SpringBoot学习(二)探究Springboot启动机制
引言:
SpringBoot为我们做的自动配置,确实方便快捷,但是对于新手来说,如果不大懂SpringBoot内部启动原理,以后难免会吃亏。所以这次博主就跟你们一起探究一下SpringBoot的启动原理。
目录
启动流程图

总览:
上图为SpringBoot启动结构图,我们发现启动流程主要分为三个部分,第一部分进行SpringApplication的初始化模块,配置一些基本的环境变量、资源、构造器、监听器,第二部分实现了应用具体的启动方案,包括启动流程的监听模块、加载配置环境模块、及核心的创建上下文环境模块,第三部分是自动化配置模块,该模块作为springboot自动配置核心,在后面的分析中会详细讨论。在下面的启动程序中我们会串联起结构中的主要功能。(摘自:SpringBoot启动流程解析)
SpringBoot启动类

从上面代码可以看出,别看它只是定义了 @SpringBootApplication 这个Annotation 和 调用SpringApplication.run方法,但是它们实现的功能可不是一星半点的。
SpringApplication启动分析
注:我这里是2.0.3版本的可能有些地方不太一样
参考链接:深入理解SpringBoot之启动探究
SpringaApplication初始化分析
首先进入run方法


会new一个SpringApplication实例,进入SpringApplication构造方法,它会调用initialize()进行初始化
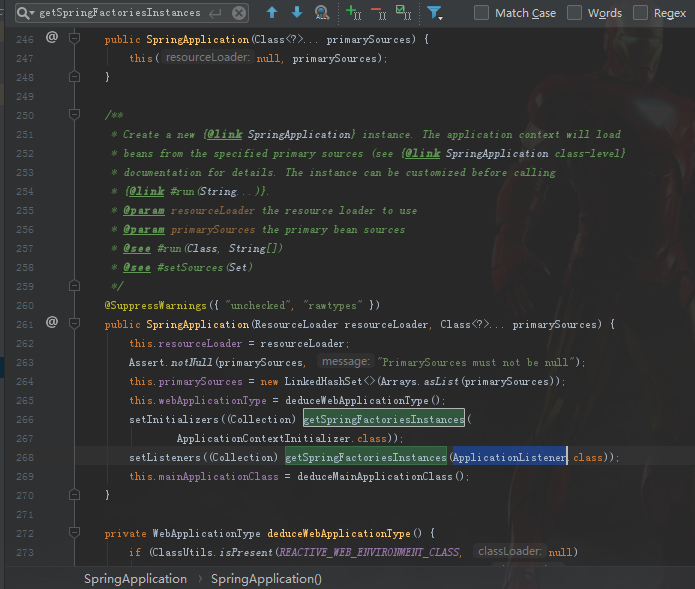
首先它会去判断运行环境根据运行环境来创建是java得ApplicationContext对象或者是web得ApplicationContext对象。
这里大家重点关注一下源代码中getSpringFacoriesInstances方法, ApplicationListener接口,ApplicationContextInitializer接口,这些接口都是通过SpringFactoriesLoader从META-INF/spring.factories文件里加载的
看一下getSpringFacoriesInstances方法的源码
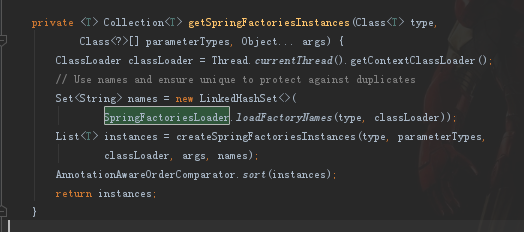
这里有一个关键类叫做SpringFactoriesLoader 该类的主要作用就是去读取META-INF/spring.factories配置文件里配置的引导对象,我们来看一下代码:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.io.support; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ConcurrentReferenceHashMap;
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /**
* General purpose factory loading mechanism for internal use within the framework.
*
* <p>{@code SpringFactoriesLoader} {@linkplain #loadFactories loads} and instantiates
* factories of a given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION} files which
* may be present in multiple JAR files in the classpath. The {@code spring.factories}
* file must be in {@link Properties} format, where the key is the fully qualified
* name of the interface or abstract class, and the value is a comma-separated list of
* implementation class names. For example:
*
* <pre class="code">example.MyService=example.MyServiceImpl1,example.MyServiceImpl2</pre>
*
* where {@code example.MyService} is the name of the interface, and {@code MyServiceImpl1}
* and {@code MyServiceImpl2} are two implementations.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 3.2
*/
public abstract class SpringFactoriesLoader { /**
* The location to look for factories.
