Java第09次实验(IO流)--实验报告
0.字节流与二进制文件
我的代码
- 用DataOutputStream和FileOutputStream将Student对象写入二进制文件student.data
package test;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class StudentFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String fileName = "d:/student.data";
try (DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName))) {
Student s = new Student(1, "wang", 19, 89);
dos.writeInt(stu1.getId());
dos.writeUTF(stu1.getName());
dos.writeInt(stu1.getAge());
dos.writeDouble(stu1.getGrade());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try (DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName))) {
int id = dis.readInt();
String name = dis.readUTF();
int age = dis.readInt();
double grade = dis.readDouble();
Student stu = new Student(id, name, age, grade);
System.out.println(stu);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
我的总结
- 二进制文件与文本文件的区别
- 二进制文件可以储存基本数据类型的变量
- 文本文件只能储存基本数据类型中的char类型变量。
- try...catch...finally的注意事项
- catch多个异常时要注意异常的先后顺序。父类异常应放在最后。
- 使用try...catch...resouces关闭资源
- 可以直接在try后面加一个括号,在括号中定义最后要关闭的资源。这样,不需要在catch后面加上finally,程序运行结束之后资源会自动关闭。
1.字符流与文本文件
我的代码
- 使用BufferedReader从编码为UTF-8的文本文件中读出学生信息,并组装成对象然后输出。
package test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName="d:/Students.txt";
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr))
{
String line=null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
{
String[] msg=line.split("\\s+");
int id=Integer.parseInt(msg[0]);
String name=msg[1];
int age=Integer.parseInt(msg[2]);
double grade=Double.parseDouble(msg[3]);
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
studentList.add(stu);
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(studentList);
}
}
- 编写public static ListreadStudents(String fileName);从fileName指定的文本文件中读取所有学生,并将其放入到一个List中
public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName)
{
List<Student> stuList = new ArrayList<>();
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr))
{
String line=null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
{
String[] msg=line.split("\\s+");
int id=Integer.parseInt(msg[0]);
String name=msg[1];
int age=Integer.parseInt(msg[2]);
double grade=Double.parseDouble(msg[3]);
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
stuList.add(stu);
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stuList;
}
- 使用PrintWriter将Student对象写入文本文件
package test;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String fileName = "d:/Students.txt";
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName, true);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "UTF-8");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(osw)) {
pw.println("1 zhang 18 85");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 使用ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream读写学生对象。
package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String fileName="d:/Students.dat";
try(
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName);
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos))
{
Student ts=new Student(1,"lily",64,90);
oos.writeObject(ts);
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
Student newStudent =(Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(newStudent);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
我的总结
- 在构造FileOutputStream时应该多传一个true来避免PrintWriter直接覆盖原文件。
- writeObject()函数的作用:让实例以文件的形式保存在磁盘上。
2.缓冲流
我的代码
- 使用PrintWriter往文件里写入一千万行的随机整数,范围在[0,10],随机种子为100.
package test;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Random;
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String fileName = "d:/bigdata.txt";
int n = 1000_0000;
Random r = new Random(100);
try(PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fileName)){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
pw.println(r.nextInt(11));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- JUNIT测试部分,测试BufferedReader与Scanner的读文件的效率
package test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class TestRead {
String fileName = "d:/bigdata.txt";
/*BufferedReader读取文件*/
@Test
