NS3中一些难以理解的常数
摘要:在NS3的学习中,PHY MAC中总有一些常数,需要理解才能修改。如帧间间隔等。那么,本文做个简单分析,帮助大家理解。针对802.11标准中MAC协议。
- void
- WifiMac::Configure80211b (void)
- {
- SetSifs (MicroSeconds (10));
- SetSlot (MicroSeconds (20));
- SetEifsNoDifs (MicroSeconds (10 + 304));
- SetPifs (MicroSeconds (10 + 20));
- SetCtsTimeout (MicroSeconds (10 + 304 + 20 + GetDefaultMaxPropagationDelay ().GetMicroSeconds () * 2));
- SetAckTimeout (MicroSeconds (10 + 304 + 20 + GetDefaultMaxPropagationDelay ().GetMicroSeconds () * 2));
- }
304是怎么来的呢??
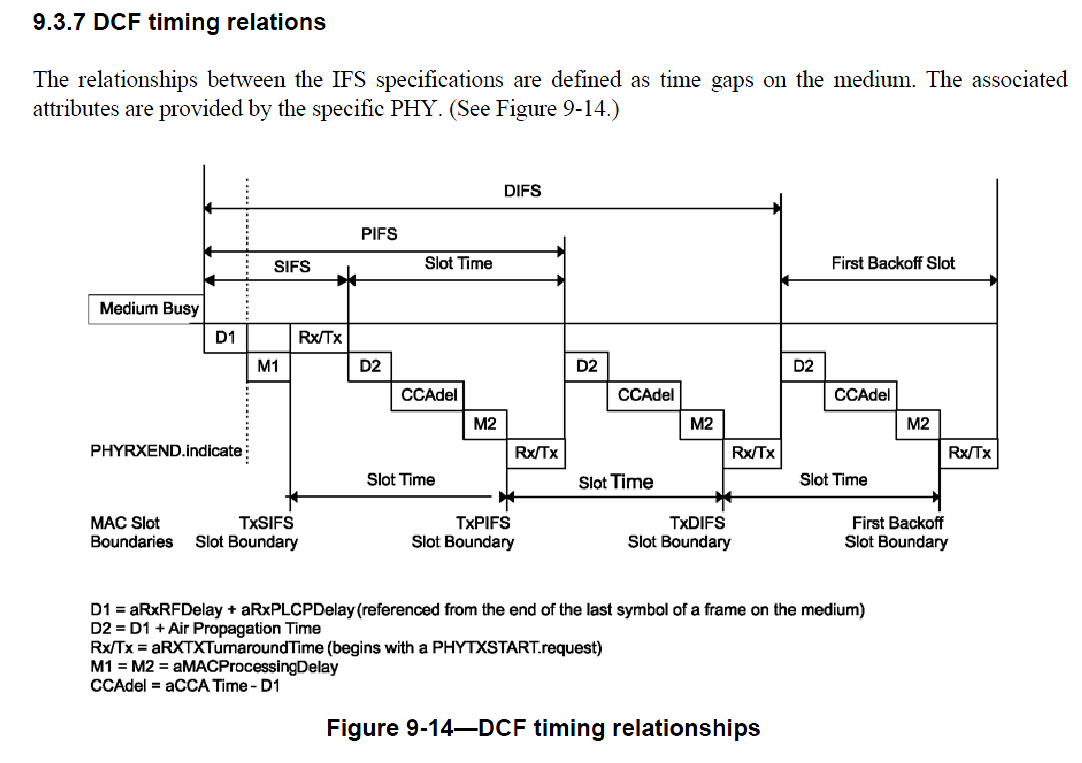
1、PHY
采用DSSS,1Mbps模式下。在802.11-2012中,17.2.2.3节中,有PPDU format规定了帧格式。如下图:
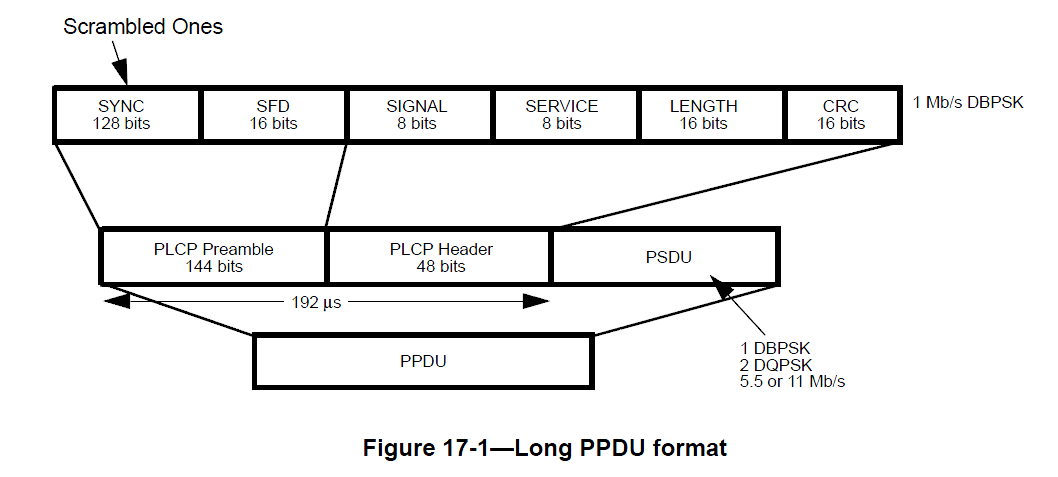
其中,大家比较关心的2个参数就是 PLCP Preamble 和 PLCP Header,分别为144bits和48bits。也就是192us,英文为192 MicroSeconds。
计算时间的相关代码,在NS3中 wifi-phy.cc中,代码如下:
- uint32_t
- WifiPhy::GetPlcpHeaderDurationMicroSeconds (WifiMode payloadMode, WifiPreamble preamble)
- {
- switch (payloadMode.GetModulationClass ())
- {
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_OFDM:
- {
- switch (payloadMode.GetBandwidth ())
- {
- case 20000000:
- default:
- // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" and Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- // also (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- // We return the duration of the SIGNAL field only, since the
- // SERVICE field (which strictly speaking belongs to the PLCP
- // header, see Section 18.3.2 and Figure 18-1) is sent using the
- // payload mode.
- return 4;
- case 10000000:
- // (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 8;
- case 5000000:
- // (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 16;
- }
- }
- //Added by Ghada to support 11n
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT:
- { //IEEE 802.11n Figure 20.1
- switch (preamble)
- {
- case WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_MF:
- // L-SIG
- return 4;
- case WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_GF:
- //L-SIG
- return 0;
- default:
- // L-SIG
- return 4;
- }
- }
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM:
- return 4;
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_DSSS:
- if (preamble == WIFI_PREAMBLE_SHORT)
- {
- // (Section 17.2.2.3 "Short PPDU format" and Figure 17-2 "Short PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 24;
- }
- else // WIFI_PREAMBLE_LONG
- {
- // (Section 17.2.2.2 "Long PPDU format" and Figure 17-1 "Short PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 48;
- }
- default:
- NS_FATAL_ERROR ("unsupported modulation class");
- return 0;
- }
- }
- uint32_t
