java se系列(三) 顺序语句、if...else、switch、While、do-while、for、break、continue
1 顺序语句
语句:使用分号分隔的代码称作为一个语句。

注意:没有写任何代码只是一个分号的时候,也是一条语句,称作空语句。

顺序语句就是按照从上往下的顺序执行的语句。
2 判断(if…else)
什么是判断语句:用于判断的语句叫判断语句。
1.格式一
if(判断条件){
如果符合条件执行的代码;
执行的代码块1;
执行的代码块2;
……………….;
执行的代码块n;
}
练习:提示用户输入一个整数。如果该整数是5的倍数,打印“5的倍数”,如果是2的倍数打印“2的倍数”
提示:为了便于让用户输入数据,我们使用Scanner这个类,固定用法Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 该类需要导入包import java.util.Scanner;
int nextInt = sc.nextInt();获取用户输入的数字
1 import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int nextInt = sc.nextInt();
if(nextInt%5==0){
System.out.println("是5的倍数");
}
if(nextInt%2==0){
System.out.println("是2的倍数");
}
}
}
2.格式二
if(判断条件){
执行的代码块1;
执行的代码块2;
……………….;
执行的代码块n;
}else{
执行的代码块1;
执行的代码块2;
……………….;
执行的代码块n;
}
案例:判断一个整数是奇数还是偶数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int nextInt = sc.nextInt();
if (nextInt % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("是偶数");
} else {
System.out.println("是奇数");
}
System.out.println("over");
}
同样道理,如果花括号中只有一条语句,那么花括号可以省略不写,初学者不推荐省略。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int nextInt = sc.nextInt();
if (nextInt % 2 == 0)
System.out.println("是偶数");
else
System.out.println("是奇数");
System.out.println("over");
}
观察发现if else语句有点类似于三元运算符.其实三元运算符是if else 的一种简写格式.
Public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 0, y = 1, b;
// if else 语句
if (x > y) {
b = x;
} else {
b = y;
}
System.out.println(b);// 1
// 3元运算
b = x > y ? x : y;
System.out.println(b); //
}
这两种格式是一样的。if else 结构 简写格式: 变量 = (条件表达式)?表达式1:表达式2;
三元运算符:
好处:可以简化if else代码。
弊端:因为是一个运算符,所以运算完必须要有一个结果。
3.格式三
if(判断条件1){
执行的代码块1;
}else if(判断条件2){
执行语句;
}else if(判断条件3){
执行语句;
}
需求: 根据用户定义的数值不同,打印对应的星期英文。if 只能进行一层判断,if else 只能进行两层判断,那么需要多层判断时呢?星期可是有7个数的。如何设计代码?使用if 语句
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 8;
if (x == 1) {
System.out.println("星期一");
}
if (x == 2) {
System.out.println("星期二");
}
if (x == 3) {
System.out.println("星期三");
}
}
如果这样设计的话,第一个if语句执行完毕后,第二个语句仍会执行(去判断),是一个顺序结构.那么事实上当前定义的星期之后会有一个.假如,第一个已经符合条件,那么剩余的执行就没有意义了。属于逻辑错误。
用if else ,如果用户输入的是7以外的数据,那么怎么处理?就需要使用else 了
方案2:使用if else if语句
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 8;
if (x == 1) {
System.out.println("星期一");
} else if (x == 2) {
System.out.println("星期二");
} else if (x == 3) {
System.out.println("星期三");
} else if (x == 4) {
System.out.println("星期四");
} else if (x == 5) {
System.out.println("星期五");
} else if (x == 6) {
System.out.println("星期六");
} else if (x == 7) {
System.out.println("星期日");
} else {
System.out.println("请输入数字1-7");
}
}
注意:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
if (x == 1) {
System.out.println("1");
}
if (x == 2) {
System.out.println("2");
}
if (x == 3) {
System.out.println("3");
} else {
System.out.println("4"); //
}
}
该if 语句不是一个整体,第一个if 是一个语句,第二个又是一个语句,最后的if else 又是一个语句。
if语句特点
- 第二种格式与三元运算符的区别:三元运算符运算完要有值出现。好处是:可以写在其他表达式中。
- 条件表达式无论写成什么样子,只看最终的结构是否是true 或者 false。
练习1:根据用户输入的月份,打印出月份所属的季节.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1;
if (x == 3) {
System.out.println("spring");
