V-rep学习笔记:机器人逆运动学数值解法(Damped Least Squares / Levenberg-Marquardt Method)
The damped least squares method is also called the Levenberg-Marquardt method. Levenberg-Marquardt算法是最优化算法中的一种。它是使用最广泛的非线性最小二乘算法,具有梯度法和牛顿法的优点。当λ很小时,步长等于牛顿法步长,当λ很大时,步长约等于梯度下降法的步长。
The damped least squares method can be theoretically justified as follows.Rather than just finding the minimum vector ∆θ that gives a best solution to equation (pseudo inverse method就是求的极小范数解), we find the value of ∆θ that minimizes the quantity:
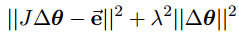
where λ ∈ R is a non-zero damping constant. This is equivalent to minimizing the quantity:

The corresponding normal equation is(根据矩阵论简明教程P83 最小二乘问题:设A∈Rm×n,b∈Rm. 若x0∈Rn是Ax=b的最小二乘解,则x0是方程组ATAx=ATb的解,称该式为Ax=b的法方程组.)
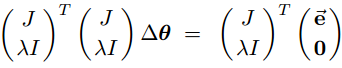
This can be equivalently rewritten as:
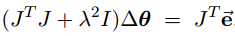
It can be shown that JTJ + λ2I is non-singular when λ is appropriate(选取适当的参数λ可以保证矩阵JTJ + λ2I非奇异). Thus, the damped least squares solution is equal to:
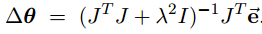
Now JTJ is an n × n matrix, where n is the number of degrees of freedom. It is easy to find that (JTJ + λ2I)−1JT= JT (JJT + λ2I)−1(等式两边同乘(JTJ + λ2I)进行恒等变形). Thus:

The advantage of the equation is that the matrix being inverted is only m×m where m = 3k is the dimension of the space of target positions, and m is often much less than n. Additionally, the equation can be computed without needing to carry out the matrix inversion, instead row operations can find f such that (JJT + λ2I) f = e and then JTf is the solution. The damping constant depends on the details of the multibody and the target positions and must be chosen carefully to make equation numerically stable. The damping constant should large enough so that the solutions for ∆θ are well-behaved near singularities, but if it is chosen too large, then the convergence rate is too slow.
以平面二连杆机构为例,使用同样的V-rep模型,将目标点放置在接近机构奇异位置处,使用DLS方法求逆解。在下面的Python程序中关节角初始值就给在奇异点上,可以看出最终DLS算法还是能收敛,而pseudo inverse方法在奇异点处就无法收敛。The damped least squares method avoids many of the pseudo inverse method’s problems with singularities and can give a numerically stable method of selecting ∆θ

