Make a DAC with a microcontroller's PWM timer
http://www.edn.com/design/analog/4337128/Make-a-DAC-with-a-microcontroller-s-PWM-timer
Many embedded-microcontroller applications require generation of analog signals. An integrated or stand-alone DAC fills the role. However, you can often use PWM signals for generating the required analog signals. You can use PWM signals to create both dc and ac analog signals. This Design Idea shows how to use a PWM timer to simultaneously create a sinusoid, a ramp, and a dc voltage. A PWM signal is a digital signal with fixed frequency but varying duty cycle. If the duty cycle of the PWM signal varies with time and you filter the PWM signal, the output of the filter is an analog signal (Figure 1).

If you build a PWM DAC in this manner, its resolution is equivalent to the resolution of the PWM signal you use to create the DAC. The PWM output signal requires a frequency that is equivalent to the update rate of the DAC, because each change in PWM duty cycle is the equivalent of one DAC sample. The frequency the PWM timer requires depends on the required PWM signal frequency and the desired resolution. The required frequency is FCLOCK=FPWM×2n, where FCLOCK is the required PWM-timer frequency, FPWM is the PWM-signal frequency, and n is the desired DAC resolution in bits.

depicts a circuit that delivers a 250-Hz sine wave, a 125-Hz ramp, and a dc signal. The desired sampling rate is 8 kHz (32 samples for each sine-wave cycle (16× oversampled), and 64 samples for each ramp cycle (32× oversampled)). These figures result in a required PWM-signal frequency of 8 kHz and a required PWM clock frequency of 2.048 MHz. It is usually best for the PWM signal frequency to be much higher than the desired bandwidth of the signals to be produced. Generally, the higher the PWM frequency, the lower the order of filter required and the easier it is to build a suitable filter. This design uses Timer B of the MSP430 in 16-bit mode and in "up" mode, in which the counter counts up to the contents of capture/compare register 0 (CCR0) and then restarts at zero. CCR0 is loaded with 255, thereby giving the counter an effective 8-bit length. You can find this register and others in a DAC demonstration program for the MSP430 microcontroller. Click here to download the program.
CCR1 and output TB1 produce the sine wave. CCR2 and TB2 generate the ramp, and CCR3 and TB3 yield the dc value. For each output, the output mode is the reset/set mode. In this mode, each output resets when the counter reaches the respective CCRx value and sets when the counter reaches the CCR0 value. This scheme provides positive pulses equivalent to the value in CCRx on each respective output. If you use the timer in 8-bit mode, the reset/set output mode is unavailable for the PWM outputs because the reset/set mode requires CCR0. The timer's clock rate is 2.048 MHz. Figure 3

