Hadoop MapReduce 二次排序原理及其应用
关于二次排序主要涉及到这么几个东西:
在0.20.0 以前使用的是
setPartitionerClass
setOutputkeyComparatorClass
setOutputValueGroupingComparator
在0.20.0以后使用是
job.setPartitionerClass(Partitioner p);
job.setSortComparatorClass(RawComparator c);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(RawComparator c);
下面的例子里面只用到了 setGroupingComparatorClass
mr自带的例子中的源码SecondarySort,我重新写了一下,基本没变。
这个例子中定义的map和reduce如下,关键是它对输入输出类型的定义:(java泛型编程)
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntPair, IntWritable>
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntPair, NullWritable, IntWritable, IntWritable>
1、首先说一下工作原理:
在map阶段,使用job.setInputFormatClass定义的InputFormat将输入的数据集分割成小数据块splites,同时InputFormat提供一个RecordReder的实现。本例子中使用的是TextInputFormat,他提供的RecordReder会将文本的字节偏移量作为key,这一行的文本作为value。这就是自定义Map的输入是<LongWritable, Text>的原因。然后调用自定义Map的map方法,将一个个<LongWritable, Text>对输入给Map的map方法。注意输出应该符合自定义Map中定义的输出<IntPair, IntWritable>。最终是生成一个List<IntPair, IntWritable>。在map阶段的最后,会先调用job.setPartitionerClass对这个List进行分区,每个分区映射到一个reducer。每个分区内又调用job.setSortComparatorClass设置的key比较函数类排序。可以看到,这本身就是一个二次排序。如果没有通过job.setSortComparatorClass设置key比较函数类,则使用key的实现的compareTo方法。在第一个例子中,使用了IntPair实现的compareTo方法,而在下一个例子中,专门定义了key比较函数类。
在reduce阶段,reducer接收到所有映射到这个reducer的map输出后,也是会调用job.setSortComparatorClass设置的key比较函数类对所有数据对排序。然后开始构造一个key对应的value迭代器。这时就要用到分组,使用jobjob.setGroupingComparatorClass设置的分组函数类。只要这个比较器比较的两个key相同,他们就属于同一个组,它们的value放在一个value迭代器,而这个迭代器的key使用属于同一个组的所有key的第一个key。最后就是进入Reducer的reduce方法,reduce方法的输入是所有的(key和它的value迭代器)。同样注意输入与输出的类型必须与自定义的Reducer中声明的一致。
2、二次排序 就是首先按照第一字段排序,然后再对第一字段相同的行按照第二字段排序,注意不能破坏第一次排序 的结果 。例如 :
echo "3 b
1 c
2 a
1 d
3 a"|sort -k1 -k2
1 c
1 d
2 a
3 a
3 b
3、具体步骤:
1 自定义key。
在mr中,所有的key是需要被比较和排序的,并且是二次,先根据partitione,再根据大小。而本例中也是要比较两次。先按照第一字段排序,然后再对第一字段相同的按照第二字段排序。根据这一点,我们可以构造一个复合类IntPair,他有两个字段,先利用分区对第一字段排序,再利用分区内的比较对第二字段排序。
所有自定义的key应该实现接口WritableComparable,因为是可序列的并且可比较的。并重载方法
//反序列化,从流中的二进制转换成IntPair
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException
//序列化,将IntPair转化成使用流传送的二进制
public void write(DataOutput out)
//key的比较
public int compareTo(IntPair o)
另外新定义的类应该重写的两个方法
//The hashCode() method is used by the HashPartitioner (the default partitioner in MapReduce)
public int hashCode()
public boolean equals(Object right)
2 由于key是自定义的,所以还需要自定义一下类:
2.1 分区函数类。这是key的第一次比较。
public static class FirstPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntPair,IntWritable>
在job中设置使用setPartitionerClasss
2.2 key比较函数类。这是key的第二次比较。这是一个比较器,需要继承WritableComparator。
public static class KeyComparator extends WritableComparator
必须有一个构造函数,并且重载 public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2)
另一种方法是 实现接口RawComparator。
在job中设置使用setSortComparatorClass。
2.3 分组函数类。在reduce阶段,构造一个key对应的value迭代器的时候,只要first相同就属于同一个组,放在一个value迭代器。这是一个比较器,需要继承WritableComparator。
public static class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator
同key比较函数类,必须有一个构造函数,并且重载 public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2)
同key比较函数类,分组函数类另一种方法是实现接口RawComparator。
在job中设置使用setGroupingComparatorClass。
另外注意的是,如果reduce的输入与输出不是同一种类型,则不要定义Combiner也使用reduce,因为Combiner的输出是reduce的输入。除非重新定义一个Combiner。
4 代码。这个例子中没有使用key比较函数类,而是使用key的实现的compareTo方法:
package SecondarySort;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
public class SecondarySort
{
//自己定义的key类应该实现WritableComparable接口
public static class IntPair implements WritableComparable<IntPair>
{
String first;
String second;
/**
* Set the left and right values.
