详解linux io flush
通过本文你会清楚知道 fsync()、fdatasync()、sync()、O_DIRECT、O_SYNC、REQ_PREFLUSH、REQ_FUA的区别和作用。
fsync() fdatasync() sync() 是什么?
首先它们是系统调用。
fsync
fsync(int fd) 系统调用把打开的文件描述符fd相关的所有缓冲元数据和数据与都刷新到磁盘上(non-volatile storage)
fsync() transfers ("flushes") all modified in-core data of (i.e., modified buffer cache pages for) the file referred to by the file descriptor fd to the disk device (or other permanent storage device) so that all changed information can be retrieved even after the system crashed or was rebooted. This includes writing through or flushing a disk cache if present. The call blocks until the device reports that the transfer has completed. It also flushes metadata information associated with the file (see stat(2)).
fdatasync
fdatasync(int fd) 类似fsync,但不flush元数据,除非元数据影响后面读数据。比如文件修改时间元数据变了就不会刷,而文件大小变了影响了后面对该文件的读取,这个会一同刷下去。所以fdatasync的性能要比fsync好。
fdatasync() is similar to fsync(), but does not flush modified metadata unless that metadata is needed in order to allow a subsequent data retrieval to be correctly handled. For example, changes to st_atime or st_mtime (respectively, time of last access and time of last modification; see stat(2)) do not require flushing because they are not necessary for a subsequent data read to be handled correctly. On the other hand, a change to the file size (st_size, as made by say ftruncate(2)), would require a metadata flush.The aim of fdatasync() is to reduce disk activity for applications that do not require all metadata to be synchronized with the disk.
sync
sync(void) 系统调用会使包含更新文件的所有内核缓冲区(包含数据块、指针块、元数据等)都flush到磁盘上。
Flush file system buffers, force changed blocks to disk, update the super block
O_DIRECT O_SYNC REQ_PREFLUSH REQ_FUA 是什么?
它们都是flag,可能最终的效果相同,但它们在不同的层面上。
O_DIRECT O_SYNC是系统调用open的flag参数,REQ_PREFLUSH REQ_FUA 是kernel bio的flag参数。
要理解这几个参数要需要知道两个页缓存:
一个是你的内存,free -h可以看到的buff/cache;
另外一个是硬盘自带的page cache。
一个io写盘的简单流程如下:
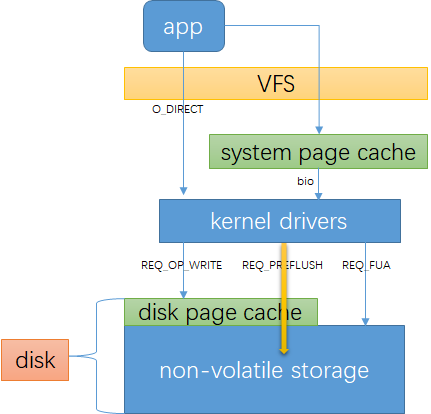
可以对比linux storage stack diagram:

O_DIRECT
O_DIRECT 表示io不经过系统缓存,这可能会降低你的io性能。它同步传输数据,但不保证数据安全。
备注:后面说的数据安全皆表示数据被写到磁盘的non-volatile storage
Try to minimize cache effects of the I/O to and from this
file. In general this will degrade performance, but it is
useful in special situations, such as when applications do
their own caching. File I/O is done directly to/from user-
space buffers. The O_DIRECT flag on its own makes an effort
to transfer data synchronously, but does not give the
guarantees of the O_SYNC flag that data and necessary metadata
are transferred. To guarantee synchronous I/O, O_SYNC must be
used in addition to O_DIRECT.