- WifiPhy::GetPlcpPreambleDurationMicroSeconds (WifiMode payloadMode, WifiPreamble preamble)
- {
- switch (payloadMode.GetModulationClass ())
- {
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_OFDM:
- {
- switch (payloadMode.GetBandwidth ())
- {
- case 20000000:
- default:
- // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure"
- // also Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 16;
- case 10000000:
- // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure"
- // also Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 32;
- case 5000000:
- // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure"
- // also Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 64;
- }
- }
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT:
- { //IEEE 802.11n Figure 20.1 the training symbols before L_SIG or HT_SIG
- return 16;
- }
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM:
- return 16;
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_DSSS:
- if (preamble == WIFI_PREAMBLE_SHORT)
- {
- // (Section 17.2.2.3 "Short PPDU format)" Figure 17-2 "Short PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 72;
- }
- else // WIFI_PREAMBLE_LONG
- {
- // (Section 17.2.2.2 "Long PPDU format)" Figure 17-1 "Long PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- return 144;
- }
- default:
- NS_FATAL_ERROR ("unsupported modulation class");
- return 0;
- }
- }
- double
- WifiPhy::GetPayloadDurationMicroSeconds (uint32_t size, WifiTxVector txvector)
- {
- WifiMode payloadMode=txvector.GetMode();
- NS_LOG_FUNCTION (size << payloadMode);
- switch (payloadMode.GetModulationClass ())
- {
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_OFDM:
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM:
- {
- // (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012
- // corresponds to T_{SYM} in the table)
- uint32_t symbolDurationUs;
- switch (payloadMode.GetBandwidth ())
- {
- case 20000000:
- default:
- symbolDurationUs = 4;
- break;
- case 10000000:
- symbolDurationUs = 8;
- break;
- case 5000000:
- symbolDurationUs = 16;
- break;
- }
- // (Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- // corresponds to N_{DBPS} in the table
- double numDataBitsPerSymbol = payloadMode.GetDataRate () * symbolDurationUs / 1e6;
- // (Section 18.3.5.4 "Pad bits (PAD)" Equation 18-11; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- uint32_t numSymbols = lrint (ceil ((16 + size * 8.0 + 6.0) / numDataBitsPerSymbol));
- // Add signal extension for ERP PHY
- if (payloadMode.GetModulationClass () == WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM)
