理解 OpenStack + Ceph (8): 基本的 Ceph 性能测试工具和方法
本系列文章会深入研究 Ceph 以及 Ceph 和 OpenStack 的集成:
(1)安装和部署
(3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构
(4)Ceph 的基础数据结构
(6)QEMU-KVM 和 Ceph RBD 的 缓存机制总结
(8)基本的性能测试工具和方法
继续学以致用,学习下基本的Ceph性能测试工具和方法。
0. 测试环境
同 Ceph 的基本操作和常见故障排除方法 一文中的测试环境。
1. 测试准备
1.1 磁盘读写性能
1.1.1 单个 OSD 磁盘写性能,大概 165MB/s。
root@ceph1:~# echo > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
root@ceph1:~# dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/lib/ceph/osd/ceph-/deleteme bs=1G count= oflag=direct
测试发现,其结果变化非常大,有时候上 75,有时是150.
1.1.2 两个OSD同时写性能,大概 18 MB/s。怎么差距那么大呢?几乎是单个磁盘的 1/10 了。
root@ceph1:~# for i in `mount | grep osd | awk '{print $3}'`; do (dd if=/dev/zero of=$i/deleteme bs=1G count= oflag=direct &) ; done
1.1.4 单个 OSD 磁盘读性能,大概 460 MB/s。
root@ceph1:~# dd if=/var/lib/ceph/osd/ceph-/deleteme of=/dev/null bs=2G count= iflag=direct
1.1.5 两个 OSD 同时读性能,大概 130 MB/s。
for i in `mount | grep osd | awk '{print $3}'`; do (dd if=$i/deleteme of=/dev/null bs=1G count= iflag=direct &); done
1.2 网络性能
在 ceph1上运行 iperf -s -p 6900,在 ceph2 上运行 iperf -c ceph1 -p 6900,反复多次,两节点之间的带宽大约在 1 Gbits/sec = 128 MB/s。
root@ceph2:~# iperf -c ceph1 -p
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to ceph1, TCP port
TCP window size: 85.0 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ ] local 192.168.56.103 port connected with 192.168.56.102 port
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ ] 0.0-10.0 sec 1.25 GBytes 1.08 Gbits/sec
2. Ceph 性能测试
2.1 RADOS 性能测试:使用 Ceph 自带的 rados bench 工具
该工具的语法为:rados bench -p <pool_name> <seconds> <write|seq|rand> -b <block size> -t --no-cleanup
- pool_name:测试所针对的存储池
- seconds:测试所持续的秒数
- <write|seq|rand>:操作模式,write:写,seq:顺序读;rand:随机读
- -b:block size,即块大小,默认为 4M
- -t:读/写并行数,默认为 16
- --no-cleanup 表示测试完成后不删除测试用数据。在做读测试之前,需要使用该参数来运行一遍写测试来产生测试数据,在全部测试结束后可以运行 rados -p <pool_name> cleanup 来清理所有测试数据。
写:
root@ceph1:~# rados bench -p rbd write --no-cleanup
Maintaining concurrent writes of bytes for up to seconds or objects
Object prefix: benchmark_data_ceph1_12884
sec Cur ops started finished avg MB/s cur MB/s last lat avg lat
-
-
...
19.9671 3.05943 2.46556
Total time run: 12.135344
Total writes made:
Write size:
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 24.721 Stddev Bandwidth: 13.5647
Max bandwidth (MB/sec):
Min bandwidth (MB/sec):
Average Latency: 2.57614
Stddev Latency: 0.781915
Max latency: 4.50816
Min latency: 1.04075
顺序读:
root@ceph1:~# rados bench -p rbd seq
sec Cur ops started finished avg MB/s cur MB/s last lat avg lat
-
Total time run: 0.601027
Total reads made:
Read size:
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 499.146 Average Latency: 0.123632
Max latency: 0.209325
Min latency: 0.030446
随机读:
root@ceph1:~# rados bench -p rbd rand
sec Cur ops started finished avg MB/s cur MB/s last lat avg lat
-
477.298 0.01702 0.116519
...