import vrep #V-rep library
import sys
import time
import math
import numpy as np # Starts a communication thread with the server (i.e. V-REP).
clientID=vrep.simxStart('127.0.0.1', 20001, True, True, 5000, 5) # clientID: the client ID, or -1 if the connection to the server was not possible
if clientID!=-1: #check if client connection successful
print 'Connected to remote API server'
else:
print 'Connection not successful'
sys.exit('Could not connect') # Exit from Python # Retrieves an object handle based on its name.
errorCode,J1_handle = vrep.simxGetObjectHandle(clientID,'j1',vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait)
errorCode,J2_handle = vrep.simxGetObjectHandle(clientID,'j2',vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait)
errorCode,target_handle = vrep.simxGetObjectHandle(clientID,'target',vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait)
errorCode,consoleHandle = vrep.simxAuxiliaryConsoleOpen(clientID,'info',5,1+4,None,None,None,None,vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait) uiHandle = -1
errorCode,uiHandle = vrep.simxGetUIHandle(clientID,"UI", vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait)
buttonEventID = -1
err,buttonEventID,aux = vrep.simxGetUIEventButton(clientID,uiHandle,vrep.simx_opmode_streaming) L1 = 0.5 # link length
L2 = 0.5
lamda = 0.2 # damping constant
stol = 1e-2 # tolerance
nm = 100 # initial error
count = 0 # iteration count
ilimit = 1000 # maximum iteration # initial joint value
# note that workspace-boundary singularities occur when q2 approach 0 or 180 degree
q = np.array([0,0]) while True:
retcode, target_pos = vrep.simxGetObjectPosition(clientID, target_handle, -1, vrep.simx_opmode_streaming) if(nm > stol):
vrep.simxAuxiliaryConsolePrint(clientID, consoleHandle, None, vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait) # "None" to clear the console window x = np.array([L1*math.cos(q[0])+L2*math.cos(q[0]+q[1]), L1*math.sin(q[0])+L2*math.sin(q[0]+q[1])])
error = np.array([target_pos[0],target_pos[1]]) - x J = np.array([[-L1*math.sin(q[0])-L2*math.sin(q[0]+q[1]), -L2*math.sin(q[0]+q[1])],\
[L1*math.cos(q[0])+L2*math.cos(q[0]+q[1]), L2*math.cos(q[0]+q[1])]]) f = np.linalg.solve(J.dot(J.transpose())+lamda**2*np.identity(2), error) dq = np.dot(J.transpose(), f)
q = q + dq nm = np.linalg.norm(error) count = count + 1
if count > ilimit:
vrep.simxAuxiliaryConsolePrint(clientID,consoleHandle,"Solution wouldn't converge\r\n",vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait)
vrep.simxAuxiliaryConsolePrint(clientID,consoleHandle,'q1:'+str(q[0]*180/math.pi)+' q2:'+str(q[1]*180/math.pi)+'\r\n',vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait)
vrep.simxAuxiliaryConsolePrint(clientID,consoleHandle,str(count)+' iterations'+' err:'+str(nm)+'\r\n',vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot_wait) err, buttonEventID, aux = vrep.simxGetUIEventButton(clientID,uiHandle,vrep.simx_opmode_buffer)
if ((err==vrep.simx_return_ok) and (buttonEventID == 1)):
'''A button was pressed/edited/changed. React to it here!'''
vrep.simxSetJointPosition(clientID,J1_handle, q[0]+math.pi/2, vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot )
vrep.simxSetJointPosition(clientID,J2_handle, q[1], vrep.simx_opmode_oneshot ) '''Enable streaming again (was automatically disabled with the positive event):'''
err,buttonEventID,aux=vrep.simxGetUIEventButton(clientID,uiHandle,vrep.simx_opmode_streaming) time.sleep(0.01)
参考:
V-rep学习笔记:机器人逆运动学数值解法(Damped Least Squares / Levenberg-Marquardt Method)的更多相关文章
- V-rep学习笔记:机器人逆运动学数值解法(The Jacobian Transpose Method)
机器人运动学逆解的问题经常出现在动画仿真和工业机器人的轨迹规划中:We want to know how the upper joints of the hierarchy would rotate ...
- V-rep学习笔记:机器人逆运动学数值解法(The Pseudo Inverse Method)
There are two ways of using the Jacobian matrix to solve kinematics. One is to use the transpose of ...
- V-rep学习笔记:机器人逆运动学数值解法(Cyclic Coordinate Descent Method)
When performing inverse kinematics (IK) on a complicated bone chain, it can become too complex for a ...
- V-rep学习笔记:机器人逆运动学解算
IK groups and IK elements VREP中使用IK groups和IK elements来进行正/逆运动学计算,一个IK group可以包含一个或者多个IK elements: I ...
- matlab学习笔记10_6 字符串与数值间的转换以及进制之间的转换
一起来学matlab-matlab学习笔记10 10_6 字符串与数值间的转换以及进制之间的转换 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 参考书籍 <matlab 程序设计与综合 ...
- ES6学习笔记(四)-数值扩展
PS: 前段时间转入有道云笔记,体验非常友好,所以笔记一般记录于云笔记中,每隔一段时间,会整理一下, 发在博客上与大家一起分享,交流和学习. 以下:
- python学习笔记(五)数值类型和类型转换
Python中的数值类型有: 整型,如2,520 浮点型,如3.14159,1.5e10 布尔类型 True和False e记法: e记法即对应数学中的科学记数法 >>> 1.5e1 ...
- ES6学习笔记(四)数值的扩展
1.二进制和八进制表示法 ES6 提供了二进制和八进制数值的新的写法,分别用前缀0b(或0B)和0o(或0O)表示. 0b111110111 === 503 // true 0o767 === 503 ...
- Python学习笔记(2)数值类型
进制转换 int函数任意进制转换为10进制 第一个参数传入一个字符串,任意进制的,第二个参数传入对这个字符串的解释,解释他为几进制 hex oct bin转换进制为16 8 或者2进制 例题中石油87 ...
随机推荐
- 【LAMP】在Debian系linux下安装LAMP
一.安装基本的编译环境 apt-get install build-essential 二.安装MySQL apt-get install mysql-server 三.安装Apache apt-ge ...
- Headless MSBuild Support for SSDT (*.sqlproj) Projects
http://sqlproj.com/index.php/2012/03/headless-msbuild-support-for-ssdt-sqlproj-projects/ Update: bre ...
- COM编程之三 QueryInterface
[1]IUnknown接口 客户同组件交互都是通过接口完成的. 在客户查询组件的其它接口时,也是通过接口完成的.而那个接口就是IUnknown. IUnknown接口的定义包含在Win32SDK中的U ...
- HTTP错误汇总(404、302、200……)
HTTP 400 - 请求无效HTTP 401.1 - 未授权:登录失败HTTP 401.2 - 未授权:服务器配置问题导致登录失败HTTP 401.3 - ACL 禁止访问资源HTTP 401.4 ...
- 统计SQL语句耗时百分比
-- sql语句耗时百分比 declare @tmptb table(id int,name varchar(50),total_worker_time bigint,rate varchar(50) ...
- 获取元素CSS值之getComputedStyle方法熟悉
by zhangxinxu from http://www.zhangxinxu.com本文地址:http://www.zhangxinxu.com/wordpress/?p=2378 一.碎碎念~前 ...
- c/c++ 常用的几个安全函数
_stprintf_s // 格式化字符串 _vsntprintf_s // 格式化 不定长参数用到
- linux死锁检测的一种思路【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/mumuxinfei/p/4365697.html 前言: 上一篇博文讲述了pstack的使用和原理. 和jstack一样, pstack能获取进 ...
- java中枚举类的使用详解
/* * 通过JDK5提供的枚举来做枚举类 */ public enum Direction2 { FRONT("前"), BEHIND("后"), LEFT( ...
- Dynamics AX 2012 R2 在报表上显示和打印条码
AX中有对条码操作的封装,用其生成BarCodeString类型的值,再配合barcode128字体,即可在显示出条码. 废话不说,上代码. BarcodeCode128 barCod ...
