SpringMVC探秘-请求之路
SpringMVC探秘-请求之路
开始
今天来分析一下SpringMVC的原理,探究SpringMVC如何把请求传递到每个Controller的方法上,从Servlet到Controller,一个请求走了哪些艰难曲折的路。
基本核心组件
在开始分析之前,先了解SpringMVC中的几个概念,后面提到的时候不至于不知道这个是干什么用的,不过不用彻底知道这个组件是如何实现的,现在只需要知道有这个东西就行了, 先混个脸熟
| 组件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| DispatcherServlet | SpringMVC中的中心,处理请求的分发,视图的解析等,本质上是一个Servlet |
| HandlerMapping | 一个映射,<URL,Handler>,可以根据URL找到匹配的Handler,这儿的Handler是HandlerExecutionChain |
| HandlerAdapter | Hander的适配器,委托这个适配器去调用具体的某个Hander |
| ViewResolver | 视图解析器,用于将视图名称解析为视图对象 View。 |
这些组件都是经过DispatcherServlet的协调,把一个请求分发到具体的一个Hander,然后根据Hander的返回值,来做不同的处理,不同的组件处理不同的逻辑。
追根溯源
请求的入口-Servlet
我们都知道Servlet是一个标准,我们的处理逻辑代码只需要写到Servlet中,而对于Http请求响应的解析处理都不需要我们关心,已经有很多服务器实现了这部分,比如熟悉的小猫猫Tomcat,它就是按照Servlet的标准来实现的。
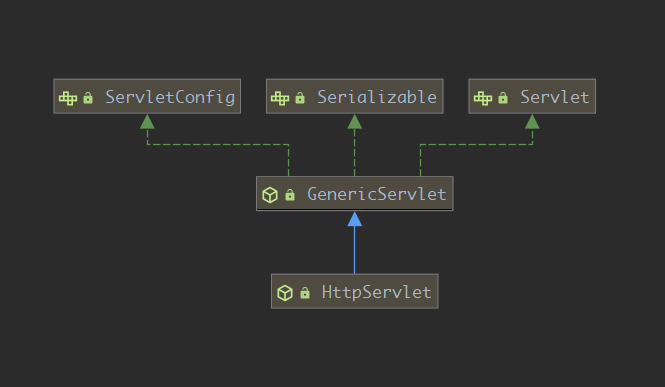
ServletConfig
/**
* A servlet configuration object used by a servlet container to pass
* information to a servlet during initialization.
* 当servlet实例化的时候,servlet容器传递给servlet的配置
*/
public interface ServletConfig {
/**
* Returns the name of this servlet instance. The name may be provided via
* server administration, assigned in the web application deployment
* descriptor, or for an unregistered (and thus unnamed) servlet instance it
* will be the servlet's class name.
* 返回servlet的名字,如果没有指定,则返回servlet的类名
* @return the name of the servlet instance
*/
public String getServletName();
/**
* Returns a reference to the {@link ServletContext} in which the caller is
* executing.
* 返回调用者当前执行环境的ServletContext引用
* @return a {@link ServletContext} object, used by the caller to interact
* with its servlet container
* @see ServletContext
*/
public ServletContext getServletContext();
/**
* Returns a <code>String</code> containing the value of the named
* initialization parameter, or <code>null</code> if the parameter does not
* exist.
* 返回一个字符串类型的值,这个值是初始化的参数
* @param name
* a <code>String</code> specifying the name of the
* initialization parameter
* @return a <code>String</code> containing the value of the initialization
* parameter
*/
public String getInitParameter(String name);
/**
* Returns the names of the servlet's initialization parameters as an
* <code>Enumeration</code> of <code>String</code> objects, or an empty
* <code>Enumeration</code> if the servlet has no initialization parameters.
