java:Spring框架1(基本配置,简单基础代码模拟实现,spring注入(DI))

1.基本配置:
步骤一:新建项目并添加spring依赖的jar文件和commons-logging.xx.jar:
步骤二:编写实体类,DAO及其实现类,Service及其实现类;
步骤三:在src下新建配置文件applicationContext.xml,并配置bean节点和property:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="userinfoJdbcDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userinfoHibDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoHibDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userinfoService" class="cn.zzsxt.service.impl.UserinfoServiceImpl">
<property name="userinfoDao" ref="userinfoHibDao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
bean节点:
id属性:用户自定义的bean的名称,使用ApplicationContext中getBean()根据此id的值从spring容器中获取已创建好的对象。
class属性:全限定的类名,spring容器会根据此类名动态创建对象
property节点:
name属性:必须与bean中待注入的属性名称一致,回调其对应的setter方法为该属性赋值。
ref属性:必须与待注入的对象的id一致,从spring容器中根据ref获取待注入的对象,然后回调setter方法将该对象赋值给属性。
步骤四:测试:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserinfoService userinfoService = applicationContext.getBean(UserinfoService.class,"userinfoService");
Userinfo user = new Userinfo();
user.setUserId(1);
user.setUserName("test");
user.setUserPass("test");
userinfoService.save(user);
}
}
2.简单基础代码模拟实现:
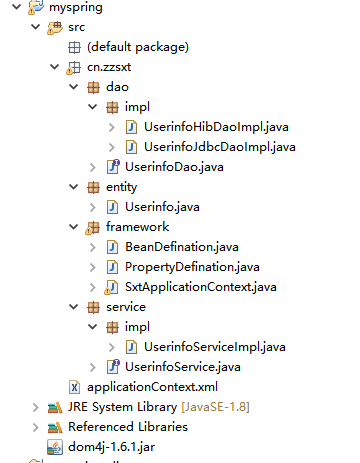
application.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<!-- UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl userinfoJdbcDao = new UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl()-->
<bean id="userinfoJdbcDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl"></bean>
<!--UserinfoHibDaoImpl userinfoHibDao = new UserinfoHibDaoImpl()-->
<bean id="userinfoHibDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoHibDaoImpl"></bean>
<!--UserinfoServiceImpl userinfoService = new UserinfoServiceImpl() -->
<bean id="userinfoService" class="cn.zzsxt.service.impl.UserinfoServiceImpl">
<!--userinfoService.setUserinfoDao(userinfoJdbcDao); -->
<property name="userinfoDao" ref="userinfoJdbcDao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
UserinfoHibDaoImpl:
package cn.zzsxt.dao.impl; import cn.zzsxt.dao.UserinfoDao;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class UserinfoHibDaoImpl implements UserinfoDao { @Override
public void save(Userinfo user) {
System.out.println("利用hibernate执行了新增,新增用户"+user);
} }
UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl:
package cn.zzsxt.dao.impl; import cn.zzsxt.dao.UserinfoDao;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl implements UserinfoDao { @Override
public void save(Userinfo user) {
System.out.println("利用jdbc执行了新增,新增用户"+user);
} }
BeanDefination:
package cn.zzsxt.framework; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* 封装配置文件applicationContext.xml中bean节点的信息
* <bean id="userinfoService" class="cn.zzsxt.service.impl.UserinfoServiceImpl">
* <property name="userinfoDao" ref="userinfoHibDao"></property>
* </bean>
* @author Think
*
*/
public class BeanDefination {
private String beanId;//封装id属性的值
private String beanClass;//封装class属性的值
//封装该bean节点的所有property子节点的信息,利用property的name做键,利用property的信息做值
private Map<String,PropertyDefination> propsMap = new HashMap<String,PropertyDefination>(); public String getBeanId() {
return beanId;
}
public void setBeanId(String beanId) {
this.beanId = beanId;
}
public String getBeanClass() {
return beanClass;
}
public void setBeanClass(String beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
}
public Map<String, PropertyDefination> getPropsMap() {
return propsMap;
}
public void setPropsMap(Map<String, PropertyDefination> propsMap) {
this.propsMap = propsMap;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BeanDefination [beanId=" + beanId + ", beanClass=" + beanClass + ", propsMap=" + propsMap + "]";
} }
PropertyDefination:
package cn.zzsxt.framework;
/**
* 封装applicationContext.xml中property节点的信息
* <property name="userinfoDao" ref="userinfoHibDao"></property>
* @author Think
*
*/
public class PropertyDefination {
private String propertyName;//封装name属性的值
private String propertyRef;//封装ref属性的值
public String getPropertyName() {
return propertyName;
}
public void setPropertyName(String propertyName) {
this.propertyName = propertyName;
}
public String getPropertyRef() {
return propertyRef;
}
public void setPropertyRef(String propertyRef) {
this.propertyRef = propertyRef;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PropertyDefination [propertyName=" + propertyName + ", propertyRef=" + propertyRef + "]";
