ES10特性详解
摘要: 最新的JS特性。

ES10 还只是一个草案。但是除了 Object.fromEntries 之外,Chrome 的大多数功能都已经实现了,为什么不早点开始探索呢?当所有浏览器都开始支持它时,你将走在前面,这只是时间问题。
在新的语言特性方面,ES10 不如 ES6 重要,但它确实添加了一些有趣的特性(其中一些功能目前还无法在浏览器中工作: 2019/02/21)
在 ES6 中,箭头函数无疑是最受欢迎的新特性,在 ES10 中会是什么呢?
- String .matchAll()
- Dynamic import()
- Array .flat() .flatMap()
- Object .fromEntries()
- String .trimStart() .trimEnd()
- well-formed JSON.stringify()
- stable Array .sort()
- new Function .toString()
- Standardized globalThis object
BigInt:任意精度整数
BigInt 是第七种 原始类型。
BigInt 是一个任意精度的整数。这意味着变量现在可以 表示²⁵³ 数字,而不仅仅是9007199254740992。
const b = 1n; // 追加 n 以创建 BigInt
在过去,不支持大于 9007199254740992 的整数值。如果超过,该值将锁定为 MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1:
const limit = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
⇨ 9007199254740991
limit + 1;
⇨ 9007199254740992
limit + 2;
⇨ 9007199254740992 <--- MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1 exceeded
const larger = 9007199254740991n;
⇨ 9007199254740991n
const integer = BigInt(9007199254740991); // initialize with number
⇨ 9007199254740991n
const same = BigInt("9007199254740991"); // initialize with "string"
⇨ 9007199254740991n
typeof
typeof 10;
⇨ 'number'
typeof 10n;
⇨ 'bigint'
等于运算符可用于两种类型之间比较
10n === BigInt(10);
⇨ true
10n == 10;
⇨ true
数学运算符只能在自己的类型中工作
200n / 10n
⇨ 20n
200n / 20
⇨ Uncaught TypeError:
Cannot mix BigInt and other types, use explicit conversions <
-运算符可以操作, + 不可用
-100n
⇨ -100n
+100n
⇨ Uncaught TypeError:
Cannot convert a BigInt value to a number
当你读到这篇文章的时候,matchAll 可能已经在 Chrome C73 中正式实现了——如果不是,它仍然值得一看。特别是如果你是一个正则表达式(regex)爱好者。
string.prototype.matchAll()
如果您运行谷歌搜索JavaScript string match all,第一个结果将是这样的:如何编写正则表达式“match all”?
最佳结果将建议 String.match 与正则表达式和 /g 一起使用或者带有 /g 的 RegExp.exec 或者带有 /g 的 RegExp.test 。
首先,让我们看看旧规范是如何工作的。
带字符串参数的 String.match 仅返回第一个匹配:
let string = 'Hello';
let matches = string.match('l');
console.log(matches[0]); // "l"
结果是单个 "l"(注意:匹配存储在 matches[0] 中而不是 matches)
在“hello”中搜索 "l" 只返回 "l"。
将 string.match 与 regex 参数一起使用也是如此:
让我们使用正则表达式 /l/ 找到字符 串“hello” 中的 “l” 字符:
let string = "Hello";
let matches = string.match(/l/);
console.log(matches[0]); // "l"
添加 /g 混合
let string = "Hello";
let ret = string.match(/l/g); // (2) [“l”, “l”];
很好,我们使用 < ES10 方式得到了多个匹配,它一直起作用。
那么为什么要使用全新的 matchAll 方法呢? 在我们更详细地回答这个问题之前,让我们先来看看 捕获组。如果不出意外,你可能会学到一些关于正则表达式的新知识。
正则表达式捕获组
在 regex 中捕获组只是从 () 括号中提取一个模式,可以使用 /regex/.exec(string) 和string.match 捕捉组。
常规捕获组是通过将模式包装在 (pattern) 中创建的,但是要在结果对象上创建 groups 属性,它是: (?<name>pattern)。
要创建一个新的组名,只需在括号内附加 ?,结果中,分组 (pattern) 匹配将成为 group.name,并附加到 match对象,以下是一个实例:
字符串标本匹配:

这里创建了 match.groups.color 和 match.groups.bird :
const string = 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull';
const regex = /(?<color>.*?)\*(?<bird>[a-z0-9]+)/g;
while (match = regex.exec(string))
{
let value = match[0];
let index = match.index;
