[Python] Python 学习 - 可视化数据操作(一)
Python 学习 - 可视化数据操作(一)
GitHub:https://github.com/liqingwen2015/my_data_view
目录
- 折线图
- 散点图
- 随机漫步
- 骰子点数概率
- 文件目录
折线图
cube_squares.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_values=list(range(1, 5000))
y_values=[pow(x, 3) for x in x_values] plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c=y_values, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, edgecolor='none', s=40) # 设置标题和样式
plt.title("Square Numbers", fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Square of Value", fontsize=14) # 设置刻度标记的大小
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=14) plt.show()

mpl_squares.py
# 简单的折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt input_values=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
squares = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25] # 绘制线条的粗细
plt.plot(input_values, squares, linewidth=5) # 设置图表标题,并给坐标轴加上标签
plt.title("Square Numbers", fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Square of Value", fontsize=14) # 设置刻度标记的大小,axis='both' 表示指定的实参影响 x 轴和 y 轴上的刻度
plt.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=14) plt.show()

散点图
scatter_squares.py
# 散点图 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_values = list(range(1, 1001))
y_values = [x**2 for x in x_values] # c:颜色
#plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c='red', edgecolor='none', s=40)
#plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c=(0, 0, 8), edgecolor='none', s=40)
plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c=y_values, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, edgecolor='none', s=40) # 设置标题和样式
plt.title("Square Numbers", fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Value", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Square of Value", fontsize=14) # 设置刻度标记的大小
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=14) plt.show() # 保存图表
#plt.savefig('squared_plot.png', bbox_inches='tight')
随机漫步
random_walk.py
from random import choice
class RandomWalk():
def __init__(self, num_points=5000):
# 初始化随机漫步的属性
self.num_points = num_points
# 所有随机漫步都始于(0, 0)
self.x_values = [0]
self.y_values = [0]
def fill_walk(self):
# 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度
while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points:
x_step = self.get_step();
y_step = self.get_step();
# 拒绝原地踏步
if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0:
continue
# 计算下一个点的 x 和 y 值
next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step
next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step
