那些年被我坑过的Python——一夫当关 第十三章(堡垒机初步设计)
堡垒机架构
堡垒机的主要作用权限控制和用户行为审计,堡垒机就像一个城堡的大门,城堡里的所有建筑就是你不同的业务系统 , 每个想进入城堡的人都必须经过城堡大门并经过大门守卫的授权,每个进入城堡的人必须且只能严格按守卫的分配进入指定的建筑,且每个建筑物还有自己的权限访 问控制,不同级别的人可以到建筑物里不同楼层的访问级别也是不一样的。还有就是,每个进入城堡的人的所有行为和足迹都会被严格的监控和纪录下来,一旦发生 犯罪事件,城堡管理人员就可以通过这些监控纪录来追踪责任人。
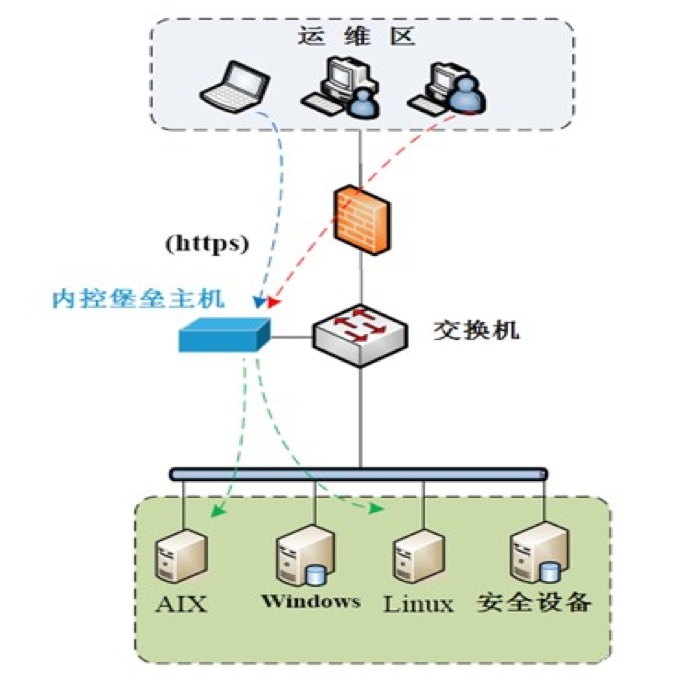
堡垒要想成功完全记到他的作用,只靠堡垒机本身是不够的, 还需要一系列安全上对用户进行限制的配合,堡垒机部署上后,同时要确保你的网络达到以下条件:
- 所有人包括运维、开发等任何需要访问业务系统的人员,只能通过堡垒机访问业务系统
- 回收所有对业务系统的访问权限,做到除了堡垒机管理人员,没有人知道业务系统任何机器的登录密码
- 网络上限制所有人员只能通过堡垒机的跳转才能访问业务系统
- 确保除了堡垒机管理员之外,所有其它人对堡垒机本身无任何操作权限,只有一个登录跳转功能
- 确保用户的操作纪录不能被用户自己以任何方式获取到并篡改
堡垒机表结构设计
对象分析:
需要堡垒机管理的对象包括:人员、人员组、系统账户+登录认证+账户权限(唯一通道)、主机、主机组、操作日志(命令、上传、下载)
对象之间的关系如下图所示:
人员想登陆到host需要通过唯一确定的通道,这个通道就是需要登陆的系统账户+登陆认证方式与信息+所属账户的sudo权限(默认是普通用户)
人员组与主机组是对人员与主机的管理对象
红色与紫色的连接线表示了绑定的含义,通过绑定五类对象(人员、人员组、"通道"、主机、主机组)实现用户登录授权
而绑定后构成的通路中会有用户的操作请求数据和主机的结果响应数据,这两类数据构成了审计的主体内容

未完待续,持续更新中...
PyYaml模块的使用
import yaml try:
from yaml import CLoader as Loader, CDumper as Dumper
except ImportError:
from yaml import Loader, Dumper def print_err(msg, quit=False):
output = "\033[31;1mError: %s\033[0m" % msg
if quit:
exit(output)
else:
print(output) def yaml_parser(yml_filename):
'''
load yaml file and return
:param yml_filename:
:return:
'''
# yml_filename = "%s/%s.yml" % (settings.StateFileBaseDir,yml_filename)
try:
yaml_file = open(yml_filename, 'r')
data = yaml.load(yaml_file)
return data
except Exception as e:
print_err(e)
PyYaml示例
http://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation
YAML syntax
A good introduction to the YAML syntax is Chapter 2 of the YAML specification.
You may also check the YAML cookbook. Note that it is focused on a Ruby implementation and uses the old YAML 1.0 syntax.
Here we present most common YAML constructs together with the corresponding Python objects.
Documents
YAML stream is a collection of zero or more documents. An empty stream contains no documents. Documents are separated with ---. Documents may optionally end with .... A single document may or may not be marked with ---.
Example of an implicit document:
- Multimedia
- Internet
- Education
Example of an explicit document:
---
- Afterstep
- CTWM
- Oroborus
...