let input = match.input;
console.log(`${value} at ${index} with '${input}'`);
console.log(match.groups.color);
console.log(match.groups.bird);
}
需要多次调用 regex.exec 方法来遍历整个搜索结果集。 在每次迭代期间调用.exec 时,将显示下一个结果(它不会立即返回所有匹配项。),因此使用 while 循环。
输出如下:
black*raven at 0 with 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull'
black
raven
lime*parrot at 11 with 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull'
lime
parrot
white*seagull at 23 with 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull'
white
seagull
但奇怪的是:
如果你从这个正则表达式中删除 /g,你将永远在第一个结果上创建一个无限循环。这在过去是一个巨大的痛苦。想象一下,从某个数据库接收正则表达式时,你不确定它的末尾是否有 /g,你得先检查一下。
使用 .matchAll() 的好理由
- 在与捕获组一起使用时,它可以更加优雅,捕获组只是使用 () 提取模式的正则表达式的一部分。
- 它返回一个迭代器而不是一个数组,迭代器本身是有用的。
- 迭代器可以使用扩展运算符 (…) 转换为数组。
- 它避免了带有 /g 标志的正则表达式,当从数据库或外部源检索未知正则表达式并与陈旧的RegEx 对象一起使用时,它非常有用。
- 使用 RegEx 对象创建的正则表达式不能使用点 (.) 操作符链接。
- 高级: RegEx 对象更改跟踪最后匹配位置的内部 .lastindex 属性,这在复杂的情况下会造成严重破坏。
.matchAll() 是如何工作的?
让我们尝试匹配单词 hello 中字母 e 和 l 的所有实例, 因为返回了迭代器,所以可以使用 for…of 循环遍历它:
// Match all occurrences of the letters: "e" or "l"
let iterator = "hello".matchAll(/[el]/);
for (const match of iterator)
console.log(match);
这一次你可以跳过 /g, .matchall 方法不需要它,结果如下:
[ 'e', index: 1, input: 'hello' ] // Iteration 1
[ 'l', index: 2, input: 'hello' ] // Iteration 2
[ 'l', index: 3, input: 'hello' ] // Iteration 3
使用 .matchAll() 捕获组示例:
.matchAll 具有上面列出的所有好处。它是一个迭代器,可以用 for…of 循环遍历它,这就是整个语法的不同。
const string = 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull';
const regex = /(?<color>.*?)\*(?<bird>[a-z0-9]+)/;
for (const match of string.matchAll(regex)) {
let value = match[0];
let index = match.index;
let input = match.input;
console.log(`${value} at ${index} with '${input}'`);
console.log(match.groups.color);
console.log(match.groups.bird);
}
请注意已经没有 /g 标志,因为 .matchAll() 已经包含了它,打印如下:
black*raven at 0 with 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull'
black
raven
lime*parrot at 11 with 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull'
lime
parrot
white*seagull at 23 with 'black*raven lime*parrot white*seagull'
white
seagull
也许在美学上它与原始正则表达式非常相似,执行while循环实现。但是如前所述,由于上面提到的许多原因,这是更好的方法,移除 /g 不会导致无限循环。
动态导入
现在可以将导入分配给变量:
element.addEventListener('click', async() => {
const module = await import(`./api-scripts/button-click.js`);
module.clickEvent();
})
Array.flat()
扁平化多维数组:
let multi = [1,2,3,[4,5,6,[7,8,9,[10,11,12]]]];
multi.flat(); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,Array(4)]
multi.flat().flat(); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,Array(3)]
multi.flat().flat().flat(); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]
multi.flat(Infinity); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]
Array.flatMap()
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
array.map(x => [x, x * 2]);
