OpenStack with Opendaylight Part 1: Intro to Pipeline
Using Vagrant to create vm nodes; devstack to start openstack using Opendaylight as ML2.
Openstack with Opendaylight deployment
Starting Openstack with Opendaylight has gotten a bit easier, but it is still something many folks have not done due to the potential pitfalls involved. In this page, I will show a few steps using Vagrant to stamp out 2 nodes to get the ball rolling. I will also focus on how ODL's OVSDB implementation creates a pipeline table [of openflow rules], that provides for tenant isolation on network overlay.
To keep it simpler, I will have Opendaylight running inside the Openstack's control node. That saves us from using another VM or running ODL in the host system. That is not a big deal for this experiment. Also in name of simplicity, I will refrain from getting into pipeline rules on L3 forwarding -- which is actually a fun subject I've been playing with. We'll save that for part 2 of this blog.
A simple diagram to show the vms (and their nested vms) is here:
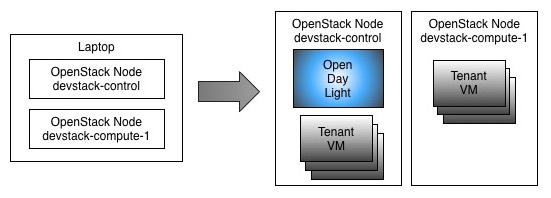
To get things going faster, I'm assuming that you have a hypervisor and Vagrant installed. I use Virtual Box, but you should be able to use anything supported by Vagrant. The only caveat on that is that you may need to hunt for a Vagrant box that suits your hypervisor. The Bento project may be a good place for that, if you are in such predicament. :) To help folks running Vmware fusion, I've already added hooks in the Vagrantfile.
Start off by cloning this github project. Please note we will be using a specific branch to pick up some scripts and config tailored to this tutorial:
$ git clone -b blogDemo https://github.com/flavio-fernandes/devstack-nodes.git odldemo
$ cd odldemo
The Vagrantfile is here. That uses puppet standalone mode, which uses hosts.json, located under puppet/hieradata. Feel free to change any values to make sense to your system config. After that, all you need to do is:
$ time vagrant up ; # this can take a little over 18 minutes on my macbook pro (Late 2013) ...
Go Devstack!
In order to configure Openstack, the Vagrant provisioning will pull in devstack -- Kilo release -- and add a local.conf file for each vm. That will be located at /home/vagrant/devstack directory. A few highlights on the local.conf is in order.
First, you can notice that all vms are using the OpenDaylight ML2 MechanismDriver as plugin. That is accomplished by addingenable_plugin networking-odl as shown in local.conf for control and compute nodes. More details on using this plugin is availablehere. Note that in the enable_plugin syntax you can specify different git repo than the official one, as well as any branch. If no branch is specified, it will use master. For sake of this blog, I'm using my forked Github repo, branch heliumkilo, which contains some specifictweaks needed.
Secondly, since ODL is running in the allinone mode and that is the default, there is no need to have it explicitly mentioned. Otherwise, that would require the ODL_MODE to be provided, as described here. Together with that, note that the ip address used to describe where ODL is has the same value as the control node. When launching ODL externally, make sure to load the following karaf feature:feature:install odl-ovsdb-openstack. You can do that at the Karaf prompt or in the file etc/org.apache.karaf.features.cfg. The ODL provisioning script for allinone does that as shown here.
Another attribute in local.conf to point out is the ODL_PORT. When ODL is co-located with control, there is a potential for the northbound neutron server in ODL to conflict with Swift. However, ODL will use port 8080 by default and networking-odl (i.e. the ml2) needs to be aware of that. This is particularly important when we are not using the allinone mode. Since in this experiment we have Swift disabled, we can let co-located ODL 'own' 8080.
Lastly, I would like to mention about ODL_BOOT_WAIT in local.conf. Because I'm using VMs in a laptop and ODL takes a while to load up all the bundles at start up, I need to make stack wait for a bit. Short of doing that could expose a bug where net-virt is not ready, but OVS southbound events may come in too early. Addressing this issue is in the Lithium roadmap.
