HDU 3360 National Treasures(二分匹配,最小点覆盖)
National Treasures
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 871 Accepted Submission(s): 291
The great hall is represented as a two dimensional grid of R × C cells. Some cells are already occupied with the museum’s guards. All remaining cells are occupied by artifacts of different types (statues, sculptures, . . . etc.) which can be replaced by new hired guards. For each artifact, few other cells in the hall are identified as critical points of the artifact depending on the artifact value, type of vault it is kept inside, and few other factors. In other words, if this artifact is going to stay in the hall then all of its critical points must have guards standing on them. A guard standing in a critical position of multiple artifacts can keep an eye on them all. A guard, however,
can not stand in a cell which contains an artifact (instead, you may remove the artifact to allow the guard to stay there). Also you can not remove an artifact and leave the space free (you can only replace an artifact with a new hired guard).
Surveying all the artifacts in the great hall you figured out that the critical points of any artifact (marked by a
 ) are always a subset of the 12 neighboring cells as shown in the grid below.
) are always a subset of the 12 neighboring cells as shown in the grid below.
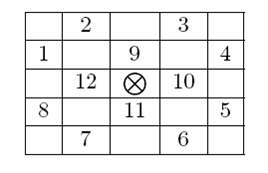
Accordingly, the type of an artifact can be specified as a non-negative integer where the i-th bit is 1 only if critical point number i from the picture above is a critical point of that artifact. For example an artifact of type 595 (in binary 1001010011) can be pictured as shown in the figure below. Note that bits are numbered from right to left (the right-most bit is bit number 1.) If a critical point of an artifact lies outside the hall grid then it is considered secure.
You are given the layout of the great hall and are asked to find the minimum number of additional guards to hire such that all remaining artifacts are secured.
The first line specifies two integers (1<= R,C <= 50) which are the dimensions of the museum hall. The next R lines contain C integers separated by one or more spaces. The j-th integer of the i-th row is -1 if cell (i, j) already contains one of the museum’s guards, otherwise it contains an integer (0 <= T <= 212) representing the type of the artifact in that cell.
The last line of the input file has two zeros.
k. G
Where k is the test case number (starting at one,) and G is the minimum number of additional guards to hire such that all remaining artifacts are secured.
512 -1 2048
2 3
512 2560 2048
512 2560 2048
0 0
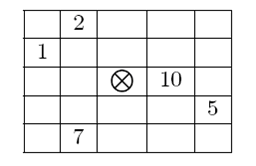
2. 2
The picture below shows the solution of the second test case where the two artifacts in the middle are replaced by guards.
题目意思很难懂。
但是看懂了就不难了。
将格子按照奇偶分成两个部分。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std; const int MAXN = ;
const int MAXM = ;
struct Edge
{
int to,next;
}edge[MAXM];
int head[MAXN],tot;
void init()
{
tot = ;
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
}
void addedge(int u,int v)
{
edge[tot].to = v;edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
}
int linker[MAXN];
bool used[MAXN];
int uN;
bool dfs(int u)
{
for(int i = head[u]; i != -;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if(!used[v])
{
used[v] = true;
if(linker[v] == - || dfs(linker[v]))
{
linker[v] = u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int hungary()
{
int res = ;
memset(linker,-,sizeof(linker));
for(int u = ;u < uN;u++)
{
memset(used,false,sizeof(used));
if(dfs(u))res++;
}
return res;
}
int dir[][] = {{-,-},{-,-},{-,},{-,},{,},
{,},{,-},{,-},{-,},{,},{,},{,-}};
int b[][];
int a[][];
int main()
{
int n,m;
int iCase = ;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) == )
{
iCase ++;
if(n == && m == )break;
uN = ;
int vN = ;
for(int i = ;i < n;i++)
for(int j = ;j < m;j++)
{
if((i+j)% == )b[i][j] = uN++;
else b[i][j] = vN++;
}
init();
for(int i = ;i < n;i++)
for(int j = ;j < m;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
for(int i = ;i < n;i++)
for(int j = ;j < m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j] == -)continue;
for(int k = ;k < ;k++)
if(a[i][j] & (<<k))
{
int tx = i+dir[k][];
int ty = j+dir[k][];
if(tx < || ty < || tx >= n || ty >= m)
continue;
if(a[tx][ty]==-)continue;
if((i+j)% == )
addedge(b[i][j],b[tx][ty]);
else
addedge(b[tx][ty],b[i][j]);
}
}
printf("%d. %d\n",iCase,hungary());
}
return ;
}
HDU 3360 National Treasures(二分匹配,最小点覆盖)的更多相关文章
- HDU 3360 National Treasures 奇偶匹配的最低点覆盖
标题来源:pid=3360">HDU 3360 National Treasures 意甲冠军:假设a[i][j] != -1 把他转成二进制 最多有12位 代表题目那张图的12个位置 ...