488.681 0.108589 0.129214
Total time run: 10.092985
Total reads made:
Read size:
Bandwidth (MB/sec): 492.223 Average Latency: 0.129631
Max latency: 0.297213
Min latency: 0.007133
2.2 RADOS 性能测试:使用 rados load-gen 工具
该工具的语法为:
# rados -p rbd load-gen
--num-objects 初始生成测试用的对象数,默认 200
--min-object-size 测试对象的最小大小,默认 1KB,单位byte
--max-object-size 测试对象的最大大小,默认 5GB,单位byte
--min-op-len 压测IO的最小大小,默认 1KB,单位byte
--max-op-len 压测IO的最大大小,默认 2MB,单位byte
--max-ops 一次提交的最大IO数,相当于iodepth
--target-throughput 一次提交IO的历史累计吞吐量上限,默认 5MB/s,单位B/s
--max-backlog 一次提交IO的吞吐量上限,默认10MB/s,单位B/s
--read-percent 读写混合中读的比例,默认80,范围[0, 100]
--run-length 运行的时间,默认60s,单位秒
在 ceph1上运行 rados -p pool100 load-gen --read-percent 0 --min-object-size 1073741824 --max-object-size 1073741824 --max-ops 1 --read-percent 0 --min-op-len 4194304 --max-op-len 4194304 --target-throughput 1073741824 --max_backlog 1073741824 的结果为:
WRITE : oid=obj-y0UPAZyRQNhnabq off=929764660 len=4194304
op 19 completed, throughput=16MB/sec
WRITE : oid=obj-nPcOZAc4ebBcnyN off=143211384 len=4194304
op 20 completed, throughput=20MB/sec
WRITE : oid=obj-sWGUAzzASPjCcwF off=343875215 len=4194304
op 21 completed, throughput=24MB/sec
WRITE : oid=obj-79r25fxxSMgVm11 off=383617425 len=4194304
op 22 completed, throughput=28MB/sec
该命令的含义是:在 1G 的对象上,以 iodepth = 1 顺序写入 block size 为 4M 的总量为 1G 的数据。其平均结果大概在 24MB/s,基本和 rados bench 的结果相当。
在 client 上,同样的配置,顺序写的BW大概在 20MB/s,顺序读的 BW 大概在 100 MB/s。
可见,与 rados bench 相比,rados load-gen 的特点是可以产生混合类型的测试负载,而 rados bench 只能产生一种类型的负载。但是 load-gen 只能输出吞吐量,只合适做类似于 4M 这样的大block size 数据测试,输出还不包括延迟。
2.3 使用 rbd bench-write 进行块设备写性能测试
2.3.1 客户端准备
在执行如下命令来准备 Ceph 客户端:
root@client:/var# rbd create bd2 --size
root@client:/var# rbd info --image bd2
rbd image 'bd2':
size MB in objects
order ( kB objects)
block_name_prefix: rb.0.3841.74b0dc51
format:
root@client:/var# rbd map bd2
root@client:/var# rbd showmapped
id pool image snap device
pool1 bd1 - /dev/rbd1
rbd bd2 - /dev/rbd2
root@client:/var# mkfs.xfs /dev/rbd2
log stripe unit ( bytes) is too large (maximum is 256KiB)
log stripe unit adjusted to 32KiB
meta-data=/dev/rbd2 isize= agcount=, agsize= blks
= sectsz= attr=, projid32bit=
data = bsize= blocks=, imaxpct=
= sunit= swidth= blks
naming =version bsize= ascii-ci=
log =internal log bsize= blocks=, version=
= sectsz= sunit= blks, lazy-count=
realtime =none extsz= blocks=, rtextents=
root@client:/var# mkdir -p /mnt/ceph-bd2
root@client:/var# mount /dev/rbd2 /mnt/ceph-bd2/
root@client:/var# df -h /mnt/ceph-bd2/
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/rbd2 1014M 33M 982M % /mnt/ceph-bd2
2.3.2 测试
rbd bench-write 的语法为:rbd bench-write <RBD image name>,可以带如下参数:
- --io-size:单位 byte,默认 4096 bytes = 4K
- --io-threads:线程数,默认 16
- --io-total:总写入字节,单位为字节,默认 1024M
- --io-pattern <seq|rand>:写模式,默认为 seq 即顺序写
分别在集群 OSD 节点上和客户端上做测试:
(1)在 OSD 节点上做测试
root@ceph1:~# rbd bench-write bd2 --io-total
bench-write io_size io_threads bytes pattern seq
SEC OPS OPS/SEC BYTES/SEC
273.19 2237969.65
286.84 2349818.65
...