} else if (x == 4) {
System.out.println("spring");
}
}
仔细观察:发现if和else if要执行的语句是一样的,可不可以合并呢。当然是可以的。怎么合并?使用逻辑运算符,那么使用哪个逻辑运算符呢, &肯定不行。需要全部为真才为真,月份是不可能同时满足的 那么使用|连接符号即可。意思只要其中一个为真,就为真。另外可以使用短路功能。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1;
if (x == 3 || x == 4 || x == 5) {
System.out.println("spring");
} else if (x == 6 || x == 7 || x == 8) {
System.out.println("Summer");
} else if (x == 9 || x == 10 || x == 11) {
System.out.println("autumn");
} else if(x == 12 || x == 1 || x == 2){
System.out.println("Winter");
} else {
System.out.println("月份不存在");
}
}
练习2:根据用户输入的成绩,进行评级,根据学生考试成绩划分ABCD
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入考试分数:");
double score = sc.nextDouble();
char grade;
if (score >= 90.0)
grade = 'A';
else if (score >= 80.0)
grade = 'B';
else if (score >= 70.0)
grade = 'C';
else if (score >= 60.0)
grade = 'D';
else
grade = 'F';
System.out.println("你的成绩是:" + grade);
}
If语句常见的错误:
1.忘记必要的括号:如果代码块中只有一条语句的时候,可以省略花括号,但是当花括号将多条语句扩在一起时,花括号就不能在省略。
double radius = 4;
double area;
if (radius >= 0)
area = radius * radius * 3.14;//编译报错,area未初始化
System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area); double radius = 4;
double area;
if (radius >= 0) {
area = radius * radius * 3.14;
System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
}
虽然代码一样多,但是第一个会编译报错(area没有出初始化),第二个正常运行。就是因为少了花括号。所以一定要仔细。
2.if语句后出现分号
double radius = 0;
double area; if (radius > 0); {
area = radius * radius * 3.14;
System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
}
相当于判断符合条件后,执行一个空语句。
double radius = 0;
double area; if (radius > 0){}{
area = radius * radius * 3.14;
System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
}
判断闰年
1:什么是闰年?可以被4整除不能被100整除,或者可以被400整除,那么这一年就是闰年(leap year)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入年份:");
int year = sc.nextInt();
// 判断年份能否被4整除
boolean isLeapYear = (year % 4 == 0);
// 年份能被4整除,并且不能被100整除并且使用&&(and)
isLeapYear = isLeapYear && (year % 100 != 0);
// 年份或者能够被400整除
isLeapYear = isLeapYear || (year % 400 == 0);
if (isLeapYear) {
System.out.println(year + "是闰年!");
}
// 简写格式;
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println(year + "是闰年!");
}
}
3 选择判断语句(switch)
switch语句,格式:
switch(表达式)
{
case 取值1: 执行语句; break;
case 取值2: 执行语句; break;
…...
default: 执行语句; break;
}
switch语句特点:
1,switch语句选择的类型只有四种:byte,short,int , char。
2,case之间与default没有顺序。先判断所有的case,没有匹配的case执行default。
3,switch语句停止的条件是遇到了break关键字或者结束switch语句的大括号。
4,如果匹配的case或者default没有对应的break,那么程序会继续向下执行,运行可以执行的语句,直到遇到break或者switch结尾结束。
5,switch case中的值必须要与switch表达式的值具有相同的数据类型。而且case后跟的值必须是常量,不能跟变量。
案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 3;
switch (x) {
case 1: System.out.println("1"); break;
case 2: System.out.println("2"); break;
case 3: System.out.println("3"); break;
default: System.out.println("ok");break;
}
}
case 就像选择题的答案之一。 break 就是如果该答案正确那么就可以跳出switch 了,意思就是说 已经找出了正确的答案了。那么这道题也就做完了。如果 case 没有匹配接着进行下一个case 匹配,直到匹配为止。 最后如果都没有匹配上,那么 switch 给提供了一个默认的答案,就是 default。
注意: ①case后跟的是冒号:
②每个case中的执行语句一定要加break;
练习:需求2:根据指定的月份,打印该月份所属的季节.
