z-index堆叠规则
一、z-index
z-index用来控制元素重叠时堆叠顺序。
适用于:已经定位的元素(即position:relative/absolute/fixed)。
一般理解就是数值越高越靠上,好像很简单,但是当z-index应用于复杂的HTML元素层次结构,其行为可能很难理解甚至不可预测。因为z-index的堆叠规则很复杂,下面一一道来。
首先解释一个名词:
stacking context:翻译就是“堆叠上下文”。每个元素仅属于一个堆叠上下文,元素的z-index描述元素在相同堆叠上下文中“z轴”的呈现顺序。
z-index取值:
默认值auto:
当页面新生成一个box时,它默认的z-index值为auto,意味着该box不会自己产生一个新的local stacking context,而是处于和父box相同的堆叠上下文中。
正/负整数
这个整数就是当前box的z-index值。z-index值为0也会生成一个local stacking context,这样该box父box的z-index就不会和其子box做比较,相当于隔离了父box的z-index和子box的z-index。
接下来从最简单的不使用z-index的情况开始将,循序渐进。
二、不使用 z-index时堆叠顺序
不使用z-index的情况,也是默认的情况,即所有元素都不用z-index时,堆叠顺序如下(从下到上)
- 根元素(即HTML元素)的background和borders
- 正常流中非定位后代元素(这些元素顺序按照HTML文档出现顺序)
- 已定位后代元素(这些元素顺序按照HTML文档出现顺序)
- 正常流中非positoned element元素,总是先于positioned element元素渲染,所以表现就是在positioned element下方,跟它在HTML中出现的顺序无关。
- 没有指定z-index值的positioned element,他们的堆叠顺序取决于在HTML文档中的顺序,越靠后出现的元素,位置越高,和position属性无关。
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Stacking without z-index</title>
<style type="text/css"> div {
font: 12px Arial;
text-align: center;
} .bold { font-weight: bold; }
.opacity{opacity: 0.7;} #normdiv {
height: 70px;
border: 1px dashed #999966;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
} #reldiv1 {
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 30px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
} #reldiv2 {
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 15px;
left: 20px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
} #absdiv1 {
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
} #absdiv2 {
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
} </style>
</head> <body>
<br /><br /> <div id="absdiv1" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #1</span>
<br />position: absolute;
</div> <div id="reldiv1" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #2</span>
<br />position: relative;
</div> <div id="reldiv2" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #3</span>
<br />position: relative;
</div> <div id="absdiv2" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #4</span>
<br />position: absolute;
</div> <div id="normdiv">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #5</span>
<br />no positioning
</div>
</body>
</html>
有图有真相:
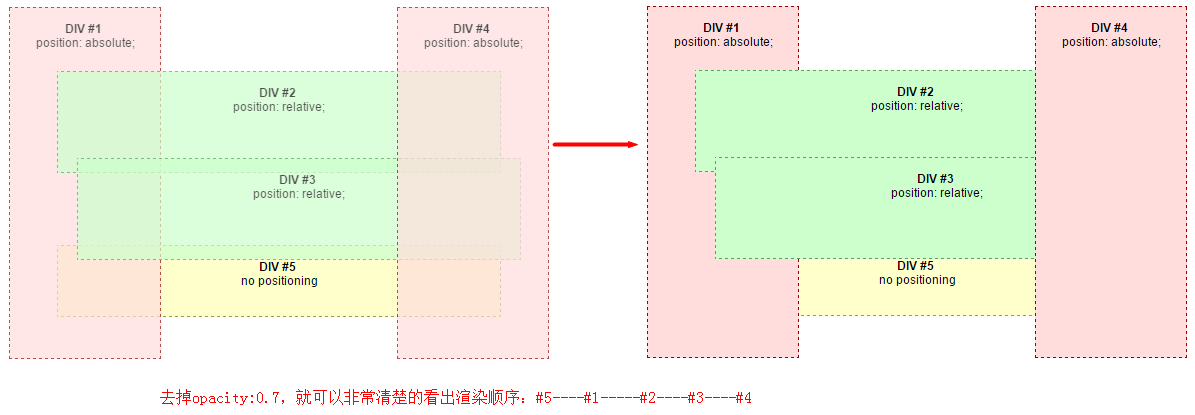
分析:
#5没有定位,处于正常流,所以根据以上规则,先于#1,#2,#3,#4这些已定位元素渲染,在最下方。
#1,#2,#3,#4都是已定位元素,且未设置z-index,所以根据其在文档中出现的顺序依次被渲染,可以去掉apacity查看清晰效果。
三、浮动堆叠顺序
浮动元素z-index位置介于非定位元素和定位元素之间。(从下到上)
- 根元素(即HTML元素)的背景和border
- 正常流中非定位后代元素(这些元素顺序按照HTML文档出现顺序)
- 浮动元素(浮动元素之间是不会出现z-index重叠的)
- 正常流中inline后代元素
- 已定位后代元素(这些元素顺序按照HTML文档出现顺序)
non-positioned元素的背景和边界没有被浮动元素影响,但是元素中的内容受影响(浮动布局特性)
