linux-基于tensorflow2.x的手写数字识别-基于MNIST数据集
数据集
数据集下载MNIST
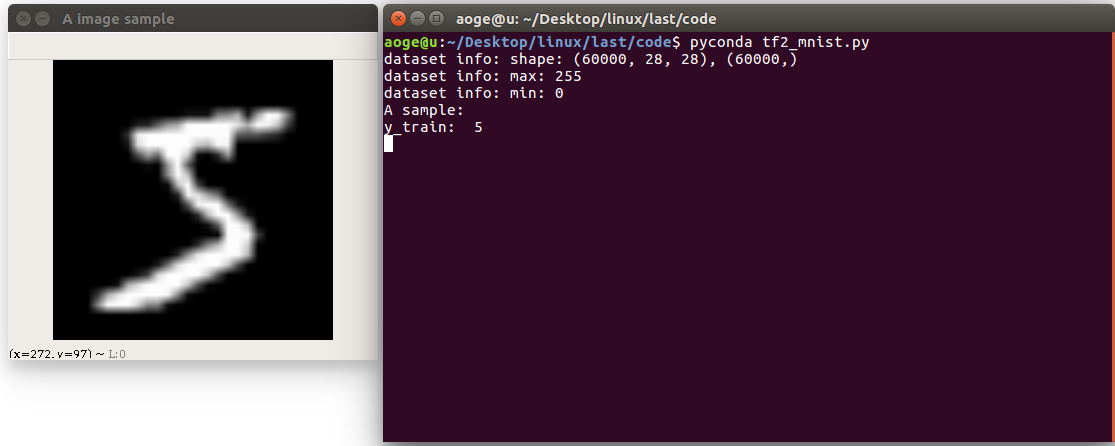
首先读取数据集, 并打印相关信息
包括
- 图像的数量, 形状
- 像素的最大, 最小值
- 以及看一下第一张图片
path = 'MNIST/mnist.npz'with np.load(path, allow_pickle=True) as f:x_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train']x_test, y_test = f['x_test'], f['y_test']print(f'dataset info: shape: {x_train.shape}, {y_train.shape}')print(f'dataset info: max: {x_train.max()}')print(f'dataset info: min: {x_train.min()}')print("A sample:")print("y_train: ", y_train[0])# print("x_train: \n", x_train[0])show_pic = x_train[0].copy()show_pic = cv2.resize(show_pic, (28 * 10, 28 * 10))cv2.imshow("A image sample", show_pic)key = cv2.waitKey(0)# 按 q 退出if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()print("show demo over")
转换为tf 数据集的格式, 并进行归一化
# convert to tf tensorx_train = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_train, dtype=tf.float32) // 255.x_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_test, dtype=tf.float32) // 255.dataset_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))dataset_train = dataset_train.batch(batch_size).repeat(class_num)
定义网络
在这里定义一个简单的全连接网络
def build_simple_net():net = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),layers.Dense(class_num)])net.build(input_shape=(None, 28 * 28))# net.summary()return net
训练
使用 SGD 优化器进行训练
def train(print_info_step=250):net = build_simple_net()# 优化器optimizer = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.01)# 计算准确率acc = metrics.Accuracy()for step, (x, y) in enumerate(dataset_train):with tf.GradientTape() as tape:# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28))# [b, 784] => [b, 10]out = net(x)# [b] => [b, 10]y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=class_num)# [b, 10]loss = tf.square(out - y_onehot)# [b]loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / batch_size# 反向传播acc.update_state(tf.argmax(out, axis=1), y)grads = tape.gradient(loss, net.trainable_variables)optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, net.trainable_variables))if acc.result() >= 0.90:net.save_weights(save_path)print(f'final acc: {acc.result()}, total step: {step}')breakif step % print_info_step == 0:print(f'step: {step}, loss: {loss}, acc: {acc.result().numpy()}')acc.reset_states()if step % 500 == 0 and step != 0:print('save model')net.save_weights(save_path)
验证
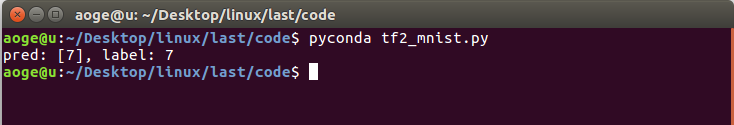
验证在测试集的模型效果, 这里仅取出第一张进行验证
def test_dataset():net = build_simple_net()# 加载模型net.load_weights(save_path)# 拿到测试集第一张图片pred_image = x_test[0]pred_image = tf.reshape(pred_image, (-1, 28 * 28))pred = net.predict(pred_image)# print(pred)print(f'pred: {tf.argmax(pred, axis=1).numpy()}, label: {y_test[0]}')
应用
分割手写数字, 并进行逐一识别
- 先将图像二值化
- 找到轮廓
- 得到数字的坐标
- 转为模型的需要的输入格式, 并进行识别
- 显示
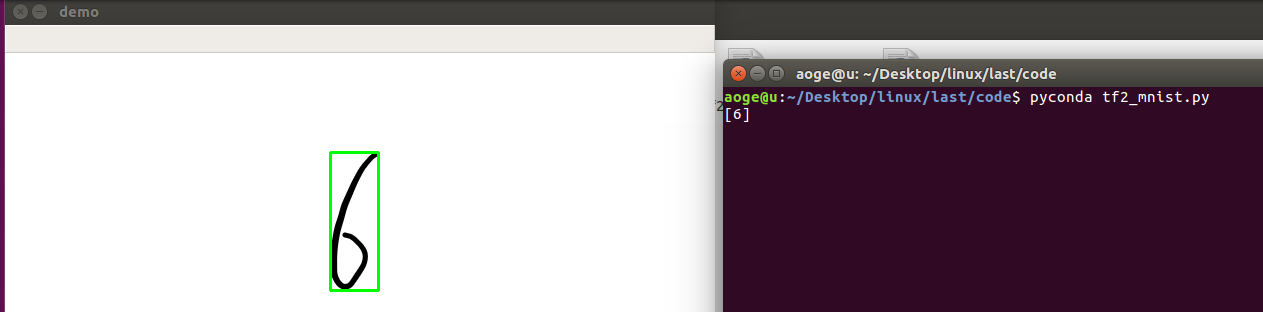
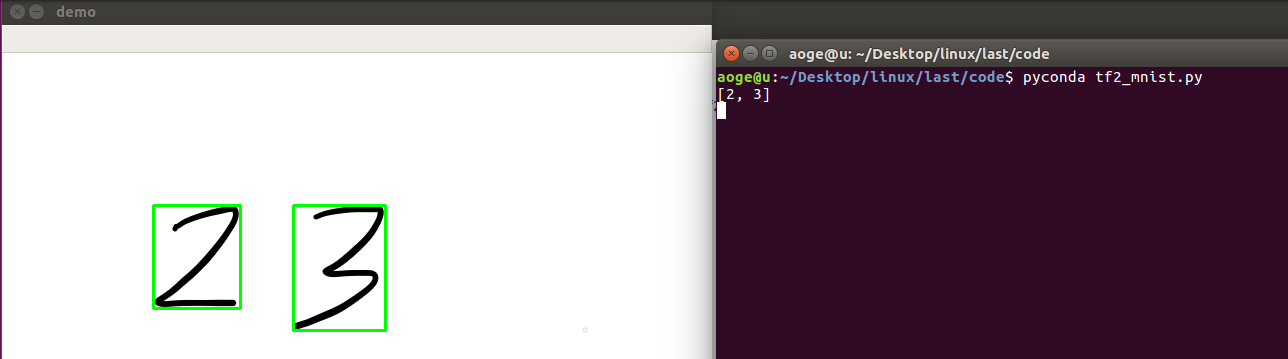
def split_number(img):result = []net = build_simple_net()# 加载模型net.load_weights(save_path)image = cv2.cvtColor(img.copy(), cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, 0)contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2)for cnt in contours[:-1]:x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)image = img[y:y+h, x:x+w]image = cv2.resize(image, (28, 28))pred_image = tf.convert_to_tensor(image, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.pred_image = tf.reshape(pred_image, (-1, 28 * 28))pred = net.predict(pred_image)out = tf.argmax(pred, axis=1).numpy()result = [out[0]] + resultimg = cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.imshow("demo", img)print(result)k = cv2.waitKey(0)# 按 q 退出if k == ord('q'):passcv2.destroyAllWindows()
效果
单数字
多数字
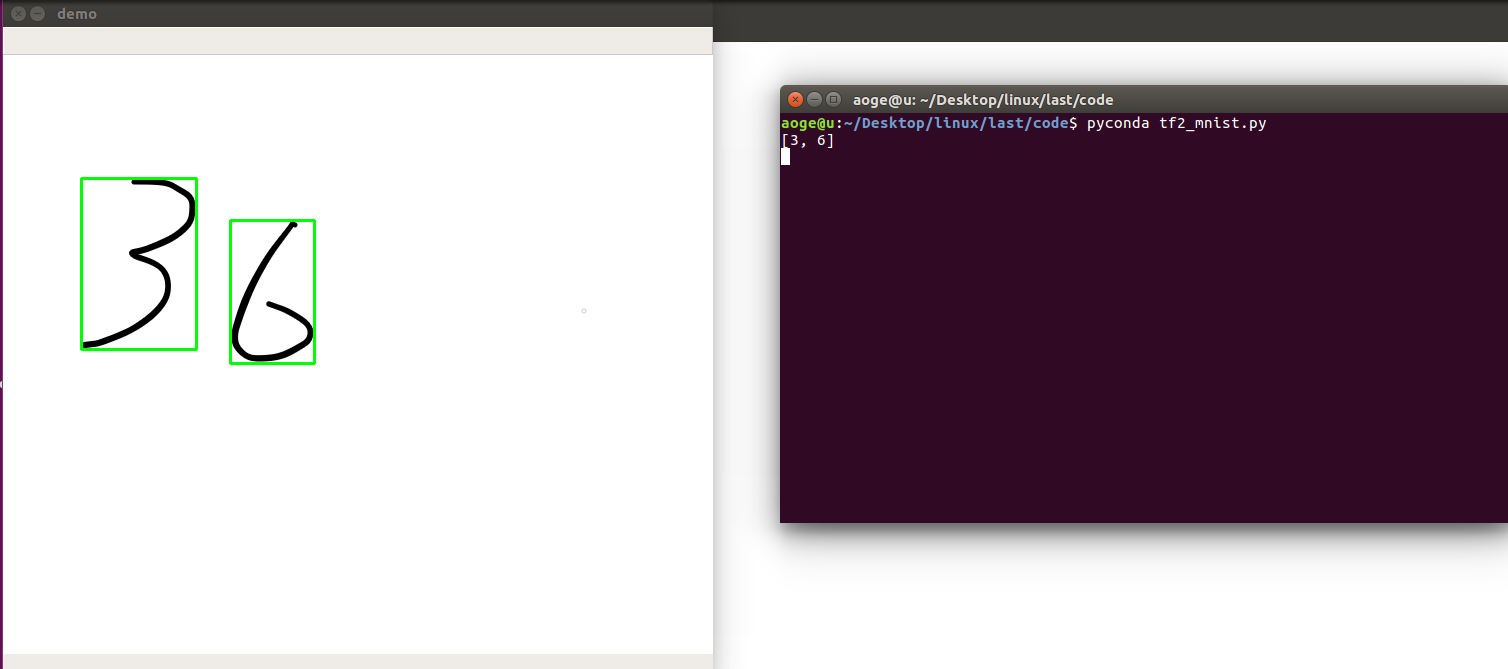
附录
所有代码, 文件 tf2_mnist.py
