lua定时器与定时任务的接口设计
在所有的服务器编程当中,定时任务永远是一个不可或缺的需求。
最直接的需求就是,每天凌晨0点0分的时候总是有一大堆的各种精力重置。
怎么来设计这个接口呢,想了几个方案:
- 每秒触发
- 每分钟触发
- 每整点触发
- 每天触发
- 每个月触发
oh no!不靠谱啊,如果这接口真设计成这样,得有多烂,灵光一现,unix下的crontab表达式非常完美的解决了这个问题。
附上crontab表达式的语法说明如下:
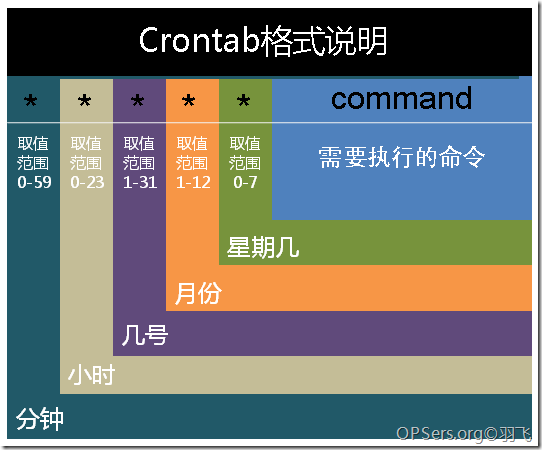
crontab特殊的符号说明:
"*"代表所有的取值范围内的数字。特别要注意哦!
"/"代表每的意思,如"*/5"表示每5个单位
"-"代表从某个数字到某个数字
","分散的数字
crontab文件的使用示例:
30 21 * * * 表示每晚的21:30
45 4 1,10,22 * * 表示每月1、10、22日的4 : 45
10 1 * * 6,0 表示每周六、周日的1 : 10
0,30 18-23 * * * 表示在每天18 : 00至23 : 00之间每隔30分钟
0 23 * * 6 表示每星期六的11 : 00 pm
* */1 * * * 每一小时
* 23-7/1 * * * 晚上11点到早上7点之间,每隔一小时
* 8,13 * * 1-5 从周一到周五的上午8点和下午1点
0 11 4 * mon-wed 每月的4号与每周一到周三的11点
0 4 1 jan * 一月一号的4点
看起来很复杂的样子,但其实够用就好,我们也不需要实现全部特性。
- 实现一个毫秒级别的定时器Update
- 根据这个update函数实现一个秒级别定时器
- 然后每秒取得自然时间与表达式中 分、时、几号、月份、星期几 分别匹配就可以实现了
- 由于定时器除了增加以外,可能还需要一个删除功能,那就再提供一个定时器命名的功能,用于增删改查定时器是本身
- 再加个测试函数。。完美
直接上代码:
--------------------------------------------
--任何一个记录产生一个实例
local Clock = {}
local Clock_mt = {__index = Clock} local function __checkPositiveInteger(name, value)
if type(value) ~= "number" or value < 0 then
error(name .. " must be a positive number")
end
end --验证是否可执行
local function __isCallable(callback)
local tc = type(callback)
if tc == 'function' then return true end
if tc == 'table' then
local mt = getmetatable(callback)
return type(mt) == 'table' and type(mt.__call) == 'function'
end
return false
end local function newClock(cid, name, time, callback, update, args)
assert(time)
assert(callback)
assert(__isCallable(callback), "callback must be a function")
return setmetatable({
cid = cid,
name = name,
time = time,
callback = callback,
args = args,
running = 0,
update = update
}, Clock_mt)
end function Clock:reset(running)
running = running or 0
__checkPositiveInteger('running', running) self.running = running
self.deleted = nil --如果已经删除的,也要复活
end local function updateEveryClock(self, dt)
__checkPositiveInteger('dt', dt)
self.running = self.running + dt while self.running >= self.time do
self.callback(unpack(self.args))
self.running = self.running - self.time
end
return false
end local function updateAfterClock(self, dt) -- returns true if expired
__checkPositiveInteger('dt', dt)
if self.running >= self.time then return true end self.running = self.running + dt if self.running >= self.time then
self.callback(unpack(self.args))