* 返回所有的初始化参数
* @return an <code>Enumeration</code> of <code>String</code> objects
* containing the names of the servlet's initialization parameters
*/
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames();
}
Servlet
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 所有的servlet都应该实现这里的方法
*
* servlet是一个运行在Web Server的小Java程序,它们接受对来自web客户端的请求并做出响应,这些请求通常通过HTTP传达
*
* 为了实现这个接口,你可以写一个基于javax.servlet.GenericServlet,或者HTTP Servletjavax.servlet.http.HttpServlet派生的servlet类
*
* 这个接口定义了实例化servlet,接受请求,从server移除的方法,这些方法被称为生命周期方法:并且按照一些的顺序调用:
* 1. servlet被实例化,调用init()方法初始化
* 2. 当有来自客户端的调用,serviceI()方法被调用
* 3. servlet退出服务,destory()方法被调用,然后执行GC
*
* 除了生命周期方法外,这个接口还提供了getServletConfig方法来获取启动信息,getServletInfo来获取
* servlet自身的基本信息,比如作者,版本,版权等
*
* @see GenericServlet
* @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet
*/
public interface Servlet {
/**
* 被servlet容器调用,表示这个servlet将要开始服务
*
* servlet实例化之后马上调用这个方法,在开始处理请求前这个方法必须调用成功
*
* 如果这个方法抛出异常或者在指定的时间段没有返回,那么这个serlet也不能处理请求
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception has occurred that interferes with the
* servlet's normal operation
*
* @see UnavailableException
* @see #getServletConfig
*/
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
/**
* 获取ServletConfig,存储了启动参数
* @return the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that initializes this
* servlet
*
* @see #init
*/
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
/**
* 被Servlet容器调用,用来对一个请求做出响应
*
* 只有当servlet中的init()方法调用成功后这个方法才会调用
*
* 应该为抛出异常或者错误的servlet返回的response设置响应码
*
* 这个方法可能被并发调用,所以开发者对于共享的资源要同步操作,共享的资源比如,文件,网络连接,
* 还有servlet的类变量和实例变量
* @param req
* the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains the
* client's request
*
* @param res
* the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that contains the
* servlet's response
*
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception occurs that interferes with the servlet's
* normal operation
*
* @exception IOException
* if an input or output exception occurs
*/
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
/**
* 获取Servlet基本信息
*
* @return a <code>String</code> containing servlet information
*/
public String getServletInfo();
/**
* 这个方法被调用,表明这个servlet已经不再处理请求,这个方法在多线程环境也只调用一次,调用后,
* service方法将不会再调用
*
* 给一个servlet释放资源的机会,比如文件,还有需要持久化的资源需和内存中的状态同步
*/
public void destroy();
}
GenericServlet
GenericServlet 实现了 Servlet 和 ServletConfig 两个接口,为这两个接口中的部分方法提供了简单的实现。比如该类实现了 Servlet 接口中的 void init(ServletConfig) 方法,并在方法体内调用了内部提供了一个无参的 init 方法,子类可覆盖该无参 init 方法。除此之外,GenericServlet 还实现了 ServletConfig 接口中的 getInitParameter 方法,用户可直接调用该方法获取到配置信息。而不用先获取 ServletConfig,然后再调用 ServletConfig 的 getInitParameter 方法获取
GenericServlet 是一个协议无关的 servlet,是一个比较原始的实现,通常我们不会直接继承该类。一般情况下,我们都是继承 GenericServlet 的子类 HttpServlet,该类是一个和 HTTP 协议相关的 Servlet。那下面我们来看一下这个类
HttpServlet
HttpServlet,从名字上就可看出,这个类是和 HTTP 协议相关。该类的关注点在于怎么处理 HTTP 请求,比如其定义了 doGet 方法处理 GET 类型的请求,定义了 doPost 方法处理 POST 类型的请求等。我们若需要基于 Servlet 写 Web 应用,应继承该类,并覆盖指定的方法。doGet 和 doPost 等方法并不是处理的入口方法,所以这些方法需要由其他方法调用才行。其他方法是哪个方法呢?对,在Servlet接口定义处理请求的方法service中。当然在HttpServlet中还有一些处理缓存的逻辑
请求分发中央-DispatcherServlt