* <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.
*/
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoriesLoader.class); private static final Map<ClassLoader, MultiValueMap<String, String>> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(); /**
* Load and instantiate the factory implementations of the given type from
* {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given class loader.
* <p>The returned factories are sorted through {@link AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}.
* <p>If a custom instantiation strategy is required, use {@link #loadFactoryNames}
* to obtain all registered factory names.
* @param factoryClass the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading (can be {@code null} to use the default)
* @see #loadFactoryNames
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any factory implementation class cannot
* be loaded or if an error occurs while instantiating any factory
*/
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryClass, "'factoryClass' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
List<String> factoryNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryClass, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryClass.getName() + "] names: " + factoryNames);
}
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(factoryNames.size());
for (String factoryName : factoryNames) {
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryName, factoryClass, classLoaderToUse));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
} /**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* @param factoryClass the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @see #loadFactories
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
*/
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
} private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue()));
result.addAll((String) entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames);
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static <T> T instantiateFactory(String instanceClassName, Class<T> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(instanceClassName, classLoader);
if (!factoryClass.isAssignableFrom(instanceClass)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Class [" + instanceClassName + "] is not assignable to [" + factoryClass.getName() + "]");
}
return (T) ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(instanceClass).newInstance();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to instantiate factory class: " + factoryClass.getName(), ex);
}
} }
通过SpringFactoriesLoader找到META-INF/spring.factories下ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类并将其实例化
再看一下ApplicationListener的源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2011 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.context; /**
* Callback interface for initializing a Spring {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext}
* prior to being {@linkplain ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() refreshed}.
*
* <p>Typically used within web applications that require some programmatic initialization
* of the application context. For example, registering property sources or activating
* profiles against the {@linkplain ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment()
* context's environment}. See {@code ContextLoader} and {@code FrameworkServlet} support
* for declaring a "contextInitializerClasses" context-param and init-param, respectively.
*
* <p>{@code ApplicationContextInitializer} processors are encouraged to detect
* whether Spring's {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} interface has been
* implemented or if the @{@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order Order}
* annotation is present and to sort instances accordingly if so prior to invocation.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#customizeContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#setContextInitializerClasses
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#applyInitializers
*/
public interface ApplicationContextInitializer<C extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> { /**
* Initialize the given application context.
* @param applicationContext the application to configure
*/
void initialize(C applicationContext); }
该接口在doc文档上描述很清楚了,在调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的refresh()之前进行的初始化操作
SpringApplication run方法
下面开始介绍run方法,先看一下源代码
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
} try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
1.启动计时
stopWatch.start();
2.创建了应用的监听器SpringApplicationRunListeners并开始监听

该接口首先从META-INF/spring.factories文件里获取所有配置的SpringApplicationRunner ,那么这个接口时干啥的呢?
我们来看一下源代码:
/*
* Copyright 2012-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader; /**
* Listener for the {@link SpringApplication} {@code run} method.
* {@link SpringApplicationRunListener}s are loaded via the {@link SpringFactoriesLoader}
* and should declare a public constructor that accepts a {@link SpringApplication}
* instance and a {@code String[]} of arguments. A new
* {@link SpringApplicationRunListener} instance will be created for each run.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Andy Wilkinson
*/
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener { /**
* Called immediately when the run method has first started. Can be used for very
* early initialization.
*/
void starting(); /**
* Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the
* {@link ApplicationContext} has been created.
* @param environment the environment
*/
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment); /**
* Called once the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created and prepared, but
* before sources have been loaded.
* @param context the application context
*/
void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context); /**
* Called once the application context has been loaded but before it has been
* refreshed.
* @param context the application context
*/
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context); /**
* The context has been refreshed and the application has started but
* {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner
* ApplicationRunners} have not been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context); /**
* Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has
* been refreshed and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and
* {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context); /**
* Called when a failure occurs when running the application.