return true
end
return false
end local function match( left, right )
if left == '*' then return true end --单整数的情况
if 'number' == type(left) and left == right then
return true
end --范围的情况 形如 1-12/5,算了,先不支持这种每隔几分钟的这种特性吧
_,_,a,b = string.find(left, "(%d+)-(%d+)")
if a and b then
return (right >= tonumber(a) and right <= tonumber(b))
end --多选项的情况 形如 1,2,3,4,5
--哎,luajit不支持gfind,
--for d in string.gfind(left, "%d+") do
--其实也可以for i in string.gmatch(left,'(%d+)') do
local pos = 0
for st,sp in function() return string.find(left, ',', pos, true) end do
if tonumber(string.sub(left, pos, st - 1)) == right then
return true
end
pos = sp + 1
end
return tonumber(string.sub(left, pos)) == right
end local function updateCrontab( self, dt )
local now = os.date('*t')
local tm = self.time
--print('updateCrontab/now:', now.min, now.hour, now.day, now.month, now.wday)
--print('updateCrontab/tm', tm.mn, tm.hr, tm.day, tm.mon, tm.wkd)
--print('match:',match(tm.mn, now.min), match(tm.hr, now.hour), match(tm.day, now.day), match(tm.mon, now.month), match(tm.wkd, now.wday))
if match(tm.mn, now.min) and match(tm.hr, now.hour)
and match(tm.day, now.day) and match(tm.mon, now.month)
and match(tm.wkd, now.wday)
then
--print('matching',self.name,self.callback,self.running)
self.callback(unpack(self.args))
self.running = self.running + 1
end
return false
end --遍历并执行所有的定时器
local function updateClockTables( tbl )
for i = #tbl, 1, -1 do
local v = tbl[i]
if v.deleted == true or v:update(1) then
table.remove(tbl,i)
end
end
end ---------------------------------------------------------- local crontab = {}
crontab.__index = crontab function crontab.new( obj )
local obj = obj or {}
setmetatable(obj, crontab)
--执行一下构造函数
if obj.ctor then
obj.ctor(obj)
end
return obj
end function crontab:ctor( )
--所有的定时器
self._clocks = self._clocks or {}
self._crons = self._crons or {}
--累积的时间差
self._diff = self._diff or 0
--已命名的定时器,设置为弱引用表
self._nameObj = {}
setmetatable(self._nameObj, {__mode="k,v"}) --取得现在的秒数,延迟到整点分钟的时候启动一个定时
self:after("__delayUpdateCrontab", 60-os.time()%60, function ( )
--在整点分钟的时候,每隔一分钟执行一次
self:every("__updateCrontab", 60, function ( )
updateClockTables(self._crons)
end)
end)
end function crontab:update( diff )
self._diff = self._diff + diff
while self._diff >= 1000 do
--TODO:这里真让人纠结,要不要支持累积时间误差呢?