self.x_values.append(next_x)
self.y_values.append(next_y)
def get_step(self):
# 决定前进方向以及沿这个方向前进的距离
direction = choice([1, -1]) # 随机选 1 或 -1
distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) # 随机选 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
return direction * distance # 正数:右移,负数:左移
rw_visual.py
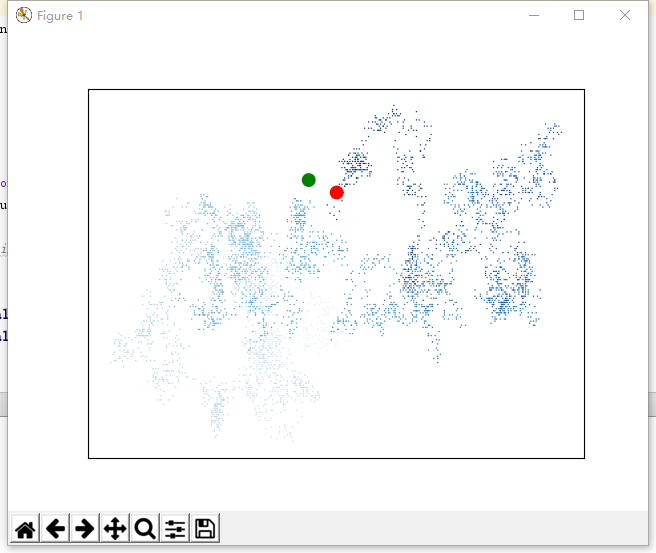
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from 随机漫步.random_walk import RandomWalk while True:
# 创建一个 RandomWalk 实例,并将其包含的点都绘制出来
rw = RandomWalk(5000)
rw.fill_walk() point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points))
plt.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, c=point_numbers, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, edgecolors='none', s=1) # 设置绘图窗口的尺寸
#plt.figure(dpi=128, figsize=(10, 6)) # 突出起点和终点
plt.scatter(0, 0, c='green', edgecolors='none', s=100)
plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red', edgecolors='none', s=100) #plt.plot(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, linewidth=10) # 隐藏坐标轴
plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show() keep_running = input("继续?(y/n):")
if keep_running == 'n':
break
骰子点数概率
die.py
from random import randint class Die():
