go微服务框架kratos学习笔记七(kratos warden 负载均衡 balancer)
go微服务框架kratos学习笔记七(kratos warden 负载均衡 balancer)
本节看看kratos的学习负载均衡策略的使用。
kratos 的负载均衡和服务发现一样也是基于grpc官方api实现的。
grpc官方的负载均衡自带了一个round-robin轮询策略、即像一个for循环一样挨个服的发请求、但这显然不能满足我们的需求、于是kratos自带了两种负载均衡策略:
WRR (Weighted Round Robin)
该算法在加权轮询法基础上增加了动态调节权重值,用户可以在为每一个节点先配置一个初始的权重分,之后算法会根据节点cpu、延迟、服务端错误率、客户端错误率动态打分,在将打分乘用户自定义的初始权重分得到最后的权重值。
P2C (Pick of two choices)
本算法通过随机选择两个node选择优胜者来避免羊群效应,并通过ewma尽量获取服务端的实时状态。
服务端: 服务端获取最近500ms内的CPU使用率(需要将cgroup设置的限制考虑进去,并除于CPU核心数),并将CPU使用率乘与1000后塞入每次grpc请求中的的Trailer中夹带返回: cpu_usage uint64 encoded with string cpu_usage : 1000
客户端: 主要参数:
server_cpu:通过每次请求中服务端塞在trailer中的cpu_usage拿到服务端最近500ms内的cpu使用率
inflight:当前客户端正在发送并等待response的请求数(pending request)
latency: 加权移动平均算法计算出的接口延迟
client_success:加权移动平均算法计算出的请求成功率(只记录grpc内部错误,比如context deadline)
目前客户端,已经默认使用p2c负载均衡算法
// NewClient returns a new blank Client instance with a default client interceptor.
// opt can be used to add grpc dial options.
func NewClient(conf *ClientConfig, opt ...grpc.DialOption) *Client {
c := new(Client)
if err := c.SetConfig(conf); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
c.UseOpt(grpc.WithBalancerName(p2c.Name))
c.UseOpt(opt...)
return c
}
demo
本节使用在笔记四kratos warden-direct方式client调用 使用的direct服务发现方式、和相关代码。
demo操作
1、分别在两个docker中启动一个grpc demo服务。
2、启动一个client demo服务采用默认p2c负载均衡方式调用grpc SayHello()方法
demo server
1、先启动demo服务 (其实就是一个kratos工具new出来的demo服务、代码可参考笔记四、或者在最后的github地址里面获取整个demo完整代码):
demo client
package dao
import (
"context"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/net/rpc/warden"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"fmt"
demoapi "call-server/api"
"google.golang.org/grpc/balancer/roundrobin"
)
// target server addrs.
const target = "direct://default/10.0.75.2:30001,10.0.75.2:30002" // NOTE: example
// NewClient new member grpc client
func NewClient(cfg *warden.ClientConfig, opts ...grpc.DialOption) (demoapi.DemoClient, error) {
client := warden.NewClient(cfg, opts...)
conn, err := client.Dial(context.Background(), target)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 注意替换这里:
// NewDemoClient方法是在"api"目录下代码生成的
// 对应proto文件内自定义的service名字,请使用正确方法名替换
return demoapi.NewDemoClient(conn), nil
}
// NewClient new member grpc client
func NewGrpcConn(cfg *warden.ClientConfig, opts ...grpc.DialOption) (*grpc.ClientConn, error) {
fmt.Println("-----tag: NewGrpcConn...")
//opts = append(opts, grpc.WithBalancerName(roundrobin.Name))
client := warden.NewClient(cfg, opts...)
conn, err := client.Dial(context.Background(), target)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return conn, nil
}
target 填上两个服务ip
其中我多加了一个NewGrpcConn() 函数 、主要用来提取grpc连接。这里我用了kratos自带的pool类型来做连接池。
池
关于这个池、它在 kratos pkg/container/pool 有两种实现方式 Slice和List方式。
package pool
import (
"context"
"errors"
"io"
"time"
xtime "github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/time"
)
var (
// ErrPoolExhausted connections are exhausted.
ErrPoolExhausted = errors.New("container/pool exhausted")
// ErrPoolClosed connection pool is closed.