Example of several documents in the same stream:
---
- Ada
- APL
- ASP - Assembly
- Awk
---
- Basic
---
- C
- C# # Note that comments are denoted with ' #' (space then #).
- C++
- Cold Fusion
Block sequences
In the block context, sequence entries are denoted by - (dash then space):
# YAML
- The Dagger 'Narthanc'
- The Dagger 'Nimthanc'
- The Dagger 'Dethanc'
# Python
["The Dagger 'Narthanc'", "The Dagger 'Nimthanc'", "The Dagger 'Dethanc'"]
Block sequences can be nested:
# YAML
-
- HTML
- LaTeX
- SGML
- VRML
- XML
- YAML
-
- BSD
- GNU Hurd
- Linux
# Python
[['HTML', 'LaTeX', 'SGML', 'VRML', 'XML', 'YAML'], ['BSD', 'GNU Hurd', 'Linux']]
It's not necessary to start a nested sequence with a new line:
# YAML
- 1.1
- - 2.1
- 2.2
- - - 3.1
- 3.2
- 3.3
# Python
[1.1, [2.1, 2.2], [[3.1, 3.2, 3.3]]]
A block sequence may be nested to a block mapping. Note that in this case it is not necessary to indent the sequence.
# YAML
left hand:
- Ring of Teleportation
- Ring of Speed right hand:
- Ring of Resist Fire
- Ring of Resist Cold
- Ring of Resist Poison
# Python
{'right hand': ['Ring of Resist Fire', 'Ring of Resist Cold', 'Ring of Resist Poison'],
'left hand': ['Ring of Teleportation', 'Ring of Speed']}
Block mappings
In the block context, keys and values of mappings are separated by : (colon then space):
# YAML
base armor class: 0
base damage: [4,4]
plus to-hit: 12
plus to-dam: 16
plus to-ac: 0
# Python
{'plus to-hit': 12, 'base damage': [4, 4], 'base armor class': 0, 'plus to-ac': 0, 'plus to-dam': 16}
Complex keys are denoted with ? (question mark then space):
# YAML
? !!python/tuple [0,0]
: The Hero
? !!python/tuple [0,1]
: Treasure
? !!python/tuple [1,0]
: Treasure
? !!python/tuple [1,1]
: The Dragon
# Python
{(0, 1): 'Treasure', (1, 0): 'Treasure', (0, 0): 'The Hero', (1, 1): 'The Dragon'}
Block mapping can be nested:
# YAML
hero:
hp: 34
sp: 8
level: 4
orc:
hp: 12
sp: 0
level: 2
# Python
{'hero': {'hp': 34, 'sp': 8, 'level': 4}, 'orc': {'hp': 12, 'sp': 0, 'level': 2}}
A block mapping may be nested in a block sequence:
# YAML
- name: PyYAML
status: 4
license: MIT
language: Python
- name: PySyck
status: 5
license: BSD
language: Python
# Python
[{'status': 4, 'language': 'Python', 'name': 'PyYAML', 'license': 'MIT'},
{'status': 5, 'license': 'BSD', 'name': 'PySyck', 'language': 'Python'}]
Flow collections
The syntax of flow collections in YAML is very close to the syntax of list and dictionary constructors in Python:
# YAML
{ str: [15, 17], con: [16, 16], dex: [17, 18], wis: [16, 16], int: [10, 13], chr: [5, 8] }
# Python
{'dex': [17, 18], 'int': [10, 13], 'chr': [5, 8], 'wis': [16, 16], 'str': [15, 17], 'con': [16, 16]}
Scalars
There are 5 styles of scalars in YAML: plain, single-quoted, double-quoted, literal, and folded:
# YAML
plain: Scroll of Remove Curse
single-quoted: 'EASY_KNOW'
double-quoted: "?"
literal: | # Borrowed from http://www.kersbergen.com/flump/religion.html
by hjw ___
__ /.-.\
/ )_____________\\ Y
/_ /=== == === === =\ _\_
( /)=== == === === == Y \
`-------------------( o )
\___/
folded: >
It removes all ordinary curses from all equipped items.
Heavy or permanent curses are unaffected.
# Python
{'plain': 'Scroll of Remove Curse',
'literal':
'by hjw ___\n'
' __ /.-.\\\n'
' / )_____________\\\\ Y\n'
' /_ /=== == === === =\\ _\\_\n'
'( /)=== == === === == Y \\\n'
' `-------------------( o )\n'
' \\___/\n',
'single-quoted': 'EASY_KNOW',
'double-quoted': '?',
'folded': 'It removes all ordinary curses from all equipped items. Heavy or permanent curses are unaffected.\n'}
Each style has its own quirks. A plain scalar does not use indicators to denote its start and end, therefore it's the most restricted style. Its natural applications are names of attributes and parameters.
Using single-quoted scalars, you may express any value that does not contain special characters. No escaping occurs for single quoted scalars except that a pair of adjacent quotes '' is replaced with a lone single quote '.
Double-quoted is the most powerful style and the only style that can express any scalar value. Double-quoted scalars allow escaping. Using escaping sequences \x** and \u****, you may express any ASCII or Unicode character.
