springboot项目抓数据后优化配置及四个补充
昨天搞了一个抓取某某平台信息的抓取功能,其中有一个地址url,昨天是写死的,之前也进行配置过,印象有些模糊,今天想配置一下,在properties文件中,由此引发了下面的一系列总结操作:
1、原始模式,引用加载模式
我所说的这种方式是通过直接代码引用文件方式,如下:
//引入的相关类
import org.apache.commons.configuration.PropertiesConfiguration;
import org.apache.commons.configuration.reloading.FileChangedReloadingStrategy;
//properties_file为 src/main/resource下的路径 比如 configuration/application.properties
PropertiesConfiguration conf = new PropertiesConfiguration(properties_file_name);
//这步我认为是很有意义的
//配置文件修改后自动重新加载
Configuration configuration = conf.setReloadingStrategy(new FileChangedReloadingStrategy());
//然后通过 configuration 的相关方法就可以获取到key对应的value
String value = configuration.getString("key")
2、springboot项目自动加载模式
springboot项目加载的默认配置文件是在 src/main/resource 目录下的application.properties文件信息,可以再该文件中进行配置,例如:
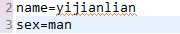
然后在所写的组件类中
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
//使用该方法就可回去属性文件中的对应的name value值
environment.getProperty("name");
3、springboot项目手动加载模式
这种方式可以有多种方式进行加载,这里进行介绍,单key加载和多key加载
单key加载:通过对单个key对应的value值逐一加载
//这里是自己所定义的属性文件key:value信息
person.name=yijianlian
person.sex =man @Component
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class PropertiesConfig { @Value("${person.name}")
public String name; @Value("${person.sex}")
public String sex ; //getter setter .. //constructor .. }
多key加载: 多key一次性加载 如下
//这里是自己所定义的属性文件key:value信息
person.name=yijianlian
person.sex =man
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") //绑定配置文件的值
public class PropertiesConfig { public String name; public String sex ; public PropertiesConfig() {
super();
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getSex() {
return sex;
} public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
补充一、yaml用法:
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的,大小写敏感
k:(空格)v: #空格不能省
#k: v:字面直接来写;
# 字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
# "":双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
# name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
# '':单引号;会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
# name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’:输出;zhangsan \n lisi
表示对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对)语法:
k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进,对象还是k: v的方式
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
行内写法:
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 18}
表示数组的语法
用- 值表示数组中的一个元素(- 和属性之间空格不能省)
pets:#(数组名)
- cat#(属性)
- dog#(属性)
- pig#(属性)
行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
如:
package com.byls.springbootdemo.bean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中
* @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定;
* prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射
*
* 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能;
*
*/
@Component//将Person类注册到容器中
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") //绑定配置文件的值
public class Person {
private String lastName;//名字
private Integer age;//年龄
private Boolean boss;//是否是老板
private Date bir;//生日 private Map<String,Object> maps;//map集合
private List<Object> lists;//list集合
private Dog dog;//Dog类对象 只有name 和 age属性 public Person() {
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", boss=" + boss +
", bir=" + bir +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
} public Person(String lastName, Integer age, Boolean boss, Date bir, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) {
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
this.boss = boss;
this.bir = bir;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
this.dog = dog;
} public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
} public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
} public void setBoss(Boolean boss) {
this.boss = boss;
} public void setBir(Date bir) {
this.bir = bir;
} public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
} public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
} public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
} public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
} public Integer getAge() {
return age;
} public Boolean getBoss() {
return boss;
} public Date getBir() {
return bir;
} public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
} public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
} public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
}
对应的yaml文件为:
person:
name: byls
age: 22
boss: true
bir: 2017/12/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- zs
- ls
dog:
name: baibai
age: 10
补充二:@ConfigurationProperties 和@Value 区别
前者是 批量注入配置文件中的属性,后者是单个注入,同时后者在业务逻辑中需要获取某个属性值时使用。
相同点,若没有指定特定文件时如:@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties") ,两者指定的公有文件都是默认配置文件application.properties或者application.yml
例如:
package com.byls.springbootdemo.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /**
* @Value的一个简单的使用场景例子
*/
@RestController //@ResponseBody和@Controller的结合
public class HelloController {
@Value("${person.name}")//使用@Value从配置文件中取单个值
private String name; @RequestMapping("/hello")//设置请求路径
public String hello(){
return "hello"+name;
}
}
补充三:springboot 中创建组件两种方式:
方式一:
@ImportResource 注解方式:
创建一个hello.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--向spring容器中添加helloService组件-->
<bean id="helloService" class="com.test.HelloService"></bean>
</beans>
然后在主函数中注解加入:
/**
* springboot主程序入口类
*/
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:hello.xml"})//依赖注入方式
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
} }
进行测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootDemoApplicationTests { @Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationIoc; //spring容器对象 @Test
public void testHelloService(){
//判断容器中是否包含某个bean 包含为true 反之为false
boolean flag = applicationIoc.containsBean("helloService"); } }
方式二:配置注入@Configuration和@Bean组合
/**
* 配置类
*/
@Configuration//指定这是一个配置类,用于替代之前的配置文件
public class HelloConfigution { //将方法的返回值添加到容器中,容器中组件的id就是方法的返回值
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService();
}
}
补充四:@Controller 和@RestController 区别
@RestController注解相当于@ResponseBody + @Controller合在一起的作用
如果只是使用@RestController注解Controller,则Controller中的方法无法返回jsp页面,
配置的视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver则不起作用,返回的内容就是Return 里的内容(String/JSON)
如果使用@RestController注解Controller,需要返回到指定页面,
则需要配置视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver,可以利用ModelAndView返回试图
如果使用@Controller注解Controller,如果需要返回JSON,XML或自定义mediaType内容到页面
则需要在对应的方法上加上@ResponseBody注解,以下两种方式均可


springboot项目抓数据后优化配置及四个补充的更多相关文章
- springboot项目启动成功后执行一段代码的两种方式
springboot项目启动成功后执行一段代码的两种方式 实现ApplicationRunner接口 package com.lnjecit.lifecycle; import org.springf ...