一旦case匹配,就会顺序执行后面的程序代码,而不管后面的case是否匹配,直到遇见break,利用这一特性可以让好几个case执行统一语句.
345 spring 678 sunmer 9 10 11 autumn 12 1 2 winter
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 3;
switch (x) {
case 3:
case 4:
case 5: System.out.println("spring"); break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8: System.out.println("sunmer"); break;
case 9:
case 10:
case 11: System.out.println("autumn"); break;
case 12:
case 0:
case 1: System.out.println("winter");
default: System.out.println("ok"); break;
}
}
练习:char 类型在switch 中的使用.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1, y = 2;
char ch = '*';
switch (ch) {
case '+': System.out.println("x*y=" + (x + y)); break;
case '-': System.out.println("x-y="+(x-y)); break;
case '*': System.out.println("x*y="+(x*y)); break;
case '/': System.out.println("x/y="+(x/y)); break;
default: System.out.println("不靠谱");
}
}
if 和switch 语句很像,具体什么场景下,应用哪个语句呢?
如果判断的具体数值不多,而是符号byte,short int char 四种类型。虽然2个语句都可以使用,建议使用switch语句.因为效率稍高.
其他情况:对区间判断,对结果为boolean 类型判断,使用if,if的使用范围更广。
if 除了能判断具体数值还能判断区间。switch 判断区间会很费劲的。要写好多case 对于运算结果是boolean型的 if 能判断 switch 是不能实现的。例如:根据学生考试成绩划分ABCD A90-100 B80-89 C70-79 D60-69 E0-59。
实际开发怎么选择呢?
如果要对具体数值进行判断,并且数值不多,那么 就用switch 来完成。switch的case条件都是编译期整数常量,编译器可以做到表格跳转查询,查找速度快。但是switch 的局限性比较大,必须是4种类型,并且值不多。一般都是使用if。 最后在jdk 7中对switch 进行了增强 还可以判断字符串。5.0 增加了对枚举的判断。
备注:JDK7.0开始可以使用switch可以使用字符串类型的数据了.
4 While循环
需求:需要打印一行字符串"hello world",100次
需要将该语句打印100遍System.out.println("hello world");那么如何解决该问题?Java提供个一个称之为循环的结构,用来控制一个操作的重复执行。
int count = 0;
while (count < 100) {
System.out.println("hello world");
count++;
}
System.out.println("over");
变量count初始化值为0,循环检查count<100 是否为true,如果为true执行循环体(while后{}之间的语句),输出"hello world"语句,然后count自增一,重复循环,直到count是100时,也就是count<100为false时,循环停止。执行循环之后的下一条语句。
Java提供了三种类型的循环语句:while循环,do-while循环和for循环。
//while语句格式:
while(条件表达式)
{
执行语句;
}
定义需求: 想要打印5次helloworld
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println("hello world");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 0;
while (x < 5) {
System.out.println("hello java ");
}
}
如果是在dos里编译和运行,是不会停止,除非系统死机。需要ctrl+c来结束。这就是真循环或者死循环。因为x<5 永远为真。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 0;
while (x < 5) {
System.out.println("hello java ");
x++;
}
}
让x自增,那么就会有不满足条件的时候。循环就会结束。
练习:想要打印出1-100之间的奇数
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1;
while (x < 100) {
System.out.println(x);
x = x + 2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int x=1;
while(x<100){
if(x%2!=0){
System.out.print(x);
}
x++;
}
System.out.println();
}
练习2:计算1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9 的值
int sum = 0;
int i = 1; while (i < 10) {
sum = sum + i;
i++;
} System.out.println(sum);
注意:要精确控制循环的次数。
常犯错误是是循环多执行一次或者少执行一次。例如会执行101次,想要执行100次,要么是count初始值为1,然后count<=100,要么是count初始值为0,coung<100
int count = 0;
while (count <=100) {
System.out.println("hello gzitcast");
count++;
}
System.out.println("over");
猜数字游戏:
编写程序随即生成一个0-100之间的随机数。程序提示用户输入一个数字,不停猜测,直到猜对为止。最后输出猜测的数字,和猜测的次数。并且如果没有猜中要提示用户输入的值是大了还是小了。
思考:如何生成1-100之间随机数?