} }
UserinfoServiceImpl:
package cn.zzsxt.service.impl; import cn.zzsxt.dao.UserinfoDao;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo;
import cn.zzsxt.service.UserinfoService; public class UserinfoServiceImpl implements UserinfoService {
private UserinfoDao userinfoDao; public void setUserinfoDao(UserinfoDao userinfoDao) {
this.userinfoDao = userinfoDao;
} @Override
public void save(Userinfo user) {
userinfoDao.save(user);
} }
SxtApplicationContext:
package cn.zzsxt.framework; import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry; import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo;
import cn.zzsxt.service.UserinfoService; public class SxtApplicationContext {
//封装所有bean节点的信息,利用bean的id做键,利用bean节点的信息做值
private Map<String,BeanDefination> beanDefinationsMap = new HashMap<String,BeanDefination>();
//封装所有动态创建的对象信息,利用bean的id做键,利用创建的对象做值
private Map<String,Object> beansMap = new HashMap<String,Object>(); public SxtApplicationContext(){
parseXML();//解析配置文件
createObject();//动态创建对象
injectObject();//为属性注入值:回调该属性的setter方法
}
/**
* 解析applicationContext.xml配置文件信息。
* 将bean节点封装成BeanDefination对象
* 将property节点封装成PropertyDefination对象
*
*/
public void parseXML(){
InputStream ips = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("/applicationContext.xml");
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
Document document = saxReader.read(ips);
//获取根节点
Element beans = document.getRootElement();//获取根节点-->beans节点
Iterator<Element> beanIter = beans.elementIterator();
while(beanIter.hasNext()){
Element bean = beanIter.next();//获取bean节点
String beanId = bean.attributeValue("id");//获取bean节点的id属性值
String beanClass = bean.attributeValue("class");//获取bean节点的class属性值
//将bean节点的信息封装成BeanDefination对象
BeanDefination beanDefination = new BeanDefination();
beanDefination.setBeanId(beanId);
beanDefination.setBeanClass(beanClass);
Iterator<Element> propertyIter = bean.elementIterator();
while(propertyIter.hasNext()){
Element property = propertyIter.next();//获取property节点
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");//获取property节点的name属性值
String propertyRef = property.attributeValue("ref");//获取property节点的ref属性值
//将property节点的信息封装成PropertyDefination对象
PropertyDefination propertyDefination = new PropertyDefination();
propertyDefination.setPropertyName(propertyName);
propertyDefination.setPropertyRef(propertyRef);
//将property节点的信息添加到beanDefination的map中
beanDefination.getPropsMap().put(propertyName, propertyDefination);
}
//将beanDefination添加到beanDefinationsMap中
beanDefinationsMap.put(beanId, beanDefination);
}
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 根据配置文件中bean节点的class属性信息动态创建对象,并将创建的对象添加到beansMap中
*/
public void createObject(){
try {
//1.遍历beanDefinationsMap(封装了所有bean节点的信息)
for (Entry<String,BeanDefination> beanEntry :beanDefinationsMap.entrySet()) {
String beanId = beanEntry.getKey();//bean的id属性的值
BeanDefination beanDefination = beanEntry.getValue();//获取bean节点的信息
String beanClass = beanDefination.getBeanClass();//bean的class属性的值
Object object = Class.forName(beanClass).newInstance();//根据bean节点的class属性值(全限定的类名)动态创建对象
//将创建的对象添加到beansMap中,利用beanId做键,利用对象做值
beansMap.put(beanId, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 根据property节点所配置的属性信息,从容器中查找待注入的对象,回调setter方法为属性赋值。
*/
public void injectObject(){
try {
for (Entry<String,BeanDefination> beanEntry :beanDefinationsMap.entrySet()) {
String beanId = beanEntry.getKey();//bean的id属性的值
//根据beanId从beansMap中创建的对象
Object target=getBean(beanId); BeanDefination beanDefination = beanEntry.getValue();//获取bean节点的信息
String beanClass = beanDefination.getBeanClass();//bean的class属性的值
Class clazz = Class.forName(beanClass);//动态加载bean
Map<String,PropertyDefination> propsMap = beanDefination.getPropsMap();//获取property节点的信息
for (Entry<String,PropertyDefination> propertyEntry : propsMap.entrySet()) {
PropertyDefination propertyDefination = propertyEntry.getValue();//获取property节点的信息
String propertyName = propertyDefination.getPropertyName();//获取property的name属性值
String propertyRef = propertyDefination.getPropertyRef();//获取property的ref属性值 Object params = getBean(propertyRef);//根据property中的ref属性值从beansMap获取待注入的对象(要求ref属性的值必须与待注入的bean的id值一致) String setterMethodName = makeSetter(propertyName);//根据property节点的name属性值,获取其对应的setter方法名 Method[] ms = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : ms) {