在认识它之前,介绍一下它在家族中的地位
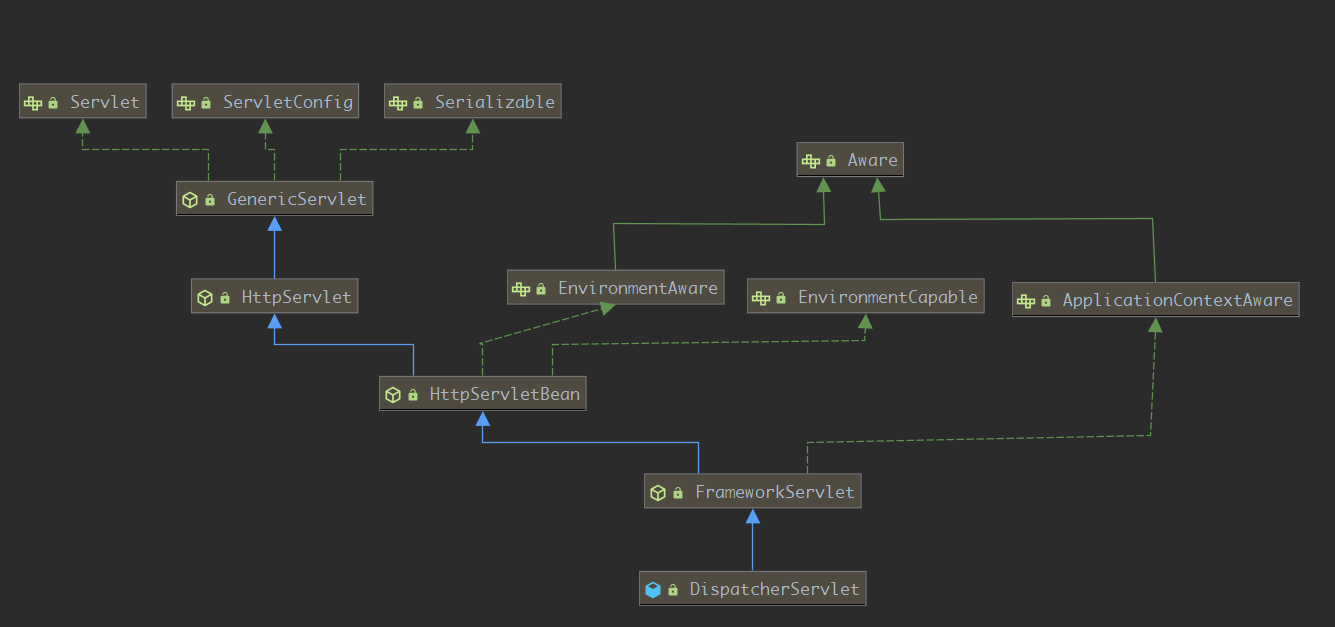
对于Servlet相关的类和接口上面已经介绍过了,这里多了一些以Aware结尾的接口,是Spring IOC中的接口,
HttpServletBean
重写了GenericServlet中的init()方法,设置servlet配置的初始化参数
FrameworkServlet
FrameworkServlet 是 Spring Web 框架中的一个基础类,该类会在初始化时创建一个容器。同时该类覆写了 doGet、doPost 等方法,并将所有类型的请求委托给 doService 方法去处理。doService 是一个抽象方法,需要子类实现。
servlet被实例化后,会调用GenericServlet的init(ServletConfig config)方法,然后会无参init()方法,HttpServletBean重写了init()方法,这个方法会调用交给子类去实现的initServletBean()方法,现在就到了FrameworkServlet中的initServletBean(),该方法会调用initWebApplicationContext(),这里创建多个容器我,他们之间的关系后面我们再说
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet就是核心的一个组件,来负责协调各个组件,同事初始化这些组件如,HanderMapping,HanderAdapter等。
中央处理器DispatcherServlet
我们继续从上面的FrameworkServlet调用的doService方法入手
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch}
* for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
// 处理请求
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
doService中就是给request设置一些参数,然后调用doDispatch()方法。doDispatch()才是真正处理请求的方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
// 这个对象包含HnadlerInterceptor集合和Handler对象
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检查是否是Multipart request,如果是并且有MultipartResolver,则返回MultipartResolver处理后的request
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// 是否被MultipartResolver处理
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 从HanderMapping获取HandlerExecutionChain
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 获取可执行处理器逻辑的适配器 HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
// HTTP缓存相关
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 执行拦截器 preHandle 方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 调用处理器逻辑,对应步骤
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 如果 controller 未返回 view 名称,这里生成默认的 view 名称
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 执行拦截器 postHandle 方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 解析并渲染视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
getHander(HttpServletRequest)
/**
* 遍历所有的HanderMapping,获取一个HanderExecutionChian
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
getHandlerAdapter
/**
* Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object.
* @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for
* @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error.
*/
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
processDispatchResult
/**
* Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is
* either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView.
*/
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
后记
整个请求的流程就走完了,但是对于HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter,如何渲染视图这块没有详细说,因为现在我也还不太懂,等后面会再写文章来说明。
再DispatcherServlet初始化后,会创建容器和创建组件,这些在本文中也没有说明,篇幅限制就另外写一篇来做解释了。
SpringMVC探秘-请求之路的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot对比SpringMVC,SpringMVC 处理请求过程
(问较多:1.SpringBoot对比SpringMVC.2.SpringMVC 处理请求过程.问:springboot的理解 Spring,Spring MVC,Spring Boot 三者比较 S ...
- [手把手教程][JavaWeb]优雅的SpringMvc+Mybatis整合之路
来源于:http://www.jianshu.com/p/5124eef40bf0 [手把手教程][JavaWeb]优雅的SpringMvc+Mybatis整合之路 手把手教你整合最优雅SSM框架:S ...
