DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.7

上代码:
x1 = rand(1,11); x2 = rand(1,11); n = 0:10;
alpha = 2; beta = 3; k = 0:500;
w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. X1 = x1 * (exp(-j*pi/500)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x1
X2 = x2 * (exp(-j*pi/500)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x2 x = alpha * x1 + beta * x2; % Linear combination of x1 & x2
X = x * (exp(-j*pi/500)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x magX1 = abs(X1); angX1 = angle(X1); realX1 = real(X1); imagX1 = imag(X1);
magX2 = abs(X2); angX2 = angle(X2); realX2 = real(X2); imagX2 = imag(X2);
magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X); %verification
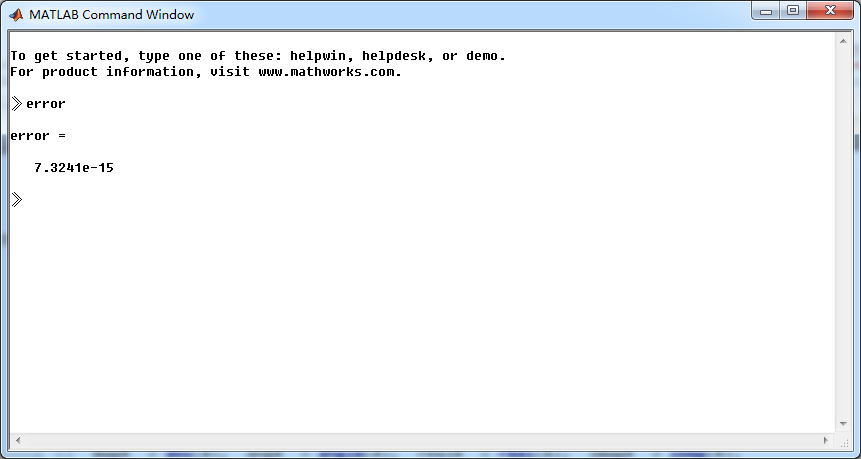
X_check = alpha*X1 + beta*X2; % Linear combination of X1 & X2
error = max(abs(X-X_check)); % Difference %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X1's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X1 its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX1); grid on; % axis([-2,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X1|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX1/pi); grid on; % axis([-2,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX1); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX1); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X1's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
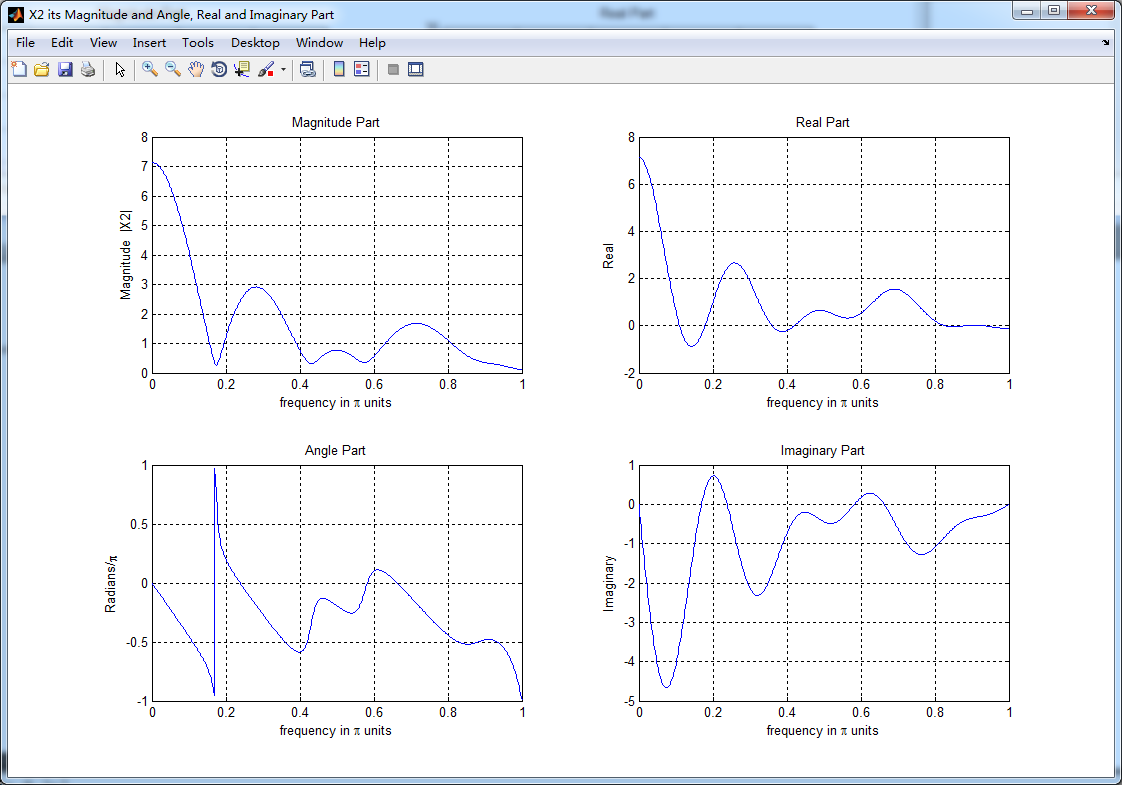
%% START X2's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X2 its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX2); grid on; % axis([-2,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X2|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX2/pi); grid on; % axis([-2,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX2); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX2); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X2's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