- {
- return numSymbols * symbolDurationUs + 6;
- }
- else
- {
- return numSymbols * symbolDurationUs;
- }
- }
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT:
- {
- double symbolDurationUs;
- double m_Stbc;
- //if short GI data rate is used then symbol duration is 3.6us else symbol duration is 4us
- //In the future has to create a stationmanager that only uses these data rates if sender and reciever support GI
- if (payloadMode.GetUniqueName() == "OfdmRate135MbpsBW40MHzShGi" || payloadMode.GetUniqueName() == "OfdmRate65MbpsBW20MHzShGi" )
- {
- symbolDurationUs=3.6;
- }
- else
- {
- switch (payloadMode.GetDataRate ()/ (txvector.GetNss()))
- { //shortGi
- case 7200000:
- case 14400000:
- case 21700000:
- case 28900000:
- case 43300000:
- case 57800000:
- case 72200000:
- case 15000000:
- case 30000000:
- case 45000000:
- case 60000000:
- case 90000000:
- case 120000000:
- case 150000000:
- symbolDurationUs=3.6;
- break;
- default:
- symbolDurationUs=4;
- }
- }
- if (txvector.IsStbc())
- m_Stbc=2;
- else
- m_Stbc=1;
- double numDataBitsPerSymbol = payloadMode.GetDataRate () *txvector.GetNss() * symbolDurationUs / 1e6;
- //check tables 20-35 and 20-36 in the standard to get cases when nes =2
- double Nes=1;
- // IEEE Std 802.11n, section 20.3.11, equation (20-32)
- uint32_t numSymbols = lrint (m_Stbc*ceil ((16 + size * 8.0 + 6.0*Nes) / (m_Stbc* numDataBitsPerSymbol)));
- return numSymbols * symbolDurationUs;
- }
- case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_DSSS:
- // (Section 17.2.3.6 "Long PLCP LENGTH field"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012)
- NS_LOG_LOGIC (" size=" << size
- << " mode=" << payloadMode
- << " rate=" << payloadMode.GetDataRate () );
- return lrint (ceil ((size * 8.0) / (payloadMode.GetDataRate () / 1.0e6)));
- default:
- NS_FATAL_ERROR ("unsupported modulation class");
- return 0;
- }
- }
- Time
- WifiPhy::CalculateTxDuration (uint32_t size, WifiTxVector txvector, WifiPreamble preamble)
- {
- WifiMode payloadMode=txvector.GetMode();
- double duration = GetPlcpPreambleDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble)
- + GetPlcpHeaderDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble)
- + GetPlcpHtSigHeaderDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble)
- + GetPlcpHtTrainingSymbolDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble,txvector)
- + GetPayloadDurationMicroSeconds (size, txvector);
- return MicroSeconds (duration);
- }
在函数CalculateTxDuration中,duration的计算方法。
那么,假如你开启4次握手机制,那么rts的duration如何计算呢?