288.00 2358395.28
288.29 2360852.64
elapsed: ops: ops/sec: 288.75 bytes/sec: 2363740.27
此时,块大小为 4k,IOPS 为 289,BW 为 2.36 MB/s (怎么 BW 是 block_size * IOPS 的两倍呢?)。
(2)在客户端上做测试
root@client:/home/s1# rbd bench-write pool.host/image.ph2 --io-total --io-size
bench-write io_size io_threads bytes pattern seq
SEC OPS OPS/SEC BYTES/SEC
3.41 27937685.86
9.04 68193147.96
8.34 62237889.75
6.29 46538807.31
...
5.86 40792216.64
5.85 40666942.19
elapsed: ops: ops/sec: 6.06 bytes/sec: 41238190.87
此时 block size 为 4M,IOPS 为 6, BW 为 41.24 MB/s。
root@client:/home/s1# rbd bench-write pool.host/image.ph2 --io-total
bench-write io_size io_threads bytes pattern seq
SEC OPS OPS/SEC BYTES/SEC
329.52 2585220.17
329.57 2521925.67
333.17 2426190.82
332.26 2392607.58
328.68 2322829.13
330.88 2316098.66
此时 block size 为 4K,IOPS 为 330 左右, BW 为 24 MB/s 左右。
备注:从 rbd bench-write vs dd performance confusion 中看起来,rados bench-write 似乎有bug。我所使用的Ceph 是0.80.11 版本,可能补丁还没有合进来。
2.4 使用 fio +rbd ioengine
2.4.1 环境准备
运行 apt-get install fio 来安装 fio 工具。创建 fio 配置文件:
root@client:/home/s1# cat write.fio
[write-4M]
description="write test with block size of 4M"
ioengine=rbd
clientname=admin
pool=rbd
rbdname=bd2
iodepth=
runtime=
rw=write #write 表示顺序写,randwrite 表示随机写,read 表示顺序读,randread 表示随机读
bs=4M
运行 fio 命令,但是出错:
root@client:/home/s1# fio write.fio
fio: engine rbd not loadable
fio: failed to load engine rbd
Bad option <clientname=admin>
Bad option <pool=rbd>
Bad option <rbdname=bd2>
fio: job write-4M dropped
fio: file:ioengines.c:, func=dlopen, error=rbd: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
其原因是因为没有安装 fio librbd IO 引擎,因此当前 fio 无法支持 rbd ioengine:
root@client:/home/s1# fio --enghelp
Available IO engines:
cpuio
mmap
sync
psync
vsync
pvsync
null
net
netsplice
libaio
rdma
posixaio
falloc
e4defrag
splice
sg
binject
在运行 apt-get install librbd-dev 命令安装 librbd 后,fio 还是报同样的错误。参考网上资料,下载 fio 代码重新编译 fio:
$ git clone git://git.kernel.dk/fio.git
$ cd fio
$ ./configure
[...]
Rados Block Device engine yes
[...]
$ make
此时 fio 的 ioengine 列表中也有 rbd 了。fio 使用 rbd IO 引擎后,它会读取 ceph.conf 中的配置去连接 Ceph 集群。
下面是 fio 命令和结果:
root@client:/home/s1/fio# ./fio ../write.fio
write-4M: (g=): rw=write, bs=4M-4M/4M-4M/4M-4M, ioengine=rbd, iodepth=
fio-2.11--g82e6
Starting process
rbd engine: RBD version: 0.1.
