Django-CSRF,AJAX,FORM
内容总览
1.CSRF相关
1>CSRF源码分析
2>ajax的实现(ajax的实例(异步计算,参数测试,上传))
3>ajax通过csrf的校验
2.FORM组件
1>基本使用
2>内部校验器
3>自定义函数内部校验
4>is_valid()源码分析
1.django的csrf源码分析
1>global_settings与CsrfViewMiddleware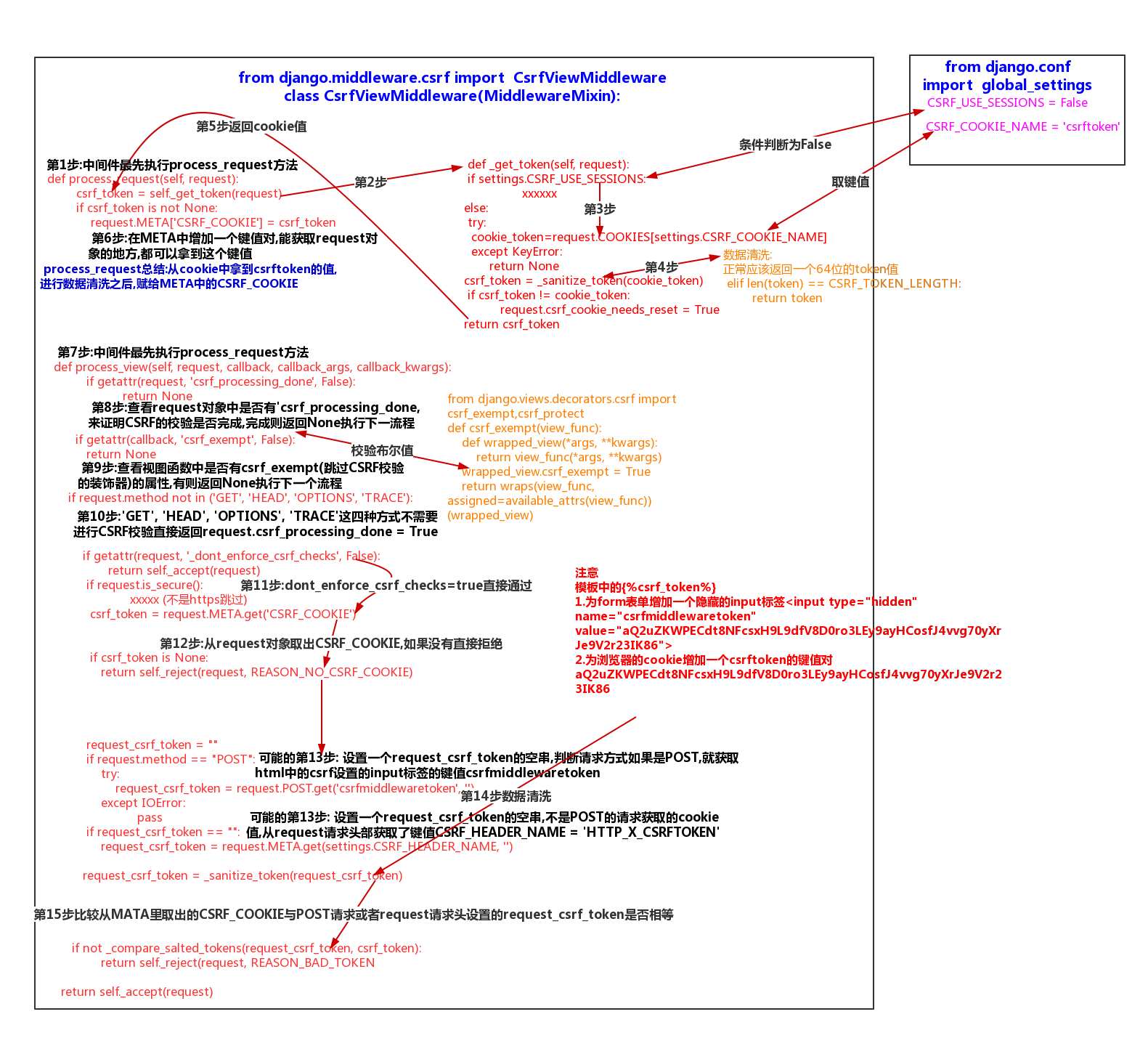
2>.ajax
a.发请求的途径
浏览器地址栏键入url--->GET
form表单提交数据 ----->根据method决定是POST/GET
a标签超链接 ---> GET
b.ajax是使用js技术发送异步请求,一般传输json数据
特点:局部刷新,当前页面不刷新
异步,客户端发出一个请求后,无需等待服务器响应结,就可以发出第二个请求
c.正常全局刷新
views
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
i1 = request.POST.get('i1')
i2 = request.POST.get('i2')
i3 = eval(f'{i1}+{i2}')
print(locals())
return render(request,'index.html',locals())
html
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="text" name="i1" value="{{ i1 }}">+<input type="text" name="i2" value="{{ i2 }}">=<input type="text" value="{{ i3 }}">
<button>计算</button>
d.ajax局部刷新
事例一:异步ajax计算
views
import time
def index(request):
return render(request,'index.html')
def calc1(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
i1 = request.POST.get('i1')
i2 = request.POST.get('i2')
i3 = eval(f'{i1}+{i2}')
time.sleep(3)
return HttpResponse(i3) #返回响应体让ajax接收
def calc2(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
i1 = request.POST.get('i1')
i2 = request.POST.get('i2')
i3 = eval(f'{i1}+{i2}')
return HttpResponse(i3)
html
<input type="text" name="i1" value="{{ i1 }}">+<input type="text" name="i2" value="{{ i2 }}">=<input type="text" name='i3' value="{{ i3 }}">
<button id="b1">计算</button>
<br>
<input type="text" name="i11" value="{{ i11 }}">+<input type="text" name="i22" value="{{ i22 }}">=<input type="text" name='i33' value="{{ i33 }}">
<button id="b2">计算</button>
$('#b1').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/calc1/',
type:'post',
data:{
i1:$("[name='i1']").val(),
i2:$("[name='i2']").val(),
},
success:function (res) {
{#res是返回的响应体#}
{#console.log(res)#}
$("[name='i3']").val(res)
}
})
});
$('#b2').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/calc2/',
type:'post',
data:{
i1:$("[name='i11']").val(),
i2:$("[name='i22']").val(),
},
success:function (res) {
{#res是返回的响应体#}
{#console.log(res)#}
$("[name='i33']").val(res)
}
})
});
事例二:参数测试
1>前端数组--->序列化--->后端接收--->反序列化--->拿到数组