通过dd命令可以清楚看到 O_DIRECT和非O_DIRECT区别,注意buff/cache的变化:
#清理缓存:
#echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
#free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 62G 1.1G 61G 9.2M 440M 60G
Swap: 31G 0B 31G
#dd without direct
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 bs=1M count=1024
1024+0 records in
1024+0 records out
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB) copied, 27.8166 s, 38.6 MB/s
#free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 62G 1.0G 60G 105M 1.5G 60G
Swap: 31G 0B 31G
#echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
#free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 62G 626M 61G 137M 337M 61G
Swap: 31G 0B 31G
#dd with direct
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 bs=1M count=1024 oflag=direct
1024+0 records in
1024+0 records out
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB) copied, 2.72088 s, 395 MB/s
#free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 62G 628M 61G 137M 341M 61G
Swap: 31G 0B 31G
O_SYNC
O_SYNC 同步io标记,保证数据安全写到non-volatile storage
Write operations on the file will complete according to the
requirements of synchronized I/O file integrity completion
REQ_PREFLUSH
REQ_PREFLUSH 是bio的request flag,表示在本次io开始时先确保在它之前完成的io都已经写到非易失性存储里。
我理解REQ_PREFLUSH之确保在它之前完成的io都写到非易失物理设备,但它自己可能是只写到了disk page cache里,并不确保安全。
可以在一个空的bio里设置REQ_PREFLUSH,表示回刷disk page cache里数据。
Explicit cache flushes
The REQ_PREFLUSH flag can be OR ed into the r/w flags of a bio submitted from
the filesystem and will make sure the volatile cache of the storage device
has been flushed before the actual I/O operation is started. This explicitly
guarantees that previously completed write requests are on non-volatile
storage before the flagged bio starts. In addition the REQ_PREFLUSH flag can be
set on an otherwise empty bio structure, which causes only an explicit cache
flush without any dependent I/O. It is recommend to use
the blkdev_issue_flush() helper for a pure cache flush.
REQ_FUA
REQ_FUA 是bio的request flag,表示数据安全写到非易失性存储再返回
Forced Unit Access
The REQ_FUA flag can be OR ed into the r/w flags of a bio submitted from the
filesystem and will make sure that I/O completion for this request is only
signaled after the data has been committed to non-volatile storage.
实验验证
重新编译了bcache内核模块,打印出bio->bi_opf,opf是bio的 operation flag,它有req flag or组成,决定io的行为。
request flag
#from linux source code include/linux/blk_types.h
enum req_opf {
/* read sectors from the device */
REQ_OP_READ = 0,
/* write sectors to the device */
REQ_OP_WRITE = 1,
/* flush the volatile write cache */
REQ_OP_FLUSH = 2,
/* discard sectors */
REQ_OP_DISCARD = 3,
/* securely erase sectors */
REQ_OP_SECURE_ERASE = 5,
/* reset a zone write pointer */
REQ_OP_ZONE_RESET = 6,
/* write the same sector many times */
REQ_OP_WRITE_SAME = 7,
/* reset all the zone present on the device */
REQ_OP_ZONE_RESET_ALL = 8,
/* write the zero filled sector many times */
REQ_OP_WRITE_ZEROES = 9,
/* SCSI passthrough using struct scsi_request */
REQ_OP_SCSI_IN = 32,
REQ_OP_SCSI_OUT = 33,
/* Driver private requests */
REQ_OP_DRV_IN = 34,
REQ_OP_DRV_OUT = 35,
REQ_OP_LAST,
};
enum req_flag_bits {
__REQ_FAILFAST_DEV = /* 8 no driver retries of device errors */
REQ_OP_BITS,
__REQ_FAILFAST_TRANSPORT, /* 9 no driver retries of transport errors */
__REQ_FAILFAST_DRIVER, /* 10 no driver retries of driver errors */
__REQ_SYNC, /* 11 request is sync (sync write or read) */
__REQ_META, /* 12 metadata io request */
__REQ_PRIO, /* 13 boost priority in cfq */
__REQ_NOMERGE, /* 14 don't touch this for merging */
__REQ_IDLE, /* 15 anticipate more IO after this one */
__REQ_INTEGRITY, /* 16 I/O includes block integrity payload */
__REQ_FUA, /* 17 forced unit access */
__REQ_PREFLUSH, /* 18 request for cache flush */
__REQ_RAHEAD, /* 19 read ahead, can fail anytime */
__REQ_BACKGROUND, /* 20 background IO */
__REQ_NOWAIT, /* 21 Don't wait if request will block */
__REQ_NOWAIT_INLINE, /* 22 Return would-block error inline */
.....
