JDK源码阅读(一) ArrayList
基于JDK7.0
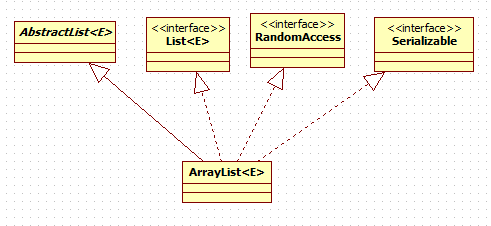
ArrayList<E>类继承了抽象类AbstractList<E> 实现了List<E> 接口,RandomAccess接口,Cloneable接口,Serializable接口
成员变量:
(1) private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; 序列化号
(2) private transient Object[] elementData; 存储ArrayList元素的数组,用transient修饰,序列化时不对transient修饰的元素进行序列化
(3) private int size; 用于标示ArrayList元素的数量
成员方法:
(1) 构造函数一共有三个
①public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 构造一个具有指定初始容量的空列表。
方法中会通过this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 来在堆内存中创建对象数组
同时initialCapacity不能小于0,否则抛出throw new IllegalArgumentException 运行时异常
②public ArrayList() 构造一个初始容量为 10 的空列表。 调用①的构造函数
③public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) 构造一个包含指定 collection 的元素的列表,这些元素是按照该 collection 的迭代器返回它们的顺序排列的。
C中的元素必须是E或者E的子类 ? extends E 重点关注一个接口Collection
package java.util; public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; private transient Object[] elementData; private int size; public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} public ArrayList() {
this(10);
} public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (size < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
} public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(minCapacity);
} private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
} private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
} public int size() {
return size;
} public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
} public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
} public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
} public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
} public Object clone() {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ArrayList<E> v = (ArrayList<E>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
} public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
} // Positional Access Operations @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
} /**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index);
} public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
} public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
} public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
} public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work return oldValue;
} public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
} public void clear() {
modCount++; // Let gc do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null; size = 0;
} public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
} public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
} protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved); // Let gc do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (size != newSize)
elementData[--size] = null;
} private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
} /**
* A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll.
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
} /**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
} public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, false);
} public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true);
} private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0;
boolean modified = false;
try {
for (; r < size; r++)
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r);
w += size - r;
}
if (w != size) {
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
} private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out array length
s.writeInt(elementData.length); // Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
s.writeObject(elementData[i]); if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
} } private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in array length and allocate array
int arrayLength = s.readInt();
Object[] a = elementData = new Object[arrayLength]; // Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
a[i] = s.readObject();
} public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
} public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
} public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
} private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
} public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
} public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
} public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
} public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
} public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification(); try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
} static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
} private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
private final AbstractList<E> parent;
private final int parentOffset;
private final int offset;
int size; SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.parent = parent;
this.parentOffset = fromIndex;
this.offset = offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} public E set(int index, E e) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;
return oldValue;
} public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
} public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return this.size;
} public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size++;
} public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size--;
return result;
} protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex,
parentOffset + toIndex);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex;
} public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
} public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false; checkForComodification();
parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size += cSize;
return true;
} public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
} public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
final int offset = this.offset; return new ListIterator<E>() {
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
} public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
} public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
} public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
} public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); try {
ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification(); try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} final void checkForComodification() {
if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
} public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex);
} private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
} private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
} private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
} private void checkForComodification() {
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
JDK源码阅读(一) ArrayList的更多相关文章
- jdk源码阅读笔记-ArrayList
一.ArrayList概述 首先我们来说一下ArrayList是什么?它解决了什么问题?ArrayList其实是一个数组,但是有区别于一般的数组,它是一个可以动态改变大小的动态数组.ArrayList ...
- JDK源码阅读(三):ArraryList源码解析
今天来看一下ArrayList的源码 目录 介绍 继承结构 属性 构造方法 add方法 remove方法 修改方法 获取元素 size()方法 isEmpty方法 clear方法 循环数组 1.介绍 ...