# 表示一个骰子类 def __init__(self, num_sides=6):
# 6 面
self.num_sides = num_sides def roll(self):
# 返回 1~6
return randint(1, self.num_sides)
die_visual.py
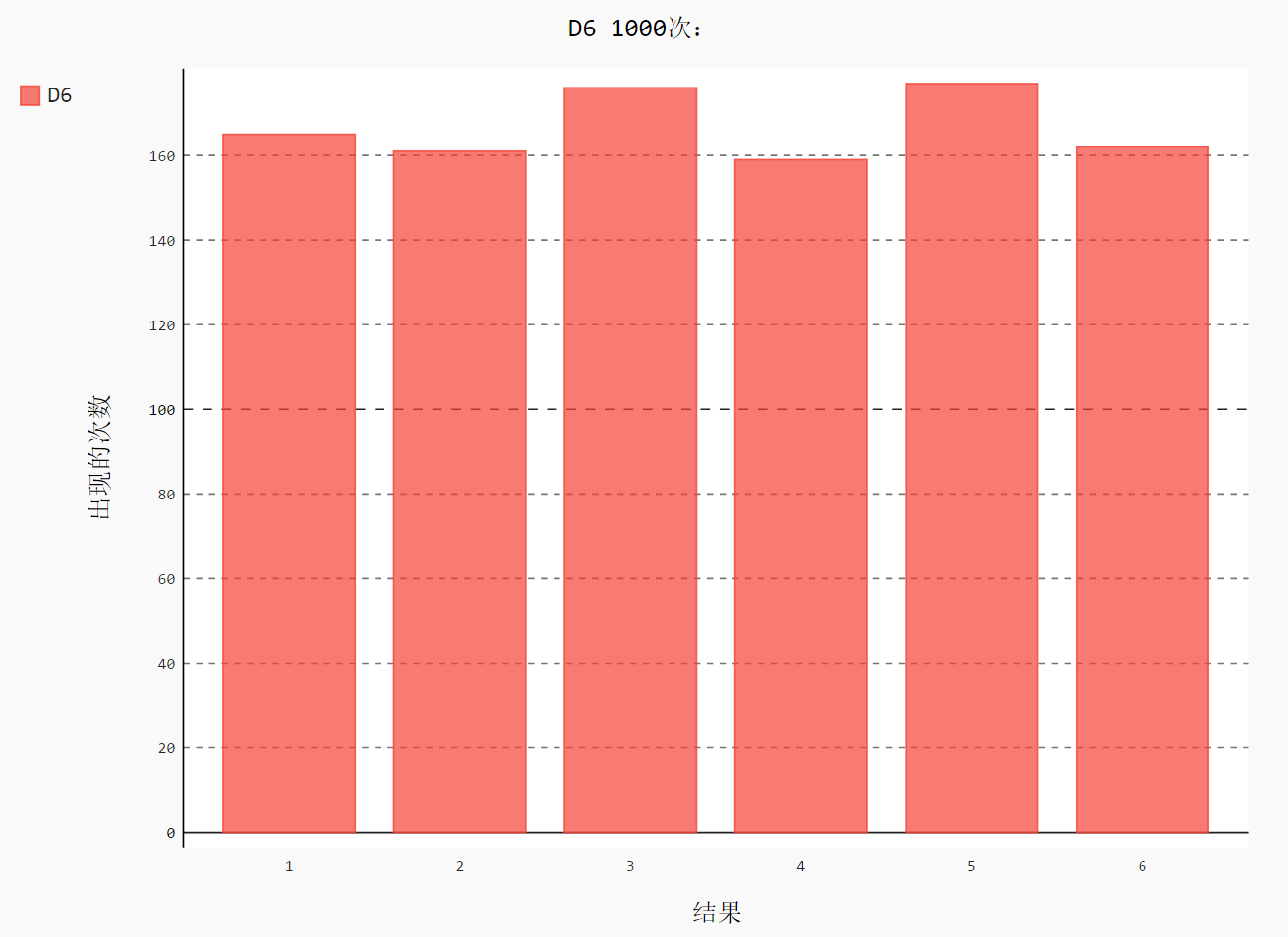
import pygal from 骰子.die import Die # 创建一个 D6
die = Die() results = []
for roll_num in range(1000):
result = die.roll()
results.append(result) frequencies = []
for value in range(1, die.num_sides+1):
# 计算某个值出现同样的次数
frequency = results.count(value)
frequencies.append(frequency) # 对结果进行可视化
hist = pygal.Bar() hist.title = "D6 1000次:"
hist.x_labels = [str(num) for num in range(1, 7)] #['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6']
hist.x_title = "结果"
hist.y_title = "概率" hist.add('D6', frequencies)
hist.render_to_file('images/die_visual.svg')
dice_visual.py
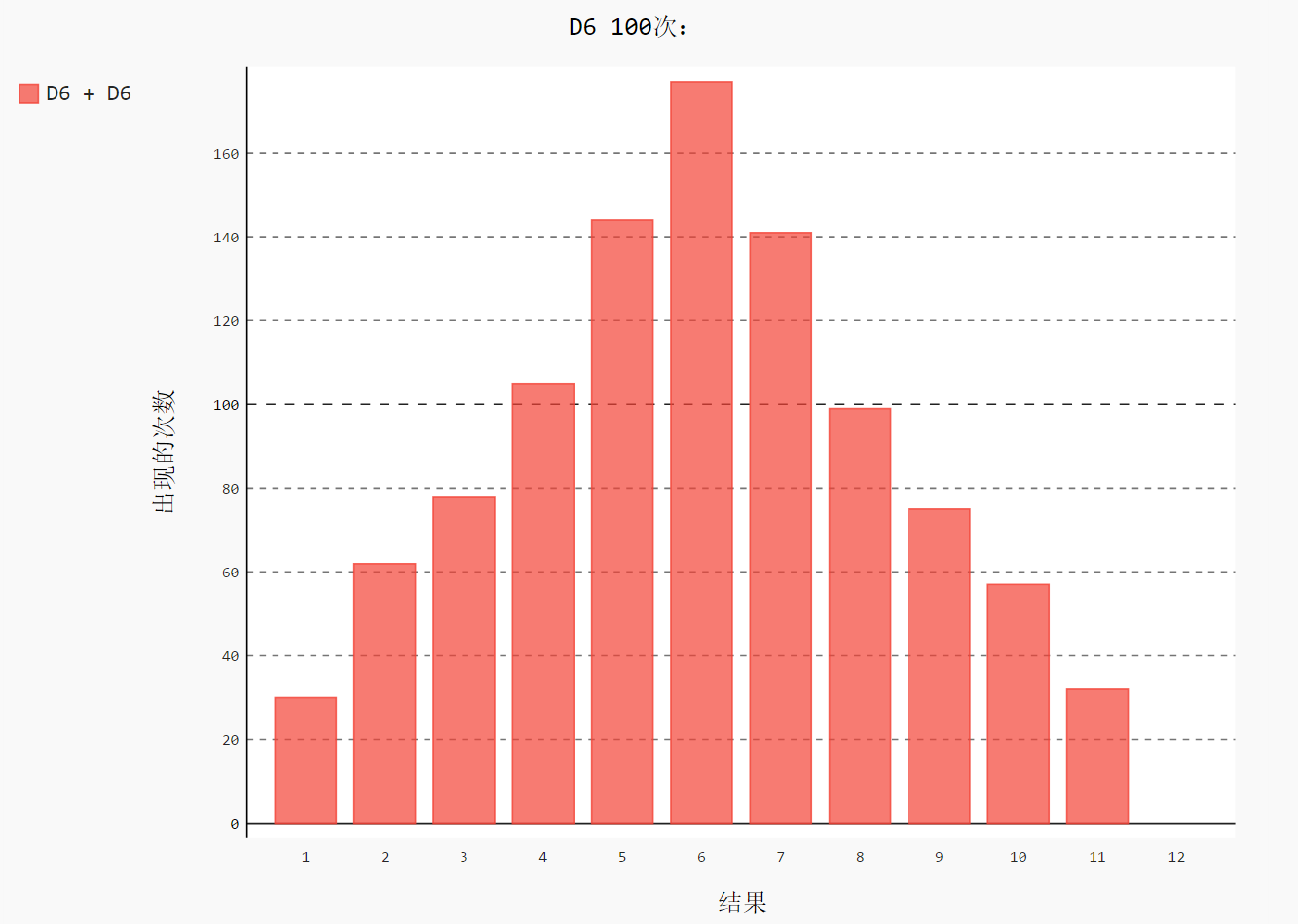
import pygal from 骰子.die import Die # 创建 2 个 D6
die_1 = Die()
die_2 = Die() results = []
for roll_num in range(1000):
result = die_1.roll() + die_2.roll()
results.append(result) frequencies = []
max_results = die_1.num_sides + die_2.num_sides
for value in range(2, max_results+1):
# 计算某个值出现同样的次数
frequency = results.count(value)
frequencies.append(frequency) # 对结果进行可视化
hist = pygal.Bar() hist.title = "D6 100次:"
hist.x_labels = [str(num) for num in range(1, 13)] #['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', '11', '12']
