MySQL数据库开发(2)
单表查询
单表查询即对单个表进行查询。
单表查询的语法
SELECT 字段1,字段2... FROM 表名
WHERE 条件
GROUP BY field
HAVING 筛选
ORDER BY field
LIMIT 限制条数
关键字的执行优先级
from
where
group by
having
select
distinct
order by
limit
1.找到表:from
2.拿着where指定的约束条件,去文件/表中取出一条条记录
3.将取出的一条条记录进行分组group by,如果没有group by,则整体作为一组
4.将分组的结果进行having过滤
5.执行select
6.去重
7.将结果按条件排序:order by
8.限制结果的显示条数
简单查询
1 #简单查询
2 SELECT id,name,sex,age,hire_date,post,post_comment,salary,office,depart_id
3 FROM employee;
4
5 SELECT * FROM employee;
6
7 SELECT name,salary FROM employee;
8
9 #避免重复DISTINCT
10 SELECT DISTINCT post FROM employee;
11
12 #通过四则运算查询
13 SELECT name, salary*12 FROM employee;
14 SELECT name, salary*12 AS Annual_salary FROM employee;
15 SELECT name, salary*12 Annual_salary FROM employee;
16
17 #定义显示格式
18 CONCAT() 函数用于连接字符串
19 SELECT CONCAT('姓名: ',name,' 年薪: ', salary*12) AS Annual_salary
20 FROM employee;
21
22 CONCAT_WS() 第一个参数为分隔符
23 SELECT CONCAT_WS(':',name,salary*12) AS Annual_salary
24 FROM employee;
where约束
where字句中可以使用:
1. 比较运算符:><>= <= <> !=
2. between 80 and 100 值在80到100之间
3. in(80,90,100) 值是80或90或100
4.like 'egon%' 模糊匹配
pattern可以是%或_,
%表示任意多字符
_表示一个字符
5.逻辑运算符:在多个条件直接可以使用逻辑运算符 and or not
1 #1:单条件查询
2 SELECT name FROM employee
3 WHERE post='sale';
4
5 #2:多条件查询
6 SELECT name,salary FROM employee
7 WHERE post='teacher' AND salary>10000;
8
9 #3:关键字BETWEEN AND
10 SELECT name,salary FROM employee
11 WHERE salary BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000;
12
13 SELECT name,salary FROM employee
14 WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000;
15
16 #4:关键字IS NULL(判断某个字段是否为NULL不能用等号,需要用IS)
17 SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee
18 WHERE post_comment IS NULL;
19
20 SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee
21 WHERE post_comment IS NOT NULL;
22
23 SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee
24 WHERE post_comment=''; 注意''是空字符串,不是null
25 ps:
26 执行
27 update employee set post_comment='' where id=2;
28 再用上条查看,就会有结果了
29
30 #5:关键字IN集合查询
31 SELECT name,salary FROM employee
32 WHERE salary=3000 OR salary=3500 OR salary=4000 OR salary=9000 ;
33
34 SELECT name,salary FROM employee
35 WHERE salary IN (3000,3500,4000,9000) ;
36
37 SELECT name,salary FROM employee
38 WHERE salary NOT IN (3000,3500,4000,9000) ;
39
40 #6:关键字LIKE模糊查询
41 通配符’%’
42 SELECT * FROM employee
43 WHERE name LIKE 'eg%';
44
45 通配符’_’
46 SELECT * FROM employee
47 WHERE name LIKE 'al__';
例子
1. 查看岗位是teacher的员工姓名、年龄
2. 查看岗位是teacher且年龄大于30岁的员工姓名、年龄
3. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资在9000-1000范围内的员工姓名、年龄、薪资
4. 查看岗位描述不为NULL的员工信息
5. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资是10000或9000或30000的员工姓名、年龄、薪资
6. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资不是10000或9000或30000的员工姓名、年龄、薪资
7. 查看岗位是teacher且名字是jin开头的员工姓名、年薪 1.select name,age from employee where post = 'teacher';
2.select name,age from employee where post='teacher' and age > 30;
3.select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary between 9000 and 10000;
4.select * from employee where post_comment is not null;
5.select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary in (10000,9000,30000);
6.select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary not in (10000,9000,30000);
7.select name,salary*12 from employee where post='teacher' and name like 'jin%';
分组查询group by
什么是分组,为什么要分组?
#1、首先明确一点:分组发生在where之后,即分组是基于where之后得到的记录而进行的 #2、分组指的是:将所有记录按照某个相同字段进行归类,比如针对员工信息表的职位分组,或者按照性别进行分组等 #3、为何要分组呢?
取每个部门的最高工资
取每个部门的员工数
取男人数和女人数 小窍门:‘每’这个字后面的字段,就是我们分组的依据 #4、大前提:
可以按照任意字段分组,但是分组完毕后,比如group by post,只能查看post字段,如果想查看组内信息,需要借助于聚合函数
ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式
#查看MySQL 5.7默认的sql_mode如下:
mysql> select @@global.sql_mode;
ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION #!!!注意
ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY的语义就是确定select target list中的所有列的值都是明确语义,简单的说来,在ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式下,target list中的值要么是来自于聚集函数的结果,要么是来自于group by list中的表达式的值。 #设置sql_mole如下操作(我们可以去掉ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式):
mysql> set global sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'; !!!SQL_MODE设置!!!
在 ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY 模式下,查询的值只能是作为分组依据的字段,或者聚合函数。
没有设置此模式也可以进行分组查询,不过可能查询的结果会没有意义,所以还是建议在此种模式下。
mysql> set global sql_mode='ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> quit #设置成功后,一定要退出,然后重新登录方可生效
Bye
GROUP BY
单独使用GROUP BY关键字分组
SELECT post FROM employee GROUP BY post;
注意:我们按照post字段分组,那么select查询的字段只能是post,想要获取组内的其他相关信息,需要借助函数 GROUP BY关键字和GROUP_CONCAT()函数一起使用 # 当想查询非分组依据的字段时,可用此函数
SELECT post,GROUP_CONCAT(name) FROM employee GROUP BY post;#按照岗位分组,并查看组内成员名
SELECT post,GROUP_CONCAT(name) as emp_members FROM employee GROUP BY post; GROUP BY与聚合函数一起使用
select post,count(id) as count from employee group by post;#按照岗位分组,并查看每个组有多少人
注:如果我们用unique的字段作为分组的依据,则每一条记录自成一组,这种分组没有意义
多条记录之间的某个字段值相同,该字段通常用来作为分组的依据
聚合函数
#强调:聚合函数聚合的是组的内容,若是没有分组,则默认一组 示例:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=1;
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=3;
having 过滤
HAVING与WHERE不一样的地方在于!!!!!!