There are two kind of block scalar styles: literal and folded. The literal style is the most suitable style for large block of text such as source code. The folded style is similar to the literal style, but two adjacent non-empty lines are joined to a single line separated by a space character.
Aliases
Note that PyYAML does not yet support recursive objects.
Using YAML you may represent objects of arbitrary graph-like structures. If you want to refer to the same object from different parts of a document, you need to use anchors and aliases.
Anchors are denoted by the & indicator while aliases are denoted by *. For instance, the document
left hand: &A
name: The Bastard Sword of Eowyn
weight: 30
right hand: *A
expresses the idea of a hero holding a heavy sword in both hands.
PyYAML now fully supports recursive objects. For instance, the document
&A [ *A ]
will produce a list object containing a reference to itself.
Tags
Tags are used to denote the type of a YAML node. Standard YAML tags are defined at http://yaml.org/type/index.html.
Tags may be implicit:
boolean: true
integer: 3
float: 3.14
{'boolean': True, 'integer': 3, 'float': 3.14}
or explicit:
boolean: !!bool "true"
integer: !!int "3"
float: !!float "3.14"
{'boolean': True, 'integer': 3, 'float': 3.14}
Plain scalars without explicitly defined tags are subject to implicit tag resolution. The scalar value is checked against a set of regular expressions
and if one of them matches, the corresponding tag is assigned to the scalar. PyYAML allows an application to add custom implicit tag resolvers.
YAML tags and Python types
The following table describes how nodes with different tags are converted to Python objects.
| YAML tag | Python type |
| Standard YAML tags | |
| !!null | None |
| !!bool | bool |
| !!int | int or long (int in Python 3) |
| !!float | float |
| !!binary | str (bytes in Python 3) |
| !!timestamp | datetime.datetime |
| !!omap, !!pairs | list of pairs |
| !!set | set |
| !!str | str or unicode (str in Python 3) |
| !!seq | list |
| !!map | dict |
| Python-specific tags | |
| !!python/none | None |
| !!python/bool | bool |
| !!python/bytes | (bytes in Python 3) |
| !!python/str | str (str in Python 3) |
| !!python/unicode | unicode (str in Python 3) |
| !!python/int | int |
| !!python/long | long (int in Python 3) |
| !!python/float | float |
| !!python/complex | complex |
| !!python/list | list |
| !!python/tuple | tuple |
| !!python/dict | dict |
| Complex Python tags | |
| !!python/name:module.name | module.name |
| !!python/module:package.module | package.module |
| !!python/object:module.cls | module.cls instance |
| !!python/object/new:module.cls | module.cls instance |
| !!python/object/apply:module.f | value of f(...) |
String conversion (Python 2 only)
There are four tags that are converted to str and unicode values: !!str, !!binary, !!python/str, and !!python/unicode.
!!str-tagged scalars are converted to str objects if its value is ASCII. Otherwise it is converted to unicode. !!binary-tagged scalars are converted to str objects with its value decoded using the base64 encoding. !!python/str scalars are converted to str objects encoded with utf-8 encoding. !!python/unicode scalars are converted to unicode objects.
Conversely, a str object is converted to
- a !!str scalar if its value is ASCII.
- a !!python/str scalar if its value is a correct utf-8 sequence.
- a !!binary scalar otherwise.
A unicode object is converted to
- a !!python/unicode scalar if its value is ASCII.
- a !!str scalar otherwise.
String conversion (Python 3 only)
In Python 3, str objects are converted to !!str scalars and bytes objects to !!binary scalars. For compatibility reasons, tags !!python/str and !!python/unicode are still supported and converted to str objects.
Names and modules
In order to represent static Python objects like functions or classes, you need to use a complex !!python/name tag. For instance, the function yaml.dump can be represented as
!!python/name:yaml.dump
Similarly, modules are represented using the tag !python/module:
!!python/module:yaml
Objects
Any pickleable object can be serialized using the !!python/object tag:
!!python/object:module.Class { attribute: value, ... }
In order to support the pickle protocol, two additional forms of the !!python/object tag are provided:
!!python/object/new:module.Class
args: [argument, ...]
kwds: {key: value, ...}
state: ...
listitems: [item, ...]
dictitems: [key: value, ...]
!!python/object/apply:module.function
args: [argument, ...]
kwds: {key: value, ...}
state: ...
listitems: [item, ...]
dictitems: [key: value, ...]
If only the args field is non-empty, the above records can be shortened:
!!python/object/new:module.Class [argument, ...]
!!python/object/apply:module.function [argument, ...]