}
bio->bi_opf 对照表
下面测试时候需要用到,可以直接跳过,有疑惑的时候回来查看。
| 十进制flag | 十六进制flag | REQ_FLG |
|---|---|---|
| 2409 | 1000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC |
| 4096 | 0001 0000 0000 0000 | REQ_META | REQ_READ |
| 34817 | 1000 1000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_IDLE |
| 399361 | 0110 0001 1000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_META | REQ_FUA | REQ_PREFLUSH |
| 264193 | 0100 0000 1000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_PREFLUSH |
| 165889 | 0010 1000 1000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_IDLE | REQ_FUA |
| 1048577 | 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_BACKGROUND |
| 0010 0000 1000 0000 0001 | REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_FUA |
测试
用测试工具dd对块设备/dev/bcache0直接测试。
笔者通过dd源码已确认:oflag=direct表示文件已O_DIRECT打开,oflag=sync 表示已O_SYNC打开,conv=fdatasync表示dd结束后会发送一个fdatasync(fd), conv=fsync表示dd结束后会发送一个fsync(fd)
- direct
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 oflag=direct bs=8k count=1
//messages
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 34817, size 8192
bi_opf 34817, size 8192:bi_opf = REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_IDLE,是一个同步写,可以看到不保证数据安全
- direct & sync
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 oflag=direct,sync bs=8k count=1
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 165889, size 8192
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 264193, size 0
bi_opf 165889, size 8192: bi_opf=REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_IDLE | REQ_FUA ,是一个同步写请求,并且该io直接写到硬盘的non-volatile storage
bi_opf 264193, size 0: bi_opf= REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_PREFLUSH ,size = 0,表示回刷disk的page cache保证以前写入的io都刷到non-volatile storage
通过这个可以理解O_SYNC为什么可以保证数据安全。
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 oflag=direct,sync bs=8k count=2
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() iop_opf 165889, size 8192
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() iop_opf 264193, size 0
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() iop_opf 165889, size 8192
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() iop_opf 264193, size 0
写两个io到设备,从上面可以看到以O_SYNC打开文件,每个write都会发送一个flush请求,这对性能的影响比较大,所以在一般实现中不已O_SYNC打开文件,而是在几个io结束后调用一次fdatasync。
- without direct
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 bs=8k count=1
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 2049, size 4096
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 2049, size 4096
bi_opf 2049, size 4096:bi_opf = REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC,同步写请求,可以看到原先8k的io在page cache里被拆成了2个4k的io写了下来,不保证数据安全
- direct & fdatasync
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 oflag=direct conv=fdatasync bs=8k count=1
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 34817, size 8192
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 264193, size 0
bi_opf 34817, size 8192:bi_opf = REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_IDLE, 同步写请求,这个不保证数据安全
bi_opf 264193, size 0:bi_opf = REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_PREFLUSH,一个disk page cache 回刷请求,这个就是fdatasync()下发的。
- direct & sync & fdatasync
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 oflag=direct,sync conv=fdatasync bs=8k count=1
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 165889, size 8192
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 264193, size 0
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 264193, size 0
bi_opf 165889, size 8192: bi_opf=REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_IDLE | REQ_FUA ,是一个同步写请求,并且该io直接写到硬盘的non-volatile storage
bi_opf 264193, size 0: bi_opf= REQ_OP_WRITE | REQ_SYNC | REQ_PREFLUSH ,size = 0,表示回刷disk的page cache保证以前写入的io都刷到non-volatile storage
结合上面的分析,这三个bio其实就是一个写io,两个flush io,分别由O_SYNC和fdatasync触发。
- direct & fsync
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/bcache0 oflag=direct conv=fsync bs=8k count=1
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 34817, size 8192
kernel: bcache: cached_dev_make_request() bi_opf 264193, size 0
同direct + fdatasync,应该是写的是一个块设备,没有元数据或元数据没有变化,所以fdatasync和fsync收到的bio是一样的
彩蛋
如何打开关闭硬盘缓存
查看当前硬盘写Cache状态
#hdparm -W /dev/sda
/dev/sda:
write-caching = 1 (on)
关闭硬盘的写Cache
#hdparm -W 0 /dev/sda
打开硬盘的写Cache
#hdparm -W 1 /dev/sda
详解linux io flush的更多相关文章
- Linux下ps命令详解 Linux下ps命令的详细使用方法
http://www.jb51.net/LINUXjishu/56578.html Linux下的ps命令比较常用 Linux下ps命令详解Linux上进程有5种状态:1. 运行(正在运行或在运行队列 ...
- linux dmesg命令参数及用法详解(linux显示开机信息命令)
linux dmesg命令参数及用法详解(linux显示开机信息命令) http://blog.csdn.net/zhongyhc/article/details/8909905 功能说明:显示开机信 ...