#########前后端交交互都应该将数据类型转化为json字符串#########
############前端使用ajax直接传一个列表的情况#############
html
<button id="b3">参数测试</button>
$('#b3').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/ajax_test/',
type:'post',
data:{
hobby:['篮球','足球','排球']
},
success:function (res) {
console.log(res)
},
error:function (res) {
console.log(33);
console.log(res)
}
})
});
views
def ajax_test(request):
print(request.POST)
#传过来的内容被格式化下属形况
#<QueryDict: {'hobby[]': ['篮球', '足球', '排球']}>
print(111,request.POST.getlist('hobby[]'))
#111 ['篮球', '足球', '排球']
hobby= request.POST.get('hobby')
print(222,hobby,type(hobby))
#222 None <class 'NoneType'>
################前端传一个json字符串的情况############
html
$('#b3').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/ajax_test/',
type:'post',
data:{
hobby:JSON.stringify(['篮球','足球','排球'])
},
success:function (res) {
console.log(res)
},
error:function (res) {
console.log(33);
console.log(res)
}
})
});
views
def ajax_test(request):
print(request.POST)
#前端序列化之后传来一个正常的字符串
#<QueryDict: {'hobby': ['["篮球","足球","排球"]']}>
print(111,request.POST.getlist('hobby[]'))
#111 []
hobby= request.POST.get('hobby')
print(222,hobby,type(hobby))
#222 ["篮球","足球","排球"] <class 'str'>
hobby_json = json.loads(hobby)
print(type(hobby_json),hobby_json[0:2])
#<class 'list'> ['篮球', '足球']
#反序列化之后可以正常拿到前端传的列表数据类型
2>后台字典--->序列化------->前端---->反序列化----->拿到字典
#######后台返回一个Jsonresponse,,前端可以直接使用数据类型########
html
$('#b3').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/ajax_test/',
type:'post',
data:{
{#hobby:['篮球','足球','排球']#}
{#hobby:JSON.stringify(['篮球','足球','排球'])#}
},
success:function (res) {
console.log(res)
},
error:function (res) {
console.log(33);
console.log(res)
}
})
});
views
def ajax_test(request):
data = {'name': 'sen', 'age': 26}
return JsonResponse(data)
#浏览器:一个数组
{name: "sen", age: 26}
age: 26
name: "sen"
__proto__: Object
###使用Httpresponse(json.dumps ,content_type='application/json')###
html
与上面一样
views
def ajax_test(request):
data = {'name': 'sen', 'age': 26}
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(data),content_type='application/json')
#浏览器也会拿到数组,如果不加content_type 只会拿到json字符串
#例如 {"name": "sen", "age": 26}
事例三:上传
views