Jobs: (f=): [W()] [100.0% done] [0KB/.0MB/0KB /s] [// iops] [eta 00m:00s]
write-4M: (groupid=, jobs=): err= : pid=: Sat Jun ::
Description : ["write test with block size of 4M"]
write: io=1024.0MB, bw=17397KB/s, iops=4, runt= 60275msec
slat (usec): min=, max=, avg=1489.10, stdev=4907.83
clat (msec): min=, max=, avg=7399.86, stdev=1328.55
lat (msec): min=, max=, avg=7401.35, stdev=1328.67
clat percentiles (msec):
| .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ],
| .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ],
| .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ],
| .00th=[], .50th=[], .90th=[], .95th=[],
| .99th=[]
bw (KB /s): min=, max=, per=100.00%, avg=259334.50, stdev=6250.72
lat (msec) : =1.17%, >==98.83%
cpu : usr=0.24%, sys=0.03%, ctx=, majf=, minf=
IO depths : =2.3%, =5.5%, =12.5%, =25.0%, =50.4%, =4.3%, >==0.0%
submit : =0.0%, =100.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, >==0.0%
complete : =0.0%, =97.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =3.0%, =0.0%, >==0.0%
issued : total=r=/w=/d=, short=r=/w=/d=, drop=r=/w=/d=
latency : target=, window=, percentile=100.00%, depth= Run status group (all jobs):
WRITE: io=.0MB, aggrb=17396KB/s, minb=17396KB/s, maxb=17396KB/s, mint=60275msec, maxt=60275msec Disk stats (read/write):
sda: ios=/, merge=/, ticks=/, in_queue=, util=6.18%
如果 iodepth = 1 的话,结果是:
root@client:/home/s1# fio/fio write.fio.dep1
write-4M: (g=): rw=write, bs=4M-4M/4M-4M/4M-4M, ioengine=rbd, iodepth=
fio-2.11--g82e6
Starting process
rbd engine: RBD version: 0.1.
Jobs: (f=): [W()] [100.0% done] [0KB/8192KB/0KB /s] [// iops] [eta 00m:00s]
write-4M: (groupid=, jobs=): err= : pid=: Sat Jun ::
Description : ["write test with block size of 4M"]
write: io=1024.0MB, bw=20640KB/s, iops=5, runt= 50802msec
2.5 使用 fio + libaio 进行测试
libaio 是 Linux native asynchronous I/O。
几种测试模式:
- 随机写:fio/fio -filename=/mnt/ceph-rbd2 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4M -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=120 -group_reporting -name=read-libaio
这些参数的含义是:
- filename:表示待测试的设备名称。
- iodepth: libaio 会用这个 iodepth 值来调用 io_setup 准备个可以一次提交 iodepth 个 IO 的上下文,同时申请个io请求队列用于保持IO。
- iodepth_batch:在压测进行的时候,系统会生成特定的IO请求,往io请求队列里面扔,当队列里面的IO个数达到 iodepth_batch 值的时候,
- iodepth_batch_complete 和 iodepth_low: 调用 io_submit 批次提交请求,然后开始调用 io_getevents 开始收割已经完成的IO。 每次收割多少呢?由于收割的时候,超时时间设置为0,所以有多少已完成就算多少,最多可以收割 iodepth_batch_complete 值个。随着收割,IO队列里面的IO数就少了,那么需要补充新的IO。 什么时候补充呢?当IO数目降到 iodepth_low 值的时候,就重新填充,保证 OS 可以看到至少 iodepth_low 数目的io在电梯口排队着。
root@client:/home/s1# fio/fio -filename=/mnt/ceph-rbd2 -direct= -iodepth -thread -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4M -size=1G -numjobs= -runtime= -group_reporting -name=read-libaio read-libaio: (g=): rw=randwrite, bs=4M-4M/4M-4M/4M-4M, ioengine=libaio, iodepth=