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
array.map(x => [x, x * 2]);
结果:
[Array(2), Array(2), Array(2), Array(2), Array(2)]
0: (2) [1, 2]
1: (2) [2, 4]
2: (2) [3, 6]
3: (2) [4, 8]
4: (2) [5, 10]
使用 flatMap 方法:
array.flatMap(v => [v, v * 2]);
[1, 2, 2, 4, 3, 6, 4, 8, 5, 10]
Object.fromEntries()
将键值对列表转换为对象:
let obj = { apple : 10, orange : 20, banana : 30 };
let entries = Object.entries(obj);
entries;
(3) [Array(2), Array(2), Array(2)]
0: (2) ["apple", 10]
1: (2) ["orange", 20]
2: (2) ["banana", 30]
let fromEntries = Object.fromEntries(entries);
{ apple: 10, orange: 20, banana: 30 }
String.trimStart() 与 String.trimEnd()
let greeting = " Space around ";
greeting.trimEnd(); // " Space around";
greeting.trimStart(); // "Space around ";
格式良好的 JSON.stringify()
此更新修复了字符 U+D800 到 U+DFFF 的处理,有时可以进入 JSON 字符串。 这可能是一个问题,因为 JSON.stringify可能会将这些数字格式化为没有等效 UTF-8 字符的值, 但 JSON 格式需要 UTF-8 编码。
解析方法使用格式良好的JSON字符串,如:
'{ “prop1” : 1, "prop2" : 2 }'; // A well-formed JSON format string
注意,要创建正确 JSON 格式的字符串,绝对需要在属性名周围加上双引号。缺少或任何其他类型的引号都不会生成格式良好的JSON。
'{ “prop1” : 1, "meth" : () => {}}'; // Not JSON format string
JSON 字符串格式与 Object Literal 不同,后者看起来几乎一样,但可以使用任何类型的引号括住属性名,也可以包含方法(JSON格式不允许使用方法):
let object_literal = { property: 1, meth: () => {} };
不管怎样,一切似乎都很好。第一个示例看起来是兼容的。但它们也是简单的例子,大多数情况下都能顺利地工作!
U+2028 和 U+2029 字符
问题是, ES10 之前的 EcmaScript 实际上并不完全支持 JSON 格式。前 ES10 时代不接受未转义行分隔符 U+2028 和段落分隔符 U+2029 字符:

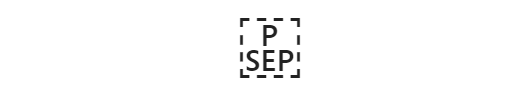
对于 U+D800 - U+DFFF 之间的所有字符也是如此
如果这些字符潜入 JSON 格式的字符串(假设来自数据库记录),你可能会花费数小时试图弄清楚为什么程序的其余部分会产生解析错误。
因此,如果你传递 eval 这样的字符串 “console.log(' hello ')”,它将执行 JavaScript语句 (通过尝试将字符串转换为实际代码),也类似于 JSON.parse 将处理你的 JSON 字符串的方式。
稳定的 Array.prototype.sort()
V8 之前的实现对包含10个以上项的数组使用了一种不稳定的快速排序算法。
一个稳定的排序算法是当两个键值相等的对象在排序后的输出中出现的顺序与在未排序的输入中出现的顺序相同时。
但情况不再是这样了,ES10 提供了一个稳定的数组排序:
var fruit = [
{ name: "Apple", count: 13, },
{ name: "Pear", count: 12, },
{ name: "Banana", count: 12, },
{ name: "Strawberry", count: 11, },
{ name: "Cherry", count: 11, },
{ name: "Blackberry", count: 10, },
{ name: "Pineapple", count: 10, }
];
// 创建排序函数:
let my_sort = (a, b) => a.count - b.count;
// 执行稳定的ES10排序:
let sorted = fruit.sort(my_sort);
console.log(sorted);
控制台输出(项目以相反的顺序出现):

代码部署后可能存在的BUG没法实时知道,事后为了解决这些BUG,花了大量的时间进行log 调试,这边顺便给大家推荐一个好用的BUG监控工具 Fundebug。
新的Function.toString()
函数是对象,并且每个对象都有一个 .toString() 方法,因为它最初存在于Object.prototype.toString() 上。 所有对象(包括函数)都是通过基于原型的类继承从它继承的。
这意味着我们以前已经有 funcion.toString() 方法了。
但是 ES10 进一步尝试标准化所有对象和内置函数的字符串表示。 以下是各种新案例:
典型的例子
function () { console.log('Hello there.'); }.toString();
控制台输出(函数体的字符串格式:)
⇨ function () { console.log('Hello there.'); }
下面是剩下的例子:
直接在方法名 .toString()
Number.parseInt.toString();
⇨ function parseInt() { [native code] }
绑定上下文
function () { }.bind(0).toString();
⇨ function () { [native code] }
内置可调用函数对象
Symbol.toString();