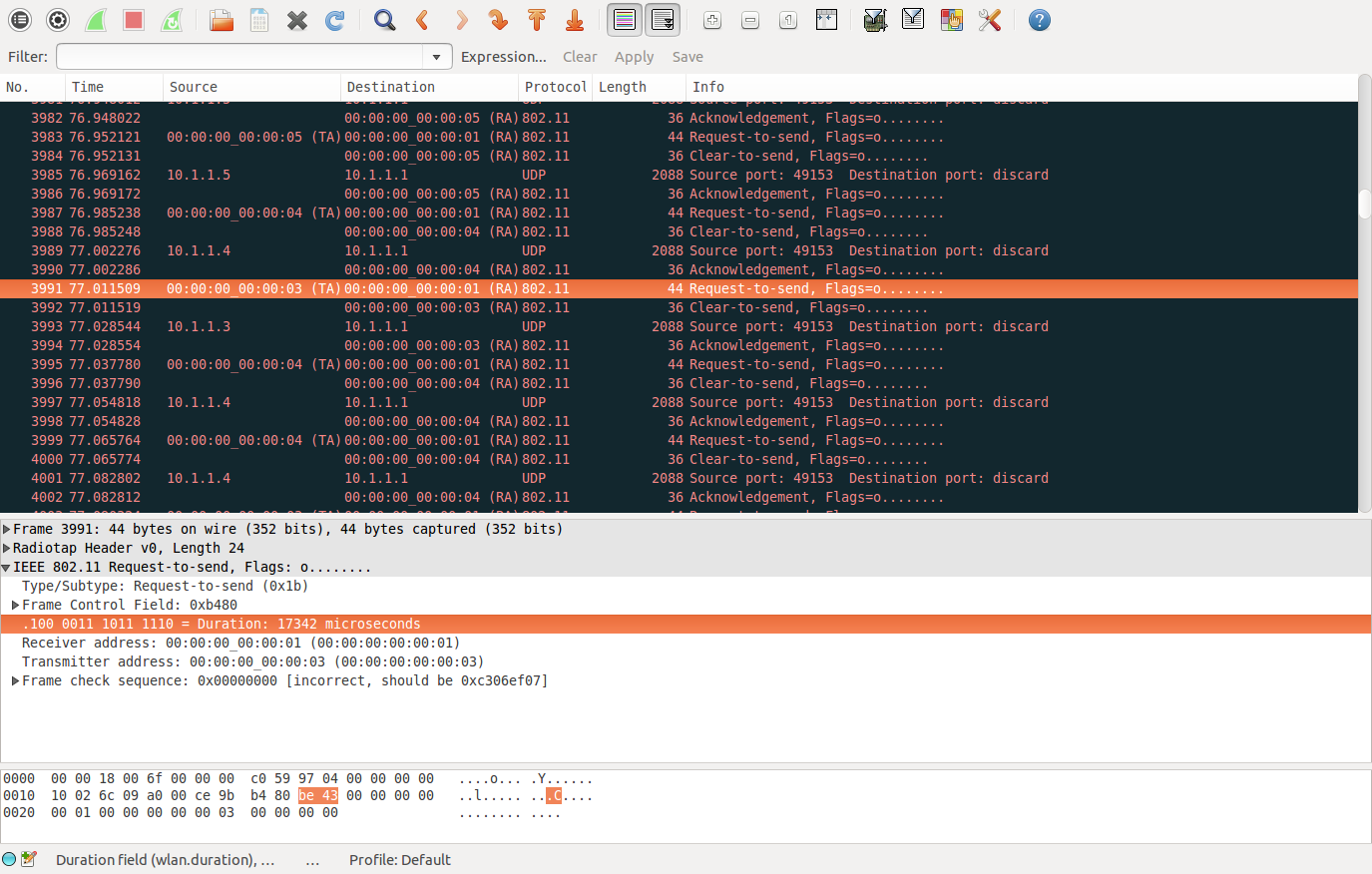
也就是当你生成pacp文件,用wiresharp打开时,看到rts帧中,那个duration是怎么得到的呢?