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Stacking and float</title>
<style type="text/css"> div {
font: 12px Arial;
text-align: center;
} .bold { font-weight: bold; }
.opacity{ opacity: 0.7;} #absdiv1 {
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 200px;
top: 10px;
right: 140px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
} #normdiv {
/* opacity: 0.7; */
height: 100px;
border: 1px dashed #999966;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0px 10px 0px 10px;
text-align: left;
} #flodiv1 {
margin: 0px 10px 0px 20px;
float: left;
width: 150px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px dashed #009900;
background-color: #ccffcc;
} #flodiv2 {
margin: 0px 20px 0px 10px;
float: right;
width: 150px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px dashed #009900;
background-color: #ccffcc;
} #absdiv2 {
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 100px;
top: 130px;
left: 100px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
} </style>
</head> <body>
<br /><br /> <div id="absdiv1" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #1</span>
<br />position: absolute;
</div> <div id="flodiv1" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #2</span>
<br />float: left;
</div> <div id="flodiv2" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #3</span>
<br />float: right;
</div> <br /> <div id="normdiv">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #4</span>
<br />no positioning
</div> <div id="absdiv2" class="opacity">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #5</span>
<br />position: absolute;
</div>
</body>
</html>
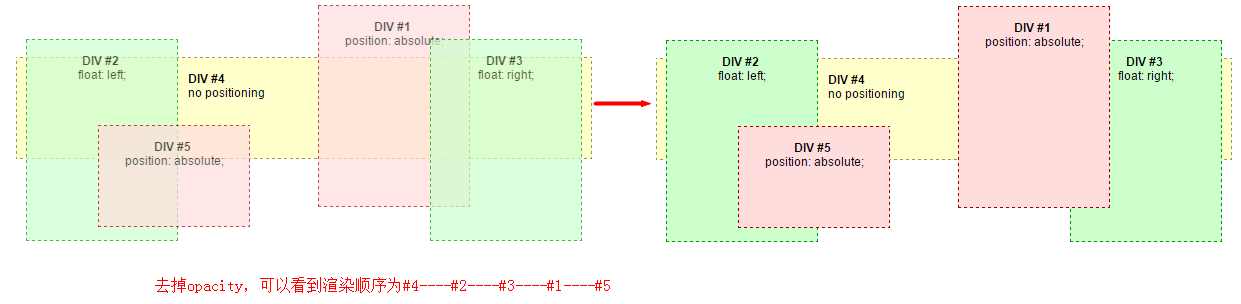
分析:
#4是正常流中非定位的元素,所以先被渲染,在最底层。
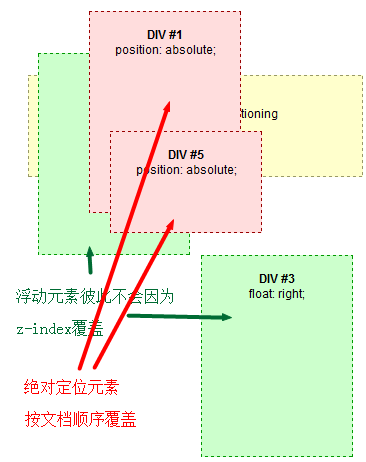
#2 #3一个左浮动,一个右浮动,接着被渲染。彼此不会因为z-index值被覆盖。见下图。
#1 #5为已定位的元素,最后被渲染,当浏览器窗口变小时,#5在#1上面,因为HTML文档中#5在#1后面。见下图。
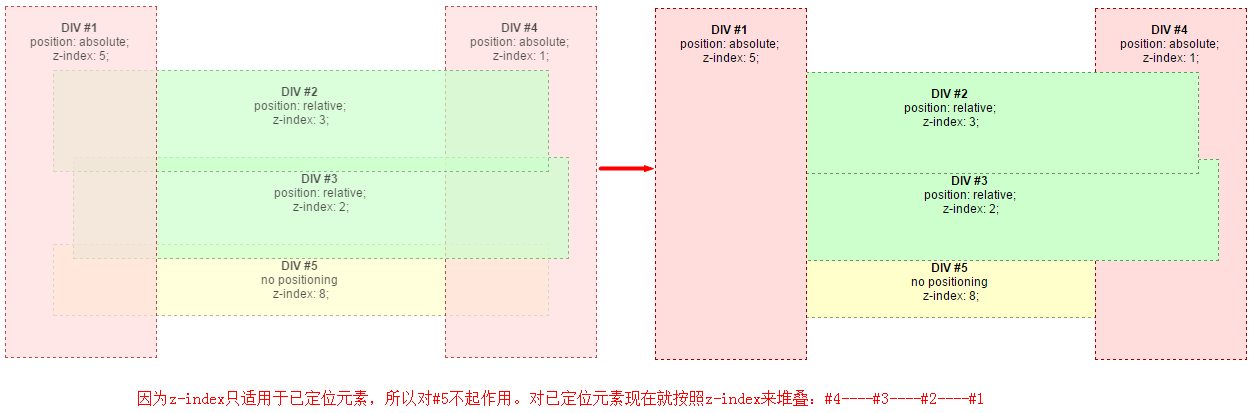
四、z-index
默认的堆叠顺序上面说了,要想改变 元素的堆叠顺序就得用到z-index。
Note:前两种情况中,虽然有元素之间的重叠覆盖,但是它们都是处在同一个z-layer的。因为没有设置z-index属性,默认的渲染层就是layer 0。所以要注意,不同层中元素之间覆盖是理所当然的,但是同一层中的元素也会发生覆盖。
z-index只适用于已经定位的元素(即position:relative/absolute/fixed)。
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Stacking without z-index</title>
<style type="text/css"> div {
font: 12px Arial;
text-align: center;
opacity: 0.7;
} .bold { font-weight: bold; } #normdiv {
z-index: 8;
height: 70px;
border: 1px dashed #999966;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
} #reldiv1 {
z-index: 3;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 30px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
} #reldiv2 {
z-index: 2;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 15px;
left: 20px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