⇨ function Symbol() { [native code] }
动态生成的函数
function* () { }.toString();
⇨ function* () { }
prototype.toString
Function.prototype.toString.call({});
⇨ Function.prototype.toString requires that 'this' be a Function"
可选的 Catch Binding
在过去,try/catch 语句中的 catch 语句需要一个变量。 try/catch 语句帮助捕获终端级别的错误:
try {
// Call a non-existing function undefined_Function
undefined_Function("I'm trying");
}
catch(error) {
// Display the error if statements inside try above fail
console.log( error ); // undefined_Function is undefined
}
在某些情况下,所需的错误变量是未使用的:
try {
JSON.parse(text); // <--- this will fail with "text not defined"
return true; <--- exit without error even if there is one
}
catch (redundant_sometmes) <--- this makes error variable redundant
{
return false;
}
编写此代码的人通过尝试强制 true 退出 try 子句。但是,这并不是实际发生的情况
(() => {
try {
JSON.parse(text)
return true
} catch(err) {
return false
}
})()
=> false
在 ES10 中,捕获错误的变量是可选的
现在可以跳过错误变量:
try {
JSON.parse(text);
return true;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
目前还无法测试上一个示例中的 try 语句的结果,但一旦它出来,我将更新这部分。
标准化 globalThis 对象
这在ES10之前, globalThis 还没有标准化。
在产品代码中,你可以自己编写这个怪物,在多个平台上“标准化”它:
var getGlobal = function () {
if (typeof self !== 'undefined') { return self; }
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { return window; }
if (typeof global !== 'undefined') { return global; }
throw new Error('unable to locate global object');
};
但即使这样也不总是奏效。因此,ES10 添加了 globalThis 对象,从现在开始,该对象用于在任何平台上访问全局作用域:
// 访问全局数组构造函数
globalThis.Array(0, 1, 2);
⇨ [0, 1, 2]
// 类似于 ES5 之前的 window.v = { flag: true }
globalThis.v = { flag: true };
console.log(globalThis.v);
⇨ { flag: true }
Symbol.description
description 是一个只读属性,它返回 Symbol 对象的可选描述。
let mySymbol = 'My Symbol';
let symObj = Symbol(mySymbol);
symObj; // Symbol(My Symbol)
symObj.description; // "My Symbol"
Hashbang 语法
也就是 unix 用户熟悉的 shebang。它指定一个解释器(什么将执行JavaScript文件?)。
ES10标准化,我不会对此进行详细介绍,因为从技术上讲,这并不是一个真正的语言特性,但它基本上统一了 JavaScript 在服务器端的执行方式。
$ ./index.js
代替
$ node index.js
ES10类: private、static 和 公共成员
新的语法字符 #octothorpe(hash tag)现在用于直接在类主体的范围内定义变量,函数,getter 和 setter ......以及构造函数和类方法。
下面是一个毫无意义的例子,它只关注新语法:
class Raven extends Bird {
#state = { eggs: 10};
// getter
get #eggs() {
return state.eggs;
}
// setter
set #eggs(value) {
this.#state.eggs = value;
}
#lay() {
this.#eggs++;
}
constructor() {
super();
this.#lay.bind(this);
}
#render() {
/* paint UI */
}
}
老实说,我认为这会让语言更难读。
关于Fundebug
Fundebug专注于JavaScript、微信小程序、微信小游戏、支付宝小程序、React Native、Node.js和Java线上应用实时BUG监控。 自从2016年双十一正式上线,Fundebug累计处理了9亿+错误事件,付费客户有Google、360、金山软件、百姓网等众多品牌企业。欢迎大家免费试用!
ES10特性详解的更多相关文章
- C#中的 特性 详解(转载)
本篇幅转载于:http://www.cnblogs.com/rohelm/archive/2012/04/19/2456088.html C#中特性详解 特性提供了功能强大的方法,用于将元数据或声明信 ...
- iOS开发——高级特性&Runtime运行时特性详解
Runtime运行时特性详解 本文详细整理了 Cocoa 的 Runtime 系统的知识,它使得 Objective-C 如虎添翼,具备了灵活的动态特性,使这门古老的语言焕发生机.主要内容如下: 引言 ...
