hdu 3478 Catch(染色 dfs 或 bfs )
A thief is running away!
We can consider the city where he locates as an undirected graph in which nodes stand for crosses and edges stand for streets. The crosses are labeled from to N–.
The tricky thief starts his escaping from cross S. Each moment he moves to an adjacent cross. More exactly, assume he is at cross u at the moment t. He may appear at cross v at moment t + if and only if there is a street between cross u and cross v. Notice that he may not stay at the same cross in two consecutive moment.
The cops want to know if there’s some moment at which it’s possible for the thief to appear at any cross in the city.
The input contains multiple test cases:
In the first line of the input there’s an integer T which is the number of test cases. Then the description of T test cases will be given.
For any test case, the first line contains three integers N (≤ ), M (≤ ), and S. N is the number of crosses. M is the number of streets and S is the index of the cross where the thief starts his escaping.
For the next M lines, there will be integers u and v in each line ( ≤ u, v < N). It means there’s an undirected street between cross u and cross v.
For each test case, output one line to tell if there’s a moment that it’s possible for the thief to appear at any cross. Look at the sample output for output format.
Case : YES
Case : NO
For the first case, just look at the table below. (YES means the thief may appear at the cross at that moment)
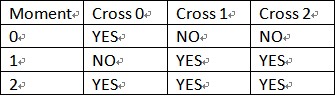
For the second input, at any moment, there’s at least one cross that the thief can’t reach.
转自别人的解释:
如果出现遍历图中的某个点都是在奇数时刻或者偶数时刻,那么小偷的藏点就是根据时间判定在某些的奇数点和偶数点了。
如果图出现奇数的环,即:有一个环由奇数个点组成,那么环中的某个点在奇数和偶数时刻都能到达(可以画图试试)。其实奇数环导致小偷藏点无规律的最大原因是:
在遍历最后奇数环的两个(必定是两个)未遍历点的时候他们是同奇(偶)的,然而还有一条边直接相连。导致在下一时刻,那两个点又可以同时变成偶(奇)。如果在回溯遍历的话,就会出现整张图在奇数时刻或者偶数时刻都能到达。
无向图G为二部图的充分必要条件是:
G至少有两个顶点,且其所有回路的长度均为偶数。
如果我们把图中奇数时刻能够到达的点归到X集合,偶数能到点归到Y集合,那么如果图中出现相同集合的点有
边相连,那么就不满足二分图的性质,即可输出YES,如果原图可二分图话,答案就是NO了。
然后就是经典的二分图判定。
///
题意:一个小偷从初始点逃到他相邻的点,从某个点到另外若干个相邻的点的时间是相同的,
也就是同个时间点,问你在同个时间点小偷能否遍历全部点,能的话输出YES,否则输出NO。
解法:DFS判断连通性+DFS染色判断是否为二分图。
如果是个二分图那么它的奇数步和偶数步是属于各自独立的集合,
如果奇数步能够遍历到偶数步,这个意思就是此小偷可以在某个时间点遍历整个图的点。
画个奇数点的环,从某个点出发一点存在一条边,同时改变改点的奇偶性。
///
总之,只要判断连通性和二分图即可
bfs实现染色:
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<bitset>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define max(a,b) (a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)
#define min(a,b) (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)
#define ll long long
#define eps 1e-10
#define MOD 1000000007
#define N 100006
#define inf 1e12 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int fa[N];
void init(){
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
fa[i]=i;
}
}
int find(int x){
return fa[x]==x?x:fa[x]=find(fa[x]);
}
bool merge(int x,int y){
int root1=find(x);
int root2=find(y);
if(root1==root2) return false;
fa[root1]=root2;
return true;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
int n,m,s;
vector<int> v[N];
int color[N];
bool bfs(){
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
color[s]=;
while(!q.empty()){
int t1=q.front();
q.pop(); for(int i=;i<v[t1].size();i++){
int t2=v[t1][i];
if(color[t2]==-){
if(color[t1]==){
color[t2]=;
}
else{
color[t2]=;
}
q.push(t2);
}
else{
if(color[t1]==color[t2]){
return true;
}
} }
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int t;
int ac=;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
v[i].clear();
}
init();
int num=n-;
for(int i=;i<m;i++){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(merge(x,y)){
num--;
}
v[x].push_back(y);
v[y].push_back(x);
}
memset(color,-,sizeof(color));
printf("Case %d: ",++ac);
if(num!=){
printf("NO\n");
continue;
} if(bfs()){
printf("YES\n");
}
else{
printf("NO\n");
} }
return ;
}
dfs实现染色:
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<bitset>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define max(a,b) (a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)
#define min(a,b) (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)
#define ll long long
#define eps 1e-10
#define MOD 1000000007
#define N 100006
#define inf 1e12 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int fa[N];
void init(){
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
fa[i]=i;
}
}
int find(int x){
return fa[x]==x?x:fa[x]=find(fa[x]);
}
bool merge(int x,int y){
int root1=find(x);
int root2=find(y);
if(root1==root2) return false;
fa[root1]=root2;
return true;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////// int n,m,s;
vector<int> v[N];
int color[N];
bool dfs(int x,int c){
color[x]=c;
for(int i=;i<v[x].size();i++){
int y=v[x][i];
if(color[y]==-){
color[y]=!c;
dfs(y,!c);
}
else{
if(color[y]==color[x]){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int ac=;
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
v[i].clear();
}
init();
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s);
int num=n-;
for(int i=;i<m;i++){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(merge(x,y)){
num--;
}
v[x].push_back(y);
v[y].push_back(x);
} printf("Case %d: ",++ac);
if(num!=){
printf("NO\n");
continue;
} memset(color,-,sizeof(color));
if(dfs(s,)){
printf("YES\n");
}
else{
printf("NO\n");
} }
return ;
}
hdu 3478 Catch(染色 dfs 或 bfs )的更多相关文章
- HDU 1241 Oil Deposits (DFS or BFS)
链接 : Here! 思路 : 搜索判断连通块个数, 所以 $DFS$ 或则 $BFS$ 都行喽...., 首先记录一下整个地图中所有$Oil$的个数, 然后遍历整个地图, 从油田开始搜索它所能连通多 ...