fio-2.11--g82e6
Starting thread
Jobs: (f=): [w()] [100.0% done] [0KB/94302KB/0KB /s] [// iops] [eta 00m:00s]
read-libaio: (groupid=, jobs=): err= : pid=: Sun Jun ::
write: io=1024.0MB, bw=102510KB/s, iops=25, runt= 10229msec
slat (usec): min=, max=, avg=1768.90, stdev=1176.00
clat (usec): min=, max=, avg=38165.11, stdev=27987.64
lat (msec): min=, max=, avg=39.94, stdev=28.00
clat percentiles (msec):
| .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ],
| .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ],
| .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ], .00th=[ ],
| .00th=[ ], .50th=[ ], .90th=[ ], .95th=[ ],
| .99th=[ ]
bw (KB /s): min=, max=, per=97.55%, avg=99999.10, stdev=36075.23
lat (usec) : =0.39%
lat (msec) : =0.39%, =0.39%, =21.48%, =57.81%, =14.45%
lat (msec) : =5.08%
cpu : usr=0.62%, sys=3.65%, ctx=, majf=, minf=
IO depths : =100.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, >==0.0%
submit : =0.0%, =100.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, >==0.0%
complete : =0.0%, =100.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, =0.0%, >==0.0%
issued : total=r=/w=/d=, short=r=/w=/d=, drop=r=/w=/d=
latency : target=, window=, percentile=100.00%, depth= Run status group (all jobs):
WRITE: io=.0MB, aggrb=102510KB/s, minb=102510KB/s, maxb=102510KB/s, mint=10229msec, maxt=10229msec Disk stats (read/write):
sda: ios=/, merge=/, ticks=/, in_queue=, util=98.71%
- 随机读:fio/fio -filename=/mnt/ceph-rbd2 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4M -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=120 -group_reporting -name=read-libaio
- 顺序写:fio/fio -filename=/mnt/ceph-rbd2 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=write -ioengine=libaio -bs=4M -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=120 -group_reporting -name=read-libaio
- 随机写:fio/fio -filename=/mnt/ceph-rbd2 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4M -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=120 -group_reporting -name=read-libaio
3. 总结
3.1 测试工具小结
| 工具 | 用途 | 语法 | 说明 |
| dd | 磁盘读写性能测试 | dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/testfile bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct/dsync/sync | https://www.thomas-krenn.com/en/wiki/Linux_I/O_Performance_Tests_using_dd |
| iperf | 网络带宽性能测试 | https://iperf.fr/ | |
| rados bench | RADOS 性能测试工具 | rados bench -p <pool_name> <seconds> <write|seq|rand> -b <block size> -t --no-cleanup |
|
| rados load-gen | RADOS 性能测试工具 |
# rados -p rbd load-gen |
|
| rbd bench-write | ceph 自带的 rbd 性能测试工具 |
rbd bench-write <RBD image name>
|
|
| fio + rbd ioengine | fio 结合 rbd IO 引擎的性能测试工具 | 参考 fio --help |
|