执行优先级从高到低:where > group by > having
1. Where 发生在分组group by之前,因而Where中可以有任意字段,但是绝对不能使用聚合函数。
2. Having发生在分组group by之后,因而Having中可以使用分组的字段,无法直接取到其他字段,可以使用聚合函数
查询排序 order by
按单列排序
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary ASC;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC; 按多列排序:先按照age排序,如果年纪相同,则按照薪资排序
SELECT * from employee
ORDER BY age,
salary DESC;
asc 递增排序,desc递减排序。
限制查询的记录数limit
示例:
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 3; #默认初始位置为0 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 0,5; #从第0开始,即先查询出第一条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 5,5; #从第5开始,即先查询出第6条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条
常用limit作分页操作
1. 分页显示,每页5条
mysql> select * from employee limit 0,5;
+----+-----------+------+-----+------------+-----------------------------------------+--------------+------------+--------+-----------+
| id | name | sex | age | hire_date | post | post_comment | salary | office | depart_id |
+----+-----------+------+-----+------------+-----------------------------------------+--------------+------------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 2017-03-01 | 老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使 | NULL | 7300.33 | 401 | 1 |
| 2 | alex | male | 78 | 2015-03-02 | teacher | | 1000000.31 | 401 | 1 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 81 | 2013-03-05 | teacher | NULL | 8300.00 | 401 | 1 |
| 4 | yuanhao | male | 73 | 2014-07-01 | teacher | NULL | 3500.00 | 401 | 1 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 28 | 2012-11-01 | teacher | NULL | 2100.00 | 401 | 1 |
+----+-----------+------+-----+------------+-----------------------------------------+--------------+------------+--------+-----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee limit 5,5;
+----+------------+--------+-----+------------+---------+--------------+----------+--------+-----------+
| id | name | sex | age | hire_date | post | post_comment | salary | office | depart_id |
+----+------------+--------+-----+------------+---------+--------------+----------+--------+-----------+
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 2011-02-11 | teacher | NULL | 9000.00 | 401 | 1 |
| 7 | jinxin | male | 18 | 1900-03-01 | teacher | NULL | 30000.00 | 401 | 1 |
| 8 | 成龙 | male | 48 | 2010-11-11 | teacher | NULL | 10000.00 | 401 | 1 |
| 9 | 歪歪 | female | 48 | 2015-03-11 | sale | NULL | 3000.13 | 402 | 2 |
| 10 | 丫丫 | female | 38 | 2010-11-01 | sale | NULL | 2000.35 | 402 | 2 |
+----+------------+--------+-----+------------+---------+--------------+----------+--------+-----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee limit 10,5;
+----+-----------+--------+-----+------------+-----------+--------------+----------+--------+-----------+
| id | name | sex | age | hire_date | post | post_comment | salary | office | depart_id |
+----+-----------+--------+-----+------------+-----------+--------------+----------+--------+-----------+
| 11 | 丁丁 | female | 18 | 2011-03-12 | sale | NULL | 1000.37 | 402 | 2 |
| 12 | 星星 | female | 18 | 2016-05-13 | sale | NULL | 3000.29 | 402 | 2 |
| 13 | 格格 | female | 28 | 2017-01-27 | sale | NULL | 4000.33 | 402 | 2 |
| 14 | 张野 | male | 28 | 2016-03-11 | operation | NULL | 10000.13 | 403 | 3 |
| 15 | 程咬金 | male | 18 | 1997-03-12 | operation | NULL | 20000.00 | 403 | 3 |
+----+-----------+--------+-----+------------+-----------+--------------+----------+--------+-----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用正则表达式查询
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP '^ale';
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'on$';
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'm{2}';
小结:对字符串匹配的方式
WHERE name = 'egon';
WHERE name LIKE 'yua%';
WHERE name REGEXP 'on$';
多表查询
多表连接查询语法
#重点:外链接语法 SELECT 字段列表
FROM 表1 INNER|LEFT|RIGHT JOIN 表2
ON 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
准备表
#建表
create table department(
id int,
name varchar(20)
); create table employee(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int,
dep_id int
); #插入数据
insert into department values
(200,'技术'),
(201,'人力资源'),
(202,'销售'),
(203,'运营'); insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
('egon','male',18,200),
('alex','female',48,201),
('wupeiqi','male',38,201),
('yuanhao','female',28,202),
('liwenzhou','male',18,200),
('jingliyang','female',18,204)
; #查看表结构和数据
mysql> desc department;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ mysql> desc employee;
+--------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | NO | | male | |
| age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| dep_id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+--------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ mysql> select * from department;
+------+--------------+
| id | name |
+------+--------------+
| 200 | 技术 |
| 201 | 人力资源 |
| 202 | 销售 |
| 203 | 运营 |
+------+--------------+ mysql> select * from employee;
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
1 交叉连接:不适用任何匹配条件。生成笛卡尔积
mysql> select * from employee,department;
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 202 | 销售 |
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 203 | 运营 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 202 | 销售 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 203 | 运营 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 200 | 技术 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 202 | 销售 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 203 | 运营 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 200 | 技术 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 203 | 运营 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 202 | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 203 | 运营 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | 200 | 技术 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | 202 | 销售 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | 203 | 运营 |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
2 内连接:只连接匹配的行 inner join
#找两张表共有的部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果
#department没有204这个部门,因而employee表中关于204这条员工信息没有匹配出来
mysql> select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------------+
| id | name | age | sex | name |
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | 18 | male | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | 48 | female | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | 38 | male | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | 28 | female | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | 18 | male | 技术 |
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------------+ #上述sql等同于
mysql> select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee,department where employee.dep_id=department.id;
3 外链接之左连接:优先显示左表全部记录
#以左表为准,即找出所有员工信息,当然包括没有部门的员工
#本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的结果
mysql> select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee left join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+------------+--------------+
| id | name | depart_name |
+----+------------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | 技术 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | 销售 |
| 6 | jingliyang | NULL |
+----+------------+--------------+
4 外链接之右连接:优先显示右表全部记录
#以右表为准,即找出所有部门信息,包括没有员工的部门