At this point, once you get everything to look the way you want, run the following scripts:
$ vagrant ssh devstack-control
$ cd devstack/ && ./stack.sh ### first stack can take a while.... time for coffee break?!? $ vagrant ssh devstack-compute-1
$ cd devstack/ && ./stack.sh
Note: devstack is not the most stable environment, due to its high level of activity. If you hit an issue with stacking, use ./unstack.shand/or vagrant reload; and start stack.sh over. Odds are you will not need that, tho.
Once that is done, you can 'lock down' the stack repo used by changing the following values in local.conf (on both control and compute nodes):
OFFLINE=True
RECLONE=no
Tenants Topology
Here is the very simple network topology of the openstack nodes we will be using for this experiment:
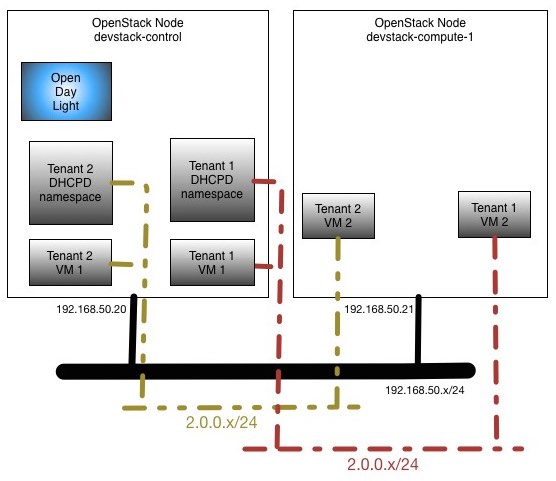
Since part of the stacking involves getting OVS in each of the nodes connecting to ODL as manager, you should be able to see that OVS is connected and bridge br-int was created. That must be the case before we do any further openstack config, on both control and compute nodes:
vagrant@devstack-control:~/devstack$ sudo ovs-vsctl show
39745b5b-2ff9-416b-ab3e-f1b81fd29fd7
Manager "tcp:192.168.50.20:6640"
is_connected: true
Bridge br-int
Controller "tcp:192.168.50.20:6633"
is_connected: true
fail_mode: secure
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
ovs_version: "2.3.2" vagrant@devstack-compute-1:~/devstack$ sudo ovs-vsctl show
6a894e1d-05d8-49be-8359-a09978281b36
Manager "tcp:192.168.50.20:6640"
is_connected: true
Bridge br-int
Controller "tcp:192.168.50.20:6633"
is_connected: true
fail_mode: secure
Port br-int
Interface br-int
ovs_version: "2.3.2"
Another critical piece in ODL that takes place even before we do any config in openstack is the pipeline tables.
ODL OVSDB Net-Virt Pipelining
Looking at the openflow 1.3 table in br-int, this is what you will observe on all nodes:
$ sudo ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 dump-flows br-int
OFPST_FLOW reply (OF1.3) (xid=0x2):
cookie=0x0, duration=8558.311s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:20
cookie=0x0, duration=8559.262s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, dl_type=0x88cc actions=CONTROLLER:65535
cookie=0x0, duration=8557.816s, table=20, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:30
cookie=0x0, duration=8557.291s, table=30, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:40
cookie=0x0, duration=8556.776s, table=40, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:50
cookie=0x0, duration=8556.273s, table=50, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:60
cookie=0x0, duration=8555.772s, table=60, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:70
cookie=0x0, duration=8555.254s, table=70, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:80
cookie=0x0, duration=8554.751s, table=80, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:90
cookie=0x0, duration=8554.247s, table=90, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:100
cookie=0x0, duration=8553.745s, table=100, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=goto_table:110
cookie=0x0, duration=8553.238s, table=110, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0 actions=drop
The reason for these rules is to provide an internal abstraction to the net-virt codebase, where different services can co-exist in br-int. The code that triggers these rules lives here and is identified in the Service enumeration:
package org.opendaylight.ovsdb.openstack.netvirt.providers.openflow13;
public enum Service {
CLASSIFIER ((short) 0, "Classifier"),
DIRECTOR ((short) 10, "Director"),
ARP_RESPONDER ((short) 20, "Distributed ARP Responder"),
INBOUND_NAT ((short) 30, "DNAT for inbound floating-ip traffic"),
EGRESS_ACL ((short) 40, "Egress Acces-control"),
LOAD_BALANCER ((short) 50, "Distributed LBaaS"),
ROUTING ((short) 60, "Distributed Virtual Routing (DVR)"),