(int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
如何提示用户输入数字,
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int guessNum = sc.nextInt();
需要将随机数和用户输入的数字进行比较。
猜一次:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;// 随机数
System.out.println("请输入0-100之间整数");
int guessNum = sc.nextInt(); if (guessNum == num) {
System.out.println("中啦");
} else if (guessNum < num) {
System.out.println("小啦");
} else {
System.out.println("大了");
}
这个程序只能才一次,如何让用户重复输入直到猜对?,可以使用while循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;//随机数
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入1-100之间整数");
int guessNum = sc.nextInt();
if (guessNum == num) {
System.out.println("中啦");
} else if (guessNum < num) {
System.out.println("小啦");
} else {
System.out.println("大了");
}
}
}
该方案发现了问题,虽然实现了让用户不停的输入,但是即使猜中了程序也不会停止。那么就需要控制循环次数了。也就是while() 括号中的条件表达式。当用户猜测的数和系统生成的数字不相等时,就需要继续循环。
int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int guessNum = -1;
while (guessNum != num) {
System.out.println("请输入1-100之间整数");
guessNum = sc.nextInt();
if (guessNum == num) {
System.out.println("中啦");
10 } else if (guessNum < num) {
System.out.println("小啦");
} else {
System.out.println("大了");
}
}
为什么将guessNum初始化值为-1?因为如果初始化为0到100之间程序会出错,因为可能是要猜的数。
1:首先程序生成了一个随机数
2:用户输入一个数字
3:循环检查用户数字和随机数是否相同,知道相同位置,循环结束
5 do while 语句
do while语句格式:
do
{
执行语句;
}while(条件表达式); //do while特点是条件无论是否满足,循环体至少被执行一次。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 0, y = 0;
do {
System.out.println(x);
x++;
} while (x < 0);
// do while do会先执行一次,不管是否满足循环条件。
while (y < 0) {
System.out.println(y);
y++;
}
}
while:先判断条件,只有条件满足才执行循环体。
do while: 先执行循环体,再判断条件,条件满足,再继续执行循环体,至少会执行一次。
简单一句话:
do while:无论条件是否满足,循环体至少执行一次。
注意一个细节:do while 后面有分号“;”
案例:改写猜数字游戏
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 记录用户输入的数字
int guess = -1;
// 记录用户输入次数
int count = 0;
// 生成1-100之间随机数
int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 循环猜数字
do {
System.out.println("请输入1-100之间的数字");
guess = sc.nextInt();
if (guess > num) {
System.out.println("太大了");
} else if (guess < num) {
System.out.println("太小了");
} else {
System.out.println("中啦");
}
count++;
} while (num != guess);
System.out.println("你猜测的数字是:" + num + "猜测了" + count + "次");
}
案例:计算器,系统自动生成2个随机数用于参与运算。
系统生成0-4之间的随机数,表示加减乘除取模运算。使用switch 进行匹配
class Couter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 生成随机数Math.random()生成0-1值,不包含0和1,
//乘以10得到0和10之间的数(double类型),不包含0和10
//强转为int,并加1得到1和10之间的数,包含1和10
int x = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
int y = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
// 创建0-4随机数 0 1 2 3 4 各表示加减乘除取模