如下图中17342 是怎么得到的呢?
你需要知道应用层的包是如何封装的,这涉及到计算机网络的知识。这里以上面的包大小举例说明,packet =2000bytes.
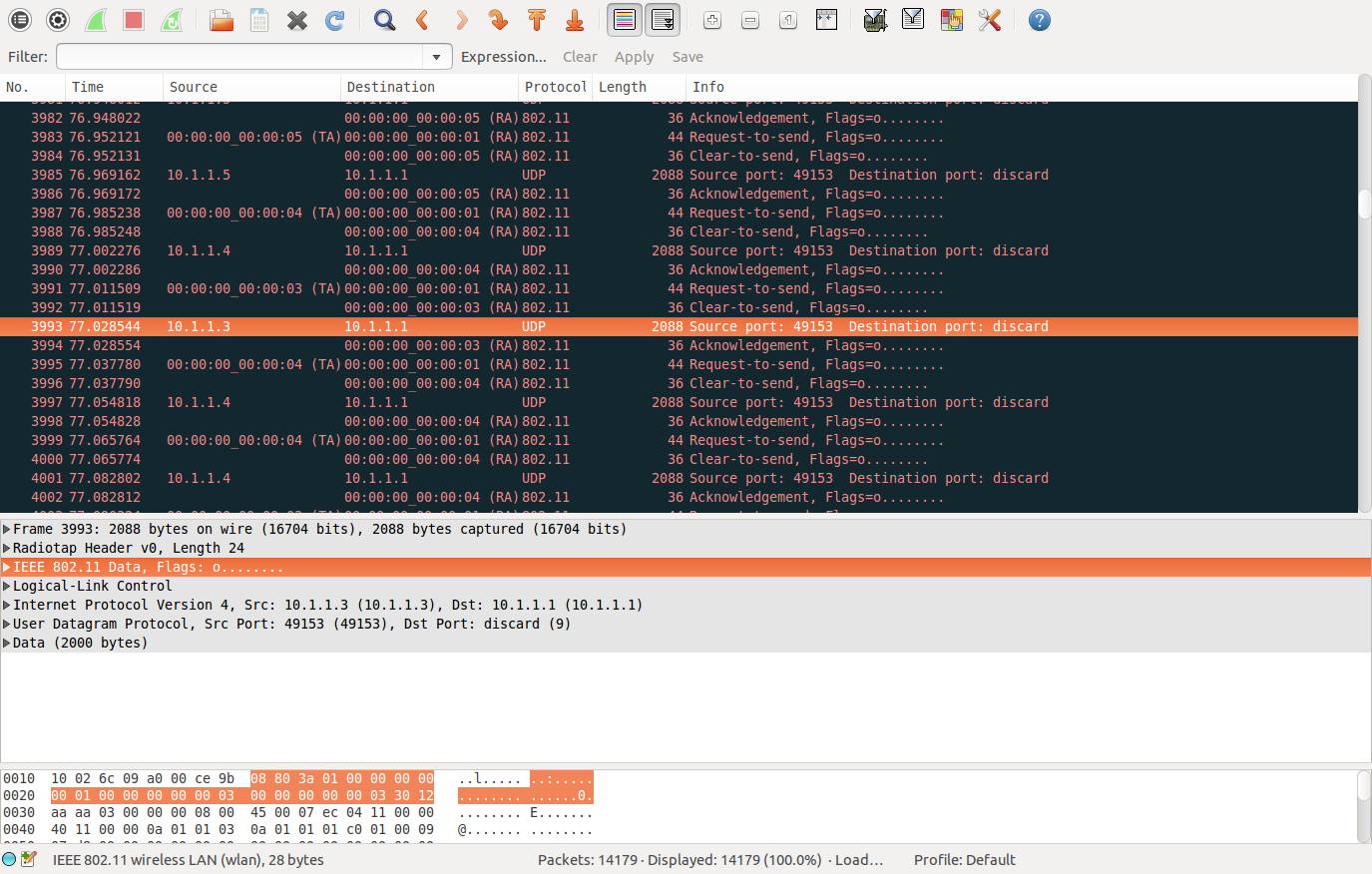
上图中可以看到:data—>udp(8)—>ip(20)—>llc(8)—>mac (28)包封装过程
ip和udp封装包头大小,一般计算机网络书中有介绍。llc 这个没搞懂为啥是8个。mac数据帧可以看下图:
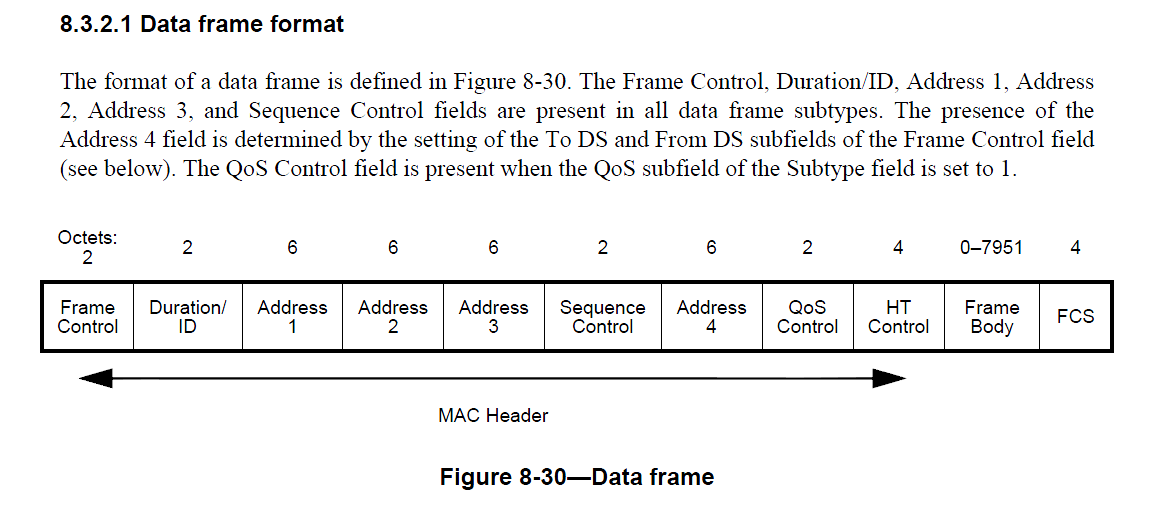
一共40字节,但是地址4,qos,ht不用。ns3中使用的是non qos mac。
好了,我们开始计算,但是还需要看一个代码在mac-low.cc:
- void
- MacLow::SendRtsForPacket (void)
- {
- NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
- /* send an RTS for this packet. */
- WifiMacHeader rts;
- rts.SetType (WIFI_MAC_CTL_RTS);
- rts.SetDsNotFrom ();
- rts.SetDsNotTo ();
- rts.SetNoRetry ();
- rts.SetNoMoreFragments ();
- rts.SetAddr1 (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 ());
- rts.SetAddr2 (m_self);
- WifiTxVector rtsTxVector = GetRtsTxVector (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr);
- Time duration = Seconds (0);
- WifiPreamble preamble;
- //standard says RTS packets can have GF format sec 9.6.0e.1 page 110 bullet b 2
- if ( m_phy->GetGreenfield()&& m_stationManager->GetGreenfieldSupported (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 ()))
- preamble= WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_GF;
- else if (rtsTxVector.GetMode().GetModulationClass () == WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT)