Reference
Warning: API stability is not guaranteed'''
The yaml package
scan(stream, Loader=Loader)
scan(stream) scans the given stream and produces a sequence of tokens.
parse(stream, Loader=Loader) emit(events, stream=None, Dumper=Dumper,
canonical=None,
indent=None,
width=None,
allow_unicode=None,
line_break=None)
parse(stream) parses the given stream and produces a sequence of parsing events.
emit(events, stream=None) serializes the given sequence of parsing events and writes them to the stream. if stream is None, it returns the produced stream.
compose(stream, Loader=Loader)
compose_all(stream, Loader=Loader) serialize(node, stream=None, Dumper=Dumper,
encoding='utf-8', # encoding=None (Python 3)
explicit_start=None,
explicit_end=None,
version=None,
tags=None,
canonical=None,
indent=None,
width=None,
allow_unicode=None,
line_break=None)
serialize_all(nodes, stream=None, Dumper=Dumper, ...)
compose(stream) parses the given stream and returns the root of the representation graph for the first document in the stream. If there are no documents in the stream, it returns None.
compose_all(stream) parses the given stream and returns a sequence of representation graphs corresponding to the documents in the stream.
serialize(node, stream=None) serializes the given representation graph into the stream. If stream is None, it returns the produced stream.
serialize_all(node, stream=None) serializes the given sequence of representation graphs into the given stream. If stream is None, it returns the produced stream.
load(stream, Loader=Loader)
load_all(stream, Loader=Loader) safe_load(stream)
safe_load_all(stream) dump(data, stream=None, Dumper=Dumper,
default_style=None,
default_flow_style=None,
encoding='utf-8', # encoding=None (Python 3)
explicit_start=None,
explicit_end=None,
version=None,
tags=None,
canonical=None,
indent=None,
width=None,
allow_unicode=None,
line_break=None)
dump_all(data, stream=None, Dumper=Dumper, ...) safe_dump(data, stream=None, ...)
safe_dump_all(data, stream=None, ...)
load(stream) parses the given stream and returns a Python object constructed from for the first document in the stream. If there are no documents in the stream, it returns None.
load_all(stream) parses the given stream and returns a sequence of Python objects corresponding to the documents in the stream.
safe_load(stream) parses the given stream and returns a Python object constructed from for the first document in the stream. If there are no documents in the stream, it returns None. safe_load recognizes only standard YAML tags and cannot construct an arbitrary Python object.
A python object can be marked as safe and thus be recognized by yaml.safe_load. To do this, derive it from yaml.YAMLObject (as explained in section Constructors, representers, resolvers) and explicitly set its class property yaml_loader to yaml.SafeLoader.
safe_load_all(stream) parses the given stream and returns a sequence of Python objects corresponding to the documents in the stream. safe_load_all recognizes only standard YAML tags and cannot construct an arbitrary Python object.
dump(data, stream=None) serializes the given Python object into the stream. If stream is None, it returns the produced stream.
dump_all(data, stream=None) serializes the given sequence of Python objects into the given stream. If stream is None, it returns the produced stream. Each object is represented as a YAML document.
safe_dump(data, stream=None) serializes the given Python object into the stream. If stream is None, it returns the produced stream. safe_dump produces only standard YAML tags and cannot represent an arbitrary Python object.
safe_dump_all(data, stream=None) serializes the given sequence of Python objects into the given stream. If stream is None, it returns the produced stream. Each object is represented as a YAML document. safe_dump_all produces only standard YAML tags and cannot represent an arbitrary Python object.
def constructor(loader, node):
# ...
return data def multi_constructor(loader, tag_suffix, node):
# ...
return data add_constructor(tag, constructor, Loader=Loader)
add_multi_constructor(tag_prefix, multi_constructor, Loader=Loader)
add_constructor(tag, constructor) specifies a constructor for the given tag. A constructor is a function that converts a node of a YAML representation graph to a native Python object. A constructor accepts an instance of Loader and a node and returns a Python object.
add_multi_constructor(tag_prefix, multi_constructor) specifies a multi_constructor for the given tag_prefix. A multi-constructor is a function that converts a node of a YAML representation graph to a native Python object. A multi-constructor accepts an instance of Loader, the suffix of the node tag, and a node and returns a Python object.
def representer(dumper, data):
# ...
return node def multi_representer(dumper, data):
# ...
return node add_representer(data_type, representer, Dumper=Dumper)
add_multi_representer(base_data_type, multi_representer, Dumper=Dumper)
add_representer(data_type, representer) specifies a representer for Python objects of the given data_type. A representer is a function that converts a native Python object to a node of a YAML representation graph. A representer accepts an instance of Dumper and an object and returns a node.
add_multi_representer(base_data_type, multi_representer) specifies a multi_representer for Python objects of the given base_data_type or any of its subclasses. A multi-representer is a function that converts a native Python object to a node of a YAML representation graph. A multi-representer accepts an instance of Dumper and an object and returns a node.
add_implicit_resolver(tag, regexp, first, Loader=Loader, Dumper=Dumper)
add_path_resolver(tag, path, kind, Loader=Loader, Dumper=Dumper)
add_implicit_resolver(tag, regexp, first) adds an implicit tag resolver for plain scalars. If the scalar value is matched the given regexp, it is assigned the tag. first is a list of possible initial characters or None.
add_path_resolver(tag, path, kind) adds a path-based implicit tag resolver. A path is a list of keys that form a path to a node in the representation graph. Paths elements can be string values, integers, or None. The kind of a node can be str, list, dict, or None.
Mark
Mark(name, index, line, column, buffer, pointer)
An instance of Mark points to a certain position in the input stream. name is the name of the stream, for instance it may be the filename if the input stream is a file. line and column is the line and column of the position (starting from 0). buffer, when it is not None, is a part of the input stream that contain the position and pointer refers to the position in the buffer.