*/
public void set(String left, String right)
{
first = left;
second = right;
}
public String getFirst()
{
return first;
}
public String getSecond()
{
return second;
}
//反序列化,从流中的二进制转换成IntPair
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException
{
first = in.readUTF();
second = in.readUTF();
}
//序列化,将IntPair转化成使用流传送的二进制
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException
{
out.writeUTF(first);
out.writeUTF(second);
}
//重载 compareTo 方法,进行组合键 key 的比较,该过程是默认行为。
//分组后的二次排序会隐式调用该方法。
public int compareTo(IntPair o)
{
if (!first.equals(o.first) )
{
return first.compareTo(o.first);
}
else if (!second.equals(o.second))
{
return second.compareTo(o.second);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
//新定义类应该重写的两个方法
//The hashCode() method is used by the HashPartitioner (the default partitioner in MapReduce)
public int hashCode()
{
return first.hashCode() * 157 + second.hashCode();
}
public boolean equals(Object right)
{
if (right == null)
return false;
if (this == right)
return true;
if (right instanceof IntPair)
{
IntPair r = (IntPair) right;
return r.first.equals(first) && r.second.equals(second) ;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* 分区函数类。根据first确定Partition。
*/
public static class FirstPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntPair, Text>
{
public int getPartition(IntPair key, Text value,int numPartitions)
{
return Math.abs(key.getFirst().hashCode() * 127) % numPartitions;
}
}
/**
* 分组函数类。只要first相同就属于同一个组。
*/
/*//第一种方法,实现接口RawComparator
public static class GroupingComparator implements RawComparator<IntPair> {
public int compare(IntPair o1, IntPair o2) {
int l = o1.getFirst();
int r = o2.getFirst();
return l == r ? 0 : (l < r ? -1 : 1);
}
//一个字节一个字节的比,直到找到一个不相同的字节,然后比这个字节的大小作为两个字节流的大小比较结果。
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2){
return WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, s1, Integer.SIZE/8,
b2, s2, Integer.SIZE/8);
}
}*/
//第二种方法,继承WritableComparator
public static class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator
{
protected GroupingComparator()
{
super(IntPair.class, true);
}
//Compare two WritableComparables.
// 重载 compare:对组合键按第一个自然键排序分组
public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2)
{
IntPair ip1 = (IntPair) w1;
IntPair ip2 = (IntPair) w2;
String l = ip1.getFirst();
String r = ip2.getFirst();
return l.compareTo(r);
}
}
// 自定义map
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntPair, Text>
{
private final IntPair keyPair = new IntPair();
String[] lineArr = null;
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
String line = value.toString();
lineArr = line.split("\t", -1);
keyPair.set(lineArr[0], lineArr[1]);
context.write(keyPair, value);
}
}
// 自定义reduce
//
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntPair, Text, Text, Text>
{
private static final Text SEPARATOR = new Text("------------------------------------------------");
public void reduce(IntPair key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
context.write(SEPARATOR, null);