L3_FORWARDING ((short) 70, "Layer 3 forwarding/lookup service"),
L2_REWRITE ((short) 80, "Layer2 rewrite service"),
INGRESS_ACL ((short) 90, "Ingress Acces-control"),
OUTBOUND_NAT ((short) 100, "SNAT for traffic accessing external network"),
L2_FORWARDING ((short) 110, "Layer2 mac,vlan based forwarding");
}
To give you an idea of how this gets used, consider the case where 2 tenant vms are trying to talk to each other. With that in mind, a potential example of how a packet would traverse the tables would be:
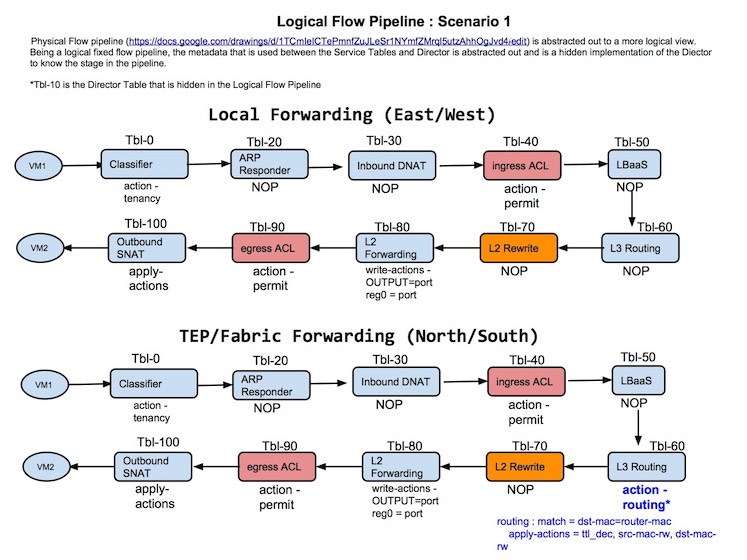
Note: The picture above does not have the current values associated to each service, yet it has historic value and still gives a good notion of what the pipeline is achieving. In other words, please do not pore over the values depicted (just get the idea behind it). :)
A future enhancement would be to include the notion of a director, which could influence the natural "flow" across the tables. That concept is on the shelf until a real world need arrives. The placeholder for director is shown as table 10.
Create Tenants
Now, let's get a little more real by creating a simple config in openstack. For that, we will create tenant1, add a network and subnet. Then, we will add 2 tenant1 vms. Just as shown in picture above.
vagrant@devstack-control:~/devstack$ /vagrant/puppet/scripts/createTenantAndVms.sh
You can see the contents of createTenantAndVms.sh here. Show/hide
Some interesting commands to see what was created is shown here: Show/hide
Looking closely at the info obtained above, you can draw a pretty good picture of the macs and their location. This is a brief summary on that:
Tenant 1's id: 097f695f8e214745984750ee7400814f
Network segmentation ID: 1001 (0x3e9)
MAC_1: fa:16:3e:46:64:2b IP: 2.0.0.1 Instance: - Host: devstack-control Desc: <DHCPd>
MAC_2: fa:16:3e:37:be:fa IP: 2.0.0.2 Instance: 1 Host: devstack-control Desc: 1_vm1
MAC_3: fa:16:3e:46:db:d5 IP: 2.0.0.3 Instance: 2 Host: devstack-compute-1 Desc: 1_vm2
We can -- of course -- play a bit to verify that 1_vm1 can reach 1_vm2 and the mac/ip addresses are in agreement with what we saw from the openstack commands: Show/hide
Now, to the nuts and bolts of the plumbing: OVS ports/interfaces. In the control node we have the following: Show/hide
In the compute-1 node we have the following: Show/hide
Looking closely at the info obtained above, you can draw a pretty good picture of the mappings between each OVS interface and openstack's tenant vms; as well as how control and compute-1 talk to each other. An important attribute that links the two worlds is theiface-id stored in interface's external_ids. That is actually the id of the Neutron port. This is a brief summary on that:
control OF port: 1 --> MAC: fa:16:3e:46:64:2b IP: 2.0.0.1 Desc: <DHCPd> ExtrnId: 085eeb79-ac3e-4e61-a0ae-91b30cc48fbd
control OF port: 2 --> MAC: 1e:ac:ec:85:4b:a1 IP: - Desc: vxlan-192.168.50.21 (connects control to compute-1)
control OF port: 3 --> MAC: fa:16:3e:37:be:fa IP: 2.0.0.2 Desc: 1_vm1 ExtrnId: 3d803796-dc00-4f81-872e-dce10947f478 compute1 OF port: 1 --> MAC: d6:85:ba:5e:16:18 IP: - Desc: vxlan-192.168.50.20 (connects compute-1 to control)
compute1 OF port: 2 --> MAC: fa:16:3e:46:db:d5 IP: 2.0.0.3 Desc: 1_vm2 ExtrnId: 4c6f3e8f-02f8-4f7e-bc6b-10ff2b95d612
Back to Pipeline
Even after showing you the various Services we support in the pipeline, our example is perhaps too simple to make it flex its muscle. That is so, because all that is needed to do L2 forwarding are tables 0 (CLASSIFIER) and 110 (L2_FORWARDING). Here is a simplification of how the flow goes: Show/hide
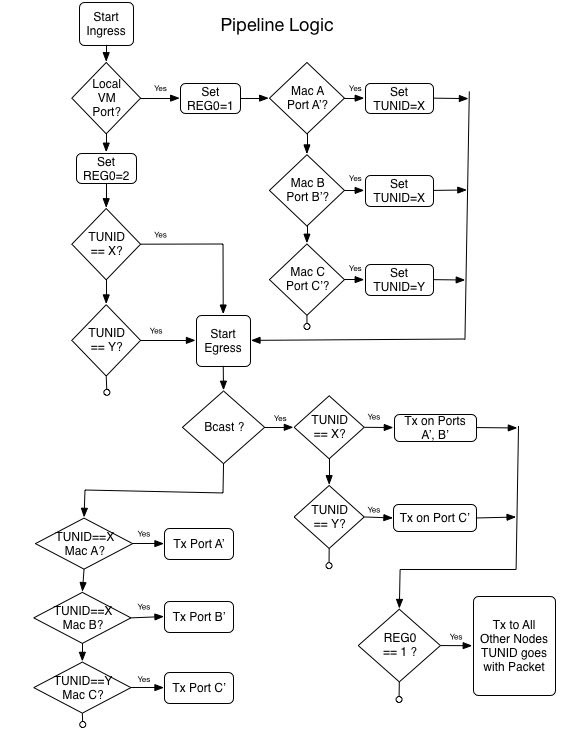
Here is what the openflow rules look like, from the control node: Show/hide
| vagrant@devstack-control:~/devstack$ sudo ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 dump-flows br-int | |