from django.http import JsonResponse
def upload(request):
if request.is_ajax():
print(request.FILES)
#<MultiValueDict: {'f1': [<InMemoryUploadedFile: 55.jpg (image/jpeg)>]}>
f1 = request.FILES.get('f1')
print(f1)
#55.jpg
with open(f1.name,'wb') as f:
for i in f1.chunks():
f.write(i)
#return HttpResponse('ok') return JsonResponse({'status':0,'msg':'上传成功'}) #以JSON的数据类型返给了前端
html
<input type="file" id="f1">
<button id="b4">上传</button>
$('#b4').click(function () {
form_obj = new FormData();
{#console.log($('#f1'));#}
{#jQuery.fn.init [input#f1]#}
{#0: input#f1#}
{#console.log($('#f1')[0].files);#}
{#FileList {0: File(54312), length: 1}#}
form_obj.append('f1',$('#f1')[0].files[0]);
$.ajax({
url:'/upload/',
type:'post',
data:form_obj,
processData:false,
{#停止ajax对文件的编码处理#}
contentType:false,
{#业务逻辑JSONRESPONSE的字符串到前端会自动反序列化成数组(字典),方便直接取值#}
success:function (res) {
console.log(res)
if(res.status == 0){ alert(res.msg);
},
})
})
3.ajax通过csrf的验证
a.自行设置通过验证的csrf_token信息
html
#注意:必须要有{% csrf_token%}
#1>POST请求携带的form数据
$('#b1').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/calc1/',
type:'post',
data:{
i1:$("[name='i1']").val(),
i2:$("[name='i2']").val(),
csrfmiddlewaretoken:$("[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val(),
},#浏览器显示:i1=1&i2=3&csrfmiddlewaretoken=0jWWADXuWLyAdj56bFFXzgadAZziwoEvu13C9AD3Ko4bA1G1JGVfxl6THiYlNKJQ
#2>设置在响应头中的键值对
$('#b2').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url:'/calc2/',
type:'post',
headers:{'X-csrftoken':$("[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val()},
data:{
i1:$("[name='i11']").val(),
i2:$("[name='i22']").val(),
},#浏览器显示: X-csrftoken:0jWWADXuWLyAdj56bFFXzgadAZziwoEvu13C9AD3Ko4bA1G1JGVfxl6THiYlNKJQ
b.django官网推荐的通过csrf验证的方式
#新建一个ajax-setup.js
#注意 以下条件需要满足一点即可:
#1>html:需要有{%csrf%}
#2>from django.views.decorators.csrf import ensure_csrf_cookie 给视图函数增加一个@ensure_csrf_cookie
function getCookie(name) {
var cookieValue = null;
if (document.cookie && document.cookie !== '') {
var cookies = document.cookie.split(';');
for (var i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
var cookie = jQuery.trim(cookies[i]);
// Does this cookie string begin with the name we want?