for (Text val : values)
{
context.write(null, val);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// 读取hadoop配置
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 实例化一道作业
Job job = new Job(conf, "secondarysort");
job.setJarByClass(SecondarySort.class);
// Mapper类型
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
// 不再需要Combiner类型,因为Combiner的输出类型<Text, IntWritable>对Reduce的输入类型<IntPair, IntWritable>不适用
//job.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
// Reducer类型
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
// 分区函数
job.setPartitionerClass(FirstPartitioner.class);
// 分组函数
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupingComparator.class);
// map 输出Key的类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntPair.class);
// map输出Value的类型
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// rduce输出Key的类型,是Text,因为使用的OutputFormatClass是TextOutputFormat
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// rduce输出Value的类型
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// 将输入的数据集分割成小数据块splites,同时提供一个RecordReder的实现。
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
// 提供一个RecordWriter的实现,负责数据输出。
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 输入hdfs路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
// 输出hdfs路径
FileSystem.get(conf).delete(new Path(args[1]), true);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
// 提交job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
5 需求:假如我们现在的需求是先按 cookieId 排序,然后按 time 排序,以便按 session 切分日志
6 测试数据与结果:
01 |
cookieId time url |
02 |
2 12:12:34 2_hao123 |
03 |
3 09:10:34 3_baidu |
04 |
1 15:02:41 1_google |
05 |
3 22:11:34 3_sougou |
06 |
1 19:10:34 1_baidu |
07 |
2 15:02:41 2_google |
08 |
1 12:12:34 1_hao123 |
09 |
3 23:10:34 3_soso |
10 |
2 05:02:41 2_google |
11 |
12 |
结果: |
13 |
------------------------------------------------ |
14 |
1 12:12:34 1_hao123 |
15 |
1 15:02:41 1_google |
16 |
1 19:10:34 1_baidu |
17 |
------------------------------------------------ |
18 |
2 05:02:41 2_google |
19 |
2 12:12:34 2_hao123 |
20 |
2 15:02:41 2_google |
21 |
------------------------------------------------ |
22 |
3 09:10:34 3_baidu |
23 |
3 22:11:34 3_sougou |
24 |
3 23:10:34 3_soso |
7 原理图(点击查看大图):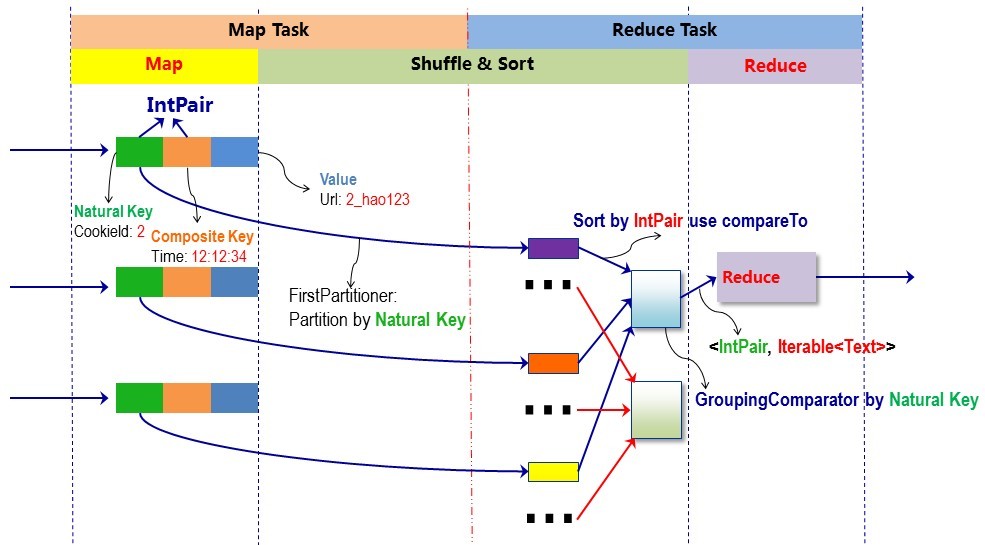
reference:
REF:
mapreduce的二次排序 SecondarySort
http://blog.csdn.net/zyj8170/article/details/7530728
学会定制MapReduce里的partition,sort和grouping,Secondary Sort Made Easy 进行二次排序
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9bf980ad0100zk7r.html
Simple Moving Average, Secondary Sort, and MapReduce (Part 3)
http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2011/04/simple-moving-average-secondary-sort-and-mapreduce-part-3/
https://github.com/jpatanooga/Caduceus/tree/master/src/tv/floe/caduceus/hadoop/movingaverage
MapReduce的排序和二次排序原理总结
http://hugh-wangp.iteye.com/blog/1491175
泛型value的二次排序
Hadoop MapReduce 二次排序原理及其应用的更多相关文章
- Hadoop学习笔记: MapReduce二次排序
本文给出一个实现MapReduce二次排序的例子 package SortTest; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; impo ...