import osimport cv2import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras import layers, Sequential, optimizers, metrics# 屏蔽通知信息和警告信息os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'# 每批几张图片batch_size = 2# 类别数class_num = 10# 保存模型的路径save_path = "./models/mnist.ckpt"# 展示样例show_demo = False# 验证测试集evaluate_dataset = False# 是否训练run_train = False# 图片路径, 仅用于 detect_image(), 当为False时不识别image_path = 'images/36.png'path = 'MNIST/mnist.npz'with np.load(path, allow_pickle=True) as f:x_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train']x_test, y_test = f['x_test'], f['y_test']if show_demo:print(f'dataset info: shape: {x_train.shape}, {y_train.shape}')print(f'dataset info: max: {x_train.max()}')print(f'dataset info: min: {x_train.min()}')print("A sample:")print("y_train: ", y_train[0])# print("x_train: \n", x_train[0])show_pic = x_train[0].copy()show_pic = cv2.resize(show_pic, (28 * 10, 28 * 10))cv2.imshow("A image sample", show_pic)key = cv2.waitKey(0)if key == ord('q'):cv2.destroyAllWindows()print("show demo over")# convert to tf tensorx_train = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_train, dtype=tf.float32) // 255.x_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_test, dtype=tf.float32) // 255.dataset_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))dataset_train = dataset_train.batch(batch_size).repeat(class_num)def build_simple_net():net = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),layers.Dense(class_num)])net.build(input_shape=(None, 28 * 28))# net.summary()return netdef train(print_info_step=250):net = build_simple_net()# 优化器optimizer = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.01)# 计算准确率acc = metrics.Accuracy()for step, (x, y) in enumerate(dataset_train):with tf.GradientTape() as tape:# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28))# [b, 784] => [b, 10]out = net(x)# [b] => [b, 10]y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=class_num)# [b, 10]loss = tf.square(out - y_onehot)# [b]loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / batch_size# 反向传播acc.update_state(tf.argmax(out, axis=1), y)grads = tape.gradient(loss, net.trainable_variables)optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, net.trainable_variables))if