if (cookie.substring(0, name.length + 1) === (name + '=')) {
cookieValue = decodeURIComponent(cookie.substring(name.length + 1));
break;
}
}
}
return cookieValue;
}
var csrftoken = getCookie('csrftoken');
function csrfSafeMethod(method) {
// these HTTP methods do not require CSRF protection
return (/^(GET|HEAD|OPTIONS|TRACE)$/.test(method));
}
$.ajaxSetup({
beforeSend: function (xhr, settings) {
if (!csrfSafeMethod(settings.type) && !this.crossDomain) {
xhr.setRequestHeader("X-CSRFToken", csrftoken);
}
}
});
html页面:最后在有需求的页面上去引入
<script src="{% static 'ajax-setup.js' %}"></script>
#注意一定页面上一定要有{%csrf%}
2.django的form组件
1>普通的form校验
缺点:校验条件自己定义,需要检验的内容非常多,很繁琐.
views
def reg(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
user = request.POST.get('user')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
if len(user) <6:
err_msg='用户名太短了'
else:
return HttpResponse('注册成功')
return render(request,'reg.html',locals())
html
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<p>
用户名:<input type="text" name="user"><span style="color: red">{{ err_msg }}</span>
</p>
<p>
密码:<input type="password" name="pwd">
</p>
<button>注册</button>
</form>
2>form组件的使用
a.导入forms模块,创建一个自定义的类去继承(form.Form),在自定义类种创建一些字段对象
b.创建一个视图方法去实例化这个自定义的类,需要POST判断的时候,将request对象传入自定义类中,再实例化一次,并且用这个对象的is_valid方法进行校验
c.事例用到的参数:
initial :默认给字段对象所对应的input框填入一个字符串,类似于placeholder
min_length,max_length:前端校验,与后端校验的使用一个检测标准最小长度与最大长度.
label:对字段对象对应的input标签,生成一个配套的label标签
widget:插件可以对字段对象的属性进行变更,例如添加一个class属性,更改input的type属性
error_messgaes:根据字段对象里使用的校验标准和默认的校验参数来定义key值和自定义显示的错误信息
CharField:所有的字段对象都可以用这个类去实例化,需要不同的字段类型只需要在widget实例化进行修改即可(例如: widget=forms.widgets.PasswordInput)
ChoiceField:所有选项类的可以根据这个类实例化去修改widget
d.模板语法的使用
对象.字段对象.属性
例如:从views传来一个form_obj的对象,
模板中使用form.as_p :生成P标签(input + label)
form_obj.user.label(取得是user字段对象得label属性)与 form_obj.user.id_for_label(取得是input的id赋给label标签的for属性) 配合,嵌套在label标签中
form_obj.user: 一个input框(属性是自定义类定义的)
form_obj.user.errors.0 :取第一个错误的html的文本值
views
from django import forms
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
#注册form
class RegForm(forms.Form):
user=forms.CharField(
initial='lin',
min_length=6,
max_length=10,
label='用户名',
widget=forms.widgets.Input(attrs={'class':'form-control'}),
error_messages={
'min_length':'长度至少为8位',
