java客户端与服务端交互通用处理 框架解析
一、综述
java 客户端与服务端交互过程中,采用NIO通讯是异步的,客户端基本采用同一处理范式,来进行同异步的调用处理。
处理模型有以下几个要素:
1. NIO发送消息后返回的Future
2. 每次发送请求生成的Callback ,回调对象保存有请求数据,获取数据时阻塞线程,服务端返回时唤醒被阻塞的业务线程 并返回数据操作
3. 一个Map 保存有请求id 与 callback实例。 一般 key= reqId, value= callback
4. 一个TimeChecker 超时检测线程, 用户循环检测map里面的请求是否超时,超时的数据之间删除。
以上4个要素基本构成了目前客户端与服务端异步通讯时的处理模式。 目前dubbo、一些mq 框架都采用此模式,理解这个模式对阅读源码非常重要。
二、 处理流程图
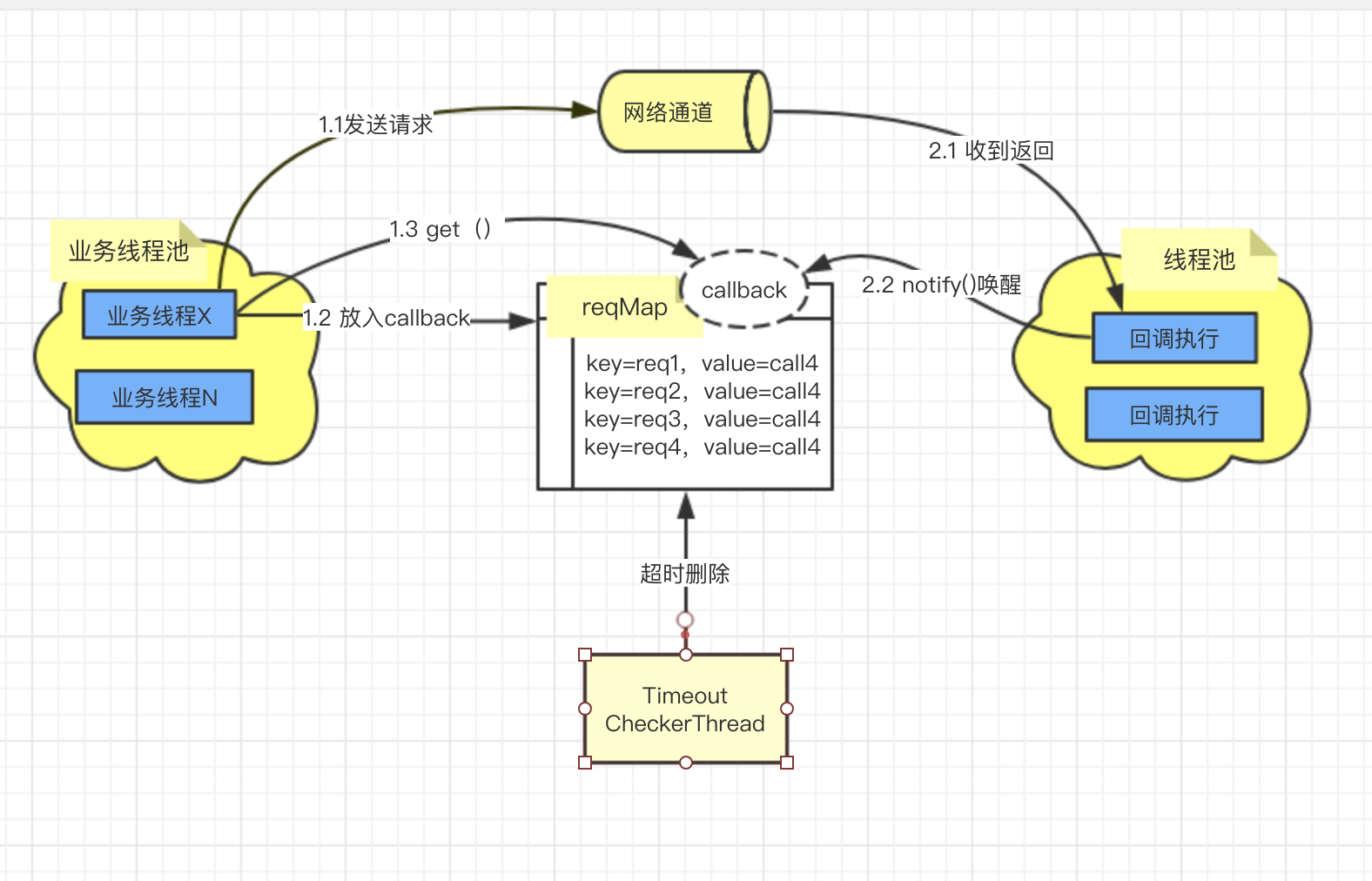
流程说明:
1. 业务线程操作
1.1 通过NIO的channel ,write数据,同时返回 future
1.2 将req与future 组成callback实例,放入reqMap
1.3 调用callbak的get() 方法。此时线程会被阻塞一定时间,等待被唤醒(持有callback的锁)。
2. 发送消息后,开始监听返回消息
2.1 网络消息received事件,会触发listenser,根据reqId从reqMap里面获取callback实例,放入线程池执行
2.2 callback实例的 回调方法,标识结果已返回,设置response, 调用notifyAll()方法,唤醒在1.3 被阻塞的线程,返回
3. TimeoutCheckerThread线程
timeoutCheckerThread 负责轮询reqMap,将超时的数据从map里面删除。超时回调删除后,1.3步骤 被阻塞的线程睡眠醒来,就会抛出超时异常
以上几个步骤与流程,就是目前通用的 client 异步操作模式, 3个独立的线程+一个Map 完成整个操作。
在dubbo、各类mq 生产端,都是如此,部分可能有所差异。例如 dubbo的超时检测,用了HashedWheelTimer,比轮询效率更高,但本质不变
三、 实例代码
代码实例在idea 中运行通过,依赖lombock插件, netty3组件,详细代码请看 git:https://github.com/xujianguo1/practise/ 下的nettydemo目录。
对于netty的具体使用不做过多解读,毕竟netty4、5 与netty3 的差异太大。
Invoker接口
package com.luguo.nettydemo.client.handler; import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.RequestMsg;
import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.AckMsg; public interface Invoker {
/**
* 同步调用,直接返回消息
*/
public AckMsg invokeSync(RequestMsg request) throws Exception; /**
* 异步调用,返回future
*/
public SimpleFuture invokeAsyc(RequestMsg requestMsg); /**
* 收到消息返回时,调用。
*/
public void invokeAck(AckMsg ackMsg);
}
Invoker 接口默认实现 DefaultInvoker ,单例
package com.luguo.nettydemo.client.handler; import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.AckMsg;
import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.RequestMsg;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong; @Slf4j
public class DefaultInvoker implements Invoker{
private long defaultTimeout = 1000;
private static final Invoker invoker = new DefaultInvoker();
private AtomicLong sequencer = new AtomicLong(0);//id序列生成器
private RequestMap reqMap = new RequestMap(); //存放请求Id与回调 private DefaultInvoker(){
Thread timeoutChecker = new Thread(new TimeoutChecker());
timeoutChecker.setName("Timeout-Checker");
timeoutChecker.start(); //启动超时检查
} public static Invoker getInstance(){
return invoker;
} public void invokeAck(AckMsg msg){
Long reqId = msg.getRequestId();
SimpleCallback callback = this.reqMap.getCallback(reqId);
this.reqMap.remove(reqId);