- ES6,ES2105核心功能一览,js新特性详解
ES6,ES2105核心功能一览,js新特性详解 过去几年 JavaScript 发生了很大的变化.ES6(ECMAScript 6.ES2105)是 JavaScript 语言的新标准,2015 年 ...
- 《Android群英传》读书笔记 (5) 第十一章 搭建云端服务器 + 第十二章 Android 5.X新特性详解 + 第十三章 Android实例提高
第十一章 搭建云端服务器 该章主要介绍了移动后端服务的概念以及Bmob的使用,比较简单,所以略过不总结. 第十三章 Android实例提高 该章主要介绍了拼图游戏和2048的小项目实例,主要是代码,所 ...
- C#各个版本中的新增特性详解
序言 自从2000年初期发布以来,c#编程语言不断的得到改进,使我们能够更加清晰的编写代码,也更加容易维护我们的代码,增强的功能已经从1.0搞到啦7.0甚至7.1,每一次改过都伴随着.NET Fram ...
- ASP.NET Core Web服务器 Kestrel和Http.sys 特性详解
ASP.NET Core Web服务器 Kestrel和Http.sys 特性详解 1.1. 名词解释 1.2. Kestrel基本工作原理 1.2.1. Kestrel的基本架构 1.2.2. Ke ...
- Android群英传笔记——第十二章:Android5.X 新特性详解,Material Design UI的新体验
Android群英传笔记--第十二章:Android5.X 新特性详解,Material Design UI的新体验 第十一章为什么不写,因为我很早之前就已经写过了,有需要的可以去看 Android高 ...
- 单元测试系列之十一:Jmockit之mock特性详解
本文是Jmockit学习过程中,根据官网所列的工具特性进行解读. 1.调用次数约束(Invocation count constraints) 可以通过调用计数约束来指定预期和/或允许匹配给定期望的调 ...
- Java9 新特性 详解
作者:木九天 < Java9 新特性 详解 > Java9 新特性 详解 摘要: 1.目录结构 2.repl工具 jShell命令 3.模块化 4.多版本兼容jar包 5.接口方 ...
随机推荐
- 最小可用id
题目:在非负数组(乱序)中找到最小的可分配的id(从1开始编号),数据量10000000. 题目解读:在一个不重复的乱序的自然数组中找到最小的缺失的那个数,比如1,2,3,6,4,5,8,11.那么最 ...
- JAVA设计模式—观察者模式和Reactor反应堆模式
被观察者(主题)接口 定义主题对象接口 /**抽象主题角色: 这个主题对象在状态上发生变化时,会通知所有观察者对象 也叫事件对象 */ public interface Subject { //增加一 ...
- [Swift]LeetCode2. 两数相加 | Add Two Numbers
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stor ...
- [Swift]LeetCode64. 最小路径和 | Minimum Path Sum
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which ...
- [Swift]LeetCode382. 链表随机节点 | Linked List Random Node
Given a singly linked list, return a random node's value from the linked list. Each node must have t ...
- the python challenge闯关记录(0-8)
0 第零关 2**38 = 274877906944 下一关的url:http://www.pythonchallenge.com/pc/def/274877906944.html 1 第一关 移位计 ...
- 本地安装MySQL详细教程
第1章 MySQL的安装与使用 1.1 MySQL安装与配置 1.1.1 MYSQL的安装 1.打开下载的mysql安装文件mysql-5.5.27-win32.zip,双击解压缩,运行“set ...
- ubuntu-18.04 设置开机启动脚本
ubuntu-18.04 设置开机启动脚本 参阅下列链接 https://askubuntu.com/questions/886620/how-can-i-execute-command-on-sta ...
- ALL_SOURCE
类型:View Owner: SYS 内容: 记录了该用户可访问的所有数据库对象的脚本信息(DDL) 字段: OWNER: 对象的Owner NAME: 对象名称 TYPE: 对象类型,如FUNCT ...
- python3+ selenium3开发环境搭建-手把手教你安装python(详细)
环境搭建 基于python3和selenium3做自动化测试,俗话说:工欲善其事必先利其器:没有金刚钻就不揽那瓷器活,磨刀不误砍柴工,因此你必须会搭建基本的开发环境,掌握python基本的语法和一个I ...