acc.result() >= 0.90:net.save_weights(save_path)print(f'final acc: {acc.result()}, total step: {step}')breakif step % print_info_step == 0:print(f'step: {step}, loss: {loss}, acc: {acc.result().numpy()}')acc.reset_states()if step % 500 == 0 and step != 0:print('save model')net.save_weights(save_path)def test_dataset():net = build_simple_net()# 加载模型net.load_weights(save_path)# 拿到测试集第一张图片pred_image = x_test[0]pred_image = tf.reshape(pred_image, (-1, 28 * 28))pred = net.predict(pred_image)# print(pred)print(f'pred: {tf.argmax(pred, axis=1).numpy()}, label: {y_test[0]}')def split_number(img):result = []net = build_simple_net()# 加载模型net.load_weights(save_path)image = cv2.cvtColor(img.copy(), cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, 0)contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2)for cnt in contours[:-1]:x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)image = img[y:y+h, x:x+w]image = cv2.resize(image, (28, 28))pred_image = tf.convert_to_tensor(image, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.pred_image = tf.reshape(pred_image, (-1, 28 * 28))pred = net.predict(pred_image)out = tf.argmax(pred, axis=1).numpy()result = [out[0]] + resultimg = cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.imshow("demo", img)print(result)k = cv2.waitKey(0)if k == ord('q'):passcv2.destroyAllWindows()if __name__ == '__main__':if run_train:train()elif evaluate_dataset:test_dataset()elif image_path:image = cv2.imread(image_path)# detect_image(image)split_number(image)
linux-基于tensorflow2.x的手写数字识别-基于MNIST数据集的更多相关文章
- 基于Numpy的神经网络+手写数字识别
基于Numpy的神经网络+手写数字识别 本文代码来自Tariq Rashid所著<Python神经网络编程> 代码分为三个部分,框架如下所示: # neural network class ...
- 手写数字识别——基于LeNet-5卷积网络模型
在<手写数字识别——利用Keras高层API快速搭建并优化网络模型>一文中,我们搭建了全连接层网络,准确率达到0.98,但是这种网络的参数量达到了近24万个.本文将搭建LeNet-5网络, ...
- 【TensorFlow-windows】(四) CNN(卷积神经网络)进行手写数字识别(mnist)
主要内容: 1.基于CNN的mnist手写数字识别(详细代码注释) 2.该实现中的函数总结 平台: 1.windows 10 64位 2.Anaconda3-4.2.0-Windows-x86_64. ...
