Spring 的依赖注入
Spring 的依赖注入
@
每博一文案
"在千千万万个选择里",我永远选择去做哪些我认为值得的事,我可能干得很漂亮,也可能搞得一塌糊涂。
但没关系,重要的是我为之努力过。”我们很难做好每件事,让人生不留下任何遗憾,尽力而为就好“享受
生活的过程,接受结果。”人生是用来体验的,不是用来演绎完美的,我慢慢能接受自己身上哪些灰暗的部分,原谅自己
的迟钝和平庸,允许自己出错,允许自己偶尔断电,带着缺憾拼命绽放,这是与自己达成和解的唯一方式。”
尽力就好,允许所有的事与愿违。和不适合你的过去说再见,哪些伤痛的不堪的,霉烂的过去绝口不提。
太阳的起落在告诉我们,永远会有崭新的一天。
“真正有价值的事情,都不是轻松舒服就能完成的”。那些晨间的寂静,不眠的星光,清醒的克制,
孤军奋战的坚持,暗暗许下的承诺,才是我热爱自己的时刻。"人生就是一步一步地打怪升级,坚持
下去,你所执着的努力一定会有所收获",
——————《网友的评论》
1. 依赖注入
依赖注入实现了控制反转的思想:
- Spring通过依赖注入的方式来完成Bean(类/对象)的管理。
- Bean的管理:Bean对象的创建,以及Bean对象中属性的赋值(或者叫做Bean对象之间的关联的维护)。
依赖注入:
- 依赖指的是对象和对象 之间的关联关系。
- 注入指的是一种数据传递行为,通过注入行为来让对象和对象产生关系。
依赖注入常见的实现方式包括两种:
- 第一种:set注入
- 第二种: 构造注入