'required':'不能为空'
}
)
pwd=forms.CharField(label='密码',
widget=forms.widgets.PasswordInput(attrs={'class':'form-control'}),
)
gender=forms.ChoiceField(choices=((1,'male'),(2,'female'),(3,'other')),
widget=forms.RadioSelect()
)
hobby = forms.ChoiceField(
# choices=((1,'篮球'),(2,'足球'),(3,'双色球')),
# choices=models.Hobby.objects.all().values_list(), #values_list取出来元组,数据全是值
label='爱好',
initial=[1,3],
widget=forms.SelectMultiple()
)
def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args,**kwargs)
self.fields['hobby'].choices=models.Hobby.objects.all().values_list()
def reg2(request):
form_obj = RegForm()
if request.method == 'POST':
form_obj =RegForm(request.POST)
if form_obj.is_valid():
return HttpResponse('注册成功')
return render(request,'reg3.html',{'form_obj':form_obj})
html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.css' %}">
</head>
<body>
<form class="form-horizontal" method="post" action="" novalidate>
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group {% if form_obj.user.errors %}has-error{% else %} has-success{% endif %}">
<label for="{{ form_obj.user.id_for_label }}" class="col-sm-2 control-label">{{ form_obj.user.label }}</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
{{ form_obj.user }}
<label class="control-label">{{ form_obj.user.errors.0 }}</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="{{ form_obj.pwd.id_for_label }}" class="col-sm-2 control-label">{{ form_obj.pwd.label }}</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
{{ form_obj.pwd }}
<span>{{ form_obj.pwd.errors }}</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="{{ form_obj.gender.id_for_label }}" class="col-sm-2 control-label">{{ form_obj.gender.label }}</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
{{ form_obj.gender }}
<span>{{ form_obj.gender.errors }}</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="{{ form_obj.hobby.id_for_label }}" class="col-sm-2 control-label">{{ form_obj.hobby.label }}</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
{{ form_obj.hobby }}
<span>{{ form_obj.hobby.errors }}</span>
</div>
</div>
{# 所有的错误提示#}
{{ form_obj.errors }}
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">注 册</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
3>form的内置校验器