YAMLError
YAMLError()
If the YAML parser encounters an error condition, it raises an exception which is an instance of YAMLError or of its subclass. An application may catch this exception and warn a user.
try:
config = yaml.load(file('config.yaml', 'r'))
except yaml.YAMLError, exc:
print "Error in configuration file:", exc
An exception produced by the YAML processor may point to the problematic position.
>>> try:
... yaml.load("unbalanced blackets: ][")
... except yaml.YAMLError, exc:
... if hasattr(exc, 'problem_mark'):
... mark = exc.problem_mark
... print "Error position: (%s:%s)" % (mark.line+1, mark.column+1) Error position: (1:22)
Tokens
Tokens are produced by a YAML scanner. They are not really useful except for low-level YAML applications such as syntax highlighting.
The PyYAML scanner produces the following types of tokens:
StreamStartToken(encoding, start_mark, end_mark) # Start of the stream.
StreamEndToken(start_mark, end_mark) # End of the stream.
DirectiveToken(name, value, start_mark, end_mark) # YAML directive, either %YAML or %TAG.
DocumentStartToken(start_mark, end_mark) # '---'.
DocumentEndToken(start_mark, end_mark) # '...'.
BlockSequenceStartToken(start_mark, end_mark) # Start of a new block sequence.
BlockMappingStartToken(start_mark, end_mark) # Start of a new block mapping.
BlockEndToken(start_mark, end_mark) # End of a block collection.
FlowSequenceStartToken(start_mark, end_mark) # '['.
FlowMappingStartToken(start_mark, end_mark) # '{'.
FlowSequenceEndToken(start_mark, end_mark) # ']'.
FlowMappingEndToken(start_mark, end_mark) # '}'.
KeyToken(start_mark, end_mark) # Either '?' or start of a simple key.
ValueToken(start_mark, end_mark) # ':'.
BlockEntryToken(start_mark, end_mark) # '-'.
FlowEntryToken(start_mark, end_mark) # ','.
AliasToken(value, start_mark, end_mark) # '*value'.
AnchorToken(value, start_mark, end_mark) # '&value'.
TagToken(value, start_mark, end_mark) # '!value'.
ScalarToken(value, plain, style, start_mark, end_mark) # 'value'.
start_mark and end_mark denote the beginning and the end of a token.
Example:
>>> document = """
... ---
... block sequence:
... - BlockEntryToken
... block mapping:
... ? KeyToken
... : ValueToken
... flow sequence: [FlowEntryToken, FlowEntryToken]
... flow mapping: {KeyToken: ValueToken}
... anchors and tags:
... - &A !!int '5'
... - *A
... ...
... """ >>> for token in yaml.scan(document):
... print token StreamStartToken(encoding='utf-8') DocumentStartToken() BlockMappingStartToken() KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'block sequence') ValueToken()
BlockEntryToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'BlockEntryToken') KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'block mapping') ValueToken()
BlockMappingStartToken() KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'KeyToken')
ValueToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'ValueToken')
BlockEndToken() KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'flow sequence') ValueToken()
FlowSequenceStartToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'FlowEntryToken')
FlowEntryToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'FlowEntryToken')
FlowSequenceEndToken() KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'flow mapping') ValueToken()
FlowMappingStartToken()
KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'KeyToken')
ValueToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'ValueToken')
FlowMappingEndToken() KeyToken()
ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value=u'anchors and tags') ValueToken()
BlockEntryToken()
AnchorToken(value=u'A')
TagToken(value=(u'!!', u'int'))
ScalarToken(plain=False, style="'", value=u'5') BlockEntryToken()
AliasToken(value=u'A') BlockEndToken() DocumentEndToken() StreamEndToken()
Events
Events are used by the low-level Parser and Emitter interfaces, which are similar to the SAX API. While the Parser parses a YAML stream and produces a sequence of events, the Emitter accepts a sequence of events and emits a YAML stream.
The following events are defined:
StreamStartEvent(encoding, start_mark, end_mark)
StreamEndEvent(start_mark, end_mark)
DocumentStartEvent(explicit, version, tags, start_mark, end_mark)
DocumentEndEvent(start_mark, end_mark)
SequenceStartEvent(anchor, tag, implicit, flow_style, start_mark, end_mark)
SequenceEndEvent(start_mark, end_mark)
MappingStartEvent(anchor, tag, implicit, flow_style, start_mark, end_mark)
MappingEndEvent(start_mark, end_mark)
AliasEvent(anchor, start_mark, end_mark)
ScalarEvent(anchor, tag, implicit, value, style, start_mark, end_mark)
The flow_style flag indicates if a collection is block or flow. The possible values are None, True, False. The style flag of a scalar event indicates the style of the scalar. Possible values are None, '', '\'', '"', '|', '>'. The implicit flag of a collection start event indicates if the tag may be omitted when the collection is emitted. The implicit flag of a scalar event is a pair of boolean values that indicate if the tag may be omitted when the scalar is emitted in a plain and non-plain style correspondingly.