#本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加右边有左边没有的结果
mysql> select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee right join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+------+-----------+--------------+
| id | name | depart_name |
+------+-----------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | 技术 |
| NULL | NULL | 运营 |
+------+-----------+--------------+
左连接、右连接都是在内连接的基础上,优先显示本表的内容
5 全外连接:显示左右两个表全部记录
全外连接:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的和右边有左边没有的结果
#注意:mysql不支持全外连接 full JOIN
#强调:mysql可以使用此种方式间接实现全外连接
select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id
union
select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id
;
#查看结果
+------+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+------+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | NULL | NULL |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 203 | 运营 |
+------+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+ #注意 union与union all的区别:union会去掉相同的纪录
符合条件连接查询
#示例1:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且employee表中的age字段值必须大于25,即找出年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门
select employee.name,department.name from employee inner join department
on employee.dep_id = department.id
where age > 25; #示例2:查询employee和department表
select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,department.name from employee,department
where employee.dep_id = department.id
and age > 25
子查询
1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字。
4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等。
1 带IN关键字的子查询
#查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名
select id,name from department
where id in
(select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25); #查看技术部员工姓名
select name from employee
where dep_id in
(select id from department where name='技术'); #查看不足1人的部门名
select name from department
where id in
(select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(id) <=1);
2 带比较运算符的子查询
#比较运算符:=、!=、>、>=、<、<=、<>
#查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄
mysql> select name,age from emp where age > (select avg(age) from emp);
+---------+------+
| name | age |
+---------+------+
| alex | 48 |
| wupeiqi | 38 |
+---------+------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) #查询大于部门内平均年龄的员工名、年龄
select t1.name,t1.age from emp t1
inner join
(select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) t2
on t1.dep_id = t2.dep_id
where t1.age > t2.avg_age;
3 带EXISTS关键字的子查询
EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。
而是返回一个真假值。True或False
当返回True时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询
#department表中存在dept_id=203,Ture
mysql> select * from employee
-> where exists
-> (select id from department where id=200);
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+ #department表中存在dept_id=205,False
mysql> select * from employee
-> where exists
-> (select id from department where id=204);
Empty set (0.00 sec)
小练习
company.employee
员工id id int
姓名 emp_name varchar
性别 sex enum
年龄 age int
入职日期 hire_date date
岗位 post varchar
职位描述 post_comment varchar
薪水 salary double
办公室 office int
部门编号 depart_id int #创建表
create table employee(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', #大部分是男的
age int(3) unsigned not null default 28,
hire_date date not null,
post varchar(50),
post_comment varchar(100),
salary double(15,2),
office int, #一个部门一个屋子
depart_id int
); #查看表结构
mysql> desc employee;
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | NO | | male | |
| age | int(3) unsigned | NO | | 28 | |
| hire_date | date | NO | | NULL | |
| post | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| post_comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
| salary | double(15,2) | YES | | NULL | |
| office | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| depart_id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ #插入记录
#三个部门:教学,销售,运营
insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values
('egon','male',18,'20170301','老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使',7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部
('alex','male',78,'20150302','teacher',1000000.31,401,1),
('wupeiqi','male',81,'20130305','teacher',8300,401,1),
('yuanhao','male',73,'20140701','teacher',3500,401,1),
('liwenzhou','male',28,'20121101','teacher',2100,401,1),
('jingliyang','female',18,'20110211','teacher',9000,401,1),
('jinxin','male',18,'19000301','teacher',30000,401,1),
('成龙','male',48,'20101111','teacher',10000,401,1), ('歪歪','female',48,'20150311','sale',3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门
('丫丫','female',38,'20101101','sale',2000.35,402,2),
('丁丁','female',18,'20110312','sale',1000.37,402,2),
('星星','female',18,'20160513','sale',3000.29,402,2),
('格格','female',28,'20170127','sale',4000.33,402,2), ('张野','male',28,'20160311','operation',10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门
('程咬金','male',18,'19970312','operation',20000,403,3),
('程咬银','female',18,'20130311','operation',19000,403,3),
('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411','operation',18000,403,3),
('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512','operation',17000,403,3)
; #ps:如果在windows系统中,插入中文字符,select的结果为空白,可以将所有字符编码统一设置成gbk 准备表和记录
SELECT
*
FROM
emp AS t1
INNER JOIN (
SELECT
post,
max(hire_date) max_date
FROM
emp
GROUP BY
post
) AS t2 ON t1.post = t2.post
WHERE
t1.hire_date = t2.max_date; 答案一(链表)
mysql> select (select t2.name from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) from emp as t1 group by post;
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| (select t2.name from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 张野 |
| 格格 |
| alex |
| egon |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select (select t2.id from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) from emp as t1 group by post;
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| (select t2.id from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 14 |
| 13 |
| 2 |
| 1 |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) #正确答案
mysql> select t3.name,t3.post,t3.hire_date from emp as t3 where id in (select (select id from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) from emp as t1 group by post);
+--------+-----------------------------------------+------------+
| name | post | hire_date |
+--------+-----------------------------------------+------------+
| egon | 老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使 | 2017-03-01 |
| alex | teacher | 2015-03-02 |
| 格格 | sale | 2017-01-27 |
| 张野 | operation | 2016-03-11 |
+--------+-----------------------------------------+------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) 答案二(子查询)
答案一为正确答案,答案二中的limit 1有问题(每个部门可能有>1个为同一时间入职的新员工),我只是想用该例子来说明可以在select后使用子查询
总结select语句的定义与执行顺序
定义顺序
SELECT DISTINCT <select_list>
FROM <left_table>
<join_type> JOIN <right_table>
ON <join_condition>
WHERE <where_condition>
GROUP BY <group_by_list>
HAVING <having_condition>
ORDER BY <order_by_condition>
LIMIT <limit_number>
执行顺序(重中之重)
(7) SELECT
(8) DISTINCT <select_list>
(1) FROM <left_table>
(3) <join_type> JOIN <right_table>
(2) ON <join_condition>
(4) WHERE <where_condition>
(5) GROUP BY <group_by_list>
(6) HAVING <having_condition>
(9) ORDER BY <order_by_condition>
(10) LIMIT <limit_number>
pymysql模块
之前我们都是通过MySQL自带的命令行客户端工具mysql来操作数据库,那如何在python程序中操作数据库呢?