- springboot项目实现jar包外配置文件管理
背景 为实现快速搭建和开发,项目以Springboot框架搭建,springboot搭建的项目可以将项目直接打成jar包并运行,无需自己安装配置Tomcat或者其他服务器,是一种方便快捷的部署方式. ...
- springboot项目启动之后初始化自定义配置类
前言 今天在写项目的时候,需要再springboot项目启动之后,加载我自定义的配置类的一些方法,百度了之后特此记录下. 正文 方法有两种: 1. 创建自定义类实现 CommandLineRunner ...
- Springcloud/Springboot项目绑定域名,使用Nginx配置Https
https://blog.csdn.net/a_squirrel/article/details/79729690 一.Https 简介(百度百科) HTTPS(全称:Hyper Text Trans ...
- SpringBoot:使用Jenkins自动部署SpringBoot项目(二)具体配置
1.启动Jenkins 在浏览器输入ip:port后,进入Jenkins初始化界面,需要查看文件,得到密码. 输入密码进入初始化界面,选择推荐插件安装. 安装完成创建账号,进入Jenkins主界面. ...
- Springboot项目绑定域名,使用Nginx配置Https
一.https 简介 HTTPS(全称:Hyper Text Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer),是以安全为目标的HTTP通道,简单讲是HT ...
- SpringBoot项目修改html后不即时编译
springboot templates 下的 html 修改后无法达到即时编译的效果,搜索资料后记录笔记.原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiangbei/p/843939 ...
- springboot项目更改代码后实时刷新问题
在spring boot使用的过程中, 发现我修改了静态文件, 前台刷新后, 没有任何变化, 必须重新启动, 才能看到, 这简直不能让人接受. 那有什么方法来解决这个问题呢. Baidu之后, 得到了 ...
- springboot 项目打包部署后设置上传文件访问的绝对路径
1.设置绝对路径 application.properties的配置 #静态资源对外暴露的访问路径 file.staticAccessPath=/upload/** #文件上传目录(注意Linux和W ...
随机推荐
- 4000余字为你讲透Codis内部工作原理
一.引言 Codis是一个分布式 Redis 解决方案,可以管理数量巨大的Redis节点.个推作为专业的第三方推送服务商,多年来专注于为开发者提供高效稳定的消息推送服务.每天通过个推平台下发的消息数量 ...
- Idea如何生成JPA的相关model,以及运行JPA项目的时候启动错误
1.如何生成JPAmodel 按照顺序执行下面的步骤 为指定的项目添加JPA的配置,这样之后生成的model就会在指定的项目内 选择JPA之后默认不用操作直接添加 没有Persistence的可以在w ...
- linux 系统的 cache 过大,解决方案
linux buff/cache过大,清理脚本 2018年06月20日 13:44:53 taozhe666 阅读数:6500 三条指令: sync echo 1 > /proc/sys/v ...
- mongo 生命周期
监听MongoDB的生命周期,只需重写org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.event.AbstractMongoEventListener的子类 ...
- Laravel 在构造方法中使用session
- Servlet基础总结
1.Servlet概念: Java Servlet 是运行在 Web 服务器或应用服务器上的程序,它是作为来自 Web 浏览器或其他 HTTP 客户端的请求和 HTTP 服务器上的数据库或应用程序之间 ...
- android 面试汇总<一>
1.1 Android Activity Q:说下Activity的生命周期? 技术点:Activity生命周期 思路:分条解释Activity从创建到销毁整个生命周期中涉及到的方法及作用 参考回答: ...
- linux(centOS7)的基本操作(四) 定时任务——crontab
概述 对于Java开发人员,定时任务并不陌生,无非是让系统在特定时间执行特定的命令或程序.例如spring提供的@Scheduled注解.OpenSymphony提供的quartz框架,都可以实现定时 ...
- 阶段3 2.Spring_06.Spring的新注解_8 spring整合junit完成
Junit的核心Runner在执行的时候不会创建容器.同时它字节码文件,也改不了 spring整合junit 想办法把junit里面的不能加载容器的main方法换掉.从而实现创建容器.有了容器就可以实 ...
- java:JavaScript3(innerHTML,post和get,单选框,多选框,下拉列表值得获取,JS中的数组,JS中的正则)
1.innerHTML用户登录验证: <!DOCTYPE> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> ...