int z = (int)(Math.random()*5);
System.out.println(z);
switch (z) {
case 0:
System.out.println(x + "+" + y + "=?");
System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(x + "+" + y + "=" + (x + y));
break;
case 1:
System.out.println(x + "-" + y + "=?");
System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(x + "-" + y + "=" + (x - y));
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(x + "*" + y + "=?");
System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(x + "*" + y + "=" + (x * y));
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(x + "/" + y + "=?");
System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(x + "/" + y + "=" + (x / y));
break;
case 4:
System.out.println(x + "%" + y + "=?");
System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(x + "%" + y + "=" + (x % y));
break;
}
}
}
int x = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
Math.random() 生成0-1之间的数字,double类型
Math.random()*10 就是0-9之间的数,是double类型
(int)(Math.random()*10)将double类型强转成int类型,去掉小数点,便于计算。
(int)(Math.random()*10)+1,生成了1到10之间随机数。
int z = (int)(Math.random()*5);
生成0-4之间的数字,可以用0表示加,1表示减,2表示乘,3表示除,4表示取模
为了减慢程序,使用了Thread.sleep(2000); 让程序等待一会。
6 for 循环
格式:
for(初始化表达式;循环条件表达式;循环后的操作表达式)
{
执行语句;
}
需求: 想要打印5次hello world
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
3.for的执行流程
for 知道要进行循环,读到x=0 的时候,在内存中开辟了空间,定义变量x 赋值为0。接着进行条件判断 x<5,为真,这个时候对满足条件后执行了循环体的内容System.out.println("hello java");当循环体执行完毕之后,执行x < 5;后的表达式即 x++ 。x自增后变为了1 ,再次进行判断 x<5 (int x=0 只执行一次),如果为真就再次运行System.out.println("hello java");如果为假,for循环结束。
for 和while的区别
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
System.out.println("hello java");
}
System.out.println(x); //编译报错
//x cannot be resolved to a variable
int y = 0;
while (y < 5) {
System.out.println("hello world");
y++;
}
System.out.println(y);
}
编译报错
解释 x 为什么会找不到,注意了变量的作用域,也就是变量的作用范围。x 只在 for 循环的大括号内有效,出了这个区域,就无效了.在内存中就消失了。x消失后,仍要访问它,肯定会报错的。
y 就不一样了,y 是定义在while 外的。while循环完毕仍有效 while的初始化动作在外边,循环结束后y 仍然存在。当定义的y只作为循环增量存在的话的,循环完毕后y就没有用了,但是y还是占着一块内存。所以,如果定义的变量只作为循环增量存在的话,就用for 循环可以节约内存。
其实for 和while 是可以互换的。
最后总结:
1、for里面的两个表达式运行的顺序,初始化表达式只读一次,判断循环条件,为真就执行循环体,然后再执行循环后的操作表达式,接着继续判断循环条件,重复找个过程,直到条件不满足为止。
2、while与for可以互换,区别在于for为了循环而定义的变量在for循环结束时就在内存中释放。而while循环使用的变量在循环结束后还可以继续使用。
3、最简单无限循环格式:while(true) , for(;;),无限循环存在的原因是并不知道循环多少次,而是根据某些条件,来控制循环。推荐使用while(true)
while(true){ }
for(;;){ }
for(;true;){ }
for 练习:
- 获取1-10的和,并打印。
- 1-100之间 7的倍数的个数,并打印。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取1到10的和1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10
int sum = 0;
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