这就用到了pymysql模块,该模块本质就是一个套接字客户端软件,使用前需要事先安装
pip3 install pymysql
import pymysql
name = input(">>: ")
pwd = input(">>: ")
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.1.24', # 连接的服务端ip地址
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123',
db='db3',
charset='utf8'
)
# 拿到游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行sql语句
sql = 'select * from user_info where name = "%s" and pwd = "%s"' % (name, pwd) # 有可能会sql注入
print(sql)
rows = cursor.execute(sql)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 运行判断
if rows:
print('登陆成功')
else:
print('登陆失败')
execute()之sql注入
注意:符号--会注释掉它之后的sql,正确的语法:--后至少有一个任意字符
根本原理:就根据程序的字符串拼接name=“%s”,我们输入一个xxx"-- haha,
用我们输入的xxx加'在程序中拼接成一个判断条件name="xxx"--haha
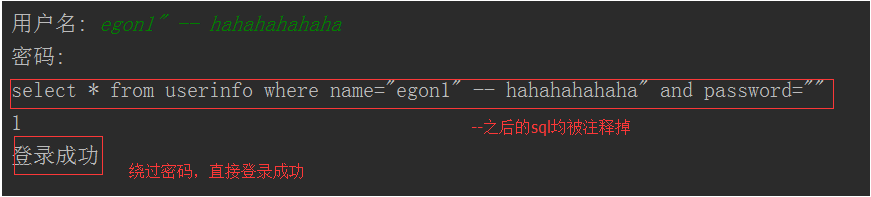
最后那一个空格,在一条sql语句中如果遇到select * from t1 where id > 3 -- and name='egon';则--之后的条件被注释掉了 #1、sql注入之:用户存在,绕过密码
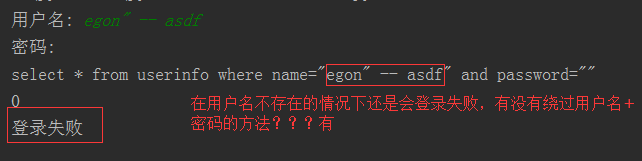
egon' -- 任意字符 #2、sql注入之:用户不存在,绕过用户与密码
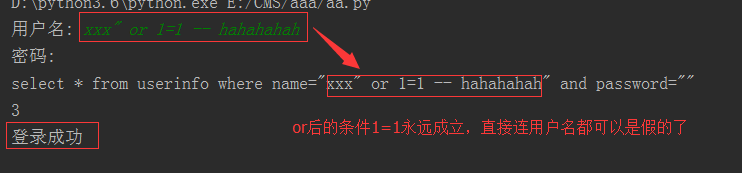
xxx' or 1=1 -- 任意字符
# 原来是我们对sql进行字符串拼接
# sql="select * from userinfo where name='%s' and password='%s'" %(user,pwd)
# print(sql)
# res=cursor.execute(sql) #改写为(execute帮我们做字符串拼接,我们无需且一定不能再为%s加引号了)
sql="select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s" #!!!注意%s需要去掉引号,因为pymysql会自动为我们加上
res=cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #pymysql模块自动帮我们解决sql注入的问题,只要我们按照pymysql的规矩来。
修改之后的代码
import pymysql
name = input(">>: ")
pwd = input(">>: ")
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.1.24',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123',
db='db3',
charset='utf8'
)
# 拿到游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = 'select * from user_info where name = %s and pwd = %s'
rows = cursor.execute(sql, (name, pwd)) # 将字符串拼接放到execute中执行可防止sql注入
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 运行判断
if rows:
print('登陆成功')
else:
print('登陆失败')
增删改--conn.commit()
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.1.24',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123',
db='db3',
charset='utf8'
) cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = 'insert into user_info(id,name,pwd) values(%s,%s,%s)' # 增 删 改 都是只对sql语句修改
rows = cursor.execute(sql, (3, 'alex', 456))
print(cursor.lastrowid) # 获取插入的最后一条数据的自增ID 在插入语句后查看 可知道插入本条数据的id
conn.commit() # 提交结果 提交结果后才会发现表中的数据修改成功
cursor.close()
conn.close() if rows:
print('修改成功')
查数据: fetchone,fetchmany,fetchall
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.1.24',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123',
db='db3',
charset='utf8'
) cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = 'select * from user_info'
rows = cursor.execute(sql)
print(rows)
print(cursor.fetchone()) # 只拿一条数据
print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) # 可指定拿多条数据
print(cursor.fetchall()) # 拿全部数据
print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) # 拿去数据时和操作文件类似 控制游标的位置 来控制拿取的数据 cursor.close()
conn.close()
拿去数据时和操作文件类似 控制游标的位置 来控制拿取的数据
控制游标的方式有两种
cursor.scroll(2, mode='absolute') # 从最开始 跳过前两条数据
print(cursor.fetchone()) print(cursor.fetchone())
cursor.scroll(1, mode='relative') # 相对于现在的位置跳过一条
print(cursor.fetchone())
获取插入的最后一条数据的自增ID
import pymysql
conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123',database='egon')
cursor=conn.cursor() sql='insert into userinfo(name,password) values("xxx","123");'
rows=cursor.execute(sql)
print(cursor.lastrowid) #在插入语句后查看 可知当前插入数据的id conn.commit() cursor.close()
conn.close()
mysql内置功能
视图
视图是一个虚拟表(非真实存在),其本质是【根据SQL语句获取动态的数据集,并为其命名】
,用户使用时只需使用【名称】即可获取结果集,可以将该结果集当做表来使用。
使用视图我们可以把查询过程中的临时表摘出来,用视图去实现,这样以后再想操作该临时表的数据时就无需重写复杂的sql了,直接去视图中查找即可,
但视图有明显地效率问题,并且视图是存放在数据库中的,如果我们程序中使用的sql过分依赖数据库中的视图,即强耦合,那就意味着扩展sql极为不便,因此并不推荐使用。
一 创建视图
#语法:CREATE VIEW 视图名称 AS SQL语句
create view teacher_view as select tid from teacher where tname='李平老师'; #于是查询李平老师教授的课程名的sql可以改写为
mysql> select cname from course where teacher_id = (select tid from teacher_view);
+--------+
| cname |
+--------+
| 物理 |
| 美术 |
+--------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) #!!!注意注意注意:
#1. 使用视图以后就无需每次都重写子查询的sql,但是这么效率并不高,还不如我们写子查询的效率高 #2. 而且有一个致命的问题:视图是存放到数据库里的,如果我们程序中的sql过分依赖于数据库中存放的视图,
那么意味着,一旦sql需要修改且涉及到视图的部分,则必须去数据库中进行修改,而通常在公司中数据库有专门的DBA负责,
你要想完成修改,必须付出大量的沟通成本DBA可能才会帮你完成修改,极其地不方便
二 使用视图
#修改视图,原始表也跟着改
mysql> select * from course;
+-----+--------+------------+
| cid | cname | teacher_id |
+-----+--------+------------+
| 1 | 生物 | 1 |
| 2 | 物理 | 2 |
| 3 | 体育 | 3 |
| 4 | 美术 | 2 |
+-----+--------+------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> create view course_view as select * from course; #创建表course的视图
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.52 sec) mysql> select * from course_view;
+-----+--------+------------+
| cid | cname | teacher_id |
+-----+--------+------------+
| 1 | 生物 | 1 |
| 2 | 物理 | 2 |
| 3 | 体育 | 3 |
| 4 | 美术 | 2 |
+-----+--------+------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> update course_view set cname='xxx'; #更新视图中的数据
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.04 sec)
Rows matched: 4 Changed: 4 Warnings: 0 mysql> insert into course_view values(5,'yyy',2); #往视图中插入数据
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec) mysql> select * from course; #发现原始表的记录也跟着修改了
+-----+-------+------------+
| cid | cname | teacher_id |
+-----+-------+------------+
| 1 | xxx | 1 |
| 2 | xxx | 2 |
| 3 | xxx | 3 |
| 4 | xxx | 2 |
| 5 | yyy | 2 |
+-----+-------+------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
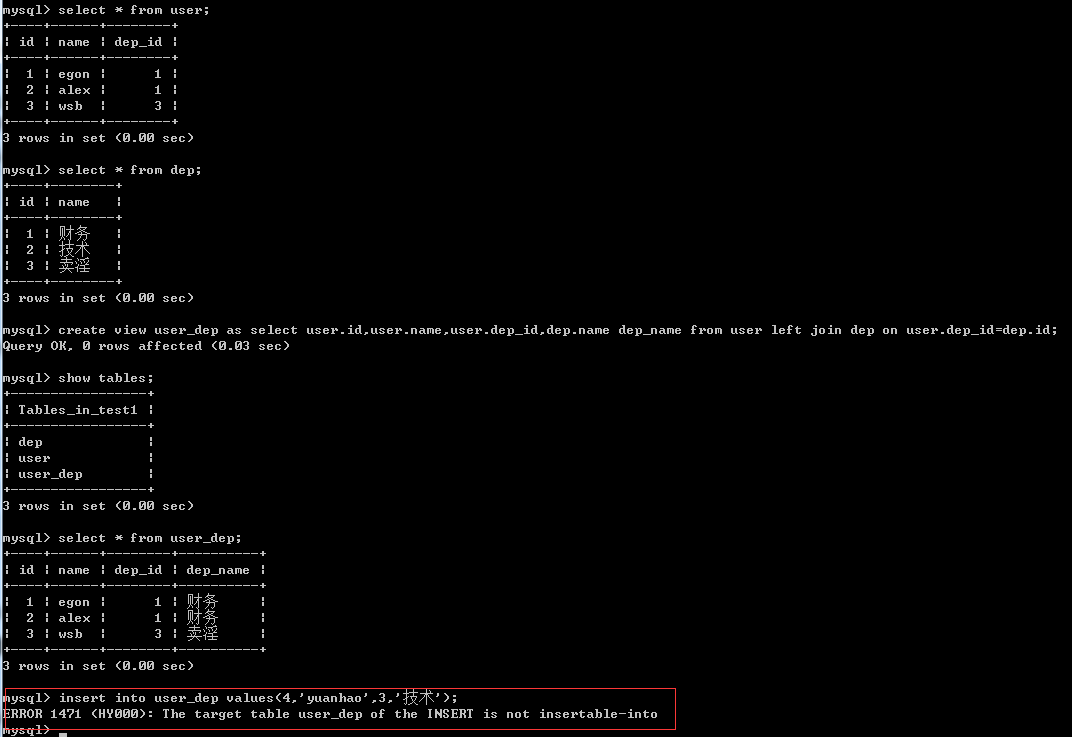
我们不应该修改视图中的记录,而且在涉及多个表的情况下是根本无法修改视图中的记录的,如下图
三 修改视图
语法:ALTER VIEW 视图名称 AS SQL语句
mysql> alter view teacher_view as select * from course where cid>3;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> select * from teacher_view;
+-----+-------+------------+
| cid | cname | teacher_id |
+-----+-------+------------+
| 4 | xxx | 2 |
| 5 | yyy | 2 |