hist.x_title = "结果"
hist.y_title = "出现的次数" hist.add('D6 + D6', frequencies)
hist.render_to_file('images/dice_visual.svg')
different_dice.py
import pygal from 骰子.die import Die # 创建一个 D6 和 D10
die_1 = Die()
die_2 = Die(10) results = []
for roll_num in range(5000):
result = die_1.roll() + die_2.roll()
results.append(result) frequencies = []
max_results = die_1.num_sides + die_2.num_sides
for value in range(2, max_results+1):
# 计算某个值出现同样的次数
frequency = results.count(value)
frequencies.append(frequency) # 对结果进行可视化
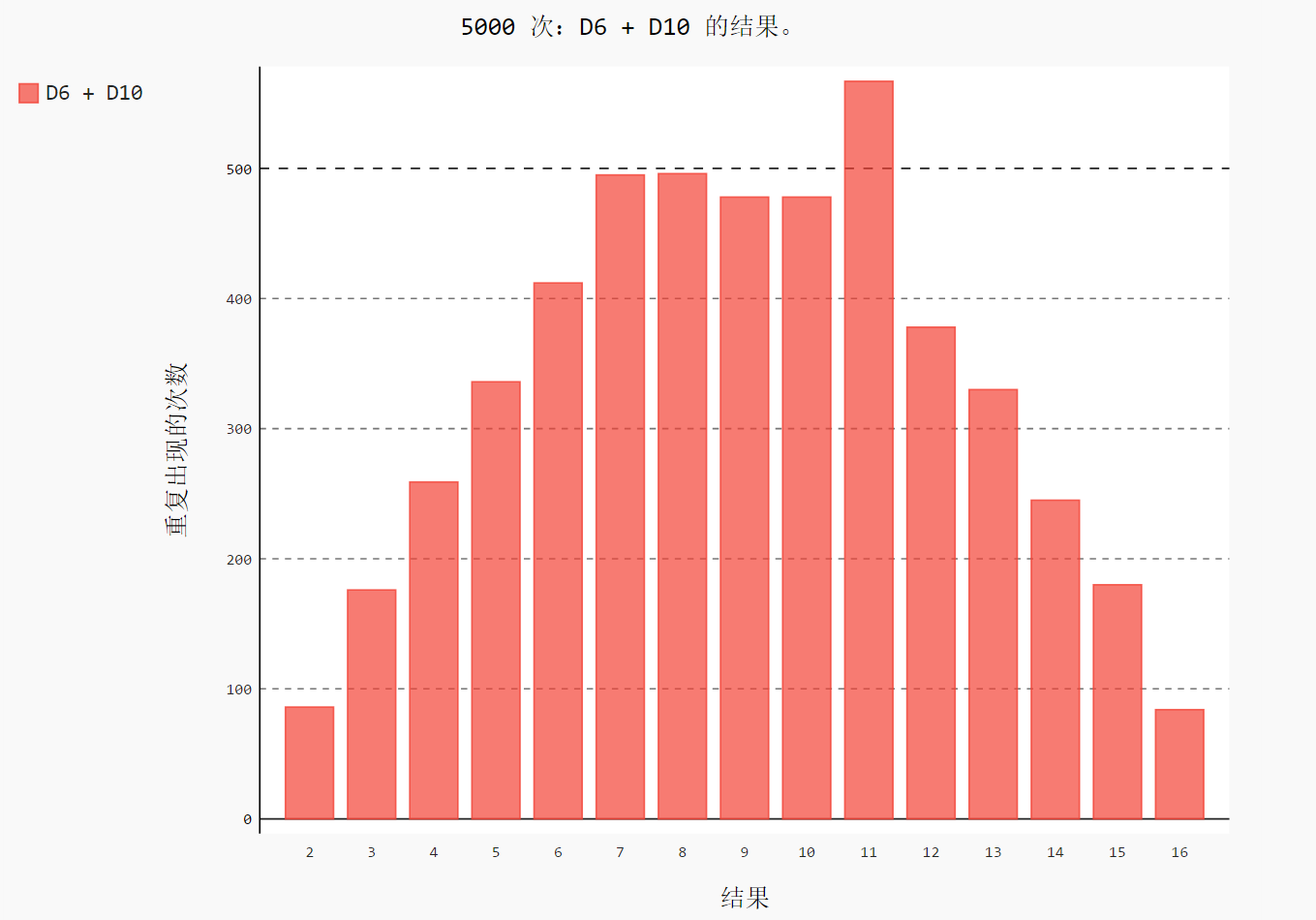
hist = pygal.Bar() hist.title = "5000 次:D6 + D10 的结果。"
hist.x_labels = [str(num) for num in range(2, 17)]
hist.x_title = "结果"
hist.y_title = "重复出现的次数" hist.add('D6 + D10', frequencies)
hist.render_to_file('images/different_visual.svg')
文件目录
GitHub:https://github.com/liqingwen2015/my_data_view
[Python] Python 学习 - 可视化数据操作(一)的更多相关文章
- python入门学习:3.操作列表
python入门学习:3.操作列表 关键点:列表 3.1 遍历整个列表3.2 创建数值列表3.3 使用列表3.4 元组 3.1 遍历整个列表 循环这种概念很重要,因为它是计算机自动完成重复工作的常 ...
- Python进阶学习_连接操作Redis数据库
安装导入第三方模块Redis pip3 install redis import redis 操作String类型 """ redis 基本命令 String set(n ...
- linux学习之——数据操作:添加与查询
说明: 在linux系统中,利用搭建的服务器,编写两个页面,一个添加信息,一个展现信息: 主要涉及到:php+mysql的操作: 数据添加页面: <html> <head> & ...