| OFPST_FLOW reply (OF1.3) (xid=0x2): | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15406.148s, table=0, n_packets=266, n_bytes=34723, in_port=1,dl_src=fa:16:3e:46:64:2b actions=set_field:0x3e9->tun_id,load:0x1->NXM_NX_REG0[],goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15395.780s, table=0, n_packets=193, n_bytes=23952, in_port=3,dl_src=fa:16:3e:37:be:fa actions=set_field:0x3e9->tun_id,load:0x1->NXM_NX_REG0[],goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30844.578s, table=0, n_packets=2, n_bytes=180, priority=0 actions=goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15395.275s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=8192,in_port=3 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15405.654s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=8192,in_port=1 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15402.453s, table=0, n_packets=35, n_bytes=2966, tun_id=0x3e9,in_port=2 actions=load:0x2->NXM_NX_REG0[],goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30845.251s, table=0, n_packets=3082, n_bytes=342102, dl_type=0x88cc actions=CONTROLLER:65535 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30844.074s, table=20, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:30 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30843.566s, table=30, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:40 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30843.065s, table=40, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:50 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30842.560s, table=50, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:60 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30842.052s, table=60, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:70 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30841.545s, table=70, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:80 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30841.040s, table=80, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:90 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30840.530s, table=90, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:100 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30839.531s, table=100, n_packets=496, n_bytes=61821, priority=0 actions=goto_table:110 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15402.964s, table=110, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=8192,tun_id=0x3e9 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=30839.028s, table=110, n_packets=6, n_bytes=508, priority=0 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15404.003s, table=110, n_packets=23, n_bytes=1812, priority=16384,reg0=0x1,tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=output:1,output:2,output:3 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15404.507s, table=110, n_packets=18, n_bytes=1546, priority=16384,reg0=0x2,tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=output:1,output:3 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15405.140s, table=110, n_packets=180, n_bytes=22986, tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:46:64:2b actions=output:1 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15394.764s, table=110, n_packets=250, n_bytes=32821, tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:37:be:fa actions=output:3 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15380.960s, table=110, n_packets=19, n_bytes=2148, tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:46:db:d5 actions=output:2 |
Here is what the openflow rules look like, from the compute-1 node: Show/hide
| vagrant@devstack-compute-1:~/devstack$ sudo ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 dump-flows br-int | |
