一条记录有对应的标题,称为表的字段 id,name,qq,age称为字段,其余的,一行内容称为一条记录 内容: 1 创建表 ...
- 0x04 MySQl 表操作
0x01 存储引擎介绍 存储引擎即表类型,mysql根据不同的表类型会有不同的处理机制 详见:http://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/articles/7213670.ht ...
- MySQL表的四种分区类型
MySQL表的四种分区类型 一.什么是表分区 通俗地讲表分区是将一大表,根据条件分割成若干个小表.mysql5.1开始支持数据表分区了. 如:某用户表的记录超过了600万条,那么就可以根据入库日期将表 ...
- MySQL表名和数据库关键字相同解决办法
今天改他们的代码的时候,遇到了MySQL表名和数据库关键字的问题. 由于表名是关键字,导致增删改查都报错. Hibernate: select leave0_.id as id22_, leave0_ ...
- MySQL 表分区详解MyiSam引擎和InnoDb 区别(实测)
一.什么是表分区通俗地讲表分区是将一大表,根据条件分割成若干个小表.mysql5.1开始支持数据表分区了.如:某用户表的记录超过了1000万条,那么就可以根据入库日期将表分区,也可以根据所在地将表分区 ...
随机推荐
- [AHOI2008] 逆序对
link 我们可以很容易的推断出$-1$是单调不降的,若$i>j$且$a_i$与$a_j$都没有填数,若填完之后$a_i>a_j$或者$a_i<a_j$,则对答案产生影响的只在$[i ...
- mybatis生成的pojo 中的属性或方法不够我们当做dto使用时
我们在写代码的时候,如果一个 mybatis生成的pojo 中的属性或方法不够我们使用(当做dto和前台交互)时,我们有两种方法: 第一: 直接在 原 pojo 中增加属性或者方法 第二:我们可以再写 ...
- 阐述ArrayList、Vector、LinkedList的存储性能和特性?
ArrayList 和Vector他们底层的实现都是一样的,都是使用数组方式存储数据,此数组元素数大于实际存储的数据以便增加和插入元素,它们都允许直接按序号索引元素,但是插入元素要涉及数组元素移动等内 ...
- Leetcode 295. 数据流的中位数
1.题目要求 中位数是有序列表中间的数.如果列表长度是偶数,中位数则是中间两个数的平均值. 例如, [2,3,4] 的中位数是 3 [2,3] 的中位数是 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5 设计一个 ...
- CentOS 下安装 LEMP 服务(nginx、MariaDB/MySQL 和 php)
转载自:https://linux.cn/article-4314-1.html 编译自:http://xmodulo.com/install-lemp-stack-centos.html 作者: D ...
- idea 多模块引用
roma-server 引用common-utils的类,所以在roma-server 的pom中配置 <dependency> <groupId>org.springfram ...
- 前端为什么要对url进行编码
为什么要对url进行编码 url有规范,在参数值中出现&字符会截断参数 url中文的问题,编码客转换为英文 也是第一种情况,url中有个参数值是url,传输的时候会出现错误 例1 有这样一串参 ...
- Leetcode:52. N-QueensII
Description Follow up for N-Queens problem. Now, instead outputting board configurations, return the ...
- Eclipse srever起来时,时间超过45s。
双击servere的名字,在属性界面上进行修改. 如下图: 修改TimeOut中的值即可.
- OScached页面缓存的入门使用
OSCache的使用: 一,环境的搭建: 1,把oscache.jar file放在 /WEB-INF/lib 目录下(Put the oscache.jar file in the /WEB-INF ...