} #absdiv1 {
z-index: 5;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
} #absdiv2 {
z-index: 1;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
} </style>
</head> <body> <br /><br /> <div id="absdiv1">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #1</span>
<br />position: absolute;
<br />z-index: 5;
</div> <div id="reldiv1">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #2</span>
<br />position: relative;
<br />z-index: 3;
</div> <div id="reldiv2">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #3</span>
<br />position: relative;
<br />z-index: 2;
</div> <div id="absdiv2">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #4</span>
<br />position: absolute;
<br />z-index: 1;
</div> <div id="normdiv">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #5</span>
<br />no positioning
<br />z-index: 8;
</div> </body>
</html>
五、stacking context
为什么上个例子中元素的堆叠顺序受z-index的影响呢?因为这些元素有些特殊的属性触发它们生存堆叠上下文(stacking context)。
问题来了,什么样的元素会生成堆叠上下文呢?符合下面规则之一的:
- 根元素(即HTML元素)
- 已定位元素(即绝对定位或相对定位)并且z-index不是默认的auto。
- a flex item with a z-index value other than "auto",
- 元素opacity属性不为1(See the specification for opacity)
- 元素transform不为none
- 元素min-blend-mode不为normal
- 元素filter属性不为none
- 元素isolation属性为isolate
- on mobile WebKit and Chrome 22+,
position: fixedalways creates a new stacking context, even when z-index is "auto" (See this post) - specifing any attribute above in
will-change - elements with
-webkit-overflow-scrollingset to "touch"
在堆叠上下文(stacking context)中 ,子元素的堆叠顺序还是按照上述规则。重点是,子元素的z-index值只在父元素范围内有效。子堆叠上下文被看做是父堆叠上下文中一个独立的模块,相邻的堆叠上下文完全没关系。
总结几句:
渲染的时候,先确定小的stacking context中的顺序,一个小的stacking context确定了以后再将其放在父stacking context中堆叠。有种由内而外,由小及大的感觉。
举例:HTML结果如下,最外层是HTML元素,包含#1 #2 #3,#3中又包含着#4,#5,#6。
Root(HTML)
- DIV #1
- DIV #2
- DIV #3
- DIV #4
- DIV #5
- DIV #6
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head> <title>Understanding CSS z-index: The Stacking Context: Example Source</title> <style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
}
html {
padding: 20px;
font: 12px/20px Arial, sans-serif;
}
div {
opacity: 0.7;
position: relative;
}
h1 {
font: inherit;
font-weight: bold;
}
#div1, #div2 {
border: 1px solid #696;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #cfc;
}
#div1 {
z-index: 5;
margin-bottom: 190px;
}
#div2 {
z-index: 2;
}
#div3 {
z-index: 4;
opacity: 1;
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
left: 180px;
width: 330px;
border: 1px solid #900;
background-color: #fdd;
padding: 40px 20px 20px;
}
#div4, #div5 {
border: 1px solid #996;
background-color: #ffc;
}
#div4 {
z-index: 6;
margin-bottom: 15px;
padding: 25px 10px 5px;
}
#div5 {