**准备工作:通过 maven 导入对应 spring6 的相关jar **
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-003-dependency-injection-blog</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 将项目的打包方式为 jar Java项目的方式-->
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!-- 导入相关的依赖仓库-->
<dependencies>
<!-- spring6 框架-->
<!--spring contest 仓库-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
1.1 构造注入
所谓的构造注入:核心就是:调用了对应的构造方法,进行一个类/对象的属性赋值。
既然要调用构造方法,进行一个属性的赋值的话,那么我们的对应属性的赋值的,构造方法必须存在才行。
构造注入:是在对象创建的时刻进行注入的。
重点:构造注入的使用的标签是:
<constructor-arg></constructor-arg>
1.1.1 通过参数名进行构造注入
格式:
<bean id="" class="">
<!-- 简单的类型使用: value 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg name="" value=""></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg name="" ref=""></constructor-arg>
</bean>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Cat {
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Zoon {
private String zoonName;
private Cat cat;
public Zoon(String zoonName, Cat cat) {
this.zoonName = zoonName;
this.cat = cat;
System.out.println("执行了该 Zoon的构造器");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Zoon{" +
"zoonName='" + zoonName + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- 简单的类型使用: value 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg name="zoonName" value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg name="cat" ref="catBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-structure.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
Zoon zoonBean = applicationContext.getBean("zoonBean", Zoon.class);
System.out.println(zoonBean);
}
}
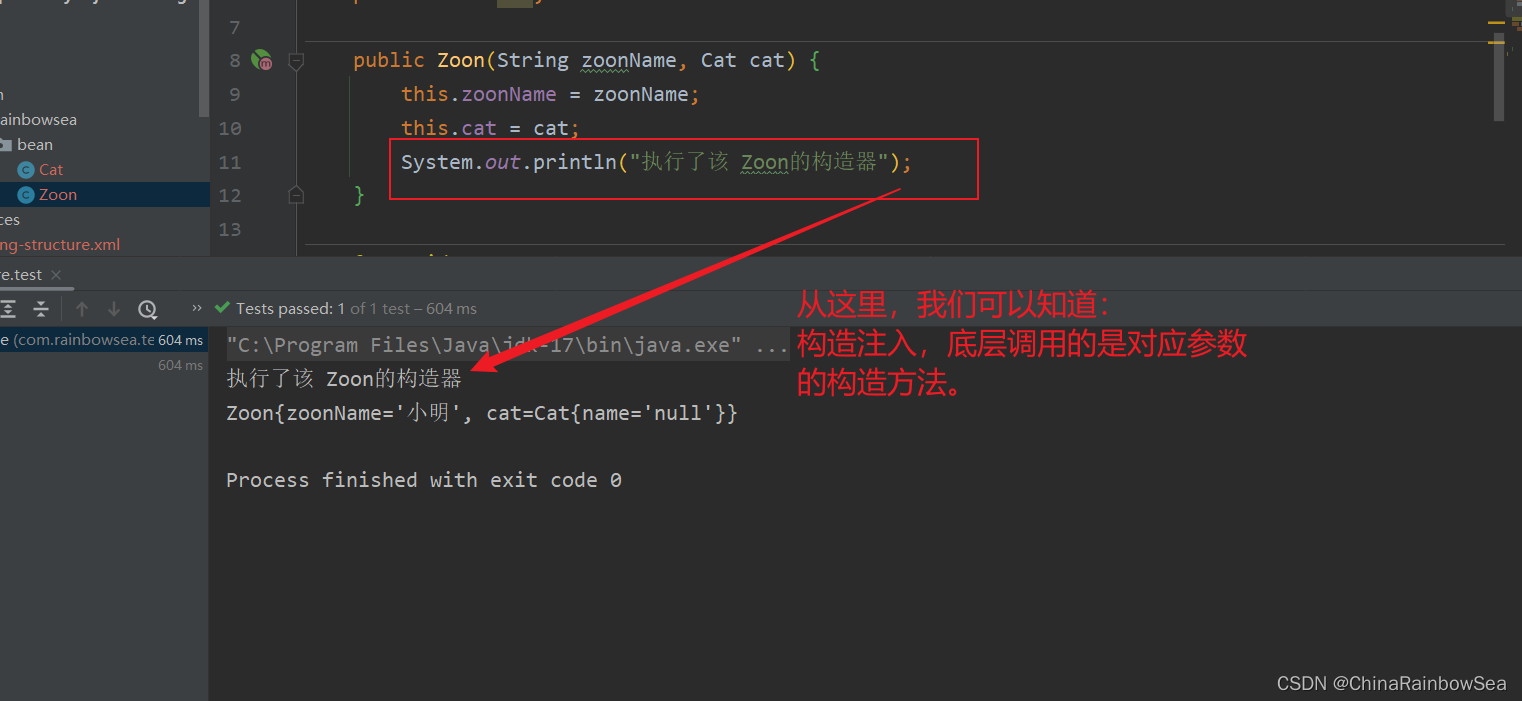
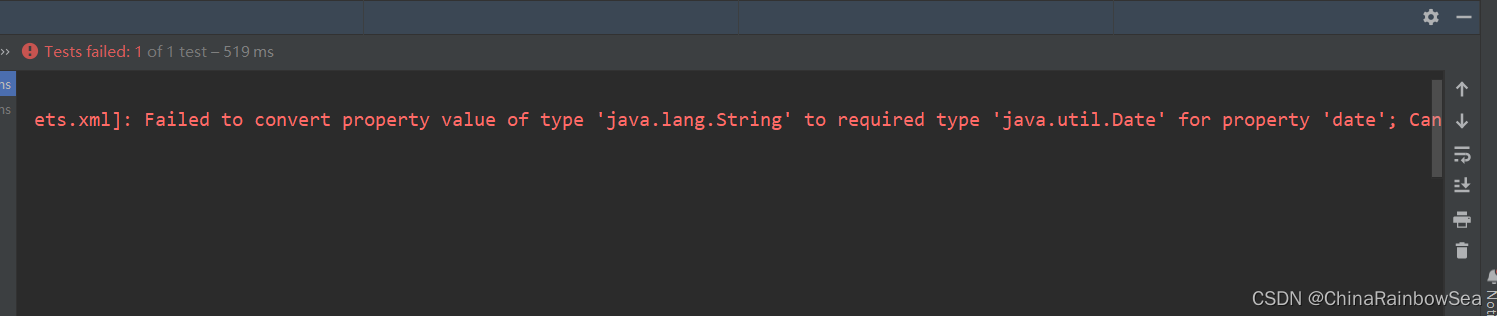
测试如果,我们将构造方法删除了,就不行了,报如下错误:
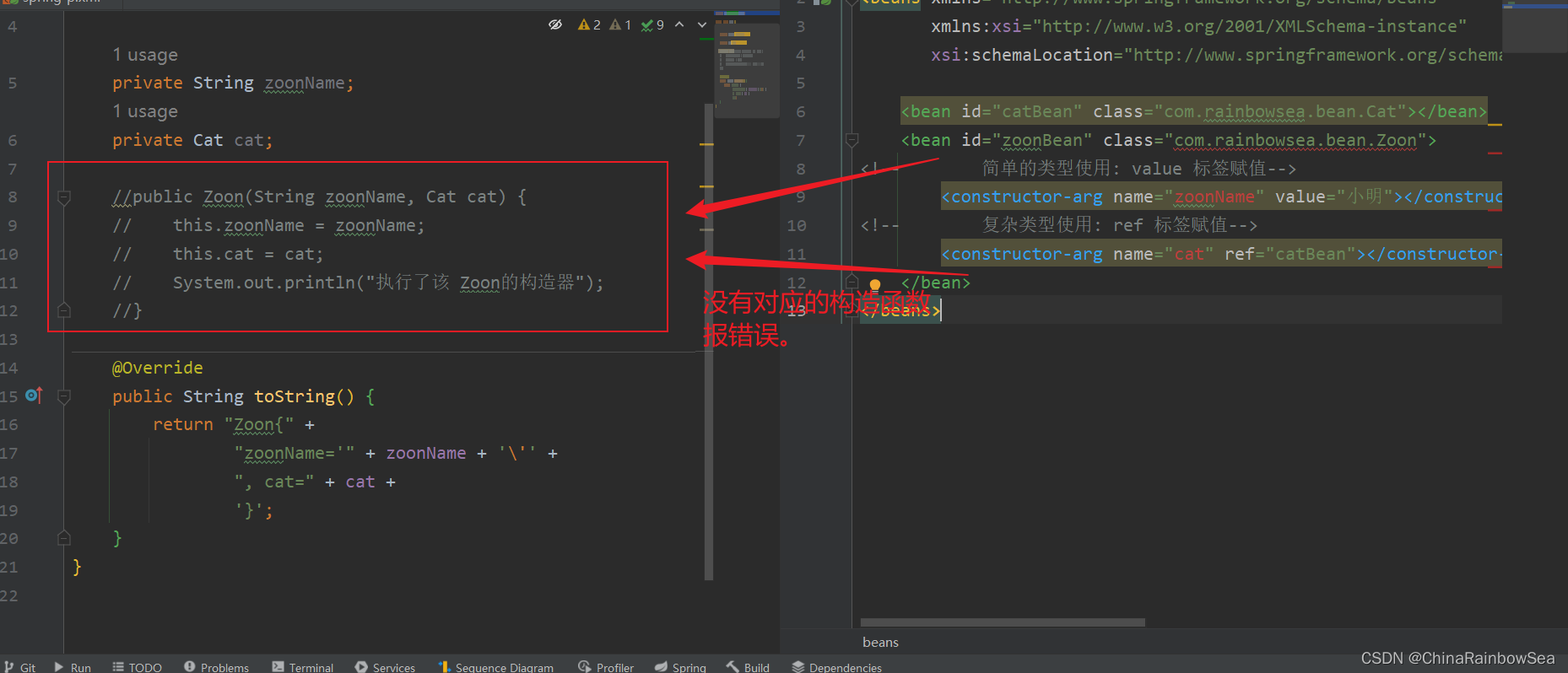
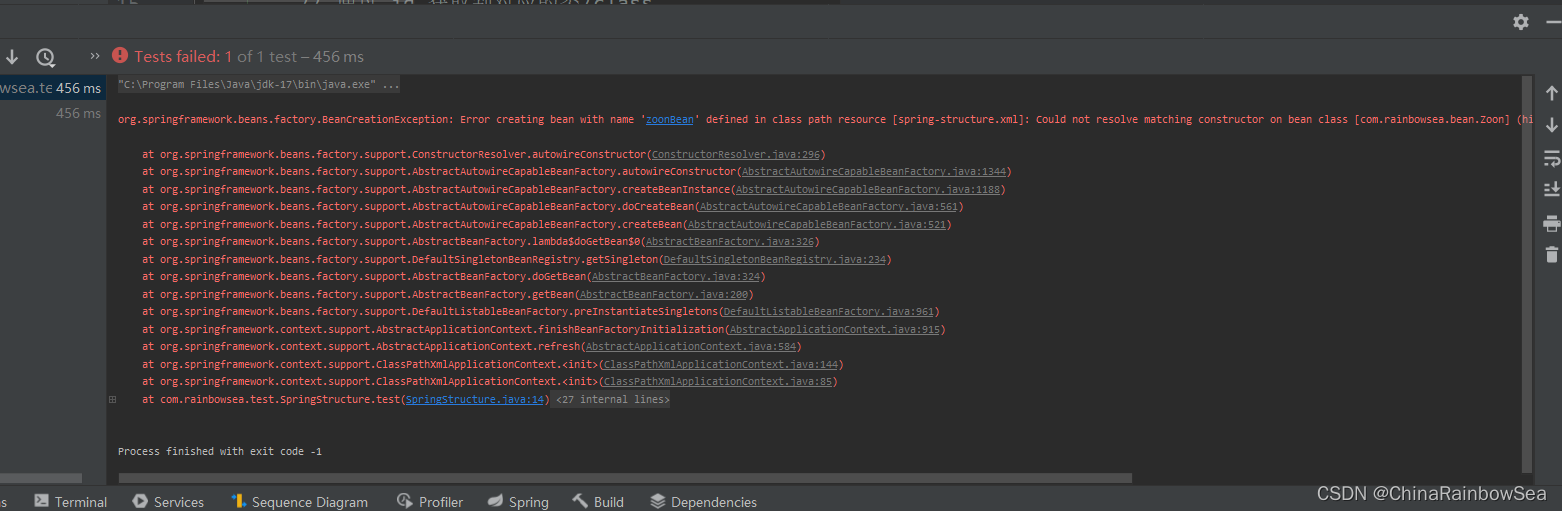
1.1.2 通过参数的下标,进行构造注入
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- index 下标注入: 注意:第一个参数是从 0 开始的,简单的类型使用: value 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value=""></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref=""></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- index 下标注入: 注意:第一个参数是从 0 开始的,简单的类型使用: value 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="catBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