- MapReduce二次排序
默认情况下,Map 输出的结果会对 Key 进行默认的排序,但是有时候需要对 Key 排序的同时再对 Value 进行排序,这时候就要用到二次排序了.下面让我们来介绍一下什么是二次排序. 二次排序原理 ...
- (转)MapReduce二次排序
一.概述 MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的.在我们实际的需求当中,往往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排序的需求 ...
- 关于MapReduce二次排序的一点解答
上一篇博客说明了怎么自定义Key,而且用了二次排序的例子来做测试,但没有详细的说明二次排序,这一篇说详细的说明二次排序,为了说明曾经一个思想的误区,特地做了一个3个字段的二次排序来说明.后面称其为“三 ...
- 详细讲解MapReduce二次排序过程
我在15年处理大数据的时候还都是使用MapReduce, 随着时间的推移, 计算工具的发展, 内存越来越便宜, 计算方式也有了极大的改变. 到现在再做大数据开发的好多同学都是直接使用spark, hi ...
- MapReduce 二次排序
默认情况下,Map 输出的结果会对 Key 进行默认的排序,但是有时候需要对 Key 排序的同时再对 Value 进行排序,这时候就要用到二次排序了.下面让我们来介绍一下什么是二次排序. 二次排序原理 ...
- mapreduce二次排序详解
什么是二次排序 待排序的数据具有多个字段,首先对第一个字段排序,再对第一字段相同的行按照第二字段排序,第二次排序不破坏第一次排序的结果,这个过程就称为二次排序. 如何在mapreduce中实现二次排序 ...
- java mapreduce二次排序
原文链接: https://www.toutiao.com/i6765808056191156748/ 目的: 二次排序就是有下面的数据 a 3 a 1 a 100 c 1 b 2 如果只按照abc排 ...
- Hadoop学习之自定义二次排序
一.概述 MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的.在我们实际的需求当中,往 往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排 ...
随机推荐
- 【html】【20】高级篇--轮播图[聚焦]
下载: http://sc.chinaz.com/jiaoben/151204445580.htm 效果: html <!doctype html> <html> <he ...
- Golang中解析json,构造json
json解析是如今(网络)应用程序开发中最不可或缺的一环了.许多语言需要库支持才可以解析.构造json,但Golang凭借着原生库就可以很好地做到这一点. json的基本表现形式有两个:struct与 ...
- bash 脚本
一.英文版 1.Advanced Bash-Scripting Guide 二.中文 1.BashGuide for Beginners 中文版
- [Guava官方文档翻译] 6. 用Guava辅助Throwable异常处理 (Throwables Explained)
我的技术博客经常被流氓网站恶意爬取转载.请移步原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hamhog/p/3537508.html ,享受整齐的排版.有效的链接.正确的代码缩进.更好的阅读体 ...
- C#通过ODAC访问Oracle12c
昨天晚上刚装好Oracle12c并配制好了PLSQL Developer开发环境.今天继续完善一下,讲讲在C#中如何访问Oracle12c. 其实我们运用老早的ADO.NET也可以连接,但是在.NET ...
- Cassandra1.2文档学习(9)—— 数据写入
数据参考:http://www.datastax.com/documentation/cassandra/1.2/webhelp/index.html#cassandra/dml/manage_dml ...
- yii YII小部件 创建登录表单表单 Login表单
YII框架必须遵循其表单的创建方法 登录模型错做与数据库操作模型是一致的,不同的是不跟数据库交互 ,用的是小部件,在创建表单之前,要在用户控制模块完成以下代码 protected --models - ...
- PHPCMS 核心代码与 www 分离部署
为了满足更多用户二次开发的兴趣与爱好,同时,为了更加安全.可以通过修改入口代码的包含方式来让主程序和www程序分开. 先看下面目录结构: (图1) 我们需要将 phpcms 目录和 index.php ...
- Linux下18b20温度传感器驱动代码及测试实例
驱动代码: #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #i ...
- [转]MonkeyRunner在Windows下的Eclipse开发环境搭建步骤(兼解决网上Jython配置出错的问题)
MonkeyRunner在Windows下的Eclipse开发环境搭建步骤(兼解决网上Jython配置出错的问题) 网上有一篇shangdong_chu网友写的文章介绍如何在Eclipse上配置M ...