- nyoj 237 游戏高手的烦恼 二分匹配--最小点覆盖
题目链接:http://acm.nyist.net/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=237 二分匹配--最小点覆盖模板题 Tips:用邻接矩阵超时,用数组模拟邻接表WA,暂时只 ...
- UVA 11419 SAM I AM(最大二分匹配&最小点覆盖:König定理)
题意:在方格图上打小怪,每次可以清除一整行或一整列的小怪,问最少的步数是多少,又应该在哪些位置操作(对输出顺序没有要求). 分析:最小覆盖问题 这是一种在方格图上建立的模型:令S集表示“行”,T集表示 ...
- HDU 3360 National Treasures(最小点覆盖)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3360 题目大意: 在一个n*m的格子中,每个格子有一个数值,-1表示空,其余表示财宝.每个财宝的数值转 ...
- HDU - 1150 Machine Schedule(二分匹配---最小点覆盖)
题意:有两台机器A和B,A有n种工作模式(0~n-1),B有m种工作模式(0~m-1),两台机器的初始状态都是在工作模式0处.现在有k(0~k-1)个工作,(i,x,y)表示编号为i的工作可以通过机器 ...
- hdu - 1150 Machine Schedule (二分图匹配最小点覆盖)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1150 有两种机器,A机器有n种模式,B机器有m种模式,现在有k个任务需要执行,没切换一个任务机器就需要重启一次, ...
- HDU 3360 National Treasures
题目大意:大厅每个位置都有一个文物或者一个守卫,文物是安全的前提是: 关键位置上必须有一个守卫,或者文物本身的位置上有一个守卫.求保证每个文物是安全的守卫的最少数量. #include <cst ...
- hdu 1853 Cyclic Tour (二分匹配KM最小权值 或 最小费用最大流)
Cyclic Tour Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/65535 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- HDU - 1054 Strategic Game(二分图最小点覆盖/树形dp)
d.一颗树,选最少的点覆盖所有边 s. 1.可以转成二分图的最小点覆盖来做.不过转换后要把匹配数除以2,这个待细看. 2.也可以用树形dp c.匈牙利算法(邻接表,用vector实现): /* 用ST ...
随机推荐
- python基础===Python 迭代器模块 itertools 简介
本文转自:http://python.jobbole.com/85321/ Python提供了一个非常棒的模块用于创建自定义的迭代器,这个模块就是 itertools.itertools 提供的工具相 ...
- Linux下用freetds执行SQL Server的sql语句和存储过程
Linux下用freetds执行SQL Server的sql语句和存储过程 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-06/61617.htm freetds相关 http ...
- atom编辑器插件atom-ternjs
这是官方文档:https://atom.io/packages/atom-ternjs 官方介绍: JavaScript code intelligence for atom with Tern. A ...
- 如何消除类型是submit类型的按钮的默认文字 ‘确认提交’
只需要加上value="" 即可.默认的文字就可以去掉了.
- mysql-备份及关联python
阅读目录 IDE工具介绍 MySQL数据库备份 mysqldump实现逻辑备份 回复逻辑备份 备份/恢复案例 自动化备份 表的导出和导入 数据库迁移 pymysql模块 一 链接.执行sql.关闭(游 ...
- Two Sum ——经典的哈希表的题
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific ta ...
- Linux:hping高级主机扫描
https://www.aliyun.com/jiaocheng/167107.html https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39762926/article/details/7 ...
- Docker for Windows 里的Shared Drives 设置不生效
原文地址:传送门 问题描述:Docker中的settings里的Shared Drives 选择对应盘符后,点击Apply后无法生效,没办法选择对应盘符进行分享. 解决办法:win+R ,键入gped ...
- Openstack 云主机深入了解 (十六)
一)云主机深入了解 1.云主机在计算节点以进程方式运行 2.监听vnc的端口,vnc默认端口从5900开始, 多台云主机,端口递增 3.云主机桥接网卡,与宿主机联通网络 提示:在openstack环境 ...
- 在SpringMVC中 /* 和 / 的区别
<url-pattern> / </url-pattern>:会匹配到 /springmvc 这样的路径型url,而不会匹配到像 .jsp 这样的后缀型的url. <ur ...