if(callback != null){
callback.setAckMsg(msg);
callback.run(); //唤醒等待的线程
} }
public void invokeCallback(RequestMsg request,SimpleCallback callback){
//NettyClient
SimpleNettyClient client = SimpleNettyClient.getClient("local");
request.setRequestId(sequencer.addAndGet(1));
request.setSendTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
if(callback != null){
reqMap.putData(request.getRequestId(),callback);
}
client.write(request,callback); } private SimpleFuture invokeFuture(RequestMsg request){
CallbackFuture callbackFuture = new CallbackFuture();
callbackFuture.setRequestMsg(request);
invokeCallback(request,callbackFuture);
return callbackFuture;
}
public AckMsg invokeSync(RequestMsg request) throws Exception {
SimpleFuture future = invokeFuture(request);
return future.get(defaultTimeout);
} public SimpleFuture invokeAsyc(RequestMsg requestMsg) {
SimpleFuture future=invokeFuture(requestMsg);
return future;
} /**
* 超时检测器
*/
private class TimeoutChecker implements Runnable{
public void run(){
while(true){
try{
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Long reqId:reqMap.requestMap.keySet()){
SimpleCallback callback = reqMap.getCallback(reqId);
if(callback.getRequestMsg().getSendTime() +defaultTimeout<now){//已经超时了
reqMap.remove(reqId); //删除超时的数据
log.warn("remove Timeout key="+reqId);
}
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e){
log.error(e.getMessage(),e);
}
}
}
}
private class RequestMap{
/**
* requestMap key=请求Id, value = 为消息与处理
*/
private Map<Long,SimpleCallback> requestMap =new ConcurrentHashMap<Long,SimpleCallback>(); public SimpleCallback getCallback(Long requestId){
return requestMap.get(requestId);
}
public void putData(Long requestId,SimpleCallback callback){
requestMap.put(requestId,callback);
}
public void remove(Long requestId){
requestMap.remove(requestId);
}
} }
CallbackFuture 返回与回调对象
package com.luguo.nettydemo.client.handler; import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.AckMsg;
import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.RequestMsg;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; @Slf4j
public class CallbackFuture implements SimpleCallback,SimpleFuture {
private RequestMsg reqMsg;
private AckMsg ackMsg;
private ChannelFuture future;
private boolean isDone = false;
public synchronized void run() { //回调方法被执行,表名已经完成了
isDone = true;
this.notifyAll();
}
public void setRequestMsg(RequestMsg msg){
this.reqMsg = msg;
}
public RequestMsg getRequestMsg(){
return reqMsg;