ErrPoolClosed = errors.New("container/pool closed")
// nowFunc returns the current time; it's overridden in tests.
nowFunc = time.Now
)
// Config is the pool configuration struct.
type Config struct {
// Active number of items allocated by the pool at a given time.
// When zero, there is no limit on the number of items in the pool.
Active int
// Idle number of idle items in the pool.
Idle int
// Close items after remaining item for this duration. If the value
// is zero, then item items are not closed. Applications should set
// the timeout to a value less than the server's timeout.
IdleTimeout xtime.Duration
// If WaitTimeout is set and the pool is at the Active limit, then Get() waits WatiTimeout
// until a item to be returned to the pool before returning.
WaitTimeout xtime.Duration
// If WaitTimeout is not set, then Wait effects.
// if Wait is set true, then wait until ctx timeout, or default flase and return directly.
Wait bool
}
type item struct {
createdAt time.Time
c io.Closer
}
func (i *item) expired(timeout time.Duration) bool {
if timeout <= 0 {
return false
}
return i.createdAt.Add(timeout).Before(nowFunc())
}
func (i *item) close() error {
return i.c.Close()
}
// Pool interface.
type Pool interface {
Get(ctx context.Context) (io.Closer, error)
Put(ctx context.Context, c io.Closer, forceClose bool) error
Close() error
}
dao
dao中添加一个连接池。
package dao
import (
"context"
"time"
demoapi "call-server/api"
"call-server/internal/model"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/cache/memcache"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/cache/redis"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/conf/paladin"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/database/sql"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/net/rpc/warden"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/sync/pipeline/fanout"
xtime "github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/time"
//grpcempty "github.com/golang/protobuf/ptypes/empty"
//"github.com/pkg/errors"
"github.com/google/wire"
"github.com/bilibili/kratos/pkg/container/pool"
"io"
"reflect"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
var Provider = wire.NewSet(New, NewDB, NewRedis, NewMC)
//go:generate kratos tool genbts
// Dao dao interface
type Dao interface {
Close()
Ping(ctx context.Context) (err error)
// bts: -nullcache=&model.Article{ID:-1} -check_null_code=$!=nil&&$.ID==-1
Article(c context.Context, id int64) (*model.Article, error)
//SayHello(c context.Context, req *demoapi.HelloReq) (resp *grpcempty.Empty, err error)
//get an demo grpcConn/grpcClient/ from rpc pool
GrpcConnPut(ctx context.Context, cc *grpc.ClientConn) (err error)
GrpcConn(ctx context.Context) (gcc *grpc.ClientConn, err error)
GrpcClient(ctx context.Context) (cli demoapi.DemoClient, err error)
}
// dao dao.
type dao struct {
db *sql.DB
redis *redis.Redis
mc *memcache.Memcache
cache *fanout.Fanout
demoExpire int32
rpcPool pool.Pool
}
// New new a dao and return.
func New(r *redis.Redis, mc *memcache.Memcache, db *sql.DB) (d Dao, cf func(), err error) {
return newDao(r, mc, db)
}
func newDao(r *redis.Redis, mc *memcache.Memcache, db *sql.DB) (d *dao, cf func(), err error) {
var cfg struct {
DemoExpire xtime.Duration
}
if err = paladin.Get("application.toml").UnmarshalTOML(&cfg); err != nil {
return
}
// new pool
pool_config := &pool.Config{
Active: 0,
Idle: 0,
IdleTimeout: xtime.Duration(0 * time.Second),
WaitTimeout: xtime.Duration(30 * time.Millisecond),
}
rpcPool := pool.NewSlice(pool_config)
rpcPool.New = func(ctx context.Context) (cli io.Closer, err error) {
wcfg := &warden.ClientConfig{}
paladin.Get("grpc.toml").UnmarshalTOML(wcfg)
if cli, err = NewGrpcConn(wcfg); err != nil {
return
}
return
}
d = &dao{
db: db,
redis: r,
mc: mc,
cache: fanout.New("cache"),
demoExpire: int32(time.Duration(cfg.DemoExpire) / time.Second),
rpcPool: rpcPool,
}
cf = d.Close
return
}
// Close close the resource.
func (d *dao) Close() {
d.cache.Close()
}
// Ping ping the resource.