* @param context the application context or {@code null} if a failure occurred before
* the context was created
* @param exception the failure
* @since 2.0.0
*/
void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception); }
看出其中包括:程序启动,环境准备,ApplicationContext准备加载,程序启动 运行 完成等。
该接口默认有一个实现类EventPublishingRunListener至关重要大家需要了解一下:
/*
* Copyright 2012-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot.context.event; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.util.ErrorHandler; /**
* {@link SpringApplicationRunListener} to publish {@link SpringApplicationEvent}s.
* <p>
* Uses an internal {@link ApplicationEventMulticaster} for the events that are fired
* before the context is actually refreshed.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Andy Wilkinson
*/
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered { private final SpringApplication application; private final String[] args; private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster; public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
} @Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
} @Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(
new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
} @Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
this.application, this.args, environment));
} @Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } @Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) {
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context);
}
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(
new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
} @Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(
new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
} @Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(
new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
} @Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application,
this.args, context, exception);
if (context != null && context.isActive()) {
// Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should
// use it at this point if we can
context.publishEvent(event);
}
else {
// An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to
// call all of the context's listeners instead
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
.getApplicationListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler());
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
} private static class LoggingErrorHandler implements ErrorHandler { private static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(EventPublishingRunListener.class); @Override
public void handleError(Throwable throwable) {
logger.warn("Error calling ApplicationEventListener", throwable);
} } }
其中SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster这个类很重要
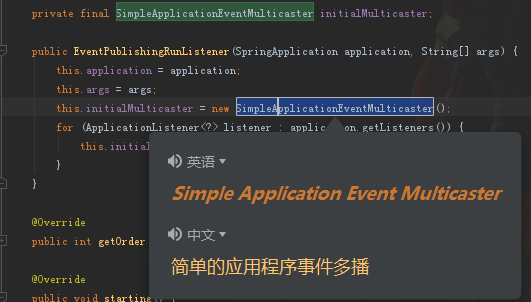
看一下源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.context.event; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.ErrorHandler; /**
* Simple implementation of the {@link ApplicationEventMulticaster} interface.
*
* <p>Multicasts all events to all registered listeners, leaving it up to
* the listeners to ignore events that they are not interested in.
* Listeners will usually perform corresponding {@code instanceof}
* checks on the passed-in event object.
*
* <p>By default, all listeners are invoked in the calling thread.
* This allows the danger of a rogue listener blocking the entire application,
* but adds minimal overhead. Specify an alternative task executor to have
* listeners executed in different threads, for example from a thread pool.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @see #setTaskExecutor
*/
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster { @Nullable
private Executor taskExecutor; @Nullable
private ErrorHandler errorHandler; /**
* Create a new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.
*/
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster() {
} /**
* Create a new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster for the given BeanFactory.
*/
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
} /**
* Set a custom executor (typically a {@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor})
* to invoke each listener with.
* <p>Default is equivalent to {@link org.springframework.core.task.SyncTaskExecutor},
* executing all listeners synchronously in the calling thread.
* <p>Consider specifying an asynchronous task executor here to not block the
* caller until all listeners have been executed. However, note that asynchronous
* execution will not participate in the caller's thread context (class loader,
* transaction association) unless the TaskExecutor explicitly supports this.
* @see org.springframework.core.task.SyncTaskExecutor
* @see org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
*/
public void setTaskExecutor(@Nullable Executor taskExecutor) {
this.taskExecutor = taskExecutor;
} /**
* Return the current task executor for this multicaster.
*/
@Nullable
protected Executor getTaskExecutor() {
return this.taskExecutor;
} /**
* Set the {@link ErrorHandler} to invoke in case an exception is thrown
* from a listener.
* <p>Default is none, with a listener exception stopping the current
* multicast and getting propagated to the publisher of the current event.
* If a {@linkplain #setTaskExecutor task executor} is specified, each
* individual listener exception will get propagated to the executor but
* won't necessarily stop execution of other listeners.
* <p>Consider setting an {@link ErrorHandler} implementation that catches
* and logs exceptions (a la
* {@link org.springframework.scheduling.support.TaskUtils#LOG_AND_SUPPRESS_ERROR_HANDLER})
* or an implementation that logs exceptions while nevertheless propagating them
* (e.g. {@link org.springframework.scheduling.support.TaskUtils#LOG_AND_PROPAGATE_ERROR_HANDLER}).
* @since 4.1
*/
public void setErrorHandler(@Nullable ErrorHandler errorHandler) {
this.errorHandler = errorHandler;
} /**
* Return the current error handler for this multicaster.