- JDK源码阅读-FileDescriptor
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-FileDescriptor 导语 操作系统使用文件描述符来指代一个打开的文件,对文件的读写操作,都需要文件描述符作为参数.Java虽然在设计上使用了抽象程度更高的流来作为文 ...
- JDK源码阅读(一):Object源码分析
最近经过某大佬的建议准备阅读一下JDK的源码来提升一下自己 所以开始写JDK源码分析的文章 阅读JDK版本为1.8 目录 Object结构图 构造器 equals 方法 getClass 方法 has ...
- 利用IDEA搭建JDK源码阅读环境
利用IDEA搭建JDK源码阅读环境 首先新建一个java基础项目 基础目录 source 源码 test 测试源码和入口 准备JDK源码 下图框起来的路径就是jdk的储存位置 打开jdk目录,找到sr ...
- JDK源码阅读-FileOutputStream
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-FileOutputStream 导语 FileOutputStream用户打开文件并获取输出流. 打开文件 public FileOutputStream(File fil ...
- JDK源码阅读-FileInputStream
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-FileInputStream 导语 FileIntputStream用于打开一个文件并获取输入流. 打开文件 我们来看看FileIntputStream打开文件时,做了什么 ...
- JDK源码阅读-ByteBuffer
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-ByteBuffer 导语 Buffer是Java NIO中对于缓冲区的封装.在Java BIO中,所有的读写API,都是直接使用byte数组作为缓冲区的,简单直接.但是在J ...
- JDK源码阅读-RandomAccessFile
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-RandomAccessFile 导语 FileInputStream只能用于读取文件,FileOutputStream只能用于写入文件,而对于同时读取文件,并且需要随意移动 ...
随机推荐
- 【转】Android Studio Essential Training
http://ask.android-studio.org/?/explore/category-video Android Studio Essential Training内容包括:- Andro ...
- 经验总结17--submitbutton,ajax提交
发篇小文章,纪念七七事变. submit一般用于提交表单,可是想使用ajax进行提交,又想按"enter"触发button. 那么就阻止提交表单的事件,进行自己定义的提交. 1.让 ...
- hadoop错误java.io.IOException Failed to replace a bad datanode on the existing pipeline due to no more good datanodes being available to try
错误: java.io.IOException: Failed to replace a bad datanode on the existing pipeline due to no more go ...
- Android(java)学习笔记193:利用谷歌API对数据库增删改查(推荐使用)
接下来我们通过项目案例来介绍:这个利用谷歌API对数据库增删改查 1.首先项目图: 2.这里的布局文件activity_main.xml: <LinearLayout xmlns:android ...
- IIS Shared Configuration
Introduction The Internet changes the ways in which companies handle their day-to-day business and h ...
- python 函数初识和文件操作
文件操作 打开文件:文件句柄 = open('文件路径', '模式') 打开文件的模式 w #以写的方式打开 (不可读,不存在则创建,存在则删除内容) a #以追加的模式打开(可读, 不存在则创建 ...
- day-7
/* 倒数7天了 某一天 某一刻 某次呼吸 我们终将再分离 而我的 自传里 曾经有你 没有遗憾的诗句 诗句里 充满感激 (小仙女博客抄来的233) 是啊 就快要结束了 曲终人散 上午被错误数据卡了一小 ...
- 当append里面的标签显示不出来的时候,用下面的方式做
$("#result_td").append(tem1+tem3) $("#result_td").append($(tem1+tem3))
- CI框架篇之预热篇(1)
CodeIgniter 的基本都了解了,现在就开始预热,如果学习一门语言一样,我们最开始都是输出一个'HELLO WORLD'一样, 现在我们也通过输出这样一个内容,来了解基本的使用. CodeIgn ...
- Intellj新增maven项目骨架
我们经常用maven骨架构建项目,本来普通的几个archetype就够用的,但是近来要来时开发liferay项目 相关的项目骨架Intellj IDEA就没有内置,所以就想添加进去, 有两个办法可以 ...