} public void setAckMsg(AckMsg ack) {
this.ackMsg = ack;
} public SimpleFuture getFuture(ChannelFuture future) {
this.future = future;
return this;
} public synchronized AckMsg get(long timeout) throws InterruptedException{ long sendTime = this.reqMsg.getSendTime();
while(!isDone){
long leftTime = timeout -(System.currentTimeMillis()-sendTime);
if(leftTime <0){//抛出一个超时
throw new RuntimeException("Request timeout ! seqId:"+reqMsg.getRequestId());
}else{
log.info(this.reqMsg.getRequestId()+"需要睡眠时间:"+leftTime);
this.wait(leftTime);
}
}
return ackMsg;
} public boolean isDone() {
return false;
} }
ClientReceiveHandler: netty 的消息接收处理,会执行回调的run方法,唤醒等待的线程。
package com.luguo.nettydemo.client.handler; import com.luguo.nettydemo.model.AckMsg;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.MessageEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler; import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; @Slf4j
public class ClientReceiveHandler extends SimpleChannelHandler {
private static Executor executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) {
final AckMsg ackMsg = (AckMsg) e.getMessage();
try {
this.executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() { //在线程池中执行回调方法
DefaultInvoker.getInstance().invokeAck(ackMsg);
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
String msg = "ack callback execute fail \r\n";
log.error(msg + ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}
SimpleNettyClient :netty的客户端启动,初始化连接服务端线程池。 write方法,将req与callback 放入map
@Slf4j
public class SimpleNettyClient {
private ClientBootstrap bootstrap;
private ChannelPool channelPool;
private static Map<String, SimpleNettyClient> clientMap= new ConcurrentHashMap<String, SimpleNettyClient>();
public SimpleNettyClient(){
bootstrap = new ClientBootstrap(new NioClientSocketChannelFactory( Executors.newCachedThreadPool(),
Executors.newCachedThreadPool()));
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline= Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4, 0, 4));
pipeline.addLast("frameEncoder", new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
pipeline.addLast("jsonDecoder", new JsonDecoder(AckMsg.class));
pipeline.addLast("jsonEncoder", new JsonEncoder(RequestMsg.class));
pipeline.addLast("handler", new ClientReceiveHandler());
return pipeline;
}
});
channelPool = new ChannelPool(Constants.channelPoolSize);
} private Channel connect(){
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress(Constants.host,