- preamble= WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_MF;
- else
- preamble=WIFI_PREAMBLE_LONG;
- if (m_txParams.HasDurationId ())
- {
- duration += m_txParams.GetDurationId ();
- }
- else
- {
- WifiTxVector dataTxVector = GetDataTxVector (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr);
- duration += GetSifs ();
- duration += GetCtsDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), rtsTxVector);
- duration += GetSifs ();
- duration += m_phy->CalculateTxDuration (GetSize (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr),
- dataTxVector, preamble);
- duration += GetSifs ();
- duration += GetAckDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), dataTxVector);
- }
- rts.SetDuration (duration);
- Time txDuration = m_phy->CalculateTxDuration (GetRtsSize (), rtsTxVector, preamble);
- Time timerDelay = txDuration + GetCtsTimeout ();
- NS_ASSERT (m_ctsTimeoutEvent.IsExpired ());
- NotifyCtsTimeoutStartNow (timerDelay);
- m_ctsTimeoutEvent = Simulator::Schedule (timerDelay, &MacLow::CtsTimeout, this);
- Ptr<Packet> packet = Create<Packet> ();
- packet->AddHeader (rts);
- WifiMacTrailer fcs;
- packet->AddTrailer (fcs);
- ForwardDown (packet, &rts, rtsTxVector,preamble);
- }
公式就是上面这个代码中提取出来的。sifs查这个802.11-2012中上图
duration += GetSifs (); 10
duration += GetCtsDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), rtsTxVector); cts:14*8+192=304
duration += GetSifs (); 10
duration += m_phy->CalculateTxDuration (GetSize (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr), dataTxVector, preamble); 2064*8+192=16704
duration += GetSifs ();10
duration += GetAckDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), dataTxVector); ack:14*8+192=304
duration = 10+304+10+16704+10+304=17342
结果符合wiresharp中那个duration。
NS3中一些难以理解的常数的更多相关文章
- 通过作用域链解析js函数一些难以理解的的作用域问题
基本原理 js函数在执行时,系统会创建一个隐式的属性scope,scope中存储的是函数的作用域链. 通过对这个scope的分析,就能解释JavaScript中许多难以理解的问题: 例1: funct ...
- Java中hashcode的理解
Java中hashcode的理解 原文链接http://blog.csdn.net/chinayuan/article/details/3345559 怎样理解hashCode的作用: 以 java. ...
- RxSwift 系列(九) -- 那些难以理解的概念
前言 看完本系列前面几篇之后,估计大家也还是有点懵逼,本系列前八篇也都是参考RxSwift官方文档和一些概念做的解读.上几篇文章概念性的东西有点多,一时也是很难全部记住,大家脑子里面知道有这么个概念就 ...
- 难以理解的AQS(下)
在上一篇博客,简单的说下了AQS的基本概念,核心源码解析,但是还有一部分内容没有涉及到,就是AQS对条件变量的支持,这篇博客将着重介绍这方面的内容. 条件变量 基本应用 我们先通过模拟一个消费者/生产 ...
- Java的内部类真的那么难以理解?
01 前言 昨天晚上,我把车停好以后就回家了.回家后才发现手机落在车里面了,但外面太冷,冷到骨头都能感受到寒意——实在是不想返回一趟去取了(小区的安保还不错,不用担心被砸车玻璃),于是打定主意过几个小 ...