| fio + libaio | fio 结合 linux aio 的 rbd 性能测试 |
3.2 测试结果比较
- 所使用的命令:
- rbd bench-write pool.host/image.ph2 --io-total 1719973000 --io-size 4096000 --io-threads 1 --io-pattern rand/seq
- rados -p pool.host bench 20 write -t 1 --no-cleanup
- rados -p pool100 load-gen --read-percent 0 --min-object-size 1073741824 --max-object-size 1073741824 --max-ops 1 --read-percent 0/100 --min-op-len 4194304 --max-op-len 4194304 --target-throughput 1073741824 --max_backlog 1073741824
- ceph tell osd.0 bench
- fio/fio -filename=/dev/rbd4 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=write/read/randwrite/randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4M -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=120 -group_reporting -name=read-libaio
- 结果(仅在作者的测试环境的客户端节点上运行以上命令的输出):
| 操作 | dd 一个 OSD | dd 两个 OSD | rados load-gen | rados bench | rbd bench-write | ceph tell osd.0 bench | fio + rbd | fio + libaio |
| 顺序写 | 165 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 74 MB/s (IOPS 9) |
40 MB/s |
21 (iops 5) | 18(iops 4) |
| 随机写 | 67.8 MB/s (IOPS 8) | 19 (iops 4) | 16(iops 4) | |||||
| 顺序读 | 460 | 130 | 100 | 109 | N/A | 111(iops 27) | 111(iops 27) | |
| 随机读 | 112 | N/A | 115(iops 28) | 128(iops 31) |
- 简单结论(由于环境、测试方法和数据有限,这些结论不一定正确,有些只是猜测,需要进一步研究,仅供参考):
- rados bench 和在两个 OSD 上同时做 dd 的性能差不多。
- fio + rbd 和 fio + libaio 的结果差不多,相比之下 fio + rbd 还要好一点点。
- fio 顺序写和读的 BW 和两个 OSD 同时写和读的 BW 差不多。
- fio 顺序写的 BW 差不多是 单个 OSD 的 bench 的一半 (因为我的 pool 的 size 为 2)。
- rados load-gen,rodos bench 和 fio rbd/libaio 的结果都差不多,可见都可以信任,只是每一种都有其特长,选择合适你的测试应用场景的某个即可。
- rdb bench-write 的值明显偏高,原因未知,也许存在 bug,详情可参考 rbd bench-write vs dd performance confusion,选择时需慎重。
3.3 影响Ceph集群性能的因素
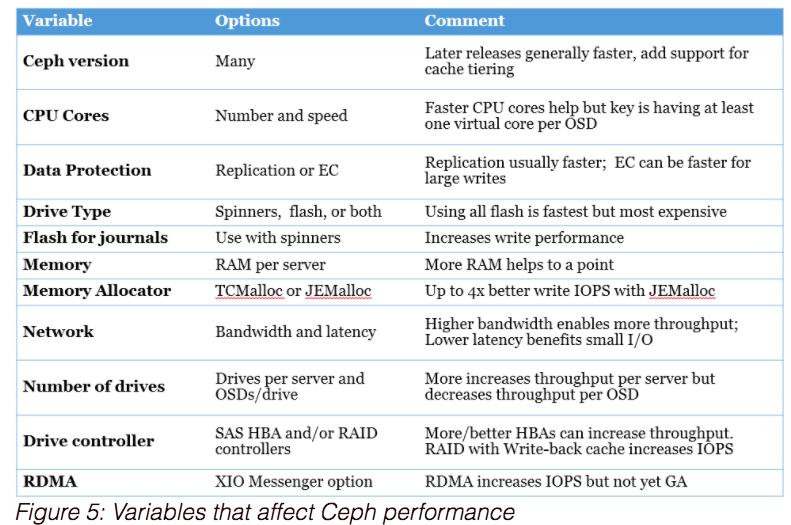
注意:作者会保持对本文不断更新。
参考链接:
- http://tracker.ceph.com/projects/ceph/wiki/Benchmark_Ceph_Cluster_Performance
- Ceph Performance Analysis: fio and RBD
- http://www.quts.me/page2/
- http://events.linuxfoundation.org/sites/events/files/slides/Vault-2015.pdf
- http://www.mellanox.com/blog/2016/02/making-ceph-faster-lessons-from-performance-testing/
理解 OpenStack + Ceph (8): 基本的 Ceph 性能测试工具和方法的更多相关文章
- Ceph性能测试工具和方法。
0. 测试环境 同 Ceph 的基本操作和常见故障排除方法 一文中的测试环境. 1. 测试准备 1.1 磁盘读写性能 1.1.1 单个 OSD 磁盘写性能,大概 165MB/s. root@ceph1 ...
- 基本的Ceph性能测试工具和方法
测试环境 1. 测试准备 1.1 磁盘读写性能 1.1.1 单个 OSD 磁盘写性能,大概 165MB/s. root@ceph1:~# echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_c ...
- ceph--磁盘和rbd、rados性能测试工具和方法
我在物理机上创建了5台虚拟机,搭建了一个ceph集群,结构如图: 具体的安装步骤参考文档:http://docs.ceph.org.cn/start/ http://www.centoscn.com/ ...
- 理解 OpenStack + Ceph (9): Ceph 的size/min_size/choose/chooseleaf/scrubbing/repair 等概念
本系列文章会深入研究 Ceph 以及 Ceph 和 OpenStack 的集成: (1)安装和部署 (2)Ceph RBD 接口和工具 (3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构 (4)Ceph 的基础数据结构 ...