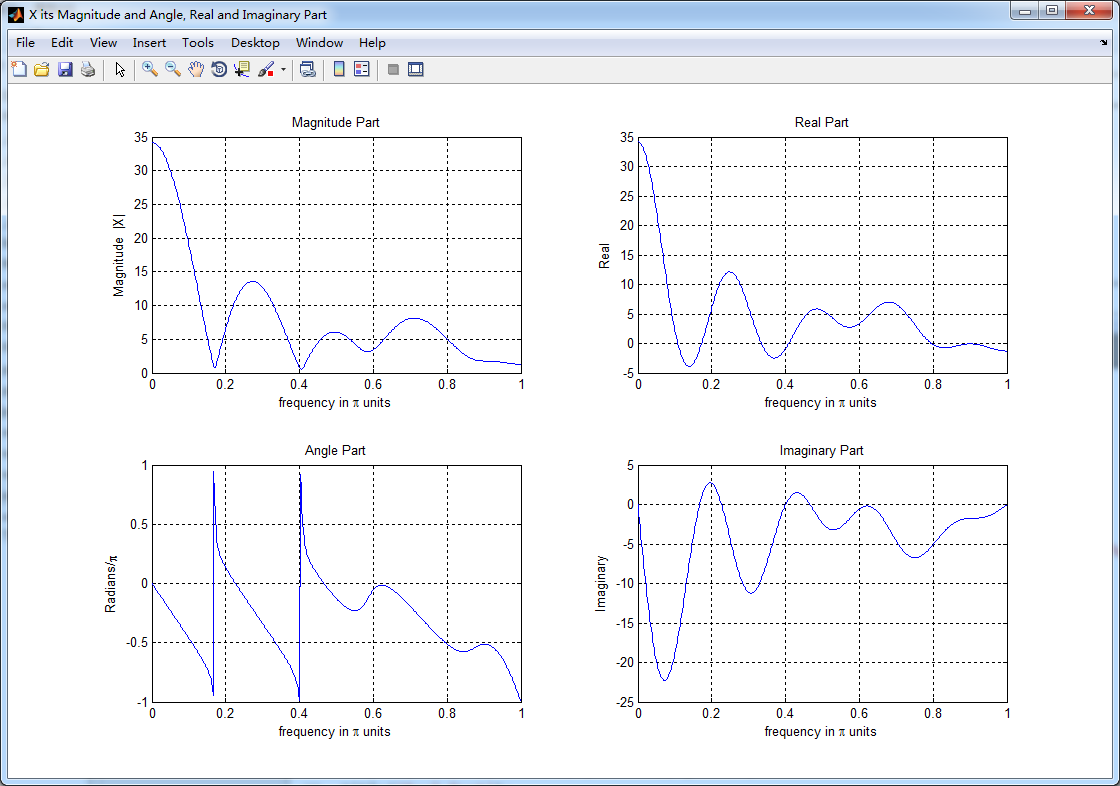
%% START X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; % axis([-2,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX/pi); grid on; % axis([-2,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
结果:

DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.7的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
随机推荐
- codeforces gym 100286 I iSharp (字符串模拟)
题目链接 给定一个字符串.输入是int& a*[]&, b, c*; 输出是 int&&[]* a;int& b;int&* c; 输入格式里逗号后面一 ...
- eclipse的使用一
The type java.lang.Object cannot be resolved. It is indirectly referenced from required .class files ...
- ASP.Net后台 实现先弹出对话框,再跳转到另一个网页的实现方法
解决办法如下: Response.Write("<script>alert('想在对话框中显示的内容');window.navigate(‘要转到的页面的URL’)</sc ...
- 用 MyEclipse 开发 Spring 入门操作
何为Spring Spring框架是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC)技术和面向切面编程(AOP)技术的容器框架,利用Spring框架可以实现对象的生命周期管理和分离应用系统中的业务逻辑组件和通用的技术服 ...
- eclipse maven新建springMVC项目(原创)
1.配置eclipse maven 2.新建maven项目 3.新建src/main/java,更新pom <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.or ...
- Genymotion
@Genymotion相关文件下载地址 http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nu9nReh @虚拟机网络代理设置 Normal 0 7.8 磅 0 2 false false false ...
- ASP.NET MVC中的Razor语法
1.Razor的基本语法 @* 多行代码时需要包含在大括号内{}和每句代码后都需要加分号; *@ @{ ViewBag.Title = "Index"; ViewBag.Name ...
- Delphi强制类型转化和类型约定
强制类型转换时一种技术,通过它能够使编译器把一种类型的变量当做另一种类型. 由于Pascal有定义新类型的功能,因此编译器在调用一个函数时候对形参和实参类型匹配的检查是非常严格的.因此为了能够通过编译 ...
- Pyqt QListWidget 展示系统环境变量
今天学习了下Pyqt的 QListWidget 控件 我们先看下这个图片 这张图片就是典型的listWidget效果,我们今天就仿这样布局新建个ListWidget 在网上找了个关于QListWidg ...
- Big Data, MapReduce, Hadoop, and Spark with Python
此书不错,很短,且想打通PYTHON和大数据架构的关系. 先看一次,计划把这个文档作个翻译. 先来一个模拟MAPREDUCE的东东... mapper.py class Mapper: def map ...