String methodName = method.getName();
if(methodName.equals(setterMethodName)){
//回调setter方法
method.invoke(target, params); }
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 根据beanId从beansMap容器中获取创建的对象
* @param beanId
* @return
*/
public Object getBean(String beanId){
return beansMap.get(beanId);
}
/**
* 根据属性名称生成对应的setter方法名: set+属性的首字母大写+其余字母
* @param fieldName
* @return
*/
public String makeSetter(String fieldName){
return "set"+fieldName.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+fieldName.substring(1);
} public static void main(String[] args) {
SxtApplicationContext applicationContext = new SxtApplicationContext();
UserinfoService userinfoService = (UserinfoService)applicationContext.getBean("userinfoService");
Userinfo user = new Userinfo();
user.setUserId(1);
user.setUserName("admin");
user.setUserPass("admin");
userinfoService.save(user);
}
}
3.spring注入(DI):
application.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="userinfoJdbcDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userinfoHibDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoHibDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userinfoService" class="cn.zzsxt.service.impl.UserinfoServiceImpl">
<property name="userinfoDao" ref="userinfoHibDao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
beans.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--
DI:依赖注入
1.setter注入:回调属性的setter方法为该属性赋值
a.为属性注入常量值:使用property的value属性
b.为属性注入对象:使用property的ref属性
2.构造方法注入(构造子注入):回调构造方法为属性赋值
-->
<bean id="user" class="cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo">
<property name="userId" value="1"></property>
<property name="userName" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="userPass" value="123"></property>
</bean>
<!--
构造方法注入:constructor-arg index代表的参数的下标
a.为属性注入常量值:使用constructor-arg中的value属性
b.为属性注入对象: 使用constructor-arg中的ref属性
-->
<bean id="user2" class="cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo2">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="2"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="lisi"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="1234"></constructor-arg>
</bean> <bean id="userinfoJdbcDao" class="cn.zzsxt.dao.impl.UserinfoJdbcDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userinfoService" class="cn.zzsxt.service.impl.UserinfoServiceImpl">
<!-- 使用setter注入 -->
<!-- <property name="userinfoDao" ref="userinfoJdbcDao"></property> -->
<!-- 使用构造函数为属性注入对象 -->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="userinfoJdbcDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
beans2.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 为集合属性注入值:在框架的集成中较为常见 -->
<bean id="myCollection" class="cn.zzsxt.entity.MyCollection">
<!-- 为list类型的属性注入值 -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
<value>list3</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 为set类型的属性注入值 -->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>set1</value>
<value>set2</value>
<value>set1</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- 为map类型的属性注入值 -->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="key1" value="value1"></entry>
<entry key="key2" value="value2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!-- 为properties类型的属性注入值 -->
<property name="props">
<props>
<prop key="p-key1">p-value1</prop>
<prop key="p-key2">p-value2</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
beans3.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="stoneAxe" class="cn.zzsxt.ioc.StoneAxe"></bean>
<bean id="steelAxe" class="cn.zzsxt.ioc.SteelAxe"></bean>
<bean id="chinese" class="cn.zzsxt.ioc.Chinese">
<property name="axe" ref="stoneAxe"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="american" class="cn.zzsxt.ioc.American">
<property name="axe" ref="steelAxe"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
MyCollection:
package cn.zzsxt.entity; import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set; public class MyCollection {
private List list;
private Set set;
private Map map;
private Properties props; public List getList() {
return list;
} public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
} public Set getSet() {
return set;
} public void setSet(Set set) {
this.set = set;
} public Map getMap() {
return map;
} public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
} public Properties getProps() {
return props;