| OFPST_FLOW reply (OF1.3) (xid=0x2): | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15739.120s, table=0, n_packets=35, n_bytes=2966, in_port=2,dl_src=fa:16:3e:46:db:d5 actions=set_field:0x3e9->tun_id,load:0x1->NXM_NX_REG0[],goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29264.258s, table=0, n_packets=10, n_bytes=1238, priority=0 actions=goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15738.584s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=8192,in_port=2 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15735.532s, table=0, n_packets=32, n_bytes=2722, tun_id=0x3e9,in_port=1 actions=load:0x2->NXM_NX_REG0[],goto_table:20 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29265.209s, table=0, n_packets=3153, n_bytes=356289, dl_type=0x88cc actions=CONTROLLER:65535 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29263.763s, table=20, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:30 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29263.238s, table=30, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:40 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29262.723s, table=40, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:50 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29262.220s, table=50, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:60 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29261.719s, table=60, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:70 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29261.201s, table=70, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:80 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29260.698s, table=80, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:90 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29260.194s, table=90, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:100 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29259.692s, table=100, n_packets=77, n_bytes=6926, priority=0 actions=goto_table:110 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15736.031s, table=110, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=8192,tun_id=0x3e9 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=29259.185s, table=110, n_packets=10, n_bytes=1238, priority=0 actions=drop | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15737.047s, table=110, n_packets=18, n_bytes=1546, priority=16384,reg0=0x1,tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=output:2,output:1 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15737.567s, table=110, n_packets=13, n_bytes=574, priority=16384,reg0=0x2,tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=output:2 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15755.001s, table=110, n_packets=12, n_bytes=1042, tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:46:64:2b actions=output:1 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15744.709s, table=110, n_packets=5, n_bytes=378, tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:37:be:fa actions=output:1 | |
| cookie=0x0, duration=15738.080s, table=110, n_packets=19, n_bytes=2148, tun_id=0x3e9,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:46:db:d5 actions=output:2 |
Notes on Table 0 (aka Classifier)
This table is where is all begins. In here, we are looking for 3 potential cases: 1) Packet from local port; 2) Packet from a neighbor node; 3) Packet destined to OF Controller (ie ODL).
1) Packet from local port
Knowing the openflow (OF) port and the source Mac, this rule will set the tun_id to be associated with the packet; and move onto the next table in the pipeline. (Lines 3 and 4 in control; Line 3 in compute-1)
Conversely, if unexpected source Mac arrives in the configured OF port, this table has explicit rules to drop the packet. (Lines 6 and 7 in control; Line 5 in compute-1)
It is possible you may have not noticed this, but tun_id is the exact value as the segmentation_id used in openstack. In our example that value is 1001 (or 0x3e9 in hex). Since there is only one broadcast domain configured so far, this is the only tun_id we see. If another network gets created -- independent of what tenant that is -- we would see a different tun_id used for the new network.