min_length,max_length,require
前端检测:只要在自定义类中的字段属性例如user定义了上述方法,并且前端开启了检测,即可在input框中对条件进行校验,无需传入数据重新实例化自定义类.
def reg2(request):
form_obj = RegForm()
if request.method == 'POST':
pass
# form_obj =RegForm(request.POST)
# if form_obj.is_valid():
# return HttpResponse('注册成功')
return render(request,'reg3.html',{'form_obj':form_obj})
后台检测:需要前端进行POST提交之后,后台进行form_obj=RegForm(request.POST)实例化,将对象的POST方法取到的数据传入对象中,这样前端传入的form_obj的对象可以在模板语言中使用错误检测,form_obj.errors.
def reg2(request):
form_obj = RegForm()
if request.method == 'POST':
# pass
form_obj =RegForm(request.POST) #需要传入request.POST方法的数据
# if form_obj.is_valid():
# return HttpResponse('注册成功')
return render(request,'reg3.html',{'form_obj':form_obj})
4>form的自定义校验(向实例化对象传入request.POST数据,实例化的同时就会执行is_valid方法)
a.使用django提供的方式校验
from django.core.validators import RegexValidator
#字段对象里使用检测机制,并自定义规则
phone = forms.CharField(
label='手机号',
validators=[RegexValidator(r'1[3-9]\d{9}','手机号不合格')]
)
b.自定以函数
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
def check_name(value):
if 'lin' in value:
raise ValidationError('不符合规格')
#字段对象直接使用自定义的函数进行校验
user=forms.CharField(
initial='lin',
min_length=6,
max_length=10,
label='用户名',
widget=forms.widgets.Input(attrs={'class':'form-control'}),
validators=[check_name],
error_messages={
'min_length':'长度至少为8位',
'required':'不能为空'
}
)
def reg2(request): form_obj = RegForm() if request.method == 'POST': # pass form_obj =RegForm(request.POST) #注意 必须实例化自定义对象,并且传入request.POST的数据才可以实现内置校验 # if form_obj.is_valid(): # print(form_obj.cleaned_data) # return HttpResponse('注册成功') return render(request,'reg3.html',{'form_obj':form_obj})
4>form的is_valid方法的源码分析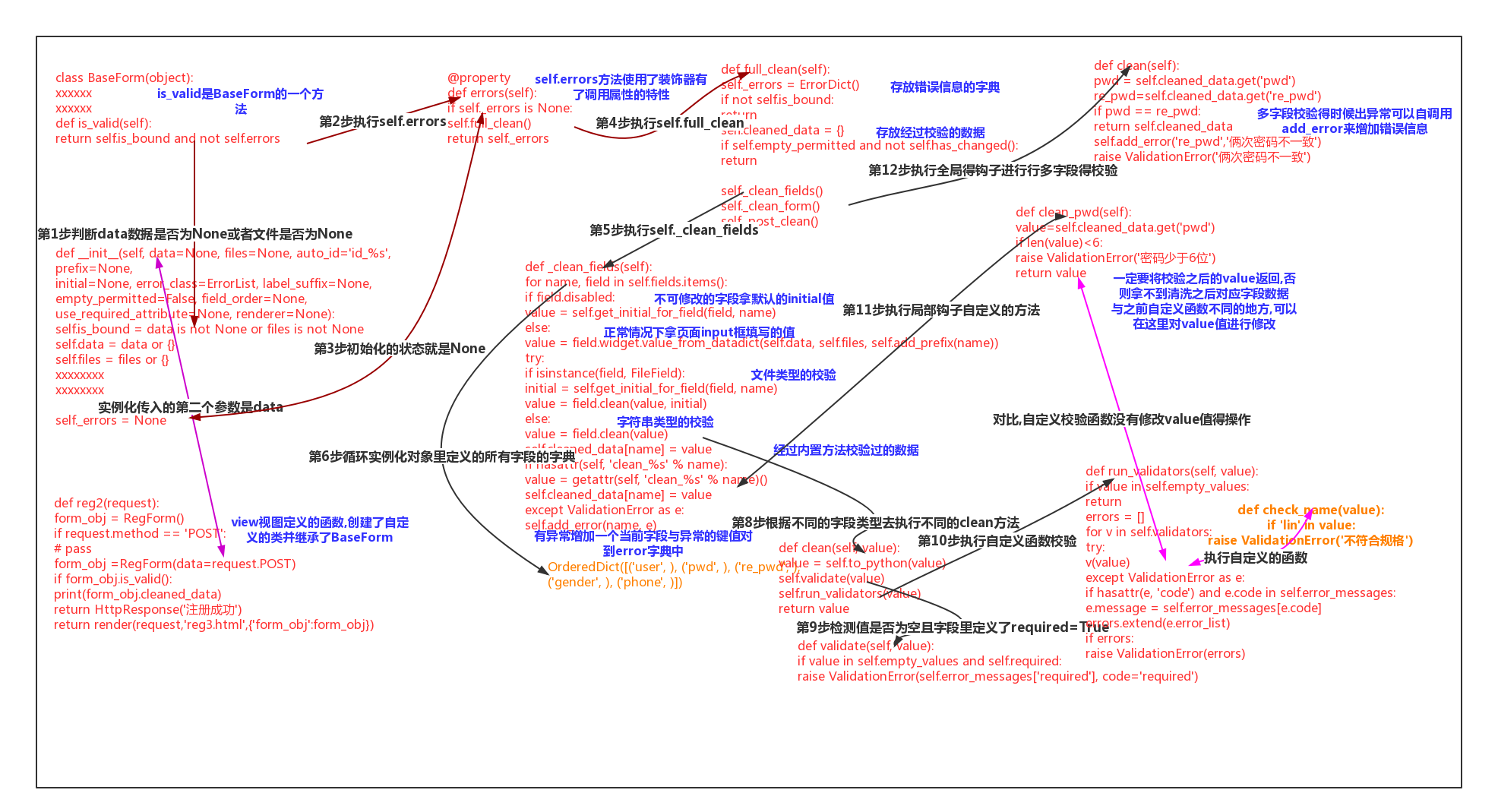
Django-CSRF,AJAX,FORM的更多相关文章
- Django 基于Ajax & form 简单实现文件上传
前端实现 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="U ...
- Django框架 之 Form表单和Ajax上传文件
Django框架 之 Form表单和Ajax上传文件 浏览目录 Form表单上传文件 Ajax上传文件 伪造Ajax上传文件 Form表单上传文件 html 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <h3& ...
- python Django之Ajax
python Django之Ajax AJAX,Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (异步的JavaScript和XML),一种创建交互式网页应用的网页开发技术方案. 异步 ...
- pythonのdjango CSRF简单使用
一.简介 django为用户实现防止跨站请求伪造的功能,通过中间件 django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware 来完成.而对于django中设置防跨站请求伪造功 ...