System.out.println((sum + x) + "=" + sum + "+" + x);
sum = sum + x;
}
System.out.println(sum);//
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1-100之间 7的倍数的个数,并打印。
int count = 0;
for (int x = 0; x <= 100; x++) {
if (x % 7 == 0) {
System.out.println(x);
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
累加思想:通过变量记录住循环操作后的结果;通过循环的形式.进行累加的动作。
计数器思想:通过一个变量记录住数据的状态变化,也是通过循环完成。
循环常见错误:
多加分号:在for括号后和循环体之间加分号是常见错误。
错误:程序编译运行都可以通过,只是不是我们想要的结果。
for(int i=0;i<100;i++);{
System.out.println("hello ");
}
正确:
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println("hello ");
}
错误;是一个死循环
int i=0;
while(i<100);{
System.out.println("hello");
i++;
}
正确:
int i=0;
while(i<100){
System.out.println("hello");
i++;
}
语句的嵌套应用
什么是嵌套形式,其实就是语句中还有语句。
想要打印出矩形:

public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
System.out.println("*");
}
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
}

这里用“*”表示矩形的边。
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
for(int y=0;y<6;y++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}

forfor 嵌套for循环练习2
打印此种格式的图案
*****
****
***
**
*
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 5; x > 0; x--) {
for(int y=x;y>0;y--){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
练习:
*
**
***
****
*****
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y <= x; y++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
练习:99乘法表
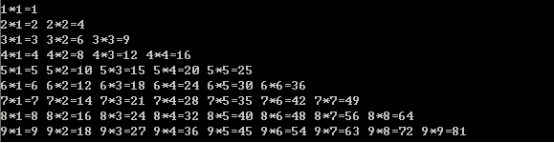
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 1; x <= 9; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y <= x; y++) {
System.out.print(y + "*" + x + "=" + x * y + '\t');
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
}
7 break、continue关键字
break关键字:break 语句用于终止最近的封闭循环或它所在的 switch 语句。控制传递给终止语句后面的语句(如果有的话)。
适用:for循环 、 switch两种循环语句。
break的用法:
- 单独使用。
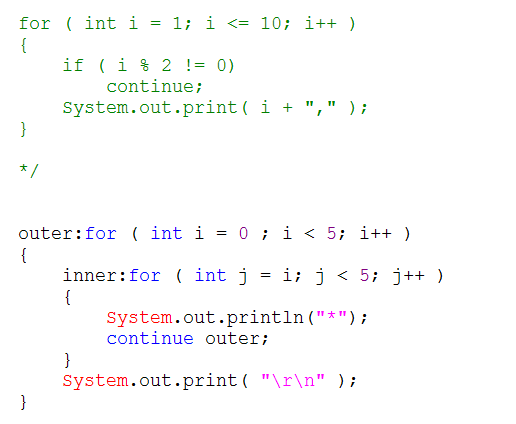
- 与标签一起使用。(标签:即一个名字,满足标识符的条件即可)。
使用细节: 不要再break语句之后,编写其他语句,永远都执行不到,编译报错。

continue关键字:语句将控制权传递给它所在的封闭迭代语句的下一次迭代。(跳出本循环,执行下一次循环)。
适用于:while 、 do while 、 for循环语句
使用细节:
1. 如果continue出现在循环的末尾(最后一条语句),那么可以省略。
2. 如果continue出现在循环的第一条语句,那么后面的语句都无法执行,所以编译报错。
3. 可以结合标记使用。

java se系列(三) 顺序语句、if...else、switch、While、do-while、for、break、continue的更多相关文章
- java‘小秘密’系列(三)---HashMap
java'小秘密'系列(三)---HashMap java基础系列 java'小秘密'系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder java'小秘密'系列(二)- ...
- java se系列(一)开发前奏
1. 软硬件知识 电子计算机:俗称电脑,是一种能够按照程序运行,自动.高速处理海量数据的现代化智能电子设备.由硬件和软件所组成,没有安装任何软件的计算机称为裸机 cpu:是一台计算机的运算核心和控制核 ...
- java多线程系列(三)---等待通知机制
等待通知机制 前言:本系列将从零开始讲解java多线程相关的技术,内容参考于<java多线程核心技术>与<java并发编程实战>等相关资料,希望站在巨人的肩膀上,再通过我的理解 ...