func (d *dao) Ping(ctx context.Context) (err error) {
return nil
}
func (d *dao) GrpcClient(ctx context.Context) (cli demoapi.DemoClient, err error) {
var cc io.Closer
if cc, err = d.rpcPool.Get(ctx); err != nil {
return
}
cli = demoapi.NewDemoClient(reflect.ValueOf(cc).Interface().(*grpc.ClientConn))
return
}
func (d *dao) GrpcConnPut(ctx context.Context, cc *grpc.ClientConn) (err error) {
err = d.rpcPool.Put(ctx, cc, false)
return
}
func (d *dao) GrpcConn(ctx context.Context) (gcc *grpc.ClientConn, err error) {
var cc io.Closer
if cc, err = d.rpcPool.Get(ctx); err != nil {
return
}
gcc = reflect.ValueOf(cc).Interface().(*grpc.ClientConn)
return
}
service
// SayHello grpc demo func.
func (s *Service) SayHello(ctx context.Context, req *pb.HelloReq) (reply *empty.Empty, err error) {
reply = new(empty.Empty)
var cc demoapi.DemoClient
var gcc *grpc.ClientConn
if gcc, err = s.dao.GrpcConn(ctx); err != nil {
return
}
defer s.dao.GrpcConnPut(ctx, gcc)
cc = demoapi.NewDemoClient(gcc)
//if cc, err = s.dao.GrpcClient(ctx); err != nil {
// return
//}
cc.SayHello(ctx, req)
fmt.Printf("hello %s", req.Name)
return
}
好了现在测试 、 布局如下 :
p2c

roundrobin
轮询方式只需要在NewGrpcConn()里面加语一句配置项即可,它会覆盖掉p2c的配置项。
opts = append(opts, grpc.WithBalancerName(roundrobin.Name))

grpc官方负载均衡工作流程
我们目前也只是使用了Api、最后来瞧瞧官方grpc的工作流程 :
gRPC开源组件官方并未直接提供服务注册与发现的功能实现,但其设计文档已提供实现的思路,并在不同语言的gRPC代码API中已提供了命名解析和负载均衡接口供扩展。
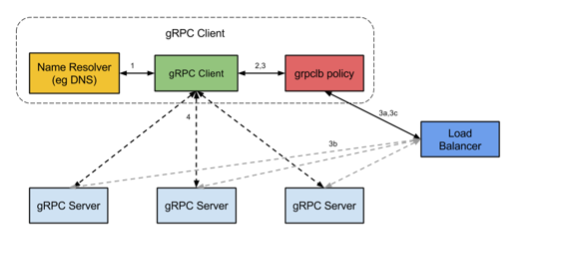
服务启动后,gPRC客户端通过resolve发起一个名称解析请求。名称会被解析为一个或更多的IP地址,每个地址指明它是一个服务器地址还是一个负载均衡器地址,并且包含一个Opt指明哪一个客户端的负载均衡策略应该被使用(例如: 轮询调度或grpclb)。
客户端实现一个负载均衡策略。
注意:如果任何一个被解析器返回的地址是均衡器地址,那么这个客户端会使用grpclb策略,而不管请求的Opt配置的是哪种负载均衡策略。否则,客户端会使用一个Opt项配置负载均衡策略。如果没有负载均衡策略,那么客户端会使用默认的取第一个可用服务器地址的策略。负载均衡策略对每一个服务器地址创建一个子通道。
当调用rpc请求时,负载均衡策略会决定应该发送到哪个子通道(例如: 哪个服务器)。
grpclb策略下,客户端按负载均衡器返回的顺序发送请求到服务器。如果服务器列表为空,调用将会阻塞直到收到一个非空的列表。
源码
本节测试代码 : https://github.com/ailumiyana/kratos-note/tree/master/warden/balancer
go微服务框架kratos学习笔记七(kratos warden 负载均衡 balancer)的更多相关文章
- go微服务框架kratos学习笔记五(kratos 配置中心 paladin config sdk [断剑重铸之日,骑士归来之时])
目录 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记五(kratos 配置中心 paladin config sdk [断剑重铸之日,骑士归来之时]) 静态配置 flag注入 在线热加载配置 远程配置中心 go微 ...
- # go微服务框架kratos学习笔记六(kratos 服务发现 discovery)
目录 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记六(kratos 服务发现 discovery) http api register 服务注册 fetch 获取实例 fetchs 批量获取实例 polls 批 ...