- hdu 3478 Catch 二分图染色
题目链接 题意 小偷逃跑,从某个点出发,每下一个时刻能够跑到与当前点相邻的点. 问是否存在某一个时刻,小偷可能在图中的任意一个点出现. 思路 结论 如果该图为连通图且不为二分图,则可能,否则不可能. ...
- HDU 2717 Catch That Cow (bfs)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2717 Catch That Cow Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Ot ...
- HDU - 3478 Catch(判奇环/二分图)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3478 题意 给一个无向图和小偷的起点,小偷每秒可以向相邻的点出发,问有没有一个时间点小偷可能出现在任何点. 分析 ...
- HDU 2717 Catch That Cow(常规bfs)
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2717 Catch That Cow Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Oth ...
- HDU 2717 Catch That Cow(BFS)
Catch That Cow Farmer John has been informed of the location of a fugitive cow and wants to catch he ...
- hdu 2717:Catch That Cow(bfs广搜,经典题,一维数组搜索)
Catch That Cow Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
- 题解报告:hdu 2717 Catch That Cow(bfs)
Problem Description Farmer John has been informed of the location of a fugitive cow and wants to cat ...
- HDU 2102 A计划 DFS与BFS两种写法 [搜索]
1.题意:一位公主被困在迷宫里,一位勇士前去营救,迷宫为两层,规模为N*M,迷宫入口为(0,0,0),公主的位置用'P'标记:迷宫内,'.'表示空地,'*'表示墙,特殊的,'#'表示时空传输机,走到这 ...
随机推荐
- SpringMVC学习系列- 表单验证
本篇我们来学习Spring MVC表单标签的使用,借助于Spring MVC提供的表单标签可以让我们在视图上展示WebModel中的数据更加轻松. 一.首先我们先做一个简单了例子来对Spring MV ...
- poj 3684 Physics Experiment(数学,物理)
Description Simon ), the first ball is released and falls down due to the gravity. After that, the b ...
- Lua Interface基础使用
Lua是一种可爱的脚本语言,由Roberto Ierusalimschy.Waldemar Celes 和 Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo所组成并于1993年开发. 其设计目的 ...
- JUnit3 结合一个除法的单元测试说明Assert.fail()的用法
之前一篇博文(JUnit基础及第一个单元测试实例(JUnit3.8))介绍了用JUnit做单元测试的基本方法,并写了一个简单的类Calculator,其中包含了整型加减乘除的简单算法. 本文通过完善其 ...
- sql执行顺序整理
sql的执行顺序,是优化sql语句执行效率必须要掌握的.各个数据库可能有细小的差别,但大体顺序是相同的,这里只做大致说明. 一.总体执行顺序 在sql语句执行之前,还有SQL语句准备执行阶段,这里不做 ...
- C# CheckedListBox控件的使用方法
1. 加入项 checkedListBox1.Items.Add("蓝色"); checkedListBox1.Items.Add("红色"); checked ...
- sql注入数据库修复方法
1.第一种情况是 需要将指定的 注入字符串全部替换掉(仅替换注入的字符串为空) declare @delStr nvarchar(500) set @delStr='<script src=ht ...
- Linux下Ant的安装
OS:CentOS6.3 ant版本:apache-ant-1.9.2-bin 第1步:下载ant apache-ant-1.9.2-bin.tar.gz 第2步:解压 tar -zxvf apach ...
- 一篇文章讲清楚android ImageView.ScaleType
2016-01-10 刚开始android编程的时候, 关于ImageView.ScaleType网络上好多, 说实话没看懂. 本文就是为了讲清楚这个, 有用的话转走, 请注明原地址和作者. 典型的代 ...
- C#代码启用事务锁Transaction进行一系列提交回滚操作
一.前言 因为很多人一般进行一系列相关数据库操作都是在存储过程里面,而且在存储过程用锁的写法也是很简单的,在这篇文章主要介绍一下C#后台代码用锁进行一系列事务操作,我建立一个简单的winform程序, ...