* @since 4.1
*/
@Nullable
protected ErrorHandler getErrorHandler() {
return this.errorHandler;
} @Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
} @Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
} private ResolvableType resolveDefaultEventType(ApplicationEvent event) {
return ResolvableType.forInstance(event);
} /**
* Invoke the given listener with the given event.
* @param listener the ApplicationListener to invoke
* @param event the current event to propagate
* @since 4.1
*/
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
} @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass().getName())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
} private boolean matchesClassCastMessage(String classCastMessage, String eventClassName) {
// On Java 8, the message simply starts with the class name: "java.lang.String cannot be cast..."
if (classCastMessage.startsWith(eventClassName)) {
return true;
}
// On Java 9, the message contains the module name: "java.base/java.lang.String cannot be cast..."
int moduleSeparatorIndex = classCastMessage.indexOf('/');
if (moduleSeparatorIndex != -1 && classCastMessage.startsWith(eventClassName, moduleSeparatorIndex + 1)) {
return true;
}
// Assuming an unrelated class cast failure...
return false;
} }
doInvokeListener方法,该方法用于执行事件的监听方法。该类最主要作用就是通知各个阶段的listener处理对应阶段的事件
3.调用SpringApplicationRunListener的start方法
看一下这个方法
public void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
4.调用prepareEnvironment事件
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
5.根据当前environment打印Banner
也就是启动时控制台打印出的Spring标志 启动的Banner就是在这一步打印出来的 也可自定义Banner 链接:Spring Boot实例教程 - 自定义Banner
6.创建的ApplicationContext对象
这里会根据this.webEnvironment的属性值来确定创建的ApplicationContext对象
/**
* Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this
* method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context
* class before falling back to a suitable default.
* @return the application context (not yet refreshed)
* @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class)
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
如果是web环境那就创建org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
否则就创建org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
7.调用prepareContext方法
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
} // Add boot specific singleton beans
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
} // Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
8.调用refreshContext
该方法最终会执行AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法,我在这里贴一下源代码:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
在这个方法里会初始化BeanFactory 初始化BeanFactoryPostProcessor 注册BeanPostProcessor 初始化MessageSource 注册事件监听器等操作。建议大家深入了解Spring的IOC加载原理
9.调用afterRefresh方法
/**
* Called after the context has been refreshed.
* @param context the application context
* @param args the application arguments
*/
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ApplicationArguments args) {
}
10.启动计时结束
stopWatch.stop();
11.调用started方法
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.started(context);
}
}
12.调用callRunners方法
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
该方法会从IOC容器里找到ApplicationRunner或者CommandLineRunner并执行其run方法,当我们需要在SpringBoot程序启动时处理我们自己的逻辑,那么就可以实现上述接口
13.启动异常处理
private void handleRunFailure(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception,
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners) {
try {
try {
handleExitCode(context, exception);
if (listeners != null) {
listeners.failed(context, exception);
}
}
finally {
reportFailure(exceptionReporters, exception);
if (context != null) {
context.close();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Unable to close ApplicationContext", ex);
}
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception);
}
至此run方法就执行完成了
SpringBoot启动总结
1. SpringBoot启动时SpringApplicationRunListener接口的相关方法至关重要,它定义了启动时的各个“时间点”。
2. SpringBoot可以从spring.factoies文件里读取配置的ApplicationListener
3. META-INF文件夹下的spring.factoies文件是SpringBoot启动的核心文件,SpringFatoriesLoader会读取该文件夹下的相关配置作为引导
4. SpringBoot启动时利用了事件机制,来发送启动时各个周期阶段的事件
SpringBoot学习(二)探究Springboot启动机制的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot学习11:springboot异常处理方式1(自定义异常页面)
SpringBoot 默认的处理异常的机制:SpringBoot 默认的已经提供了一套处理异常的机制.一旦程序中出现了异常 SpringBoot 会向/error 的 url 发送请求.在 sprin ...
- SpringBoot学习(二)-->Spring的Java配置方式
二.Spring的Java配置方式 Java配置是Spring4.x推荐的配置方式,可以完全替代xml配置. 1.@Configuration 和 @Bean Spring的Java配置方式是通过 @ ...