- 理解 OpenStack + Ceph (5):OpenStack 与 Ceph 之间的集成 [OpenStack Integration with Ceph]
理解 OpenStack + Ceph 系列文章: (1)安装和部署 (2)Ceph RBD 接口和工具 (3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构 (4)Ceph 的基础数据结构 (5)Ceph 与 OpenS ...
- 理解 OpenStack + Ceph (2):Ceph 的物理和逻辑结构 [Ceph Architecture]
本系列文章会深入研究 Ceph 以及 Ceph 和 OpenStack 的集成: (1)安装和部署 (2)Ceph RBD 接口和工具 (3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构 (4)Ceph 的基础数据结构 ...
- 理解 OpenStack + Ceph (7): Ceph 的基本操作和常见故障排除方法
本系列文章会深入研究 Ceph 以及 Ceph 和 OpenStack 的集成: (1)安装和部署 (2)Ceph RBD 接口和工具 (3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构 (4)Ceph 的基础数据结构 ...
- 理解 OpenStack + Ceph (3):Ceph RBD 接口和工具 [Ceph RBD API and Tools]
本系列文章会深入研究 Ceph 以及 Ceph 和 OpenStack 的集成: (1)安装和部署 (2)Ceph RBD 接口和工具 (3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构 (4)Ceph 的基础数据结构 ...
- 理解 OpenStack + Ceph (1):Ceph + OpenStack 集群部署和配置
本系列文章会深入研究 Ceph 以及 Ceph 和 OpenStack 的集成: (1)安装和部署 (2)Ceph RBD 接口和工具 (3)Ceph 物理和逻辑结构 (4)Ceph 的基础数据结构 ...
随机推荐
- 【探讨】javascript事件机制底层实现原理
前言 又到了扯淡时间了,我最近在思考javascript事件机制底层的实现,但是暂时没有勇气去看chrome源码,所以今天我来猜测一把 我们今天来猜一猜,探讨探讨,javascript底层事件机制是如 ...
- 3D打印公司网站dedecms大气模板
模板描述:1. 用FTP将安装包上传到服务器解压(或者解压在上传): 2. http://您的域名/install/ 进入到安装界面, 按照正常步骤安装即可:不要修改数据库表前缀,否则会造成原先数据无 ...
- IOS5中的Safari不兼容Javascript中的Date问题,做下笔录吧!奶奶的,折腾我半天!
在做Mobile终端的Website开发中,我遇到一个很懊恼的问题. 在IOS5以上版本(不包含IOS5)中的Safari浏览器能正确解释出Javascript中的 new Date('2013-10 ...
- 在Kali Linux下安装与配置OpenVas
以下是我的Kali版本号: 执行安装命令: apt-get install openvas 安装完成后可以在漏洞分析菜单下查看到OpenVas相关选项. 以下为安装完成后需要用到的几个命令: open ...
- Web自动化测试 Selenium 1/3
Selenium 名字的来源 在这里,我还想说一下关于 Selenium 名字的来源,很有意思的 : > : Selenium 的中文名为 “ 硒 ” ,是一种化学元素的名字,它 对 汞 ( M ...
- PhpStorm下Laravel代码智能提示
phpstorm&Laravel PHPstorm是我见过的最好的PHP的IDE,前年用的时候就毫不犹豫的抛弃了zend studio :) ,Laravel是我用过最好的框架,除了做手游后台 ...
- iOS UIProgressView控件用法
IOS中进度条控件的用法总结. 进度条控件是IOS开发中一个简单的系统控件,使用总结如下: 初始化一个进度条: - (instancetype)initWithProgressViewStyle:(U ...
- android am命令以及hotkey文件的编写
1.拨打电话:am start -a android.intent.action.CALL -d tel:10086 这里-a表示动作,-d表述传入的数据,还有-t表示传入的类型. 2. 打开一个网页 ...
- 【代码笔记】iOS-竖状图
一,效果图. 二,工程图. 三,代码. RootViewController.h #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface RootViewController ...
- iOS中如何知道app版本已更新
主要用于程序升级,开启程序后是否显示新特性两个方面. 1.苹果app版本 苹果规定,程序的版本只能升不能降.例如1.0->1.1可以,1.1->1.0就不可以,不允许上架. 2.app版本 ...