Example:
>>> document = """
... scalar: &A !!int '5'
... alias: *A
... sequence: [1, 2, 3]
... mapping: [1: one, 2: two, 3: three]
... """ >>> for event in yaml.parse(document):
... print event StreamStartEvent() DocumentStartEvent() MappingStartEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=True) ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'scalar')
ScalarEvent(anchor=u'A', tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:int', implicit=(False, False), value=u'5') ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'alias')
AliasEvent(anchor=u'A') ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'sequence')
SequenceStartEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=True)
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'1')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'2')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'3')
SequenceEndEvent() ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'mapping')
MappingStartEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=True)
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'1')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'one')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'2')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'two')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'3')
ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=None, implicit=(True, False), value=u'three')
MappingEndEvent() MappingEndEvent() DocumentEndEvent() StreamEndEvent() >>> print yaml.emit([
... yaml.StreamStartEvent(encoding='utf-8'),
... yaml.DocumentStartEvent(explicit=True),
... yaml.MappingStartEvent(anchor=None, tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:map', implicit=True, flow_style=False),
... yaml.ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', implicit=(True, True), value=u'agile languages'),
... yaml.SequenceStartEvent(anchor=None, tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:seq', implicit=True, flow_style=True),
... yaml.ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', implicit=(True, True), value=u'Python'),
... yaml.ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', implicit=(True, True), value=u'Perl'),
... yaml.ScalarEvent(anchor=None, tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', implicit=(True, True), value=u'Ruby'),
... yaml.SequenceEndEvent(),
... yaml.MappingEndEvent(),
... yaml.DocumentEndEvent(explicit=True),
... yaml.StreamEndEvent(),
... ]) ---
agile languages: [Python, Perl, Ruby]
...
Nodes
Nodes are entities in the YAML informational model. There are three kinds of nodes: scalar, sequence, and mapping. In PyYAML, nodes are produced by Composer and can be serialized to a YAML stream by Serializer.
ScalarNode(tag, value, style, start_mark, end_mark)
SequenceNode(tag, value, flow_style, start_mark, end_mark)
MappingNode(tag, value, flow_style, start_mark, end_mark)
The style and flow_style flags have the same meaning as for events. The value of a scalar node must be a unicode string. The value of a sequence node is a list of nodes. The value of a mapping node is a list of pairs consisting of key and value nodes.
Example:
>>> print yaml.compose("""
... kinds:
... - scalar
... - sequence
... - mapping
... """)
MappingNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:map', value=[
(ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'kinds'), SequenceNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:seq', value=[
ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'scalar'),
ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'sequence'),
ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'mapping')]))])
>>> print yaml.serialize(yaml.SequenceNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:seq', value=[
... yaml.ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'scalar'),
... yaml.ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'sequence'),
... yaml.ScalarNode(tag=u'tag:yaml.org,2002:str', value=u'mapping')]))
- scalar
- sequence
- mapping
Loader
Loader(stream)
SafeLoader(stream)
BaseLoader(stream) # The following classes are available only if you build LibYAML bindings.
CLoader(stream)
CSafeLoader(stream)
CBaseLoader(stream)
Loader(stream) is the most common of the above classes and should be used in most cases. stream is an input YAML stream. It can be a string, a Unicode string, an open file, an open Unicode file.
Loader supports all predefined tags and may construct an arbitrary Python object. Therefore it is not safe to use Loader to load a document received from an untrusted source. By default, the functions scan, parse, compose, construct, and others use Loader.
SafeLoader(stream) supports only standard YAML tags and thus it does not construct class instances and probably safe to use with documents received from an untrusted source. The functions safe_load and safe_load_all use SafeLoader to parse a stream.
BaseLoader(stream) does not resolve or support any tags and construct only basic Python objects: lists, dictionaries and Unicode strings.
CLoader, CSafeLoader, CBaseLoader are versions of the above classes written in C using the LibYAML library.
Loader.check_token(*TokenClasses)
Loader.peek_token()
Loader.get_token()
Loader.check_token(*TokenClasses) returns True if the next token in the stream is an instance of one of the given TokenClasses. Otherwise it returns False.
Loader.peek_token() returns the next token in the stream, but does not remove it from the internal token queue. The function returns None at the end of the stream.
Loader.get_token() returns the next token in the stream and removes it from the internal token queue. The function returns None at the end of the stream.
Loader.check_event(*EventClasses)
Loader.peek_event()
Loader.get_event()
Loader.check_event(*EventClasses) returns True if the next event in the stream is an instance of one of the given EventClasses. Otherwise it returns False.
Loader.peek_event() returns the next event in the stream, but does not remove it from the internal event queue. The function returns None at the end of the stream.
Loader.get_event() returns the next event in the stream and removes it from the internal event queue. The function returns None at the end of the stream.
Loader.check_node()
Loader.get_node()
Loader.check_node() returns True is there are more documents available in the stream. Otherwise it returns False.
Loader.get_node() construct the representation graph of the next document in the stream and returns its root node.
Loader.check_data()
Loader.get_data() Loader.add_constructor(tag, constructor) # Loader.add_constructor is a class method.
Loader.add_multi_constructor(tag_prefix, multi_constructor) # Loader.add_multi_constructor is a class method. Loader.construct_scalar(node)
Loader.construct_sequence(node)
Loader.construct_mapping(node)
Loader.check_data() returns True is there are more documents available in the stream. Otherwise it returns False.