Constants.port));
// 等待连接创建成功
if (future.awaitUninterruptibly(3000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
log.info("Client is conneted to " + Constants.host + ":" + Constants.port);
} else {
log.warn("Client is not conneted to " + Constants.host + ":"
+ Constants.port);
}
}
return future.getChannel();
} public static SimpleNettyClient getClient(String clientName){
SimpleNettyClient client = clientMap.get(clientName);//这里可以扩展,进行负载均衡算法选择目标
if(client==null){
synchronized (clientMap){
if( clientMap.get(clientName)==null){//二次检查
client = new SimpleNettyClient();
clientMap.put(clientName,client);
return client;
}
return clientMap.get(clientName);
} }else{
return client;
}
}
public SimpleFuture write(RequestMsg requestMsg, SimpleCallback callback){
Channel channel = this.channelPool.get();
if(channel==null){
channel = connect();
}
ChannelFuture future = channel.write(requestMsg);
this.channelPool.released(channel);
// if(requestMsg.getMsgType() ==1){
// future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener(){
// public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
// if(channelFuture.isSuccess()){
// return;
// }else{
// //可以添加 写异常的返回
// }
// }
// });
// }
if(callback != null){
callback.setRequestMsg(requestMsg);
return callback.getFuture(future);
}
return null;
} private class ChannelPool {
private ArrayBlockingQueue<Channel> channels; public ChannelPool(int poolSize) {
this.channels = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Channel>(poolSize);
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
channels.add(connect());
}
} public Channel get(){
try{
return this.channels.take();
}catch (Exception e){ }
return null;
} /**
* 同步释放netty channel
*/
public void released(Channel ch) {
channels.add(ch);
}
} }
以上即为一个通用的客户端处理流程。 启动代码与req,ack,encoder、decoder 相关代码未贴出,在github上面下载即可。git:https://github.com/xujianguo1/practise/ 下的nettydemo目录。
测试时,先执行StartServer,启动服务端监听程序, 然后启动StartClientTest 客户端程序。
四、总结
网络客户端通讯,处理流程基本相同。
各大开源框架都是在该模式下实现功能的扩充,理解该模式,能很好的阅读各种存在客户端与服务端通讯的开源代码。
例如:1. 接入注册中心,实现server的发现,同时执行路由策略,实现负载均衡。
2. 发送与接收时,执行统计功能。
3. 在不关心返回 的场景(例如:mq的异步发送),上层会接入distruptor框架,提升发送性能
java客户端与服务端交互通用处理 框架解析的更多相关文章
- Android客户端与服务端交互之登陆示例
Android客户端与服务端交互之登陆示例 今天了解了一下android客户端与服务端是怎样交互的,发现其实跟web有点类似吧,然后网上找了大神的登陆示例,是基于IntentService的 1.后台 ...
- c++ 网络编程(一)TCP/UDP windows/linux 下入门级socket通信 客户端与服务端交互代码
原文作者:aircraft 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/DOMLX/p/9601511.html c++ 网络编程(一)TCP/UDP 入门级客户端与服务端交互代码 网 ...