Another key action taken in this path is the setting of REG0. This is a metadata that is attached to the packet. It plays an important role on how to proceed should we determine that packet needs to be flooded. In this particular path, we set REG0 with value 1. (Lines 3 and 4 in control; Line 3 in compute-1)
2) Packet from a neighbor node
When packet arrives on table 0 from another openstack node, it already carries the tun_id it belongs to. Notice that we also know what OF port the packet will be coming in, which is part of the match. Because this packet came from a neighbor, this will explicitly set REG0 with value 2. (Line 8 in control node; Line 6 in compute-1)
3) Packet destined to OF Controller (ie ODL)
This is a simple case of sending packet to controller, based on dl_type (aka ether type 0x88cc, LLDP). By elimination you can see that we will only pay attention to these LLDP packets if they are not part of cases (1) and (2) above. That is the intended behavior. (Line 9 in control node; Line 7 in compute-1)
The code used to populate this table is located here.
Notes on Table 110 (aka L2_Fwd)
By the time the flow logic reaches this table, all that is left to do is to either: 4) Flood packet based on {tun_id, REG0} tuple; 5) Send Unicast Packet to a known {tun_id, mac} tuple.
4) Flood packet based on {tun_id, REG0} tuple
Flooding is triggered based on the Mac destination of the packet. We currently check for the left-most bit only, to also perform the flood on multicast packets. That is why the check is against a mask dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 instead ofdl_dst=ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff.
There is a further decision to be made when it comes to flooding: do we also send packet to all other neighboring openstack nodes? To determine that, it is essential to know the origin of the packet, back on table 0. And that is the role of REG0 in the pipeline!
When REG0 carries the value of 2, it originated from a neighbor node and that means it should never be flooded out of the receiving node. Only the local port(s) for the given tun_id will receive the flood. (Line 22 in control node; Line 20 in compute-1)
When REG0 carries the value of 1, it originated locally, thus flooding needs to include neighbor nodes. Note that as packet is sent all to tunnel ports, the tun_id is preserved, so the receiving neighbor node will have that info as packet reaches its classifier table. Also, it may be worth mentioning that if there were more than 2 openstack nodes, this rule would contain an action with more output ports listed. (Line 21 in control node; Line 19 in compute-1)
5) Send Unicast Packet to a known {tun_id, mac} tuple
Looking at known tun_id and mac, we can determine what port to use. What this means is that A) all nodes have knowledge of all macs of all broadcast domains, independent of it being local or not; B) because tun_id is taken into account, it is very okay -- yet potentially confusing to operators -- to re-use macs across broadcast domains; C) macs associated to ports used by dhcp servers are also taken into consideration by this logic. (Lines 23 thru 25 in control node; Line 21 thru 23 in compute-1)
The code used to populate this table is located here.
Create More Tenants
If you made it to this point, you are now a master in ovsdb l2 pipelining! I leave it to you to continue the fun. By doing the commands below, you can easily create another tenant and spin up vms for it. Then, using the commands above, have a look on how the new tenant vms affect the openstack tables and openflow 1.3 rules. Remember to pay close attention to tun_id. I urge you to try it out and let me know how it goes!
vagrant@devstack-control:~/devstack$ export TNT_ID=2 ; export VM_COUNT=5 ; \
/vagrant/puppet/scripts/createTenantAndVms.sh vagrant@devstack-control:~/devstack$ source openrc user${TNT_ID} tenant${TNT_ID} ; export OS_PASSWORD=user${TNT_ID} ; \
neutron port-list
Next up -- as mentioned before -- I will show you how we use this pipeline framework to give us L3 functionality. Stay tuned. ;)
Some related links you may find interesting:
- Introduction to Cloud Overlay Networks - VXLAN -- David Mahler
- Part 2 of this blog: Pipelines used for handling East/West L3 Forwarding
- Part 3 of this blog: L3 North-South
OpenStack with Opendaylight Part 1: Intro to Pipeline的更多相关文章
- [cloud][sdn] openstack openflow opendaylight openvswitch
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-relation-between-OpenStack-OpenDaylight-OpenFlow-and-Open-vSwitch- ...
- OpenStack与OpenDaylight的对接过程
由于项目中需要使用OpenDaylight(Oxygen)替换OpenStack(Otaca)中的neutron-openvswitch-agent,能找到的一些资料都是比较旧的版本,官网上的文档也一 ...
