python学习之路-12
线程池
上下文管理
- 线程池中关于上下文管理的相关代码 点我查看更详细的上下文管理介绍
import contextlib
@contextlib.contextmanager
def worker_state(state_list, worker_thread):
"""
用户记录线程中正在等待的线程数
:param state_list:
:param worker_thread:
:return:
"""
state_list.append(worker_thread)
try:
yield
finally:
state_list.remove(worker_thread)
free_list = []
current_thread = "aaa"
with worker_state(free_list, current_thread):
print(123)
print(456)
- socket_server 之上下文管理
import contextlib
import socket
@contextlib.contextmanager
def context_socket(host, port):
sk = socket.socket()
sk.bind((host, port))
sk.listen(5)
try:
yield sk
finally:
sk.close()
with context_socket("127.0.0.1", 8888) as sock:
sock.sendall(bytes("hehe", encoding="utf-8"))
redis
redis连接池
redis自定义列表
redis事务操作
redis发布订阅
- 创建发布订阅类
# release_subscription.py
import redis
class RedisHelper:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(**kwargs)
self.__conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
def release(self, msg, channel):
"""
redis发布端
:param msg: 发送的内容
:param channel: # 发布的频道
:return:
"""
self.__conn.publish(channel, msg)
return True
def subscription(self, channel):
"""
redis订阅端
:param channel: # 订阅的频道
:return:
"""
pub = self.__conn.pubsub()
pub.subscribe(channel)
pub.parse_response()
return pub
- 实例化发布端
# redis_release.py
# 导入发布订阅模块
import release_subscription
obj = release_subscription.RedisHelper(host="127.0.0.1")
obj.release("hehe", "fm103.9")
- 实例化订阅端
# redis_sub.py
# 导入发布订阅模块
import release_subscription
obj = release_subscription.RedisHelper(host="127.0.0.1")
data = obj.subscription("fm103.9")
print(data.parse_response())
RabbitMQ
基于RabbitMQ实现的消息队列
- 生产者
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host="127.0.0.1"))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello') # 创建一个队列,如果存在则不产生任何效果
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello',
body='Hello World!') # 给队列发送消息 "Hello World!"
print(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
connection.close()
- 消费者
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='127.0.0.1'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback, # 回调函数, 如果从队列中取到数据之后则执行回调函数
queue='hello', # 队列名
no_ack=True)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
消息不丢失
- 如果消费者遇到情况(its channel is closed, connection is closed, or TCP connection is lost)挂掉了,那么,通过设置 no-ack=False,RabbitMQ会重新将该任务添加到队列中
# 消费者代码
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='10.211.55.4'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
import time
time.sleep(10)
print 'ok'
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=False) # 设置no_ack=False保证消息不丢失
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
- durable 消息不丢失
# 生产者代码
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='127.0.0.1'))
channel = connection.channel()
# make message persistent
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True) # 设置durable=True
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello',
body='Hello World!',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode=2, # make message persistent
))
print(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
connection.close()
# 消费者代码
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='127.0.0.1'))
channel = connection.channel()
# make message persistent
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True) # 设置durable=True
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
import time
time.sleep(10)
print 'ok'
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=False) # 设置no_ack=False
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
消费者消息获取顺序
# 默认情况下,消息队列里的数据是按照顺序被消费者拿走,例如:消费者1去队列中获取 奇数 序列的任务,消费者2去队列中获取偶数序列的任务
通过设置channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1) 表示谁来谁取,不再按照奇偶数排列
# 消费者端代码
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='10.211.55.4'))
channel = connection.channel()
# make message persistent
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
import time
time.sleep(10)
print 'ok'
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1) # 通过设置该参数,让消费者不按默认顺序取