- python基础学习之文件操作&函数
1.文件处理相关 1.编码问题 ①python2与python3中的默认编码: py2默认使用ASCII码,py3默认使用utf-8 ②为什么会出现中文乱码,中文乱码的情况有哪些? #sys.stdo ...
- Python基础学习七 Excel操作
python操作excel,python操作excel使用xlrd.xlwt和xlutils模块, xlrd模块是读取excel的,xlwt模块是写excel的,xlutils是用来修改excel的. ...
- python基础学习笔记——文件操作
文件操作 初始文件操作 使用Python来读写文件是非常简单的操作,我们使用open()函数来打开一个文件,获取到文件句柄,然后通过文件句柄就可以进行各种各样的操作了 根据打开方式的不同能够执行的操作 ...
- python自动化测试学习笔记-6excel操作xlwt、xlrd、xlutils模块
python中通过xlwt.xlrd和xlutils操作xls xlwt模块用于在内存中生成一个xls/xlsx对象,增加表格数据,并把内存中的xls对象保存为本地磁盘xls文件; xlrd模块用于把 ...
- [python][django学习篇][6]操作数据库
查询(取)数据 >>> Category.objects.all() <QuerySet [<Category: Category object>]> > ...
- 莫烦python教程学习笔记——数据预处理之normalization
# View more python learning tutorial on my Youtube and Youku channel!!! # Youtube video tutorial: ht ...
随机推荐
- 201771010126 王燕《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十二周学习总结
实验十二 图形程序设计 实验时间 2018-11-14 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握Java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API: 创建空框架 . 在Java中,常采用框架(Frame) ...
- css实用属性
background-size: 100% 100%; 背景通过拉伸实现填充 自适应 overflow: hidden; ...
- Oracle 闪回 找回数据
使用闪回技术,实现基于磁盘上闪回恢复区的自动备份与还原. 一.恢复表对象 1.创建学生表 create table STUDENT ( idno INTEGER, name VARCHAR2(30), ...
- 编译的时候出现 usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lxxx 的错误
比如错误为: usr/bin/ld: cannot find -labc 首先要明白的是 labc 代表的是 libabc.so 明白了这个之后,我们就知道了问题是:在编译的过程中,需要 libabc ...
- Oracle--配置并保存PL/SQL Developer界面
之前一直用SQL Server,现在刚接触Oracle,用PL/SQL Developer 客户端,在设置自已的使用习惯后保存界面 PL/SQL Developer初始界面布局,当你设置后,重新启动, ...
- 别以为真懂Openstack: 虚拟机创建的50个步骤和100个知识点(3)
四.Nova-compute 步骤17:nova-compute接收到请求后,通过Resource Tracker将创建虚拟机所需要的资源声明占用 步骤18:调用Neutron API配置Networ ...
- 【RL-TCPnet网络教程】第22章 RL-TCPnet之网络协议IP
第22章 RL-TCPnet之网络协议IP 本章节为大家讲解IP(Internet Protocol,网络协议),通过前面章节对TCP和UDP的学习,需要大家对IP也有个基础的认识. (本章 ...
- Linux中搭建Maven私服
linux安装maven 先解压maven的压缩包apache-maven-3.5.4-bin.tar.gz 命令: tar -zavf pache-maven-3.5.4-bin.tar.gz ...
- jQuery Mobile中表单的使用体会
jQuery Mobile是手机端(移动端)页面制作用的框架,包括CSS和JavaScript,此处简单总结一下表单的书写,主要涉及CSS部分.框架提供了表单的一些样式,但在实际使用的时候,我们可能会 ...
- Netty(三) 什么是 TCP 拆、粘包?如何解决?
前言 记得前段时间我们生产上的一个网关出现了故障. 这个网关逻辑非常简单,就是接收客户端的请求然后解析报文最后发送短信. 但这个请求并不是常见的 HTTP ,而是利用 Netty 自定义的协议. 有个 ...