z-index: 1;
margin-top: 15px;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
#div6 {
z-index: 3;
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 180px;
width: 150px;
height: 125px;
border: 1px solid #009;
padding-top: 125px;
background-color: #ddf;
text-align: center;
}
</style> </head>
<body> <div id="div1">
<h1>Division Element #1</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 5;</code>
</div> <div id="div2">
<h1>Division Element #2</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 2;</code>
</div> <div id="div3"> <div id="div4">
<h1>Division Element #4</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 6;</code>
</div> <h1>Division Element #3</h1>
<code>position: absolute;<br/>
z-index: 4;</code> <div id="div5">
<h1>Division Element #5</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 1;</code>
</div> <div id="div6">
<h1>Division Element #6</h1>
<code>position: absolute;<br/>
z-index: 3;</code>
</div> </div> </body>
</html>
效果:

分析一下:
1、因为设置了div {opacity: 0.7; position: relative;},所以#1~#6的z-index都是有效的。
2、为什么#4的z-index比#1高,但是却在#1下面?因为#4的z-index虽然值大,但它的作用域在包含块#3内,而#1的z-index的作用域在html内,和#3同属html,而#3的z-index小于#1。
3、为什么#2的z-index值比#5的大,还在下面?同上。
4、#3的z-index是4,但该值和#4,#5,#6的z-index不具有可比性,它们不在一个上下文环境。
5、如何轻易的判断两个元素的堆叠顺序?
z-index对堆叠顺序的控制类似于排版时候一大章下几个小节的样子,或者版本号中一个大的版本号跟着小版本号。
Root-z-index值为默认auto,即
- DIV #2 - z-index 值为
- DIV #3 - z-index 值为
- DIV #5 - z-index值为 1,其父元素z-index值 4,所以最终值为4.1
- DIV #6 - z-index值为 3,其父元素z-index值 4,所以最终值为4.3
- DIV #4 - z-index值为 6,其父元素z-index值 4,所以最终值为4.6
- DIV #1 - z-index 值为
想看更多例子,可参考文章最后的资源链接。
六、 合理使用z-index数值
如果现有三个堆叠的层,从上到下分别为:DIV3,DIV2,DIV1,设置时以100为间隔,设置DIV1的z-index为0,DIV2的z-index为100,设置DIV3的z-index为200。这样后期如果需要在DIV1和DIV2之间加入一些层的话,以10为间隔,设置z-index为10,20等。再需要向z-index0和z-index10之间加入一层的话以5为间隔。这样的写法可以方便后期扩展添加内容。
尽量避免给z-index使用负值。当然不是绝对的,比如在做图文替换的时候可以使用负值。
七、资源链接
- Stacking without z-index : Default stacking rules
- Stacking and float : How floating elements are handled
- Adding z-index : Using z-index to change default stacking
- The stacking context : Notes on the stacking context
- Stacking context example 1 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the last level
- Stacking context example 2 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on all levels
- Stacking context example 3 : 3-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the second level
本文作者starof,因知识本身在变化,作者也在不断学习成长,文章内容也不定时更新,为避免误导读者,方便追根溯源,请诸位转载注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/starof/p/4424926.html有问题欢迎与我讨论,共同进步。
z-index堆叠规则的更多相关文章
- z-index的堆叠规则
原文: https://www.cnblogs.com/starof/p/4424926.html 对于所有定位,最后都不免遇到两个元素试图放在同一位置上的情况.显然,其中一个必须盖住另一个.但,如何 ...