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=False)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
发布订阅
发布订阅和简单的消息队列区别在于,发布订阅会将消息发送给所有的订阅者,而消息队列中的数据被消费一次便消失。所以,RabbitMQ实现发布和订阅时,会为每一个订阅者创建一个队列,而发布者发布消息时,会将消息放置在所有相关队列中。
通过设置exchange 和 type=fanout实现该功能
- 发布端
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='127.0.0.1'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout') # 通过设置exchange来与队列通信
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "info: Hello World!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange='logs',
routing_key='',
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
connection.close()
- 订阅端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='127.0.0.1'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout')
# 生成一个随机的queue
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
# 将queue与exchange绑定,发布端给exchange发消息的时候,与该exchange绑定的queue都会收到发布端发布的消息
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs',
queue=queue_name)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
发布订阅-关键字
上面的例子发送消息时明确指定某个队列并向其中发送消息,RabbitMQ还支持根据关键字发送,即队列绑定关键字,发送者将数据根据关键字发送到消息exchange,exchange根据关键字判定应该将数据发送至指定队列。
通过设置exchange 和 type = direct实现该功能
- 发布端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct')
severity = "info"
message = 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='direct_logs',
routing_key=severity,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (severity, message))
connection.close()
- 订阅端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
severities = ["info", "error"]
for severity in severities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='direct_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=severity) # 将exchange与关键字routing_key绑定
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
发布订阅-关键字模糊匹配
通过设置type=topic,可以让队列绑定几个模糊的关键字,之后发送者将数据发送到exchange,exchange将传入”路由值“和 ”关键字“进行匹配,匹配成功,则将数据发送到指定队列
# 表示可以匹配 0 个 或 多个 单词
* 表示只能匹配 一个 单词
发送者路由值 队列中
old.boy.python old.* -- 不匹配
old.boy.python old.# -- 匹配
- 发布端
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='127.0.0.1'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic')
routing_key = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'anonymous.info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='topic_logs',
routing_key=routing_key,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (routing_key, message))
connection.close()
- 订阅端
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
binding_keys = sys.argv[1:]
if not binding_keys:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [binding_key]...\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for binding_key in binding_keys:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='topic_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=binding_key)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
MySQL
PyMySQL
一、安装模块
pip install pymysql
二、使用
- 执行SQL(增删改操作)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数
effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2'")
# sql语句中有一个占位符
# 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数
# effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2' where nid > %s", (1,))
# sql语句中有多个占位符
# 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数
# effect_row = cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",1),("1.1.1.11",2)])
# 提交,不然无法保存新建或者修改的数据
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
- 插入数据的时候获取新创建数据自增ID
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",1),("1.1.1.11",2)])
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 获取最新自增ID
new_id = cursor.lastrowid
- 查询操作
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("select * from hosts")
# 获取第一行数据
row_1 = cursor.fetchone()
# 获取前n行数据
# row_2 = cursor.fetchmany(3)
# 获取所有数据
# row_3 = cursor.fetchall()
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 注:在fetch数据时按照顺序进行,可以使用cursor.scroll(num,mode)来移动游标位置,如:
cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动,将游标移动到下一个位置
cursor.scroll(-3,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动,将游标移动到上三个位置
cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 绝对位置移动,将游标移动到第2个位置
cursor.scroll(10,mode='absolute') # 绝对位置移动,将游标移动到第10个位置
- fetch数据类型
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1')
# 游标设置为字典类型
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
r = cursor.execute("select * from hosts")
result = cursor.fetchone() # 返回的是一个字典,以字段名为key,value为值
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
Python ORM --> SQLAchemy
SQLAlchemy是Python编程语言下的一款ORM框架,该框架建立在数据库API之上,使用关系对象映射进行数据库操作,简言之便是:将对象转换成SQL,然后使用数据API执行SQL并获取执行结果。
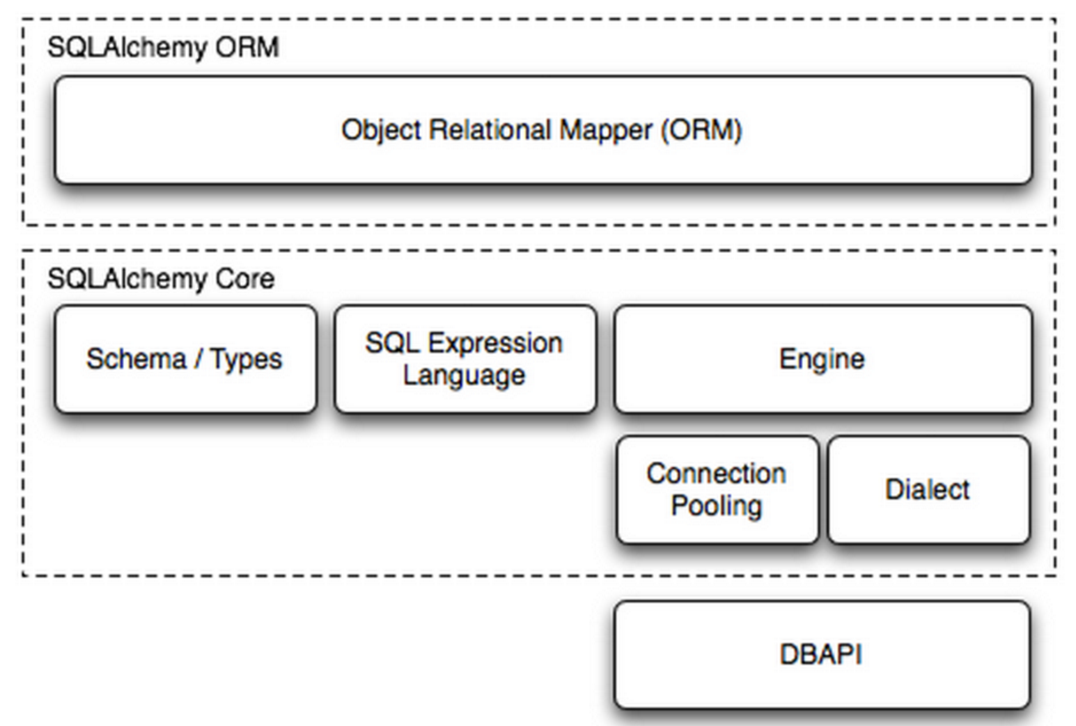
SQLAlchemy本身无法操作数据库,其必须以来pymsql等第三方插件,Dialect用于和数据API进行交流,根据配置文件的不同调用不同的数据库API,从而实现对数据库的操作,如:
MySQL-Python
mysql+mysqldb://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname>
pymysql
mysql+pymysql://<username>:<password>@<host>/<dbname>[?<options>]
MySQL-Connector
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname>
cx_Oracle
oracle+cx_oracle://user:pass@host:port/dbname[?key=value&key=value...]
更多详见:http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/latest/dialects/index.html
一、底层处理
使用 Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 进行数据库操作,Engine使用ConnectionPooling连接数据库,然后再通过Dialect执行SQL语句
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://tuocigaoshou:Eb^BEF38E9FBC36CA775@111.204.117.99:3306/test", max_overflow=5)
# 执行SQL 插入一条数据 (增删改)
cur = engine.execute("insert into users (name, extra) values ('aaa', 'aaa')")
print(cur.lastrowid) # 可以获取到新插入数据行的自增id
# 执行SQL 插入多条数据
cur = engine.execute("insert into users (name, extra) values (%s, %s)", [["bbb", "bbb"], ["ccc", "ccc"],])
print(cur.lastrowid) # 插入多条数据的时候只能获取到第一行的自增id
# 执行SQL 另一种插入方式,只能插入一条
cur = engine.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, extra) VALUES (%(name)s, %(extra)s)", name="ddd", extra="ddd")
# 执行SQL 查询
cur = engine.execute('select * from users')
# 获取第一行数据
print(cur.fetchone())
# 获取第n行数据
print(cur.fetchmany(3))
# 获取所有数据
print(cur.fetchall())
二、ORM功能使用
使用 ORM/Schema Type/SQL Expression Language/Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 所有组件对数据进行操作。根据类创建对象,对象转换成SQL,执行SQL。
- 创建表
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, ForeignKey, UniqueConstraint, Index
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://tuocigaoshou:Eb^BEF38E9FBC36CA775@111.204.117.99:3306/test", max_overflow=5)
Base = declarative_base()
# 创建单表
class Users(Base): # 必须继承Base类
__tablename__ = 'users' # 表名
# 创建三列数据
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) # primary_key 主键,自增ID
name = Column(String(32))
extra = Column(String(16))
# 联合索引
__table_args__ = (
UniqueConstraint('id', 'name', name='uix_id_name'),
Index('ix_id_name', 'name', 'extra'),
)
# 一对多
class Favor(Base):
__tablename__ = 'favor'
nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) # primary_key 主键,自增ID
caption = Column(String(50), default='red', unique=True) # unique唯一约束
class Person(Base):
__tablename__ = 'person'
nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) # primary_key 主键,自增ID
name = Column(String(32), index=True, nullable=True)
favor_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("favor.nid")) # 外键
# 多对多
class Group(Base):
__tablename__ = 'group'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String(64), unique=True, nullable=False)
class Server(Base):
__tablename__ = 'server'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True)
hostname = Column(String(64), unique=True, nullable=False)
port = Column(Integer, default=22)
class ServerToGroup(Base): # 通过第三张表创建上两张表多对多的关系
__tablename__ = 'servertogroup'
nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True)
server_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('server.id'))
group_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('group.id'))
# Base.metadata.create_all(engine) # 创建表,会执行Base类的所有子类创建所有表
# Base.metadata.drop_all(engine) # 删除表,会执行Base类的所有子类删除所有表
python学习之路-12的更多相关文章
- Python学习之路12☞模块与包
一 模块 1.1 什么是模块? 一个模块就是一个包含了python定义和声明的文件,文件名就是模块名字加上.py的后缀. 1.2 为何要使用模块? 如果你退出python解释器然后重新进入,那么你之前 ...