- 对于新手来说,Python 中有哪些难以理解的概念?
老手都是从新手一路过来的,提起Python中难以理解的概念,可能很多人对于Python变量赋值的机制有些疑惑,不过对于习惯于求根究底的程序员,只有深入理解了某个事物本质,掌握了它的客观规律,才能得心应 ...
- js中的闭包理解一
闭包是一个比较抽象的概念,尤其是对js新手来说.书上的解释实在是比较晦涩,对我来说也是一样. 但是他也是js能力提升中无法绕过的一环,几乎每次面试必问的问题,因为在回答的时候.你的答案的深度,对术语的 ...
- Fouandation(NSString ,NSArray,NSDictionary,NSSet) 中常见的理解错误区
Fouandation 中常见的理解错误区 1.NSString //快速创建(实例和类方法) 存放的地址是 常量区 NSString * string1 = [NSString alloc]init ...
- linux中socket的理解
对linux中socket的理解 一.socket 一般来说socket有一个别名也叫做套接字. socket起源于Unix,都可以用“打开open –> 读写write/read –> ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces Gym101170J:Jupiter Orbiter(最大流)
题目链接 题意 有n次事件,q个队列,s个传感器.每个传感器接到一个队列,每个队列有一个容量. 接下来执行n次事件,每次事件都会有一个最大发送数据量d.和s个数据a,代表这次给每个s填入a的数据量. ...
- (ps2018)Adobe Photoshop CC 2018 中文版破解版
ps2018新功能 1.更紧密连接的 Photoshop.全新的智慧型锐利化. 2.智慧型增加取样.内含 Extended 功能.Camera RAW 8 和图层支援 3.可编辑的圆角矩形.多重形状和 ...
- docker-compose exec时 出现"fork/exec /proc/self/exe: no such file or directory" 报错
问题:跟往常一样执行docker-compos exec redis sh时出现如下错误,而容器是运行状态中. # docker-compose exec redis sh rpc error: co ...
- 20131207-ADO.NET-第十六天
[1]快捷键 工具箱:ctrl+w+x 首字母定位控件范围 属性:F4 或ctrl+w+p Tab跳转 ,home 与end也有效 [2]连接字符串 string str = "Data S ...
- STM32F072从零配置工程-串口USART配置
也是使用HAL库进行配置,通过STMCube生成代码,可以通过这个简单的配置过程看到STMCube生成代码的一种规范: 从main函数入手观察其外设配置结构: 首先是HAL_Init()进行所有外设的 ...
- VMware上安装虚拟机-教程
xl_echo编辑整理,欢迎转载,转载请声明文章来源.欢迎添加echo微信(微信号:t2421499075)交流学习. 百战不败,依不自称常胜,百败不颓,依能奋力前行.--这才是真正的堪称强大!! - ...
- windbg 配置符号路径
(转)WINDBG的符号下载与符号路径问题 安装与配置 windbg 的 symbol (符号) 本篇是新手自己写的一点心得.建议新手看看.同时希望前辈多多指教. 写这篇的动机:在网上找了一上午的 w ...
- 基于TCP协议的套接字编程
06.26自我总结 1.关于Socket Socket是应用层与TCP/IP协议族通信的中间软件抽象层,它是一组接口.在设计模式中,Socket其实就是一个门面模式,它把复杂的TCP/IP协议族隐藏在 ...
- 阿里百川HotFix2.0热修复初体验
博客原地址:http://blog.csdn.net/allan_bst/article/details/72904721 一.什么是热修复 热修复说白了就是"打补丁",比如你们公 ...
- 基于ng-zorro的ASP.NET ZERO前端实现
Abp官方提供的企业版(ASP.NET ZERO)[以下简称Zero]模板中前端使用的是Metronic,本篇博客介绍使用ng-zorro和ng-alain替换官方前端,以及使用官方生成器自动生成代码 ...