- springMvc REST 请求和响应
前言: 突然怎么也想不起来 springMvc REST 请求的返回 类型了! (尴尬+究竟) 然后本着 方便的想法 百度了一下 发现了个问题,大家在写 springMvc RES ...
- SpringMvc Controller请求链接忽略大小写(包含拦截器)及@ResponseBody返回String中文乱码处理
SpringMvc Controller请求链接忽略大小写(包含拦截器)及@ResponseBody返回String中文乱码处理... @RequestMapping(value = "/t ...
- SpringMVC之请求参数的获取方式
转载出处:https://www.toutiao.com/i6510822190219264516/ SpringMVC之请求参数的获取方式 常见的一个web服务,如何获取请求参数? 一般最常见的请求 ...
- Springmvc Get请求Tomcat、WebLogic中文乱码问题
Springmvc Get请求Tomcat.WebLogic中文乱码问题 学习了:http://www.cnblogs.com/qingdaofu/p/5633225.html http://www. ...
- 16 SpringMVC 的请求参数的绑定与常用注解
1.SpringMVC 绑定请求参数 (1)支持的数据类型 基本类型参数: 包括基本类型和 String 类型POJO 类型参数: 包括实体类,以及关联的实体类数组和集合类型参数: 包括 List 结 ...
- Spring系列 SpringMVC的请求与数据响应
Spring系列 SpringMVC的请求与数据响应 SpringMVC的数据响应 数据响应的方式 y以下案例均部署在Tomcat上,使用浏览器来访问一个简单的success.jsp页面来实现 Suc ...
- SpringMVC RequestMapping & 请求参数
SpringMVC 概述 Spring 为展现层提供的基于 MVC 设计理念的优秀的Web 框架,是目前最主流的 MVC 框架之一 Spring3.0 后全面超越 Struts2,成为最优秀的 MVC ...
随机推荐
- mybatis学习笔记(三)
使用mapper接口来实现数据操作 创建UserMapper接口,添加方法,方法名要与UserMappper.xml中id所一致并且接口名要与编写sql语句的xmL文件名同名.namespace 中的 ...
- CentOS6.9部署Redis3.2.9+FastDFS_4.06+Nginx1.5.0
CentOS6.9部署Redis3.2.9+FastDFS_4.06+Nginx1.5.0 原文链接:https://www.toutiao.com/i6481931577499582990/ 一.上 ...
- 硬核 - Java 随机数相关 API 的演进与思考(上)
本系列将 Java 17 之前的随机数 API 以及 Java 17 之后的统一 API 都做了比较详细的说明,并且将随机数的特性以及实现思路也做了一些简单的分析,帮助大家明白为何会有这么多的随机数算 ...
- SCALA-基础知识学习(一)
概述 本人开始学习scala的时候,是在使用和开发spark程序的时候,在此为了整理.记录和分享scala的基础知识,我写这篇关于scala的基础知识,希望与广大读者共同学习沟通进步.如果有些代码比较 ...
- ArcGIS把导入的shp按渔网区块分割成更小的文件
前言 前端地图的开发需要导入城市的3D建筑白模,如果直接导入整个城市的json,文件大小高达76M,浏览器会直接崩溃,所以需要用ArcGIS分割成更小的文件后再给前端导入展示. ArcGIS版本:10 ...
- 【Android UI设计与开发】8.顶部标题栏(一)ActionBar 奥义·详解
一.ActionBar介绍 在Android 3.0中除了我们重点讲解的Fragment外,Action Bar也是一个非常重要的交互元素,Action Bar取代了传统的tittle bar和men ...
- K8s中的volumes-容器数据存放类型及位置
学习对象:kubectl explain pod.spec.volumes.pod.spec.containers.image.volumeMounts 介绍Volumes 容器内部也有自己的空间,但 ...
- 抓包分析与mock实战
Charles下载安装 官网下载安装:https://www.charlesproxy.com/ 电脑证书配置 如果不配置证书,无法抓取https协议 配置证书: 1 - 打开Charles,在hel ...
- cesium 3dtiles模型单体化点击高亮效果
前言 cesium 官网的api文档介绍地址cesium官网api,里面详细的介绍 cesium 各个类的介绍,还有就是在线例子:cesium 官网在线例子,这个也是学习 cesium 的好素材. c ...
- maven常用打包命令
常用maven命令 执行与构建过程(编译,测试,打包)相关的命令必须进入pom.xml所在位置执行 mvn clean:清理(打包好的程序放在生成的名为target的文件中,清理即删除文件中打包好的程 ...