- Django之Ajax文件上传
请求头ContentType ContentType指的是请求体的编码类型,常见的类型共有3种: 1 application/x-www-form-urlencoded(看下图) 这应该是最常见的 P ...
- Django CSRF提交遇见的问题
简介 django为用户实现防止跨站请求伪造的功能,通过中间件 django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware 来完成.而对于django中设置防跨站请求伪造功能有 ...
- python 全栈开发,Day75(Django与Ajax,文件上传,ajax发送json数据,基于Ajax的文件上传,SweetAlert插件)
昨日内容回顾 基于对象的跨表查询 正向查询:关联属性在A表中,所以A对象找关联B表数据,正向查询 反向查询:关联属性在A表中,所以B对象找A对象,反向查询 一对多: 按字段:xx book ----- ...
- django csrf使用教程,解决Forbidden (403)CSRF verification failed. Request aborted.
Django版本号:1.11.15 django中post请求报错:Forbidden (403)CSRF verification failed. Request aborted. HelpReas ...
- Django 2.0 学习(22):Django CSRF
Django CSRF CSRF攻击过程 攻击说明: 1.用户C打开浏览器,访问受信任网站A,输入用户名和密码请求登陆网站A: 2.在用户信息通过验证后,网站A产生Cookie信息并返回给浏览器,此时 ...
- Django 之Ajax&Json&CORS&同源策略&Jsonp用法
什么是Json 定义: JSON(JavaScript Object Notation, JS 对象标记) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.它基于 ECMAScript (w3c制定的js规范)的一个子集 ...
随机推荐
- FLOAT 和 DOUBLE区别
以下是 FLOAT 和 DOUBLE 的区别: float : 单精度浮点数 double : 双精度浮点数 ·浮点数以 8 位精度存储在 FLOAT 中,并且有四个字节. ·浮点数存储在 DOUBL ...
- 用redis实现分布式锁,秒杀案例(转)
分布式锁的简单实现代码: 需要的jar包: jedis-2.9.0.jar. commons-pool2-2.4.2.jar import java.util.List; import java.ut ...
- ftm国际化解决方案
记录一下踩过的坑,在使用ftm:message的时候我发现这个的国际化是依赖于本地浏览器的语言环境的!关于自主设置这个语言的方法有如下3种:(个人建议使用第二种,可以更加灵活且有效!第一种我这边没有生 ...
- windows环境下mysql密码重置
1.打开cmd窗口,输入命令[mysqld --skip-grant-tables]回车. 2.再打开一个cmd窗口,输入命令[mysql]回车. 3.输入命令[use mysql; ] 连接权限数据 ...
- Nginx 过滤sub模块
L70 通过 --with-http_sub_module 编译进nginx sub_filter 指令 Syntax: sub_filter string replacement; Default: ...
- [LOJ3087][GXOI/GZOI2019]旅行者——堆优化dijkstra
题目链接: [GXOI/GZOI2019]旅行者 我们考虑每条边的贡献,对每个点求出能到达它的最近的感兴趣的城市(设为$f[i]$,最短距离设为$a[i]$)和它能到达的离它最近的感兴趣的城市(设为$ ...
- NSParagraphStyle 的属性
UILabel * label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 20, 20)]; label.font = [UIFont sys ...
- win10的MySQL客户端连接centos7虚拟机的mysql服务端连接不上解决办法
分别在win10和Centos虚拟机上装有MYSQL,但用电脑的mysql客户端连接centos7的服务端报错如下: 解决办法: 如果可以从虚拟机连接到电脑的MYSQL服务端, 那就是CentOS7的 ...
- [leetcode] 5.Longest Palindromic Substring-2
想了很多方法 搞轴对称,算对称轴,偶数都高出了一堆0.5在那加加减减,最后发现在移轴之前可能就返回了. class Solution: def longestPalindrome(self, s: s ...
- SQL学习指南第四篇
SQL必知必会(第4版)学习笔记 插入数据 插入有几种方式: 插入完整的行 插入行的一部分 插入某些查询的结果(INSERT SELECT) 注意:省略列 如果表的定义允许,则可以在 INSERT 操 ...