shows the sine and ramp waveforms. The sine wave in this example uses 32 samples per cycle. The sample values are in a table at the beginning of the program. A pointer points to the next value in the sine table, so that, at the end of each PWM cycle, the new value of the sine wave is written to the capture/compare register of the PWM timer.
The ramp in this example does not require a table of data values. Rather, the ramp simply increments the duty cycle for each cycle of the PWM signal until it reaches the maximum and then starts over at the minimum duty cycle. This gradual increase in PWM-signal duty cycle results in a ramp voltage when the signal passes through a filter. You control the dc level by simply setting and not changing the value of the PWM-signal duty cycle. The dc level is directly proportional to the duty cycle of the PWM signal. Figure 2 shows the reconstruction filters used for each signal in this example. The filter for the ac signals is a simple two-pole, stacked-RC filter, which is simple and has no active components. This type of filter necessitates a higher sampling rate than would be required if the filter had a higher order. With the type of filter shown in Figure 2, you should use at least a 16× oversampling rate.
The filter yields its best response when R2>>R1. Also, setting the cutoff frequency too close to the bandwidth edge causes a fair amount of attenuation. To reduce the amount of attenuation in the filter, set the cutoff frequency above the bandwidth edge but much lower than the frequency of the PWM signal. The filter for the dc value serves for charge storage rather than ac-signal filtering. Therefore, it uses a simple, single-pole RC filter. Figure 4
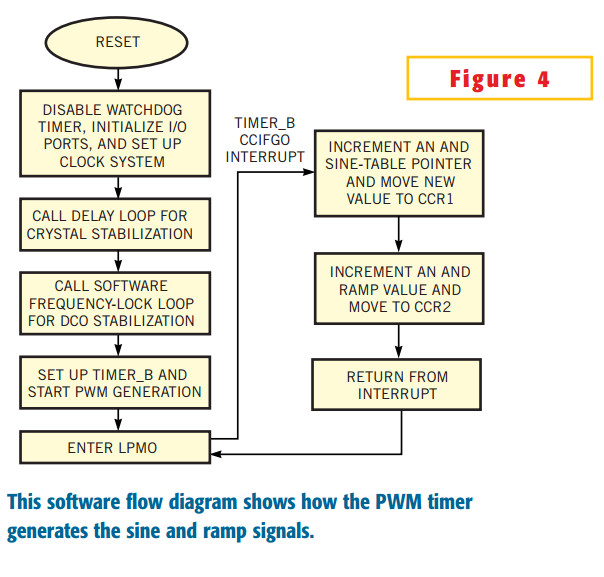
shows the software flow for the DAC. After a reset, the routine stops the watchdog timer, configures the output ports, and sets up the clock system. Next, the software calls a delay to allow the 32,768-Hz crystal to stabilize to calibrate the DCO (digitally controlled oscillator).
Next, the routine calls the calibration routine to set the operating frequency to 2.048 MHz. After the DCO calibration, the program sets up Timer_B, CCR1 and CCR2 for PWM generation and then starts the timer. Finally, the MSP430 goes into low-power mode 0 (LPM0) to conserve power. The CPU wakes up to handle each CCIFG0 interrupt from the PWM timer and then re-enters LPM0. (See references 1, 2, and 3 for more information on the DCO and the MSP430 family.)
Make a DAC with a microcontroller's PWM timer的更多相关文章
- 【STM32】PWM DAC基本原理(实验:PWM实现DAC)
虽然STM32F103ZET6具有内部DAC,但是也仅仅只有两条DAC通道,并且STM32还有其他的很多型号是没有DAC的.通常情况下,采用专用的D/A芯片来实现,但是这样就会带来成本的增加. 不过S ...
- Create a DAC from a microcontroller's ADC
Few microcontrollers include a DAC. Although you can easily find an inexpensive DAC to control from ...
- Cortex-A9 PWM Timer
PWM定时器 4412时钟为我们提供了PWM定时器,在4412中共有5个32位的定时器,这些定时器可发送中断信号给ARM子系统.另外,定时器0.1.2.3包含了脉冲宽度调制(PWM),并 ...
- PWM DAC vs. Standalone
http://analogtalk.com/?p=534 http://analogtalk.com/?p=551 Posted by AnalogAdvocate on April 09, 2010 ...
- PWM DAC Low Pass Filtering
[TI博客大赛][原创]LM3S811之基于PWM的DAC http://bbs.ednchina.com/BLOG_ARTICLE_3005301.HTM http://www.fpga4fun.c ...
- how to generate an analog output from a in-built pwm of Atmega 32AVR microcontrloller?
how to generate an analog output from a in-built pwm of Atmega 32AVR microcontrloller? you need a re ...
- M451 PWM对照数据手册分析
PWM_T Struct Reference Control Register » Pulse Width Modulation Controller(PWM) typedef struct { ...
- 说说M451例程之PWM的寄存器讲解
M451提供了两路PWM发生器.每路PWM支持6通道PWM输出或输入捕捉.有一个12位的预分频器把时钟源分频后输入给16位的计数器,另外还有一个16位的比较器.PWM计数器支持向上,向下,上下计数方式 ...
- 说说M451例程之PWM
/**************************************************************************//** * @file main.c * @ve ...
随机推荐
- Linux学习笔记:ps -ef、ps aux、kill -9
一.查看进程命令 1.ps命令 Linux中的ps命令是Process Status的缩写. ps命令用来列出系统中当前运行的那些进程. ps命令列出的是当前那些进程的快照,就是执行ps命令的那个时刻 ...
- CVE-2012-0003 Microsoft Windows Media Player ‘winmm.dll’ MIDI文件解析远程代码执行漏洞 分析
[CNNVD]Microsoft Windows Media Player ‘winmm.dll’ MIDI文件解析远程代码执行漏洞(CNNVD-201201-110) Microsoft Wi ...
- SQL Server中的快捷键
新建查询:Ctrl + N 反撤销:Ctrl + Y 撤销:Ctrl + Z 查找:Ctrl + F 启动调试:Alt + F5 注释:Ctrl + K + C 取消注释:Ctrl + K + U 执 ...
- 【LOJ】#2541. 「PKUWC2018」猎人杀
题解 一道神仙的题>< 我们毙掉一个人后总的w的和会减少,怎么看怎么像指数算法 然而,我们可以容斥-- 设\(\sum_{i = 1}^{n} w_{i} = Sum\) 我们把问题转化一 ...
- docker动态绑定端口
一.背景 在创建容器的时候,我们可以使用命令 docker container run -p host:container container-name 的方式来绑定端口,还可以使用docker-co ...
- 阿里云修改CentOS Linux服务器的主机名
阿里云主机的默认主机名是为AY开头的随机名称,如何修改为易于区分的友好名称呢?请看下面的操作步骤: 1. vi /etc/hosts i键,修改主机名,esc键,:wq键保存退出 2. vi /etc ...
- [CodeForces - 678F] Lena and Queries 线段树维护凸包
大致题意: 给出三种操作 1.往平面点集中添加一个点 2.删除第i次添加的点 3.给出一个q,询问平面点集中的q*x+y的最大值 首先对于每个询问,可将z=q*x+y转化为y=z-q*x,即过点(x, ...
- UVA - 10815 - Andy's First Dictionary STL
Andy, 8, has a dream - he wants to produce his very own dictionary. This is not an easy task for him ...
- JavaScript 网页脚本语言 由浅入深 (随笔)
1)基础 学习目的: 1. 客户端表单验证 2. 页面动态效果 3. jQuery的基础 什么是JavaScript? 一种描述性语言,也是一种基于对象和事件驱动的,并具有安全性能的脚本语言 java ...
- In 和Exists
1.exist,not exist一般都是与子查询一起使用. In可以与子查询一起使用,也可以直接in (a,b.....) 2.exist会针对子查询的表使用索引. not exist会对主子查询都 ...