void testB() {
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(fileName)))){
String str = null;
int count = 0;
long sum = 0;
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
sum += num;
count++;
}
System.out.println("BufferedReader:");
System.out.format("count=%d,sum=%d,average=%.5f\n",count,sum,sum*1.0/count);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*Scanner读取文件*/
@Test
void testS() {
try(Scanner sc = new Scanner(new File(fileName))){
int count = 0;
long sum = 0;
while(sc.hasNextLine()) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
count++;
sum += num;
}
System.out.println("Scanner:");
System.out.format("count=%d,sum=%d,average=%.5f\n",count,sum,sum*1.0/count);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- JUNIT测试结果
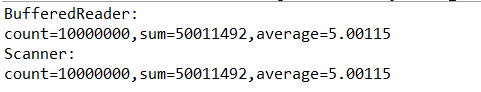
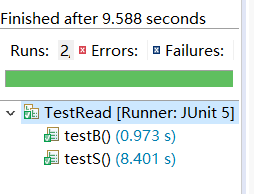
我的总结
- 一开始的时候,我把Random放在了try…catch的for循环里面,导致每次都新建一个随机种子为100的Random对象,导致每次生成的数字都是4,在老师的提醒下,才发现Random类对象只要定义一个就好了。
- 将随机数写入文件的时候,一开始我忘记设置随机种子了,导致文件中的数据平均值不是一个定值。
- JUNIT中要测试的方法前要加上@Test。
3.字节流之对象流
结合使用ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream与FileInputStream、FileOuputStream实现对Student对象的读写。
编写如下两个方法:
- public static void writeStudent(List stuList)
- public static List readStudents(String fileName)
我的代码
public static void writeStudent(List<Student> stuList)
{
String fileName="d:/Students.dat";
try ( FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName);
ObjectOutputStream ois=new ObjectOutputStream(fos))
{
ois.writeObject(stuList);
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName)
{
List<Student> stuList=new ArrayList<>();
try ( FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
stuList=(List<Student>)ois.readObject();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stuList;
}
我的总结
- 使用对象流的时候,写入的是一个对象,而不是多个对象。所以在读取的时候不能像BufferedReader一样一行一行的读取,而是直接读取出一个集合。
5.文件操作
编写一个程序,可以根据指定目录和文件名,搜索该目录及子目录下的所有文件,如果没有找到指定文件名,则显示无匹配,否则将所有找到的文件名与文件夹名显示出来。
编写public static void findFile(Path dir,String fileName)方法.
以dir指定的路径为根目录,在其目录与子目录下查找所有和filename
相同的文件名,一旦找到就马上输出到控制台。
我的代码
递归方法
package test;
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Path dir = Paths.get("D:\\", "testStream", "5");
findFile(dir, "c.txt");
}
public static void findFile(Path dir, String fileName) {
File file = dir.toFile();
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File now : files) {
if (now.isFile()) {
if (now.getName().equals(fileName)) {
System.out.println(now.getAbsolutePath());
return;
}
} else if (now.isDirectory()) {
findFile(now.toPath(), fileName);
}
}
}
}
我的总结
- File类和Path类可以互相转化。
- Paths类可以直接获得Path对象。
6.正则表达式
我的代码
- 如何判断一个给定的字符串是否是10进制数字格式?尝试编程进行验证。
package test;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
Pattern pattern=Pattern.compile("^[+-]?[0-9]+(\\.\\d+)?");
Matcher matcher=null;
while(sc.hasNext())
{
String str=sc.next();
matcher=pattern.matcher(str);
System.out.println(matcher.matches());
}
sc.close();
}
}
- 修改HrefMatch.java
- 匹配网页中的数字字符串
package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.PatternSyntaxException;
public class HrefMatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try
{
// get URL string from command line or use default
String fileName="D:\\test\\File\\HrefMatch.htm";
// open reader for URL
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName));
// read contents into string builder
StringBuilder input = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while ((ch = in.read()) != -1)
input.append((char) ch);
String patternString = "[+-]?[0-9]+(\\.\\d+)?";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input);
while (matcher.find())
{
int start = matcher.start();
int end = matcher.end();
String match = input.substring(start, end);
System.out.println(match);
}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (PatternSyntaxException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
我的总结
- 正则表达式理解的还不是很透彻,匹配图片字符串的要求还没有完成。
Java第09次实验(IO流)--实验报告的更多相关文章
- Java第09次实验(IO流)-实验报告
0. 字节流与二进制文件 使用DataOutputStream与FileOutputStream将Student对象写入二进制文件student.data 二进制文件与文本文件的区别 try...ca ...