- Fresco 源码分析(二) Fresco客户端与服务端交互(3) 前后台打通
4.2.1.2.4 PipelineDraweeControllerBuilder.obtainController()源码分析 续 上节中我们提到两个核心的步骤 obtainDataSourceSu ...
- Fresco 源码分析(二) Fresco客户端与服务端交互(1) 解决遗留的Q1问题
4.2 Fresco客户端与服务端的交互(一) 解决Q1问题 从这篇博客开始,我们开始讨论客户端与服务端是如何交互的,这个交互的入口,我们从Q1问题入手(博客按照这样的问题入手,是因为当时我也是从这里 ...
- java网络编程客户端与服务端原理以及用URL解析HTTP协议
常见客户端与服务端 客户端: 浏览器:IE 服务端: 服务器:web服务器(Tomcat),存储服务器,数据库服务器. (注:会用到Tomact服务器,在webapps下有一个自己创建的目录myweb ...
- android 38 Abdroid客户端和服务端交互
服务端: package com.sxt.day05; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import javax.ser ...
- UDP网络程序,客户端和服务端交互原理
创建一个udp客户端程序的流程是简单,具体步骤如下: 创建客户端套接字 发送/接收数据 关闭套接字 UDP是面向无连接的通讯协议,UDP数据包括目的端口号和源端口号信息,由于通讯不需要连接,所以可以实 ...
- spring-oauth-server实践:使用授权方式四:client_credentials 模式的客户端和服务端交互
spring-oauth-server入门(1-11)使用授权方式四:client_credentials 模式的客戶端 一.客户端逻辑 1.界面入口(credentials_access_token ...
- Fresco 源码分析(二) Fresco客户端与服务端交互(2) Fresco.initializeDrawee()分析 续
4.2.1.2 Fresco.initializeDrawee()的过程 续 继续上篇博客的分析Fresco.initializeDrawee() sDraweeControllerBuilderSu ...
随机推荐
- C# 知识点回忆..
方便查阅: 数据结构与算法 1.线性表: (1)数据结构2 - 线性表 (2)数据结构和算法 c#– 1.单项链表 委托和事件 委托1:C#4.0图解教程 - 第15章 委托 委托2:<C#本质 ...
- wordpress网站迁移
1.首先从原网站导出数据库文件 进入mysql文件夹:/etc/mysql mysqldump -uroot -p wordpress > wordpress.sql 2.将原网站文件打包 ta ...
- Ubuntu系统常见问题
搜狗拼音输入法 下载地址 : http://pinyin.sogou.com/linux/?r=pinyin 安装帮助: http://pinyin.sogou.com/linux/help.php ...
- IE外挂
//引用 Windows/system32/Shell32.dll //引用COM组件 shdocvw.dll (Microsoft Internet Controls) //引用COM组件 msht ...
- git 相关学习
1.Git 的一些快捷键 第一次创建本git 本地仓库 :: git init //在本地创建一个 Git仓库 :要在该目录下 第一次 要配置GitHub 的 账号和邮箱: git config ...
- js,JQ 图片转换base64 base64转换为file对象,blob对象
//将图片转换为Base64 function getImgToBase64(url,callback){ var canvas = document.createElement('canvas'), ...
- Linux系统下配置网络、JAVA环境,配置tomcat,mysql
一.配置网络 1.进入自己的系统,并跳转到network-scripts 2.编辑 3.查看系统的信息 4.将其添加到刚刚的if-cfg-eth0中 5.重启网络 6.这个时候ping百度还是ping ...
- android studio 开发免安装的app之目录结构
尚未深入分析,暂且外链到我看到的,对此有帮助的博客,在此,感谢你们. 1.https://blog.csdn.net/tscyds/article/details/74331085 2.https:/ ...
- 小程序app.onLaunch中获取用户信息,index.onLoad初次载入时取不到值的问题
问题描述: //app.js App({ globalData:{ nickname:'' }, onLaunch: function () { let that=this; //假设已经授权成功 w ...
- ISP PIPLINE (十二) Sharpening
什么是sharpening? 不解释,从左到右为sharpen , 从右到左为blur. 简单理解为边缘增强,使得轮廓清晰.增强对比度. 如何进行sharpening? 下面是实际sharpen的过程 ...