self._diff = self._diff - 1000
--开始对所有的定时器心跳,如果返回true,则从列表中移除
updateClockTables(self._clocks)
end
end function crontab:remove( name )
if name and self._nameObj[name] then
self._nameObj[name].deleted = true
end
end --通过判断callback的真正位置,以及参数类型来支持可变参数
--返回值顺序 number, string, number, function, args
--总的有如下5种情况
--1) cid,name,time,callback,args
--2) name,cid,time,callback,args
--3) name,time,callback,args
--4) cid,time,callback,args
--5) time,callback,args
local function changeParamsName( p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 )
if __isCallable(p4) then
if type(p1) == 'string' then
return p2,p1,p3,p4,p5
else
return p1,p2,p3,p4,p5
end
elseif __isCallable(p3) then
if type(p1) == 'string' then
return nil,p1,p2,p3,p4
else
return p1,nil,p2,p3,p4
end
else
return nil,nil,p1,p2,p3
end
end function crontab:every( cid, name, time, callback, args )
--支持可变参数
cid, name, time, callback, args = changeParamsName(cid, name, time, callback,args)
__checkPositiveInteger('time', time)
local clock = newClock(cid, name, time, callback, updateEveryClock, args or {})
table.insert(self._clocks,clock)
if name and name ~= '' then
self._nameObj[name] = clock
end
return clock
end function crontab:after( cid, name, time, callback, args )
cid, name, time, callback, args = changeParamsName(cid, name, time, callback,args)
__checkPositiveInteger('time', time)
local clock = newClock(cid, name, time, callback, updateAfterClock, args or {})
table.insert(self._clocks,clock)
if name and name ~= '' then
self._nameObj[name] = clock
end
return clock
end --增加计划任务,精度到达分钟级别
--表达式:分钟[0-59] 小时[0-23] 每月的几号[1-31] 月份[1-12] 星期几[1-7]
-- 星期天为1,
-- "*"代表所有的取值范围内的数字
-- "-"代表从某个数字到某个数字
-- "/"代表每的意思,如"*/5"表示每5个单位,未实现
-- ","分散的数字
-- 如:"45 4-23/5 1,10,22 * *"
function crontab:addCron(cid, name, crontab_str, callback, args )
cid, name, crontab_str, callback, args = changeParamsName(cid, name, crontab_str, callback, args)
--print(cid, name, crontab_str, callback)
local t = {}
for v in string.gmatch(crontab_str,'[%w._/,%-*]+') do
--如果可以转成整型直接转了,等下直接对比
local i = tonumber(v)
table.insert(t, i and i or v)
end
if table.getn(t) ~= 5 then
return error(string.format('crontab string,[%s] error!',crontab_str))
end local time = {mn = t[1], hr = t[2], day = t[3], mon = t[4], wkd = t[5]}
local clock = newClock(cid, name, time, callback, updateCrontab, args or {})
table.insert(self._crons,clock)
if name and name ~= '' then
self._nameObj[name] = clock
end
end return crontab
再看看测试代码:
--传说中的测试代码
local function RunTests()
-- the following calls are equivalent:
local function printMessage(a )
print('Hello',a)
end local cron = crontab.new() local c1 = cron:after( 5, printMessage)
local c2 = cron:after( 5, print, {'Hello'}) c1:update(2) -- will print nothing, the action is not done yet
c1:update(5) -- will print 'Hello' once c1:reset() -- reset the counter to 0 -- prints 'hey' 5 times and then prints 'hello'
while not c1:update(1) do
print('hey')
end -- Create a periodical clock:
local c3 = cron:every( 10, printMessage) c3:update(5) -- nothing (total time: 5)
c3:update(4) -- nothing (total time: 9)
c3:update(12) -- prints 'Hello' twice (total time is now 21) -------------------------------------
c1.deleted = true
c2.deleted = true
c3.deleted = true ------------------------------
--测试一下match
print('----------------------------------')
assert(match('*',14) == true)
assert(match('12-15',14) == true)
assert(match('18-21',14) == false)
assert(match('18,21',14) == false)
assert(match('18,21,14',14) == true) --加一个定时器1分钟后执行
cron:update(1000) --加入一个定时器每分钟执行
cron:addCron('每秒执行', '* * * * *', print, {'.......... cron'}) cron:update((60-os.time()%60)*1000)
cron:update(30*1000)
cron:update(31*1000)
cron:update(1)
cron:update(60*1000) --打印两次
end
也可以直接到 https://github.com/linbc/crontab.lua 下载代码
参考资料:
http://www.cise.ufl.edu/~cop4600/cgi-bin/lxr/http/source.cgi/commands/simple/cron.c
https://github.com/kikito/cron.lua
lua定时器与定时任务的接口设计的更多相关文章
- Java生鲜电商平台-定时器,定时任务quartz的设计与架构
Java生鲜电商平台-定时器,定时任务quartz的设计与架构 说明:任何业务有时候需要系统在某个定点的时刻执行某些任务,比如:凌晨2点统计昨天的报表,早上6点抽取用户下单的佣金. 对于Java开源生 ...