- go微服务框架kratos学习笔记四(kratos warden-quickstart warden-direct方式client调用)
目录 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记四(kratos warden-quickstart warden-direct方式client调用) warden direct demo-server gr ...
- go微服务框架kratos学习笔记八 (kratos的依赖注入)
目录 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记八(kratos的依赖注入) 什么是依赖注入 google wire kratos中的wire Providers injector(注入器) Binding ...
- go微服务框架kratos学习笔记九(kratos 全链路追踪 zipkin)
目录 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记九(kratos 全链路追踪 zipkin) zipkin使用demo 数据持久化 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记九(kratos 全链路追踪 zipkin ...
- 微服务框架surging学习之路——序列化 (转载https://www.cnblogs.com/alangur/p/10407727.html)
微服务框架surging学习之路——序列化 1.对微服务的理解 之前看到在群里的朋友门都在讨论微服务,看到他们的讨论,我也有了一些自己的理解,所谓微服务就是系统里的每个服务都 可以自由组合.自由组 ...
- golang微服务框架go-micro 入门笔记2.4 go-micro service解读
本章节阐述go-micro 服务发现原理 go-micro架构 下图来自go-micro官方 阅读本文前你可能需要进行如下知识储备 golang分布式微服务框架go-micro 入门笔记1:搭建go- ...
- golang微服务框架go-micro 入门笔记2.3 micro工具之消息接收和发布
本章节阐述micro消息订阅和发布相关内容 阅读本文前你可能需要进行如下知识储备 golang分布式微服务框架go-micro 入门笔记1:搭建go-micro环境, golang微服务框架go-mi ...
- golang微服务框架go-micro 入门笔记2.2 micro工具之微应用利器micro web
micro web micro 功能非常强大,本文将详细阐述micro web 命令行的功能 阅读本文前你可能需要进行如下知识储备 golang分布式微服务框架go-micro 入门笔记1:搭建go- ...
随机推荐
- 【codeforces 764C】Timofey and a tree
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- Linux 内核总线注册
如同我们提过的, 例子源码包含一个虚拟总线实现称为 lddbus. 这个总线建立它的 bus_type 结构, 如下: struct bus_type ldd_bus_type = { .name = ...
- 2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第一场)A Equivalent Prefixes(单调栈/二分+分治)
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/881/A来源:牛客网 Two arrays u and v each with m distinct elements ...
- 【Linux】tar压缩解压缩笔记
tar -c, --create create a new archive(建立压缩档案) -x, --extract, --get extract files from an archive(解压) ...
- django框架(1)
一什么是web框架? 框架,即framework,特指为解决一个开放性问题而设计的具有一定约束性的支撑结构,使用框架可以帮你快速开发特定的系统,简单地说,就是你用别人搭建好的舞台来做表演. 对于所有的 ...
- WPF继续响应被标记为已处理事件的方法
WPF继续响应被标记为已处理事件的方法 WPF中在冒泡事件或者隧道事件会随其层间关系在visual tree上层层传递,但是,某些事件传递到某些控件是即会”终止“(不再响应相应的注册事件),给人一种事 ...
- fastdfs基本安装流程和集成springboot总结
FastDFS介绍 1.简介 FastDFS 是一个开源的高性能分布式文件系统(DFS). 它的主要功能包括:文件存储,文件同步和文件访问,以及高容量和负载平衡.主要解决了海量数据存储问题,特别适合以 ...
- 【汇编】AX内容依次倒排序
;P99,5.13,ax内容倒序 ;思路,ax左移一位最高位进cf里,bx右移一位把cf里值进bx的最高位, ;循环16次即实现ax16位内容倒序存储在bx中 DATA SEGMENT DATA EN ...
- Linux学习笔记(一):什么是挂载?mount的用处在哪?
关于挂载的作用一直不是很清楚,今天在阅读教材时看见了mount这个命令,发现它的用处很隐晦但非常强大.奈何教材说的不明朗,因此在网上整合了一些优秀的解释,看完之后豁然开朗. 1.提一句Windows下 ...
- shell 概览
shell能做什么: 1. 自动化批量系统初始化程序(update,软件安装,时区设置,安全策略...) 2. 自动化批量软件部署程序(LAMP,LNMP,Tomcat,LVS,Nginx) 3. 管 ...