- python学习之路-day2-pyth基础2
一. 模块初识 Python的强大之处在于他有非常丰富和强大的标准库和第三方库,第三方库存放位置:site-packages sys模块简介 导入模块 import sys 3 sys模 ...
- Python学习之路-Day2-Python基础2
Python学习之路第二天 学习内容: 1.模块初识 2.pyc是什么 3.python数据类型 4.数据运算 5.bytes/str之别 6.列表 7.元组 8.字典 9.字符串常用操作 1.模块初 ...
- Python学习之路【第一篇】-Python简介和基础入门
1.Python简介 1.1 Python是什么 相信混迹IT界的很多朋友都知道,Python是近年来最火的一个热点,没有之一.从性质上来讲它和我们熟知的C.java.php等没有什么本质的区别,也是 ...
- python学习之路------你想要的都在这里了
python学习之路------你想要的都在这里了 (根据自己的学习进度后期不断更新哟!!!) 一.python基础 1.python基础--python基本知识.七大数据类型等 2.python基础 ...
- Python学习之路-Day2-Python基础3
Python学习之路第三天 学习内容: 1.文件操作 2.字符转编码操作 3.函数介绍 4.递归 5.函数式编程 1.文件操作 打印到屏幕 最简单的输出方法是用print语句,你可以给它传递零个或多个 ...
- Python学习之路-Day1-Python基础
学习python的过程: 在茫茫的编程语言中我选择了python,因为感觉python很强大,能用到很多领域.我自己也学过一些编程语言,比如:C,java,php,html,css等.但是我感觉自己都 ...
- python学习之路网络编程篇(第四篇)
python学习之路网络编程篇(第四篇) 内容待补充
- python 学习之路开始了
python 学习之路开始了.....记录点点滴滴....
随机推荐
- 【转】WCF、WebAPI、WCFREST、WebService之间的区别
在.net平台下,有大量的技术让你创建一个HTTP服务,像Web Service,WCF,现在又出了Web API.在.net平台下,你有很多的选择来构建一个HTTP Services.我分享一下我对 ...
- 基于Cordova5.0开发自己定义插件(android)
1.开发插件java部分 watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvenhmMjE2MjE2/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fi ...
- 如何单独编译Android源代码中的模块
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6566662 第一次下载好Android源代码工 ...
- AngularJS移动开发中的坑汇总
使用AngualrJs开发移动App已经快半年了,逐渐积累了非常多AngularJS的问题,特别是对于用惯了Jquery的开发人员,转到AngularJS还是须要克服非常多问题的.不像Jquery那样 ...
- LVM管理
一.步骤: 1.创建新的分区,并修改分区类型为8e 2.创建物理卷PV 3.将新建的PV添加到要扩展的VG中 4.用命令lvextend或lvresize来将新加入的PE添加到要扩展的LV中 5.用命 ...
- .NET基础拾遗(3)字符串、集合和流3
三.流和序列化 3.1 流概念及.NET中常见流 无论什么信息,文字,声音,图像,只要进入了计算机就都被转化为数字,以数字方式运算.存储.由于计算机中使用二进制运算,因此数字只有两个:0 与 1,就是 ...
- C# 超级简单的Telnet (TcpClient)客户端
基于Sockets 没什么好说的,代码说明了所有 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Sy ...
- JQuery或JavaScript获取网页的宽度、高等
最近多次使用JQery或JavaScript获取网页的宽度或者高度,在网上搜索N久之后发现很多都是粘贴上去并没有详细的介绍,这里我将会对经常使用的一些获取页面宽高的属性,方法做详细的介绍,以便能够更加 ...
- css3 content画出各种图形
原链接:http://www.phpjz.cn/web/201311/1700.html 之前看到一些网站用户content这个词,觉得很奇怪,原来是css3新增的一个样式,发现还挺好用的,特别是用移 ...
- seajs初尝 加载jquery返回null解决学习日志含示例下载
原文地址:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/bmuaEb 如需demo示例,请点击下方链接下载: http://yunpan.cn/cVEybKs8nV7CF 提取码 ...