+-----+-------+------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
四 删除视图
语法:DROP VIEW 视图名称 DROP VIEW teacher_view
触发器
使用触发器可以定制用户对表进行【增、删、改】操作时前后的行为,注意:没有查询
一 创建触发器
# 插入前
CREATE TRIGGER tri_before_insert_tb1 BEFORE INSERT ON tb1 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
...
END # 插入后
CREATE TRIGGER tri_after_insert_tb1 AFTER INSERT ON tb1 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
...
END # 删除前
CREATE TRIGGER tri_before_delete_tb1 BEFORE DELETE ON tb1 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
...
END # 删除后
CREATE TRIGGER tri_after_delete_tb1 AFTER DELETE ON tb1 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
...
END # 更新前
CREATE TRIGGER tri_before_update_tb1 BEFORE UPDATE ON tb1 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
...
END # 更新后
CREATE TRIGGER tri_after_update_tb1 AFTER UPDATE ON tb1 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
...
END
#准备表
CREATE TABLE cmd (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
USER CHAR (32),
priv CHAR (10),
cmd CHAR (64),
sub_time datetime, #提交时间
success enum ('yes', 'no') #0代表执行失败
); CREATE TABLE errlog (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
err_cmd CHAR (64),
err_time datetime
); #创建触发器
delimiter //
CREATE TRIGGER tri_after_insert_cmd AFTER INSERT ON cmd FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.success = 'no' THEN #等值判断只有一个等号
INSERT INTO errlog(err_cmd, err_time) VALUES(NEW.cmd, NEW.sub_time) ; #必须加分号
END IF ; #必须加分号
END//
delimiter ; #往表cmd中插入记录,触发触发器,根据IF的条件决定是否插入错误日志
INSERT INTO cmd (
USER,
priv,
cmd,
sub_time,
success
)
VALUES
('egon','0755','ls -l /etc',NOW(),'yes'),
('egon','0755','cat /etc/passwd',NOW(),'no'),
('egon','0755','useradd xxx',NOW(),'no'),
('egon','0755','ps aux',NOW(),'yes'); #查询错误日志,发现有两条
mysql> select * from errlog;
+----+-----------------+---------------------+
| id | err_cmd | err_time |
+----+-----------------+---------------------+
| 1 | cat /etc/passwd | 2017-09-14 22:18:48 |
| 2 | useradd xxx | 2017-09-14 22:18:48 |
+----+-----------------+---------------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) 插入后触发触发器
特别的两个对象:NEW表示即将插入的数据行,OLD表示即将删除的数据行。
二 使用触发器
触发器无法由用户直接调用,而知由于对表的【增/删/改】操作被动引发的。
三 删除触发器
drop trigger tri_after_insert_cmd;
存储过程
一 存储过程介绍
存储过程包含了一系列可执行的sql语句,存储过程存放于MySQL中,通过调用它的名字可以执行其内部的一堆sql
使用存储过程的优点:
1. 用于替代程序写的SQL语句,实现程序与sql解耦
2. 基于网络传输,传别名的数据量小,而直接传sql数据量大
使用存储过程的缺点:
1. 程序员扩展功能不方便
二 创建简单存储过程(无参)
delimiter // # 将//作为结束符
create procedure p1()
BEGIN
select * from blog;
INSERT into blog(name,sub_time) values("xxx",now());
END //
delimiter ; # 将结束变为; #在mysql中调用
call p1() #在python中基于pymysql调用
cursor.callproc('p1')
print(cursor.fetchall())
三 创建存储过程(有参)
对于存储过程,可以接收参数,其参数有三类:
in 仅用于传入参数用
out 仅用于返回值用
inout 既可以传入又可以当作返回值
delimiter //
create procedure p2(
in n1 int,
in n2 int
)
BEGIN select * from blog where id > n1;
END //
delimiter ; #在mysql中调用
call p2(3,2) #在python中基于pymysql调用
cursor.callproc('p2',(3,2))
print(cursor.fetchall()) in:传入参数
delimiter //
create procedure p3(
in n1 int,
out res int
)
BEGIN
select * from blog where id > n1;
set res = 1;
END //
delimiter ; #在mysql中调用
set @res=0; #0代表假(执行失败),1代表真(执行成功)
call p3(3,@res);
select @res; #在python中基于pymysql调用
cursor.callproc('p3',(3,0)) #0相当于set @res=0
print(cursor.fetchall()) #查询select的查询结果 cursor.execute('select @_p3_0,@_p3_1;') #@p3_0代表第一个参数,@p3_1代表第二个参数,即返回值
print(cursor.fetchall()) out:返回值
delimiter //
create procedure p4(
inout n1 int
)
BEGIN
select * from blog where id > n1;
set n1 = 1;
END //
delimiter ; #在mysql中调用
set @x=3;
call p4(@x);
select @x; #在python中基于pymysql调用
cursor.callproc('p4',(3,))
print(cursor.fetchall()) #查询select的查询结果 cursor.execute('select @_p4_0;')
print(cursor.fetchall()) inout:既可以传入又可以返回
四 执行存储过程
-- 无参数
call proc_name() -- 有参数,全in
call proc_name(1,2) -- 有参数,有in,out,inout
set @t1=0;
set @t2=3;
call proc_name(1,2,@t1,@t2) 执行存储过程 在MySQL中执行存储过程-- 无参数
call proc_name() -- 有参数,全in
call proc_name(1,2) -- 有参数,有in,out,inout
set @t1=0;
set @t2=3;
call proc_name(1,2,@t1,@t2) 执行存储过程 在MySQL中执行存储过程
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 执行存储过程
cursor.callproc('p1', args=(1, 22, 3, 4))
# 获取执行完存储的参数
cursor.execute("select @_p1_0,@_p1_1,@_p1_2,@_p1_3")
result = cursor.fetchall() conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close() print(result) 在python中基于pymysql执行存储过程
五 删除存储过程
drop procedure proc_name;
应用程序与数据库结合使用
方式一:
Python:调用存储过程
MySQL:编写存储过程
运行效率高但是开发效率低,很少用。
方式二:
Python:编写纯生SQL
MySQL:
运行效率低,但是可维护性高,但写原生sql比较复杂。
方式三:
Python:ORM->纯生SQL
MySQL:
运行效率比方式二低,因为多一步转化过程,但是基于面向对象,可维护性高,开发效率高。
函数
MySQL中提供了许多内置函数,例如:
一、数学函数
ROUND(x,y)
返回参数x的四舍五入的有y位小数的值 RAND()
返回0到1内的随机值,可以通过提供一个参数(种子)使RAND()随机数生成器生成一个指定的值。 二、聚合函数(常用于GROUP BY从句的SELECT查询中)
AVG(col)返回指定列的平均值
COUNT(col)返回指定列中非NULL值的个数
MIN(col)返回指定列的最小值
MAX(col)返回指定列的最大值
SUM(col)返回指定列的所有值之和
GROUP_CONCAT(col) 返回由属于一组的列值连接组合而成的结果 三、字符串函数 CHAR_LENGTH(str)
返回值为字符串str 的长度,长度的单位为字符。一个多字节字符算作一个单字符。
CONCAT(str1,str2,...)
字符串拼接
如有任何一个参数为NULL ,则返回值为 NULL。
CONCAT_WS(separator,str1,str2,...)
字符串拼接(自定义连接符)
CONCAT_WS()不会忽略任何空字符串。 (然而会忽略所有的 NULL)。 CONV(N,from_base,to_base)
进制转换
例如:
SELECT CONV('a',16,2); 表示将 a 由16进制转换为2进制字符串表示 FORMAT(X,D)
将数字X 的格式写为'#,###,###.##',以四舍五入的方式保留小数点后 D 位, 并将结果以字符串的形式返回。若 D 为 0, 则返回结果不带有小数点,或不含小数部分。
例如:
SELECT FORMAT(12332.1,4); 结果为: '12,332.1000'
INSERT(str,pos,len,newstr)
在str的指定位置插入字符串
pos:要替换位置其实位置
len:替换的长度
newstr:新字符串
特别的:
如果pos超过原字符串长度,则返回原字符串
如果len超过原字符串长度,则由新字符串完全替换
INSTR(str,substr)
返回字符串 str 中子字符串的第一个出现位置。 LEFT(str,len)
返回字符串str 从开始的len位置的子序列字符。 LOWER(str)
变小写 UPPER(str)
变大写 REVERSE(str)
返回字符串 str ,顺序和字符顺序相反。 SUBSTRING(str,pos) , SUBSTRING(str FROM pos) SUBSTRING(str,pos,len) , SUBSTRING(str FROM pos FOR len)
不带有len 参数的格式从字符串str返回一个子字符串,起始于位置 pos。带有len参数的格式从字符串str返回一个长度同len字符相同的子字符串,起始于位置 pos。 使用 FROM的格式为标准 SQL 语法。也可能对pos使用一个负值。假若这样,则子字符串的位置起始于字符串结尾的pos 字符,而不是字符串的开头位置。在以下格式的函数中可以对pos 使用一个负值。 mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Quadratically',5);