Loader.get_data() constructs and returns a Python object corresponding to the next document in the stream.
Loader.add_constructor(tag, constructor): see add_constructor.
Loader.add_multi_constructor(tag_prefix, multi_constructor): see add_multi_constructor.
Loader.construct_scalar(node) checks that the given node is a scalar and returns its value. This function is intended to be used in constructors.
Loader.construct_sequence(node) checks that the given node is a sequence and returns a list of Python objects corresponding to the node items. This function is intended to be used in constructors.
Loader.construct_mapping(node) checks that the given node is a mapping and returns a dictionary of Python objects corresponding to the node keys and values. This function is intended to be used in constructors.
Loader.add_implicit_resolver(tag, regexp, first) # Loader.add_implicit_resolver is a class method.
Loader.add_path_resolver(tag, path, kind) # Loader.add_path_resolver is a class method.
Loader.add_implicit_resolver(tag, regexp, first): see add_implicit_resolver.
Loader.add_path_resolver(tag, path, kind): see add_path_resolver.
Dumper
Dumper(stream,
default_style=None,
default_flow_style=None,
canonical=None,
indent=None,
width=None,
allow_unicode=None,
line_break=None,
encoding=None,
explicit_start=None,
explicit_end=None,
version=None,
tags=None)
SafeDumper(stream, ...)
BaseDumper(stream, ...) # The following classes are available only if you build LibYAML bindings.
CDumper(stream, ...)
CSafeDumper(stream, ...)
CBaseDumper(stream, ...)
Dumper(stream) is the most common of the above classes and should be used in most cases. stream is an output YAML stream. It can be an open file or an open Unicode file.
Dumper supports all predefined tags and may represent an arbitrary Python object. Therefore it may produce a document that cannot be loaded by other YAML processors. By default, the functions emit, serialize, dump, and others use Dumper.
SafeDumper(stream) produces only standard YAML tags and thus cannot represent class instances and probably more compatible with other YAML processors. The functions safe_dump and safe_dump_all use SafeDumper to produce a YAML document.
BaseDumper(stream) does not support any tags and is useful only for subclassing.
CDumper, CSafeDumper, CBaseDumper are versions of the above classes written in C using the LibYAML library.
Dumper.emit(event)
Dumper.emit(event) serializes the given event and writes it to the output stream.
Dumper.open()
Dumper.serialize(node)
Dumper.close()
Dumper.open() emits StreamStartEvent.
Dumper.serialize(node) serializes the given representation graph into the output stream.
Dumper.close() emits StreamEndEvent.
Dumper.represent(data) Dumper.add_representer(data_type, representer) # Dumper.add_representer is a class method.
Dumper.add_multi_representer(base_data_type, multi_representer) # Dumper.add_multi_representer is a class method. Dumper.represent_scalar(tag, value, style=None)
Dumper.represent_sequence(tag, value, flow_style=None)
Dumper.represent_mapping(tag, value, flow_style=None)
Dumper.represent(data) serializes the given Python object to the output YAML stream.
Dumper.add_representer(data_type, representer): see add_representer.
Dumper.add_multi_representer(base_data_type, multi_representer): see add_multi_representer.
Dumper.represent_scalar(tag, value, style=None) returns a scalar node with the given tag, value, and style. This function is intended to be used in representers.
Dumper.represent_sequence(tag, sequence, flow_style=None) return a sequence node with the given tag and subnodes generated from the items of the given sequence.
Dumper.represent_mapping(tag, mapping, flow_style=None) return a mapping node with the given tag and subnodes generated from the keys and values of the given mapping.
Dumper.add_implicit_resolver(tag, regexp, first) # Dumper.add_implicit_resolver is a class method.
Dumper.add_path_resolver(tag, path, kind) # Dumper.add_path_resolver is a class method.
Dumper.add_implicit_resolver(tag, regexp, first): see add_implicit_resolver.
Dumper.add_path_resolver(tag, path, kind): see add_path_resolver.
YAMLObject
class MyYAMLObject(YAMLObject):
yaml_loader = Loader
yaml_dumper = Dumper yaml_tag = u'...'
yaml_flow_style = ... @classmethod
def from_yaml(cls, loader, node):
# ...
return data @classmethod
def to_yaml(cls, dumper, data):
# ...
return node
Subclassing YAMLObject is an easy way to define tags, constructors, and representers for your classes. You only need to override the yaml_tag attribute. If you want to define your custom constructor and representer, redefine the from_yaml and to_yaml method correspondingly.
Deviations from the specification
need to update this section
- rules for tabs in YAML are confusing. We are close, but not there yet. Perhaps both the spec and the parser should be fixed. Anyway, the best rule for tabs in YAML is to not use them at all.
- Byte order mark. The initial BOM is stripped, but BOMs inside the stream are considered as parts of the content. It can be fixed, but it's not really important now.