} public void setProps(Properties props) {
this.props = props;
} }
Userinfo:
package cn.zzsxt.entity;
public class Userinfo {
private int userId;
private String userName;
private String userPass;
public Userinfo(int userId, String userName, String userPass) {
this.userId = userId;
this.userName = userName;
this.userPass = userPass;
}
public Userinfo() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getUserPass() {
return userPass;
}
public void setUserPass(String userPass) {
this.userPass = userPass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Userinfo [userId=" + userId + ", userName=" + userName + ", userPass=" + userPass + "]";
}
}
UserinfoServiceImpl:
package cn.zzsxt.service.impl; import cn.zzsxt.dao.UserinfoDao;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo;
import cn.zzsxt.service.UserinfoService;
/**
* 开闭原则:
* @author Think
*
*/
public class UserinfoServiceImpl implements UserinfoService {
// private UserinfoDao userinfoDao = new UserinfoHibDaoImpl();
private UserinfoDao userinfoDao; public UserinfoServiceImpl() {
} public UserinfoServiceImpl(UserinfoDao userinfoDao) {
System.out.println("带参构造函数被调用了...");
this.userinfoDao = userinfoDao;
} public void setUserinfoDao(UserinfoDao userinfoDao) {
this.userinfoDao = userinfoDao;
} @Override
public void save(Userinfo user) {
userinfoDao.save(user);
} }
Test:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo;
import cn.zzsxt.service.UserinfoService; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserinfoService userinfoService = applicationContext.getBean(UserinfoService.class,"userinfoService");
Userinfo user = new Userinfo();
user.setUserId(1);
user.setUserName("test");
user.setUserPass("test");
userinfoService.save(user);
}
}
Test2:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo2;
import cn.zzsxt.service.UserinfoService; public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Userinfo user = ac.getBean(Userinfo.class,"user");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("-------------");
Userinfo2 user2 = ac.getBean(Userinfo2.class,"user2");
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println("--------------------");
UserinfoService userinfoService = ac.getBean(UserinfoService.class,"userinfoService");
userinfoService.save(user);
}
}
Test3:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.zzsxt.entity.MyCollection;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo;
import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo2;
import cn.zzsxt.service.UserinfoService; public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans2.xml");
MyCollection myCollection = ac.getBean(MyCollection.class,"myCollection");
System.out.println(myCollection.getList());
System.out.println(myCollection.getSet());
System.out.println(myCollection.getMap());
System.out.println(myCollection.getProps()); }
}
Axe:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc;
public interface Axe {
public void chop();
}
StoneAxe:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc;
public class StoneAxe implements Axe {
@Override
public void chop() {
System.out.println("我是石斧,砍人很钝!");
}
}
SteelAxe:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc;
public class SteelAxe implements Axe {
@Override
public void chop() {
System.out.println("我是鉄斧,砍人很锋利!");
}
}
Person:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc;
public interface Person {
public void useAxe();
}
Chinese:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc;
public class Chinese implements Person {
private Axe axe;
public void setAxe(Axe axe) {
this.axe = axe;
}
@Override
public void useAxe() {
System.out.println("我是中国人民解放军,现在向你发出严重警告!");
axe.chop();
}
}
American:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc;
public class American implements Person {
private Axe axe;
public void setAxe(Axe axe) {
this.axe = axe;
}
@Override
public void useAxe() {
System.out.println("我是美国大兵,你瞅啥!");
axe.chop();
}
}
Test:
package cn.zzsxt.ioc; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans3.xml");
Person p = (Person)ac.getBean("chinese");
p.useAxe();
System.out.println("-----------------");
Person p2 = (Person)ac.getBean("american");
p2.useAxe(); }
}
java:Spring框架1(基本配置,简单基础代码模拟实现,spring注入(DI))的更多相关文章
- 《Java Spring框架》SpringXML配置详解
Spring框架作为Bean的管理容器,其最经典最基础的Bean配置方式就是纯XML配置,这样做使得结构清晰明了,适合大型项目使用.Spring的XML配置虽然很繁琐,而且存在简洁的注解方式,但读懂X ...