-> 'ratically' mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('foobarbar' FROM 4);
-> 'barbar' mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Quadratically',5,6);
-> 'ratica' mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Sakila', -3);
-> 'ila' mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Sakila', -5, 3);
-> 'aki' mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Sakila' FROM -4 FOR 2);
-> 'ki' 四、日期和时间函数
CURDATE()或CURRENT_DATE() 返回当前的日期
CURTIME()或CURRENT_TIME() 返回当前的时间
DAYOFWEEK(date) 返回date所代表的一星期中的第几天(1~7)
DAYOFMONTH(date) 返回date是一个月的第几天(1~31)
DAYOFYEAR(date) 返回date是一年的第几天(1~366)
DAYNAME(date) 返回date的星期名,如:SELECT DAYNAME(CURRENT_DATE);
FROM_UNIXTIME(ts,fmt) 根据指定的fmt格式,格式化UNIX时间戳ts
HOUR(time) 返回time的小时值(0~23)
MINUTE(time) 返回time的分钟值(0~59)
MONTH(date) 返回date的月份值(1~12)
MONTHNAME(date) 返回date的月份名,如:SELECT MONTHNAME(CURRENT_DATE);
NOW() 返回当前的日期和时间
QUARTER(date) 返回date在一年中的季度(1~4),如SELECT QUARTER(CURRENT_DATE);
WEEK(date) 返回日期date为一年中第几周(0~53)
YEAR(date) 返回日期date的年份(1000~9999) 重点:
DATE_FORMAT(date,format) 根据format字符串格式化date值 mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2009-10-04 22:23:00', '%W %M %Y');
-> 'Sunday October 2009'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2007-10-04 22:23:00', '%H:%i:%s');
-> '22:23:00'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('1900-10-04 22:23:00',
-> '%D %y %a %d %m %b %j');
-> '4th 00 Thu 04 10 Oct 277'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('1997-10-04 22:23:00',
-> '%H %k %I %r %T %S %w');
-> '22 22 10 10:23:00 PM 22:23:00 00 6'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('1999-01-01', '%X %V');
-> '1998 52'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2006-06-00', '%d');
-> '00' 五、加密函数
MD5()
计算字符串str的MD5校验和
PASSWORD(str)
返回字符串str的加密版本,这个加密过程是不可逆转的,和UNIX密码加密过程使用不同的算法。 六、控制流函数
CASE WHEN[test1] THEN [result1]...ELSE [default] END
如果testN是真,则返回resultN,否则返回default
CASE [test] WHEN[val1] THEN [result]...ELSE [default]END
如果test和valN相等,则返回resultN,否则返回default IF(test,t,f)
如果test是真,返回t;否则返回f IFNULL(arg1,arg2)
如果arg1不是空,返回arg1,否则返回arg2 NULLIF(arg1,arg2)
如果arg1=arg2返回NULL;否则返回arg1 七、控制流函数小练习
#7.1、准备表
/*
Navicat MySQL Data Transfer Source Server : localhost_3306
Source Server Version : 50720
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Database : student Target Server Type : MYSQL
Target Server Version : 50720
File Encoding : 65001 Date: 2018-01-02 12:05:30
*/ SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; -- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for course
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `course`;
CREATE TABLE `course` (
`c_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`c_name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`t_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`c_id`),
KEY `t_id` (`t_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ----------------------------
-- Records of course
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES ('1', 'python', '1');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES ('2', 'java', '2');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES ('3', 'linux', '3');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES ('4', 'web', '2'); -- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for score
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `score`;
CREATE TABLE `score` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`s_id` int(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`c_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`num` double DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=12 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ----------------------------
-- Records of score
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('1', '1', '1', '79');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('2', '1', '2', '78');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('3', '1', '3', '35');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('4', '2', '2', '32');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('5', '3', '1', '66');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('6', '4', '2', '77');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('7', '4', '1', '68');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('8', '5', '1', '66');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('9', '2', '1', '69');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('10', '4', '4', '75');
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('11', '5', '4', '66.7'); -- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for student
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`s_id` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`s_name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`s_age` int(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`s_sex` char(1) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`s_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ----------------------------
-- Records of student
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('1', '鲁班', '12', '男');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('2', '貂蝉', '20', '女');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('3', '刘备', '35', '男');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('4', '关羽', '34', '男');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('5', '张飞', '33', '女'); -- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for teacher
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `teacher`;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`t_id` int(10) NOT NULL,
`t_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`t_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ----------------------------