- 如何用Tacker将NFV带入OpenStack?
最初社区里很多人争论过NFV是否属于OpenStack,而后来可以确定的是OpenStack的确占据了NFV会话中的很大一部分,并且形象地反映在了下面的ETSI MANO概念架构图中,OpenStac ...
- Open Daylight integration with OpenStack: a tutorial
Open Daylight integration with OpenStack: a tutorial How to deploy OpenDaylight and integrate it wit ...
- 通过Tacker将NFV引入OpenStack
14年的这个时候,我们还在OpenStack社区中为NFV是否属于OpenStack而争论不休.如今这一争议已经被解决了.OpenStack已经成为NFV讨论中的重要部分,正如下面的ETSI MANO ...
- 万台规模下的SDN控制器集群部署实践
目前在网络世界里,云计算.虚拟化.SDN.NFV这些话题都非常热.今天借这个机会我跟大家一起来一场SDN的深度之旅,从概念一直到实践一直到一些具体的技术. 本次分享分为三个主要部分: SDN & ...
- 2014:超越炒作,进入部署SDN的时代
2013 年,我们看到了非常多新的SDN 产品.体系结构.营销活动和各种会议,一些新的标准和开源组织也进入了这个领域.当时的SDN 刚刚从炒作周期的高点回归下来.转眼到了2014 年,这一年我们会看到 ...
- 2019-04-18-NFV基础概念
NFV技术的起源和概念 在移动互联网时代,运营商面临内外困局.就自身而言,采用的流量增长-网络扩容-收入增长的商业模型正在失效,庞大.僵化的电信基础网络,不能够满足用户的丰富需求:就竞争对手而言,互联 ...
- openstack Icehouse发布
OpenStack 2014.1 (Icehouse) Release Notes General Upgrade Notes Windows packagers should use pbr 0.8 ...
随机推荐
- DropdownList异步刷新GridView数据
前台代码: <div style=" clear:both; width:800px; text-align:center; margin-left:auto; margin-righ ...
- 如何运行Python程序
注:以下均基于windows下操作,并且安装的是最新的python3.3版本. 安装完python之后,我们可以做两件事情, 1.将安装目录中的Doc目录下的python331.chm使用手册复制到桌 ...
- 【转】虚拟 IO 服务器(VIOS)和 IBM i
Power 主机上的虚拟化应用,简单阐述虚拟 IO 服务器的功能,用途,优点,以及虚拟 IO 服务器在高级虚拟化技术的作用.举例说明虚拟 IO 服务器与 IBM i 分区直接互联特性. 引言 随着信息 ...
- Velocity模板引擎介绍
整理下Velocity使用方法,整理比较详细用例 1 Velocity基础语法 1.1 用户和开发人员参考文档 http://velocity.apache.org/engine/releases/v ...
- 父标签浮动(float)“塌陷”问题
浮动“塌陷” float参见: http://www.cnblogs.com/bigtreei/p/8110090.html http://www.w3school.com.cn/css/css_po ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>修改Android签名证书keystore的密码、别名alias以及别名密码
转载于:http://blog.k-res.net/archives/1229.html 和 http://blog.k-res.net/archives/1671.html ADT允许自定义调试用 ...
- request doesn't contain a multipart/form-data or multipart/mixed stream ……
有文件控件"file"的表单,在提交的时候,直接使用了ajax提交,结果报了一堆错,原来这个东东要提交表单,还要用post方式,最后更改为: $("#saveForm&q ...
- selenium模块控制浏览器
利用selenium模块控制浏览器 导入selenium模块:from selenium import webdriver browserFirefox = webdriver.Firefox()#打 ...
- Loadrunder脚本篇——web_custom_request函数介绍
c语言版本: int web_custom_request(const char *RequestName, , [EXTRARES, ,] LAST ); 参数说明: RequestName ...
- Fidder详解之抓包
前言 本文是博主发表的第一篇文章,如有傻逼之处,请大家见谅.最近遇到很多人说接口相关的问题,比如:什么是接口,我该怎么做接口测试,还有我总是抓不到APP上的https请求(这个巨坑,不知道坑了多少小白 ...