- Spring框架-IOC和AOP简单总结
参考博客: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22583741/article/details/79589910 1.Spring框架是什么,为什么,怎么用 1.1 Spring框架是 ...
- 基于spring框架的apache shiro简单集成
关于项目的安全保护,我一直想找一个简单配置就能达到目的的方法,自从接触了shiro,这个目标总算达成了,以下结合我使用shiro的经验,谈谈比较轻便地集成该功能. 首先我们先了解一下shiro是什么. ...
- String框架搭建的基本步骤,及从 IOC & DI 容器中获取 Bean(spring框架bean的配置)--有实现数据库连接池的链接
Spring框架的插件springsource-tool-suite-3.4.0.RELEASE-e4.3.1-updatesite(是一个压缩包)导入步骤: eclipse->help-> ...
- Spring 自定义注解,配置简单日志注解
java在jdk1.5中引入了注解,spring框架也正好把java注解发挥得淋漓尽致. 下面会讲解Spring中自定义注解的简单流程,其中会涉及到spring框架中的AOP(面向切面编程)相关概念. ...
- Spring框架bean的配置(2):SpEL:引用 Bean、属性和方法。。。
将这些架包放入在工程目录下建立的lib文件夹里,并解压 commons-logging-1.1.1 spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEAS ...
- Spring MVC 学习 之 - 配置简单demo
1.环境参数: Maven:3.1.1 JDK :1.6 2.项目文件结构图: 3.各文件配置: 3.1. pom.xml <project xmlns="http://maven. ...
- Spring框架bean的配置(3):基于注解的配置
1.基于注解的配置: @Component: 基本注解, 标识了一个受 Spring 管理的组件 @Respository: 标识持久层组件 @Service: 标识服务层(业务层)组件 @Contr ...
- [翻译]Spring框架参考文档(V4.3.3)-第二章Spring框架介绍 2.1 2.2 翻译--2.3待继续
英文链接:http://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/html/overview.ht ...
随机推荐
- [牛客] [# 1108 E] Grid
2019牛客国庆集训派对day3 链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/1108/E来源:牛客网 题意 在一个$10 ^ 9 * 10 ^ 9$ 的方格中,每次 ...
- mvn高级构建
指定pom文件,打包指定的module,并且自动打包这个模块所依赖的其他模块. mvn clean install -f vmc-business-parent/pom.xml -pl vmc-sch ...
- radio(单选框)/checkbox(复选框) 美化
由于某种原因,可能需要对单选框(radio)或复选框(checkbox)进行美化,那么直接修改样式是行不通,要实现就需要添加js,以下js依赖于jquery radio.js: function ra ...
- 【UOJ#37】 [清华集训2014] 主旋律
题目链接 题目描述 给定一张强联通图,求有多少种边的存在情况满足图依然强联通. \(n\leq15\) Sol 首先正难则反,考虑用总数减去不强联通的. 考虑一张不强联通的图,缩点后一定是一个 DAG ...
- 【PKUSC2019】线弦图【计数】【树形DP】【分治FFT】
Description 定义线图为把无向图的边变成点,新图中点与点之间右边当且仅当它们对应的边在原图中有公共点,这样得到的图. 定义弦图为不存在一个长度大于3的纯环,纯环的定义是在环上任取两个不相邻的 ...
- pip安装源和虚拟环境的搭建
一.pip安装源 1.介绍 采用国内源,加速下载模块的速度 常用pip源: 豆瓣:https://pypi.douban.com/simple 阿里:https://mirrors.aliyun.co ...
- Python3学习笔记(十五):常用时间模块time和datetime
一.time模块 1.时间戳 time.time() :从1970-01-01到至今的秒数 import time print(time.time()) 1529238004.2784646 2.等待 ...
- Spring配置文件beans标签报错问题解决
因为有很多配置是复制过来的,附带的很多注释的格式会导致报错,所以可以要试试把注释去掉,只有配置文件的话可能就不会报错了.
- java通讯录获取汉字首字母
1.本文只是使用了pinyin4J的主要功能,还有更多更好耍的功能,大家可以去研究官网文档.哈哈 2.pinyin4j的官方下载地址:https://sourceforge.net/projects/ ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ结合Spring
ActiveMQ结合 Spring开发■ Spring提供了对JMS的支持,需要添加 Spring支持jms的包,如下: <dependency> <groupId>org.a ...