- 深入理解CSS定位中的堆叠z-index
× 目录 [1]定义 [2]堆叠规则 [3]堆叠上下文[4]兼容 前面的话 对于所有定位,最后都不免遇到两个元素试图放在同一位置上的情况.显然,其中一个必须盖住另一个.但,如何控制哪个元素放在上层,这 ...
- 【基础】MVC路由规则
一.RouteData解析过程 在ASP.NET MVC中,服务器收到来自客户端的请求后,会经过一些列的处理拿到请求的数据,比如在Pipeline 管线事件中,通过订阅适当的事件,将HttpConte ...
- Makefile隐含规则
两个隐含规则; 将所有的name.o的依赖自动推导为name.c并使用规则$(CC) -c $(FLAGS) $(CPPFLAGS)得到目标.这个规则中只有-c是隐含规则中有的,后面两个变量是留给用户 ...
- MVC的URL路由规则
MVC的URL路由规则 Routing的作用:它首先是获取到View传过来的请求,并解析Url请求中Controller和Action以及数据,其次他将识别出来的数据传递给Controller的Act ...
- iptables命令、规则、参数详解
表 (table)包含4个表:4个表的优先级由高到低:raw-->mangle-->nat-->filterraw---RAW表只使用在PREROUTING链和OUTPUT链上 ...
- Linux防火墙iptables规则设置(转)
iptables命令是Linux上常用的防火墙软件,是netfilter项目的一部分.可以直接配置,也可以通过许多前端和图形界面配置. 一.语法 iptables(选项)(参数) 二.选项 -t< ...
- MVC中url路由规则
Routing:首先获取视图页面传过来的请求,并接受url路径中的controller和action以及参数数据,根据规则将识别出来的数据传递给某controller中的某个action方法 MapR ...
- 【转】iptables命令、规则、参数详解
表 (table)包含4个表:4个表的优先级由高到低:raw-->mangle-->nat-->filterraw---RAW表只使用在PREROUTING链和OUTPUT链上 ...
随机推荐
- Spring4学习笔记2-配置Bean
1.配置bean 配置形式:Xml和注解方式 Bean的配置方式:通过全类名(反射).工厂.FactoryBean 1.1 id必须唯一 2 Spring提供两种类型的IOC容器的实现 BeanFac ...
- Devrama Slider - 支持任意 HTML 的内容滑块
Devrama Slider 是一个图片滑块,支持很多特色功能.除了支持图片滑动,其它的 HTML 内容也支持.主要特色:响应式.图片预加载.图片延迟加载.进度条.自定义导航栏和控制按钮等等. 在线演 ...
- Web 开发最有用的50款 jQuery 插件集锦——《图片特效篇》
<Web 开发最有用的50款 jQuery 插件集锦>系列文章向大家分享最具创新的50款 jQuery 插件,这些插件分成以下类别:网页布局插件,导航插件,表格插件,滑块和转盘插件,图表插 ...
- 【今日推荐】移动 Web 开发的10个最佳 JavaScript 框架
选择正确的 JavaScript 框架,对于开发移动 Web 应用程序是至关重要的,也是移动应用程序开发的一项重要任务.开发人员可以使用框架实现的功能高效地达到他们的开发目标.这些预实现的组件采用优秀 ...
- ASP.NET使用jQuery AJAX实现MD5加密实例
一个asp.net ajax例子,使用jquery,实现md5加密.在.NET 4.0,Visual Studio 2010上成功运行. 效果体验:http://tool.keleyi.com/t/m ...
- Electron笔记
一个能让你用Web技术开发桌面应用的开源项目.这里做一个笔记(非正式文章): 官网地址:http://electron.atom.io/ API相关 Electron提供的主进程接口.渲染进程接口.共 ...
- Sublime Text3 支持Less
1.安装Sublime 插件 (1)安装LESS插件:因为Sublime不支持Less语法高亮,所以,先安装这个插件,方法: ctrl+shift+p>install Package>输入 ...
- javascript --- Function模式
回调函数 在javascript中,当一个函数A作为另外一个函数B的其中一个参数时,则称A函数为回调函数,即A可以在函数B的运行周期内执行(开始,中间,结束). 举例来说,有一个函数用于生成node. ...
- ECMAScript对文件夹图片幻灯片播放
代码如下: var curContext = null; var curWeb = null; var picListTitle = "PictureLib"; var folde ...
- Android Design Principles
Android Design Principles Enchant Me Delight me in surprising ways 用惊奇的方式取悦用户 漂亮的界面,仔细放置的动画,一个恰到时机的音 ...