-- Records of teacher
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('1', '大王');
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('2', 'alex');
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('3', 'egon');
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('4', 'peiqi'); #7.2、统计各科各分数段人数.显示格式:课程ID,课程名称,[100-85],[85-70],[70-60],[ <60] select score.c_id,
course.c_name,
sum(CASE WHEN num BETWEEN 85 and 100 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) as '[100-85]',
sum(CASE WHEN num BETWEEN 70 and 85 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) as '[85-70]',
sum(CASE WHEN num BETWEEN 60 and 70 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) as '[70-60]',
sum(CASE WHEN num < 60 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) as '[ <60]'
from score,course where score.c_id=course.c_id GROUP BY score.c_id;
#1 基本使用
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2009-10-04 22:23:00', '%W %M %Y');
-> 'Sunday October 2009'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2007-10-04 22:23:00', '%H:%i:%s');
-> '22:23:00'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('1900-10-04 22:23:00',
-> '%D %y %a %d %m %b %j');
-> '4th 00 Thu 04 10 Oct 277'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('1997-10-04 22:23:00',
-> '%H %k %I %r %T %S %w');
-> '22 22 10 10:23:00 PM 22:23:00 00 6'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('1999-01-01', '%X %V');
-> '1998 52'
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2006-06-00', '%d');
-> '00' #2 准备表和记录
CREATE TABLE blog (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
NAME CHAR (32),
sub_time datetime
); INSERT INTO blog (NAME, sub_time)
VALUES
('第1篇','2015-03-01 11:31:21'),
('第2篇','2015-03-11 16:31:21'),
('第3篇','2016-07-01 10:21:31'),
('第4篇','2016-07-22 09:23:21'),
('第5篇','2016-07-23 10:11:11'),
('第6篇','2016-07-25 11:21:31'),
('第7篇','2017-03-01 15:33:21'),
('第8篇','2017-03-01 17:32:21'),
('第9篇','2017-03-01 18:31:21'); #3. 提取sub_time字段的值,按照格式后的结果即"年月"来分组
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(sub_time,'%Y-%m'),COUNT(1) FROM blog GROUP BY DATE_FORMAT(sub_time,'%Y-%m'); #结果
+-------------------------------+----------+
| DATE_FORMAT(sub_time,'%Y-%m') | COUNT(1) |
+-------------------------------+----------+
| 2015-03 | 2 |
| 2016-07 | 4 |
| 2017-03 | 3 |
+-------------------------------+----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) 需要掌握函数:date_format
一 自定义函数
#!!!注意!!!
#函数中不要写sql语句(否则会报错),函数仅仅只是一个功能,是一个在sql中被应用的功能
#若要想在begin...end...中写sql,请用存储过程
delimiter //
create function f1(
i1 int,
i2 int)
returns int
BEGIN
declare num int;
set num = i1 + i2;
return(num);
END //
delimiter ;
delimiter //
create function f5(
i int
)
returns int
begin
declare res int default 0;
if i = 10 then
set res=100;
elseif i = 20 then
set res=200;
elseif i = 30 then
set res=300;
else
set res=400;
end if;
return res;
end //
delimiter ;
二 删除函数
drop function func_name;
三 执行函数
# 获取返回值
select UPPER('egon') into @res;
SELECT @res; # 在查询中使用
select f1(11,nid) ,name from tb2;
事物
事务用于将某些操作的多个SQL作为原子性操作,一旦有某一个出现错误,即可回滚到原来的状态,从而保证数据库数据完整性。
create table user(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(32),
balance int
); insert into user(name,balance)
values
('wsb',1000),
('egon',1000),
('ysb',1000); #原子操作
start transaction;
update user set balance=900 where name='wsb'; #买支付100元
update user set balance=1010 where name='egon'; #中介拿走10元
update user set balance=1090 where name='ysb'; #卖家拿到90元
commit; #出现异常,回滚到初始状态
start transaction;
update user set balance=900 where name='wsb'; #买支付100元
update user set balance=1010 where name='egon'; #中介拿走10元
uppdate user set balance=1090 where name='ysb'; #卖家拿到90元,出现异常没有拿到
rollback; # 回滚
commit;
mysql> select * from user;
+----+------+---------+
| id | name | balance |
+----+------+---------+
| 1 | wsb | 1000 |
| 2 | egon | 1000 |
| 3 | ysb | 1000 |
+----+------+---------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
#介绍
delimiter //
create procedure p4(
out status int
)
BEGIN
1. 声明如果出现异常则执行{
set status = 1;
rollback;
} 开始事务
-- 由秦兵账户减去100
-- 方少伟账户加90
-- 张根账户加10
commit;
结束 set status = 2; END //
delimiter ; #实现
delimiter //
create PROCEDURE p5(
OUT p_return_code tinyint
)
BEGIN
DECLARE exit handler for sqlexception
BEGIN
-- ERROR
set p_return_code = 1;
rollback;
END; DECLARE exit handler for sqlwarning
BEGIN
-- WARNING
set p_return_code = 2;
rollback;
END; START TRANSACTION;
DELETE from tb1; #执行失败
insert into blog(name,sub_time) values('yyy',now());
COMMIT; -- SUCCESS
set p_return_code = 0; #0代表执行成功 END //
delimiter ; #在mysql中调用存储过程
set @res=123;
call p5(@res);
select @res; #在python中基于pymysql调用存储过程
cursor.callproc('p5',(123,))
print(cursor.fetchall()) #查询select的查询结果 cursor.execute('select @_p5_0;')
print(cursor.fetchall()) 事务
流程控制
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE proc_if ()
BEGIN declare i int default 0;
if i = 1 THEN
SELECT 1;
ELSEIF i = 2 THEN
SELECT 2;
ELSE
SELECT 7;
END IF; END //
delimiter ; if条件语句
循环语句
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE proc_while ()
BEGIN DECLARE num INT ;
SET num = 0 ;
WHILE num < 10 DO
SELECT
num ;
SET num = num + 1 ;
END WHILE ; END //
delimiter ; while循环
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE proc_repeat ()
BEGIN DECLARE i INT ;
SET i = 0 ;
repeat
select i;
set i = i + 1;
until i >= 5
end repeat; END //
delimiter ; repeat循环
BEGIN
declare i int default 0;
loop_label: loop
set i=i+1;
if i<8 then
iterate loop_label;
end if;
if i>=10 then
leave loop_label;
end if;
select i;
end loop loop_label;
END
loop
注:本博客大部分参考linhaifeng老师博客园https://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/articles/7356064.html
MySQL数据库开发(2)的更多相关文章
- PHP+mysql数据库开发搜索功能:中英文分词+全文检索(MySQL全文检索+中文分词(SCWS))
PHP+mysql数据库开发类似百度的搜索功能:中英文分词+全文检索 中文分词: a) robbe PHP中文分词扩展: http://www.boyunjian.com/v/softd/robb ...