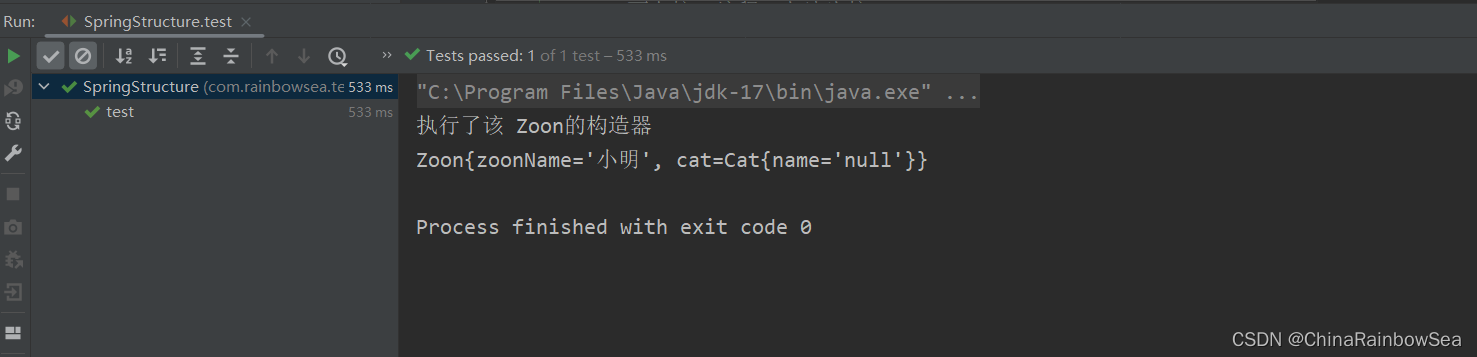
1.1.3 不指定参数下标,不指定参数名字,通过自动装配的方式
格式:但是这种方式不建议:因为可读性十分的差。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- 简单的类型使用: value 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg value="xxx"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg ref="xxx"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- 简单的类型使用: value 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref 标签赋值-->
<constructor-arg ref="catBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
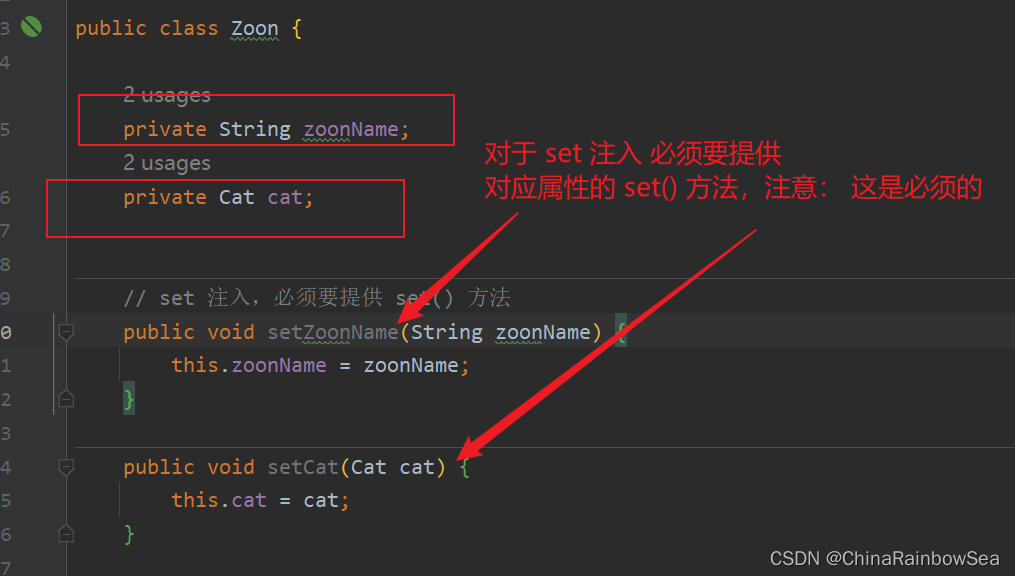
1.2 set 注入
set 注入顾名思义:是基于 set () 方法实现的,底层通过反射机制调用属性对应的 set() 方法然后给属性赋值。这种方式 要求属性必须对外提供 set() 方法。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Zoon {