- java基础系列(三)---HashMap
java基础系列(三)---HashMap java基础系列 java基础系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder java基础系列(二)---Integer ...
- Java爬虫系列三:使用Jsoup解析HTML
在上一篇随笔<Java爬虫系列二:使用HttpClient抓取页面HTML>中介绍了怎么使用HttpClient进行爬虫的第一步--抓取页面html,今天接着来看下爬虫的第二步--解析抓取 ...
- java se系列(十二)集合
1.集合 1.1.什么是集合 存储对象的容器,面向对象语言对事物的体现,都是以对象的形式来体现的,所以为了方便对多个对象的操作,存储对象,集合是存储对象最常用的一种方式.集合的出现就是为了持有对象.集 ...
- java se系列(十一)线程
1 线程的概述 进程:正在运行的程序,负责了这个程序的内存空间分配,代表了内存中的执行区域. 线程:就是在一个进程中负责一个执行路径. 多线程:就是在一个进程中多个执行路径同时执行. 图上的一键优化与 ...
- java se系列(四) 函数、数组、排序算法、二分法、二维数组
1 函数 1.1 数的概述 发现不断进行加法运算,为了提高代码的复用性,就把该功能独立封装成一段独立的小程序,当下次需要执行加法运算的时候,就可以直接调用这个段小程序即可,那么这种封装形形式的具体表 ...
- java se系列(二) 关键字、注释、常量、进制转换、变量、数据类型转换、运算符
1 关键字 1.1 关键字的概述 Java的关键字对java的编译器有特殊的意义,他们用来表示一种数据类型,或者表示程序的结构等,关键字不能用作变量名.方法名.类名.包名. 1.2 常见的关键字 备注 ...
随机推荐
- Ajax步骤
var request = new XMLHttpRequest(); request.open("GET","get.php",ture); request. ...
- Appium移动端自动化测试之元素定位(三)
1.name定位 driver.find_element_by_id(') driver.find_element_by_id(') driver.find_element_by_name('登录') ...
- 基于任务的异步编程模式,Task-based Asynchronous Pattern
术语: APM 异步编程模型,Asynchronous Programming Model,其中异步操作由一对 Begin/End 方法(如 FileStream.BeginRea ...
- 20169219 NMap+Wireshark实验报告
Tcpdump介绍 用简单的话来定义tcpdump,就是:dump the traffic on a network,根据使用者的定义对网络上的数据包进行截获的包分析工具. tcpdump可以将网络中 ...
- delphi 获取windows任务栏的高度
function GetWinTrayWnd: Integer; // 获取windows任务栏高度 var TrayWnd: HWnd; //任务栏句柄 Rec : TRect; begin Tra ...
- 门面(Facade)模式
门面(Facade)模式 也叫 外观模式. 外观模式:为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得子系统更加容易使用 /* * 门面(Facade)角色:客户端可以 ...
- [转]-webkit-overflow-scrolling:touch的应用
-webkit-overflow-scrolling 用来控制元素在移动设备上是否使用滚动回弹效果. 在移动端上,在你用overflow-y:scorll属性的时候,你会发现滚动的效果很木,很慢,这时 ...
- MessageBox.Show() 多重用法
MessageBox.Show (String) 显示具有指定文本的消息框. 由 .NET Compact Framework 支持. MessageBox.Show (IWin32Window, S ...
- Nexus 私有仓库
Nexus3.6和Nexus2.x安装不同,2.x版本需要安装服务,再启动.而3.6版本则更加简单. 步骤如下: jdk环境:1.8 Nexus3.6解压(注意,路径不要带空格及中文),解压后有两个文 ...
- Response Assertion(响应断言)
响应断言可以让你添加匹配字符串来匹配请求和响应的各个字符串. 匹配字符串可以是1.Contains和Matches正则表达式:2.Equals和SubString文本类型,大小写敏感. Apply t ...