- 原生Jdbc操作Mysql数据库开发步骤
原生Jdbc操作Mysql数据库开发步骤 原生的Jdbc就是指,不使用任何框架,仅用java.sql包下的方法实现数据库查询等的操作. 下面是开发步骤: 1.导入数据库驱动包 ...
- MySQL 数据库开发的 36 条军规
MySQL 数据库开发的 36 条军规 写在前面的话: 总是在灾难发生后,才想起容灾的重要性: 总是在吃过亏后,才记得曾经有人提醒过. (一)核心军规 (1)不在数据库做运算:cpu计算务必移至业务层 ...
- MySQL数据库开发规范-EC
最近一段时间一边在线上抓取SQL来优化,一边在整理这个开发规范,尽量减少新的问题SQL进入生产库.今天也是对公司的开发做了一次培训,PPT就不放上来了,里面有十来个生产SQL的案例.因为规范大部分还是 ...
- mysql数据库开发常见问题及优化
mysql 数据库是被广泛应用的关系型数据库,其体积小.支持多处理器.开源并免费的特性使其在 Internet 中小型网站中的使用率尤其高.在使用 mysql 的过程中不规范的 SQL 编写.非最优的 ...
- 微渠道发展 BAE交通运输平台和java呼声,微信mysql数据库开发实例 --图文开发教程
持续更新 BAE java开展mysql数据库 图文教程 BAE java语言发展mysql源码下载: 目前微信的发展.BAE开展.java开展.mysql教程开发非常,的介绍基于BAE平台.java ...
- MySQL数据库开发规范知识点
前言: 设计规范更多的是为了确保数据库设计的合理性.为了项目最终的协调稳定性,而命名规范则更多的是为了确保设计的正式和统一. 约定优先于配置(Convention Over Configuration ...
- MySQL优化技巧之四:mysql数据库开发常见问题及优化[转]
mysql 数据库是被广泛应用的关系型数据库,其体积小.支持多处理器.开源并免费的特性使其在 Internet 中小型网站中的使用率尤其高.在使用 mysql 的过程中不规范的 SQL 编写.非最优的 ...
- 第四模块:网络编程进阶&数据库开发 第2章·MySQL数据库开发
01-MySQL开篇 02-MySQL简单介绍 03-不同平台下安装MySQL 04-Windows平台MySQL密码设置与破解 05-Linux平台MySQL密码设置与破解 06-Mac平台MySQ ...
- MySQL数据库开发的36条原则【华为云技术分享】
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明. 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/devcloud/article/detai ...
随机推荐
- P9562 [SDCPC2023] G-Matching 题解
题目描述 给定长度为 \(n\) 的整数序列 \(a_1, a_2, \cdots, a_n\),我们将从该序列中构造出一张无向图 \(G\).具体来说,对于所有 \(1 \le i < j \ ...
- Serverless 可观测性的过去、现在与未来
简介: 函数计算可观测性经历了 1.0 -> 2.0 的发展,从闭门造车的可观测发展成开源的可观测,从平台的可观测发展为开发者的可观测,从FaaS Only 的可观测演进成了云原生的可观测. 作 ...
- 阿里云RDS深度定制-XA Crash Safe
简介: 近几年,随着分布式数据库系统的兴起,特别是基于MySQL分布式数据库系统,会用到XA来保证全局事务的一致性.众所周知,MySQL对XA事务的支持是比较弱的,存在很多问题.为了满足分布式数据库 ...
- WPF 实现自定义的笔迹橡皮擦
本文来告诉大家使用比较底层的方法来实现 WPF 的笔迹橡皮擦 在 WPF 里面,对于笔迹来说,应该放在 Stroke 类里面,而不是作为点的集合存储.在 Stroke 类里面将作为管理笔迹的类提供笔迹 ...
- Django之ajax简介
1.MTV与MVC 框架类型:MVC: M:models V:views C:controller Django用的框架就是MTV MTV: M:models T:templates V:views ...
- k8s控制节点etcd删除并重新加入
官方参考:https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-upgrade-etcd/ 1.删除etcd节点 cd ...
- Oracle、达梦:_ 英文下划线 让LIKE查询失效的解决方案:ESCAPE关键字
oracle/dm:_ 英文下划线让like查询失效的解决方案:ESCAPE关键字 -- 可以查询出带(\)的值 SELECT "f1","f2" FROM & ...
- SAP集成技术(四)五种集成架构
本文中,我们将介绍并解释五个主要的模型.我们主要区分直接集成.中间件导向集成以及两个一般的架构概念.直接集成(例如点对点集成)中的标准化很少,但中间件导向的拓扑(例如中心辐射型拓扑以及企业服务总线)追 ...
- 【python爬虫案例】用python爬豆瓣电影TOP250排行榜!
目录 一.爬虫对象-豆瓣电影TOP250 二.python爬虫代码讲解 三.同步视频 四.获取完整源码 一.爬虫对象-豆瓣电影TOP250 前几天,我分享了一个python爬虫案例,爬取豆瓣读书TOP ...
- ITIL4 服务价值系统(SVS):一场服务管理的革新之旅
在这个数字化时代,每一家企业都在追求高效的服务管理和卓越的客户体验.今天,我们就来聊一聊ITIL4中的服务价值系统(Service Value System, SVS)--一个让服务管理变得更加直观和 ...