Empty plain scalars are not allowed if alias or tag is specified.This is done to prevent anomalities like [ !tag, value], which can be interpreted both as [ !<!tag,> value ] and [ !<!tag> "", "value" ]. The spec should be fixed.- Indentation of flow collections. The spec requires them to be indented more than their block parent node. Unfortunately this rule renders many intuitively correct constructs invalid, for instance,
block: {
} # this is indentation violation according to the spec. - ':' is not allowed for plain scalars in the flow mode.
{1:2} is interpreted as { 1 : 2 }.
那些年被我坑过的Python——一夫当关 第十三章(堡垒机初步设计)的更多相关文章
- python学习笔记-(十三)堡垒机
1.课前准备: 本次学习堡垒机相关知识:之前,需要安装Python的paramiko模块,该模块基于SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作. 前提: python3.5程序安装到默认路径下并已添加pa ...
- python第七十六天--堡垒机完成
堡垒机windows ,linux 都通过测试初始化说明: #进入根目录 1.初始化表结构 #python3 bin/start.py syncdb 2.创建堡垒机用户 #python3 bin/st ...
- python 教程 第十三章、 特殊的方法
第十三章. 特殊的方法 1) 特殊的方法 __init__(self,...) 这个方法在新建对象恰好要被返回使用之前被调用. __del__(self) 恰好在对象要被删除之前调用. __st ...
- 那些年被我坑过的Python——你来我往(第九章 selectors)
进程.线程.协程(微线程).队列的概念理解 进程进程是所有相关资源的集合,而线程是和CPU交互的最小单元进程至少包含一个线程,是主线程线程线程之间可以共享资源线程同时修改同一份数据时必须加锁,mute ...
- 进击的Python【第十三章】:Web前端基础之HTML与CSS样式
进击的Python[第十四章]:Web前端基础之HTML与CSS样式 一.web框架的本质 众所周知,对于所有的Web应用,本质上其实就是一个socket服务端,用户的浏览器其实就是一个socket客 ...
- Python成长笔记 - 基础篇 (十三)--堡垒机
堡垒机架构 堡垒机的主要作用权限控制和用户行为审计,堡垒机就像一个城堡的大门,城堡里的所有建筑就是你不同的业务系统 , 每个想进入城堡的人都必须经过城堡大门并经过大门守卫的授权,每个进入城堡的人必须且 ...
- 进击的Python【第十七章】:jQuery的基本应用
进击的Python[第十七章]:jQuery的基本应用
- Python之路第一课Day9--随堂笔记之一(堡垒机实例以及数据库操作)未完待续....
一.堡垒机前戏 开发堡垒机之前,先来学习Python的paramiko模块,该模块机遇SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作 SSHClient 用于连接远程服务器并执行基本命令 基于用户名密码连接: ...
- Python之路:堡垒机实例
堡垒机前戏 开发堡垒机之前,先来学习Python的paramiko模块,该模块机遇SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作 SSHClient 用于连接远程服务器并执行基本命令 基于用户名密码连接: 1 ...
随机推荐
- 406. Queue Reconstruction by Height
一开始backtrack,设计了很多剪枝情况,还是TLE了 ..后来用PQ做的. 其实上面DFS做到一半的时候意识到应该用PQ做,但是不确定会不会TLE,就继续了,然后果然TLE了.. PQ的做法和剪 ...
- linux 监控命令
先总结下常用的一些监控工具: ##linux命令 w 系统负载 lsof -p pid 进程打开的文件 lsof -i:port 端口的运行情况 free -m 内存情况 vmstat 进程.内存.内 ...
- TortoiseSVN搭建本地版本库及简单操作使用
TortoiseSVN是windows上一款著名的版本控制软件,对于我们管理自己的代码,特别是对一个团队来说,非常重要. 本文探讨的是如何搭建本地的版本库. (1)安装TortoiseSVN之后需要创 ...
- Cubieboard 开箱和入门 | Name5566 分类: cubieboard 2014-11-08 17:27 251人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Cubieboard 开箱和入门 2014 年 01 月 29 日 by name5566 Categories: Computer Science, Cubieboard Hello Cubiebo ...
- 用.class文件创建对象
第一步: 给你一个编译好的class文件以及它的包名,创建一个对象出来. 1)class文件源代码 package com.wsc.classloader; public class Tool{ p ...
- 实战DeviceIoControl 之中的一个:通过API訪问设备驱动程序
P.bhw98 { PADDING-RIGHT: 0px; PADDING-LEFT: 0px; FONT-SIZE: 9pt; PADDING-BOTTOM: 0px; MARGIN: 10px 0 ...
- Android如何创建背景透明的Dialog
一:控制Dialog 的背景方法:1.定义一个无背景主题主题<!--去掉背景Dialog--> <style name="NobackDialog" parent ...
- java EE 学习
http://blog.csdn.net/liushuijinger/article/category/1342030/1
- spring beans源码解读之--BeanFactory进化史
BeanFactory是访问bean容器的根接口,它是一个bean容器的基本客户端视图. 先让我们看看beanfactory的前生后世吧! beanFactory有四个重要的子接口: SimpleJn ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记46:Set集合之TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习2(自然排序:Comparable)
1. TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习2: (1)Student.java package cn.itcast_06; /* * 如果一个类的元素要想能够进行自然排序,就必须实现自然排序接口 * ...