- SpringBoot学习<二>——SpringBoot的默认配置文件application和多环境配置
一.SpringBoot的默认文件appliction 上一篇文章已经说明,springboot启动会内嵌tomcat,端口也是默认的8080,如果我们想要改变端口如果做呢? 在springboot项 ...
- springboot学习问题一:启动springboot报错端口被占用解决办法
一:问题 二:分析原因 springboot启动默认端口为8080,现在提示被占用,那我们可以修改springboot的启动端口,换一个未被占用的端口即可 三:解决方法 打开application.p ...
- 微服务学习二:springboot与swagger2的集成
现在测试都提倡自动化测试,那我们作为后台的开发人员,也得进步下啊,以前用postman来测试后台接口,那个麻烦啊,一个字母输错就导致测试失败,现在swagger的出现可谓是拯救了这些开发人员,便捷之处 ...
- SpringBoot学习(二):配置文件
1.配置文件 SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名是固定的: •application.properties •application.yml 配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoo ...
- springboot学习二:配置文件配置
springboot默认读取application*.properties #######spring配置####### spring.profiles.active=dev //引入开发配置文件 a ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习4-helloworld探究
1.POM文件 <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spr ...
- SpringBoot学习(二)
spring-boot-starter-parent Maven的用户可以通过继承spring-boot-starter-parent项目来获得一些合理的默认配置.这个parent提供了以下特性: 默 ...
- springboot学习(二十二)_ 使用@Constraint注解自定义验证注解
最近项目在使用如@NotNull @Max 等配合@vaild 注解进行验证传过来的参数校验,然后通过统一异常处理,直接返回给前端,不用在业务代码中对这些参数进行校验.但是官方提供的并不能全部满足项目 ...
随机推荐
- unzip 命令指定解压路径
在使用unzip进行文件包解压,可以用来解压zip/jar/war包类型,有时解压时需要解压到指定路径时可以使用参数 -d 来指定,例如: unzip services-bak.jar -d ./we ...
- cmd控制台 wrapper | OpenSCManager failed - 拒绝访问。 (0x5)解决
在windows上安装mycat执行命令时, D:\develop\Mycat\bin>mycat.bat install 返回wrapper | OpenSCManager failed - ...
- JS 生成唯一值UUID
md5加密new Date()生成的值可能不是唯一的,另一种生成唯一值的方式: getUID: function() { // 获取唯一值 return 'xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxx ...
- WebGL简易教程(五):图形变换(模型、视图、投影变换)
[toc] 1. 概述 通过之前的教程,对WebGL中可编程渲染管线的流程有了一定的认识.但是只有前面的知识还不足以绘制真正的三维场景,可以发现之前我们绘制的点.三角形的坐标都是[-1,1]之间,Z值 ...
- Java面向对象程序设计第6章1-12
1.this和super各有几种用法? this this 用法有三种,主要应用场合: 表示当前对象引用,常用于形参或局部变量与类的成员变 量同名的情形,使用this.成员名表示当前对象的成员 表示当 ...
- Java 学习笔记之 线程Yield
线程Yield: yield()方法的作用是放弃当前的CPU资源,将它让给其他的任务去占用CPU执行时间,但放弃的时间不确定,有可能刚刚放弃,马上又获得CPU时间片. public class Yie ...
- 《构建之法》MSF&需求分析
第七章 MSF MSF基本原则 推动信息共享与沟通 为共同的远景而工作 充分授权和信任 各司其职,对项目共同负责 交付增量的价值 保持敏捷,预期和适应变化 投资质量 学习所有的经验 与顾客合作 MSF ...
- 重学Golang系列(一): 深入理解 interface和reflect
前言 interface(即接口),是Go语言中一个重要的概念和知识点,而功能强大的reflect正是基于interface.本文即是对Go语言中的interface和reflect基础概念和用法的一 ...
- PHP高效产生m个n范围内的不重复随机数(m<=n)
该算法非常巧妙的取随机数的位置(数组的下标),替代取随机数本身,每次取到一个随机数之后,就将其在取值范围中排除,下一次仅会在剩下的数字中取,一次遍历就可以完成随机数的选取,效率相当高. functio ...
- Spring Boot 定时任务 @Scheduled
项目开发中经常需要执行一些定时任务,比如在每天凌晨,需要从 implala 数据库拉取产品功能活跃数据,分析处理后存入到 MySQL 数据库中.类似这样的需求还有许多,那么怎么去实现定时任务呢,有以下 ...