- Java开发笔记(九十九)定时器与定时任务
前面介绍了线程的几种运行方式,不管哪种方式,一旦调用了线程实例的start方法,都会立即启动线程的事务处理.然而某些业务场景在事务执行时间方面有特殊需求,例如期望延迟若干时间之后才开始事务运行,又如期 ...
- 数据仓储之DLL层接口设计
一.接口设计 1.1. IBaseRepository.cs public interface IBaseRepository<T> { T Add(T entity); bool Upd ...
- RESTful接口设计原则/最佳实践(学习笔记)
RESTful接口设计原则/最佳实践(学习笔记) 原文地址:http://www.vinaysahni.com/best-practices-for-a-pragmatic-restful-api 1 ...
- Web API接口设计经验总结
在Web API接口的开发过程中,我们可能会碰到各种各样的问题,我在前面两篇随笔<Web API应用架构在Winform混合框架中的应用(1)>.<Web API应用架构在Winfo ...
- Verilog学习笔记简单功能实现(七)...............接口设计(并行输入串行输出)
利用状态机实现比较复杂的接口设计: 这是一个将并行数据转换为串行输出的变换器,利用双向总线输出.这是由EEPROM读写器的缩减得到的,首先对I2C总线特征介绍: I2C总线(inter integra ...
- 优秀的API接口设计原则及方法(转)
一旦API发生变化,就可能对相关的调用者带来巨大的代价,用户需要排查所有调用的代码,需要调整所有与之相关的部分,这些工作对他们来说都是额外的.如果辛辛苦苦完成这些以后,还发现了相关的bug,那对用户的 ...
- atitit.基于http json api 接口设计 最佳实践 总结o7
atitit.基于http json api 接口设计 最佳实践 总结o7 1. 需求:::服务器and android 端接口通讯 2 2. 接口开发的要点 2 2.1. 普通参数 meth,p ...
- App接口设计
关于APP接口设计 http://blog.csdn.net/gebitan505/article/details/37924711/
随机推荐
- 关于View端
View--------------Request 1 URL vs n View 同一个URL可以对应多个View, HTML(通过Request请求获得) 例如SAO项目中的step1--> ...
- [NodeJS] Deploy a Node Application with the Now CLI
Now offers a friction-free way to deploy node applications right from the terminal. In this lesson, ...
- [ES6] 12. Shorthand Properties in ES6
Where destructuring in ES6 allows you to easily get properties out of an object, this shorthand prop ...
- VC编译连接选项详解(转)
大家可能一直在用VC开发软件,但是对于这个编译器却未必很了解.原因是多方面的.大多数情况下,我们只停留在“使用”它,而不会想去“了解”它.因为它只是一个工具,我们宁可把更多的精力放在C++语言和软件设 ...
- 清除DataTable中的空行记录
第一种方法: string filter = ""; ; i < dt.Columns.Count; i++) { ) filter += dt.Columns[i].Col ...
- Golang学习 - unicode 包
------------------------------------------------------------ const ( MaxRune = '\U0010FFFF' // Unico ...
- Linux 测试网速
Linux 测试网速 1.直接wget -O /dev/null http://speedtest.wdc01.softlayer.com/downloads/test10.zip 一个10M的文件, ...
- tachyon 集群容错
集群容错就是HA.这次顺带也练一下hadoop的HA 环境: centos6.5+jdk1.7+hadoop2.2.0+tachyon0.5.0+zookeeper3.4.6 hadoop 192.1 ...
- Xcode 8 用处不大的新特性:CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION
来源:酷酷的哀殿 链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/067f4674f75f Xcode 8 的 clang 新的警告控制,当所有路径都通过一个函数都调用自身时,会产生一个警告 ...
- CSU 1552: Friends 图论匹配+超级大素数判定
1552: Friends Time Limit: 3 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 163 Solved: 34[Submit][Status][Web Boa ...