- Java输入、输入、IO流 类层次关系梳理
本文主要关注在Java编程中涉及到的IO相关的类库.方法.以及对各个层次(抽线.接口继承)的流之间的关系进行梳理 相关学习资料 http://baike.baidu.com/view/1007958. ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记71:NIO之 NIO的(New IO流)介绍
1. I/O 简介 I/O ( 输入/输出 ):指的是计算机与外部世界或者一个程序与计算机的其余部分的之间的接口.它对于任何计算机系统都非常关键,因而所有 I/O 的主体实际上是内置在操作系统中的. ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记68:Properties和IO流集合使用
1. Properties和IO流集合使用 这里的集合必须是Properties集合: public void load(Reader reader):把文件中的数据读取到集合中 public v ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记66:Properties的概述 和 使用(作为Map集合使用)
1. Properties的概述 Properties:属性集合类.是一个可以和IO流相结合使用的集合类. 该类主要用于读取以项目的配置文件(以.properties结尾的文件 和 xml文件). ...
- Java笔记(二十六)……IO流上 字节流与字符流
概述 IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输 Java对数据的操作时通过流的方式 Java用于操作流的对象都在IO包中 流按操作的数据分为:字节流和字符流 流按流向不同分为:输入流和输出流 IO流常用基类 ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记22:FileInputStream / FileOutputStream 复制文本文件案例1
1. 使用字节流FileInputStream / FileOutputStream 复制文本文件案例: 分析: (1)数据源:从哪里来 a.txt -- 读取数据 -- FileInpu ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记17:FileOutputStream构造方法使用
1. 可以参照之前写的笔记: Android(java)学习笔记167:Java中操作文件的类介绍(File + IO流) 2. FileOutputStream(常用的)构造方法: FileOu ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记16:IO流的概述和分类
1. IO流的分类 流向: (1)输入流:读取数据到内存 (2)输出流:写入数据到硬盘(磁盘) 操作的数据类型: (1)字节流:操作的数据是字节 ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记01:异常的概述和分类
IO流操作的时候会出现很多问题,java中叫作异常,所以我们先介绍一下异常: 1. 程序的异常:Throwable(Throwable类是java中所有异常或错误的超类) (1)严重问题:Error ...
随机推荐
- sql server SQL 服务器 - RDBMS
SQL 服务器 - RDBMS --现代的 SQL 服务器构建在 RDBMS 之上. DBMS - 数据库管理系统(Database Management System) --数据库管理系统是一种可以 ...
- io:轻松地创建缓存
介绍 io模块是python中专门用来进行流处理的模块 StringIO 提供字符串形式的缓存,可以不断地往里面写入数据,最后一次性读出 import io # 创建相应的缓存 buf = io.St ...
- 关于windows下无法删除文件,需要TrueInstaller权限的问题
笔者办公室的笔记本今天突然弹出来一个ie浏览器,这不是为了下载其他浏览器而存在的浏览器吗?现在还臭不要脸的弹出来,然鹅我在删除文件夹的时候,提示我无法删除,必须要有TrueInstaller的权限,那 ...
- Bss段的作用及初始化
初始化的全局变量:数据段 局部变量:栈 malloc:堆 未初始化的全局变量:Bss段 arm-linux-readelf -a 应用程序 可查看文件运行架构.大小端.共享库等信息 初始化Bss ...
- dpkg -i libequinox-osgi-java_3.8.1-8_all.deb
dpkg -i libequinox-osgi-java_3.8.1-8_all.deb dpkg -i libequinox-osgi-java_3.8.1-8_all.deb https://ww ...
- Nginx 的简介
1. 什么是 nginx :Nginx 是高性能的 HTTP 和反向代理的服务器,处理高并发能力是十分强大的,能经受高负 载的考验,有报告表明能支持高达 50,000 个并发连接数. 2. 正向代理 ...
- 阿里云--安装nginx AND访问超时
首先先安装PCRE pcre-devel 和Zlib,因为配置nginx的时候会需要这两个东西PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions) 是一个Perl库,包括 ...
- repo 回退当前分支下所有仓库到指定日期前的最新代码版本
回退命令: repo forall -c 'commitID=git log --before "2019-11-24 23:59" -1 --pretty=format:&quo ...
- window下,nodejs安装http-server,并开启HTTP服务器
1.下载nodejs 官方下载地址:https://nodejs.org/en/ 2.在cmd命令中,输入node -v 输入出版本号,代表安装成功. 3.输入 npm install http-s ...
- [深度学习] pytorch学习笔记(1)(数据类型、基础使用、自动求导、矩阵操作、维度变换、广播、拼接拆分、基本运算、范数、argmax、矩阵比较、where、gather)
一.Pytorch安装 安装cuda和cudnn,例如cuda10,cudnn7.5 官网下载torch:https://pytorch.org/ 选择下载相应版本的torch 和torchvisio ...