- 从苦逼到牛逼,详解Linux运维工程师的打怪升级之路
做运维也快四年多了,就像游戏打怪升级,升级后知识体系和运维体系也相对变化挺大,学习了很多新的知识点. 运维工程师是从一个呆逼进化为苦逼再成长为牛逼的过程,前提在于你要能忍能干能拼,还要具有敏锐的嗅觉感 ...
- 详解Linux运维工程师
运维工程师是从一个呆逼进化为苦逼再成长为牛逼的过程,前提在于你要能忍能干能拼,还要具有敏锐的嗅觉感知前方潮流变化.如:今年大数据,人工智能比较火……(相对表示就是 Python 比较火) 之前写过运维 ...
- 一文详解 Linux 系统常用监控工一文详解 Linux 系统常用监控工具(top,htop,iotop,iftop)具(top,htop,iotop,iftop)
一文详解 Linux 系统常用监控工具(top,htop,iotop,iftop) 概 述 本文主要记录一下 Linux 系统上一些常用的系统监控工具,非常好用.正所谓磨刀不误砍柴工,花点时间 ...
- 详解Linux交互式shell脚本中创建对话框实例教程_linux服务器
本教程我们通过实现来讲讲Linux交互式shell脚本中创建各种各样对话框,对话框在Linux中可以友好的提示操作者,感兴趣的朋友可以参考学习一下. 当你在终端环境下安装新的软件时,你可以经常看到信息 ...
- linux useradd(adduser)命令参数及用法详解(linux创建新用户命令)
linux useradd(adduser)命令参数及用法详解(linux创建新用户命令) useradd可用来建立用户帐号.帐号建好之后,再用passwd设定帐号的密码.而可用userdel删除帐号 ...
- 详解linux运维工程师入门级必备技能
详解linux运维工程师入门级必备技能 | 浏览:659 | 更新:2013-12-24 23:23 | 标签:linux it自动化运维就是要很方便的运用各种工具进行管理维护,有效的实施服务器保护 ...
- watch命令详解(linux)
watch命令详解(linux) 在维护系统时经常需要实时查看系统的运行情况,比如实时的系统连接数之类的.在linux可以通过watch命令,实时监控每一条命令执行的结果动态变化. ...
随机推荐
- 【转】通俗理解Java序列化与反序列化
一.序列化和反序列化的概念 把对象转换为字节序列的过程称为对象的序列化. 把字节序列恢复为对象的过程称为对象的反序列化. 对象的序列化主要有两种用途: 1) 把对象的字节序列永久地保存到硬盘上,通常存 ...
- JS方法使用中文出参数 ,报错异常
正常这样加载数字没问题,但是当参数是中文时就会报错 <li onclick='onSeach(‘’" + name+ "');'>" + name+ &quo ...
- Python之反向迭代
需求:得到反方向迭代一个序列解决:使用内置的 reversed() 函数 a = [1, 2, 3, 4] for x in reversed(a): print(x) # 4 3 2 1 反向迭代仅 ...
- 【学习总结】Python-3-字符串函数split()的妙用
参考: 菜鸟教程-Python3-Python字符串-split() 语法: str.split(str="", num=string.count(str)) 参数 str -- ...
- go中字符串类型string的用法
示例 // 字符串类型string的用法 package main import ( "fmt" "unsafe" ) func main() { // 字符串 ...
- Web前端基础学习-1
HTML5/CSS简介 首先来说一说什么是HTML5,HTML5可以认为是字面上的意义,也就是HTML的第五代产品,当然从另一个角度来说它是一种新的富客户端解决方案. HTML5 将成为 HTML.X ...
- django框架常用的数据库迁移命令
python manage.py makemigrations 默认所有修改过的model层转为迁移文件 python manage.py migrate 默认将所有的迁移文件都执行,更新数据库 ...
- Opacity函数-transparentize()、 fade-out()函数
transparentize() 和 fade-out() 函数所起作用刚好与 opacify() 和 fade-in() 函数相反,让颜色更加的透明.这两个函数会让透明值做减法运算,当计算出来的结果 ...
- Git初始化本地仓库及管理远程仓库github
1.首先在本地安装git,地址:https://git-scm.com/downloads.下载安装好git工具. 2.将自己在github上的注册的用户名和邮箱写入本地git的配置文件中: (1). ...
- $NOIP2018$ 爆踩全场记
NOIP2018 Day-1 路还很长. 这里就是起点. 这是最简单的一步,但这是最关键的一步. 联赛就在眼前了,一切好像都已经准备好了,一切好像又都没准备好. 相信自己吧,\(mona\),这绝对不 ...