- 【TensorFlow-windows】(三) 多层感知器进行手写数字识别(mnist)
主要内容: 1.基于多层感知器的mnist手写数字识别(代码注释) 2.该实现中的函数总结 平台: 1.windows 10 64位 2.Anaconda3-4.2.0-Windows-x86_64. ...
- TensorFlow.NET机器学习入门【5】采用神经网络实现手写数字识别(MNIST)
从这篇文章开始,终于要干点正儿八经的工作了,前面都是准备工作.这次我们要解决机器学习的经典问题,MNIST手写数字识别. 首先介绍一下数据集.请首先解压:TF_Net\Asset\mnist_png. ...
- 基于卷积神经网络的手写数字识别分类(Tensorflow)
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dat ...
- 基于多层感知机的手写数字识别(Tensorflow实现)
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dat ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python机器学习:基于支持向量机SVM的手写数字识别
from numpy import * def img2vector(filename): returnVect = zeros((1,1024)) fr = open(filename) for i ...
- 【TensorFlow-windows】(一)实现Softmax Regression进行手写数字识别(mnist)
博文主要内容有: 1.softmax regression的TensorFlow实现代码(教科书级的代码注释) 2.该实现中的函数总结 平台: 1.windows 10 64位 2.Anaconda3 ...
随机推荐
- 微信小程序实战,用vue3实现每日浪漫情话推荐~
之前做了个恋爱话术微信小程序,实现高情商的恋爱聊天. 但最近突然发现,每天早上给女朋友发一段优美情话可以让她开心一整天,但无奈自己的语言水平确实有限,不能随手拈来,着实让人有点不爽. 不过办法总比困难 ...
- 《手把手教你》系列基础篇(八十五)-java+ selenium自动化测试-框架设计基础-TestNG自定义日志-下篇(详解教程)
1.简介 TestNG为日志记录和报告提供的不同选项.现在,宏哥讲解分享如何开始使用它们.首先,我们将编写一个示例程序,在该程序中我们将使用 ITestListener方法进行日志记录. 2.Test ...
- Java学习day39
类加载的作用:将class文件字节码内容加载到内存中,并将这些静态数据转换成方法区的运行时数据结构,然后在堆中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区中类数据的访问入口. 类 ...
- http协议 知识点
前端工程师,也叫Web前端开发工程师.他是随着web发展,细分出来的行业.第一步要学好HTML.CSS和JavaScript!接着就要学习交互,HTTP协议.Tomcat服务器.PHP服务器端技术是必 ...
- RecyclerView + SQLite 简易备忘录-----中(1)
在上一节讲完了登录界面的内容,现在随着Activity的跳转,来到MainActivity. 1.主界面activity_main.xml 由上图,activity_main.xml的内容很简单. 首 ...
- python基础练习题(题目 矩阵对角线之和)
day25 --------------------------------------------------------------- 实例038:矩阵对角线之和 题目 求一个3*3矩阵主对角线元 ...
- 开发并发布npm包,支持TypeScript提示,rollup构建打包
前言: 工作了几年,想把一些不好找现成的库的常用方法整理一下,发布成npm包,方便使用.也学习一下开发发布流程. 主要用到的工具:npm. 开发库:babel.typescript.rollup.es ...
- 架构师必备:Redis的几种集群方案
结论 有以下几种Redis集群方案,先说结论: Redis cluster:应当优先考虑使用Redis cluster. codis:旧项目如果仍在使用codis,可继续使用,但也推荐迁移到Redis ...
- HashMap中红黑树插入节点的调整过程
如果有对红黑树的定义及调整过程有过研究,其实很容易理解HashMap中的红黑树插入节点的调整过程. "红黑树定义及调整过程"的参考文章:<红黑树原理.查找效率.插入及变化规则 ...
- 搭建PWN学习环境
环境清单 系统环境 Ubuntu22.04 编写脚本 pwntools ZIO 调试 IDA PRO gdb pwndbg ROP工具 checksec ROPgadget one_gadget Li ...