private String zoonName;
private Cat cat;
// set 注入,必须要提供 set() 方法
public void setZoonName(String zoonName) {
this.zoonName = zoonName;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Zoon{" +
"zoonName='" + zoonName + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
set注入的格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="xxx" class="xxx">
<!-- set 注入使用: <property></property> 标签:
同样的: value 为简单类型的赋值-->
<property name="xxx" value=""></property>
<!--
同样的: ref 为复杂类型的赋值-->
<!-- name 属性怎么指定值,set 方法的方法名: ,然后把剩下的单词字母变小写,写到这里-->
<!-- ref 翻译为引用,英语单词: references ,ref 后面指定的是 bean 的id-->
<!-- id 是唯一的不可以重复的出现的 ref 和 value 是一样的。-->
<property name="xxx" ref="xxx"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
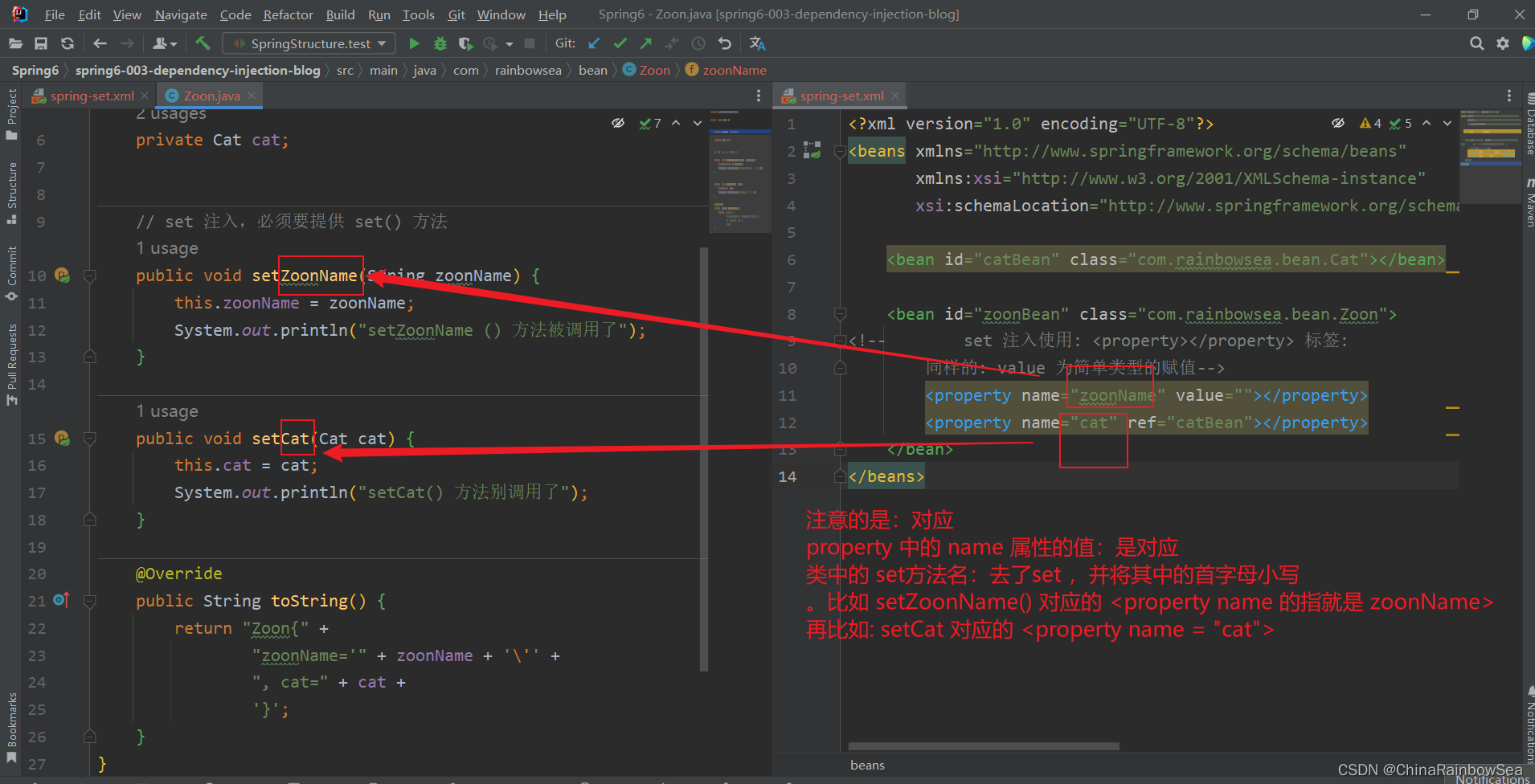
需要注意的是:
- 其中的
<property name="xxx"></property>中的 name 必须是 对应类当中的 set() 方法。去了,set,其次是 首字母小写 。这是不可以乱写的。 - Eg:
说明property标签的name是:setUserDao()方法名演变得到的。演变的规律是:
● setUsername() 演变为 username
● setPassword() 演变为 password
● setUserDao() 演变为 userDao
● setUserService() 演变为 userService
- 具体的如下图所示:
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-set.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
Zoon zoonBean = applicationContext.getBean("zoonBean", Zoon.class);
System.out.println(zoonBean);
}
}
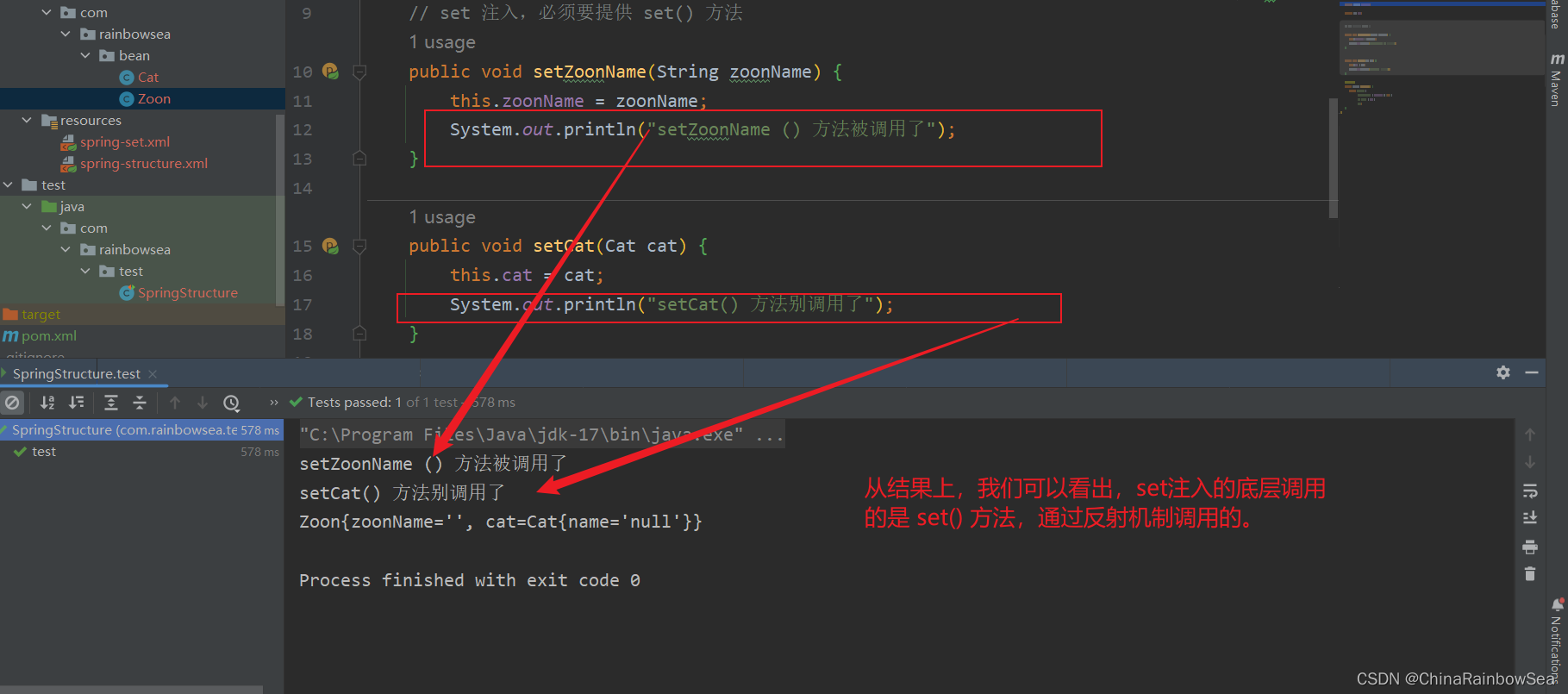
测试:我们如果把: 对应的 set 方法注释掉了,运行测试一下。
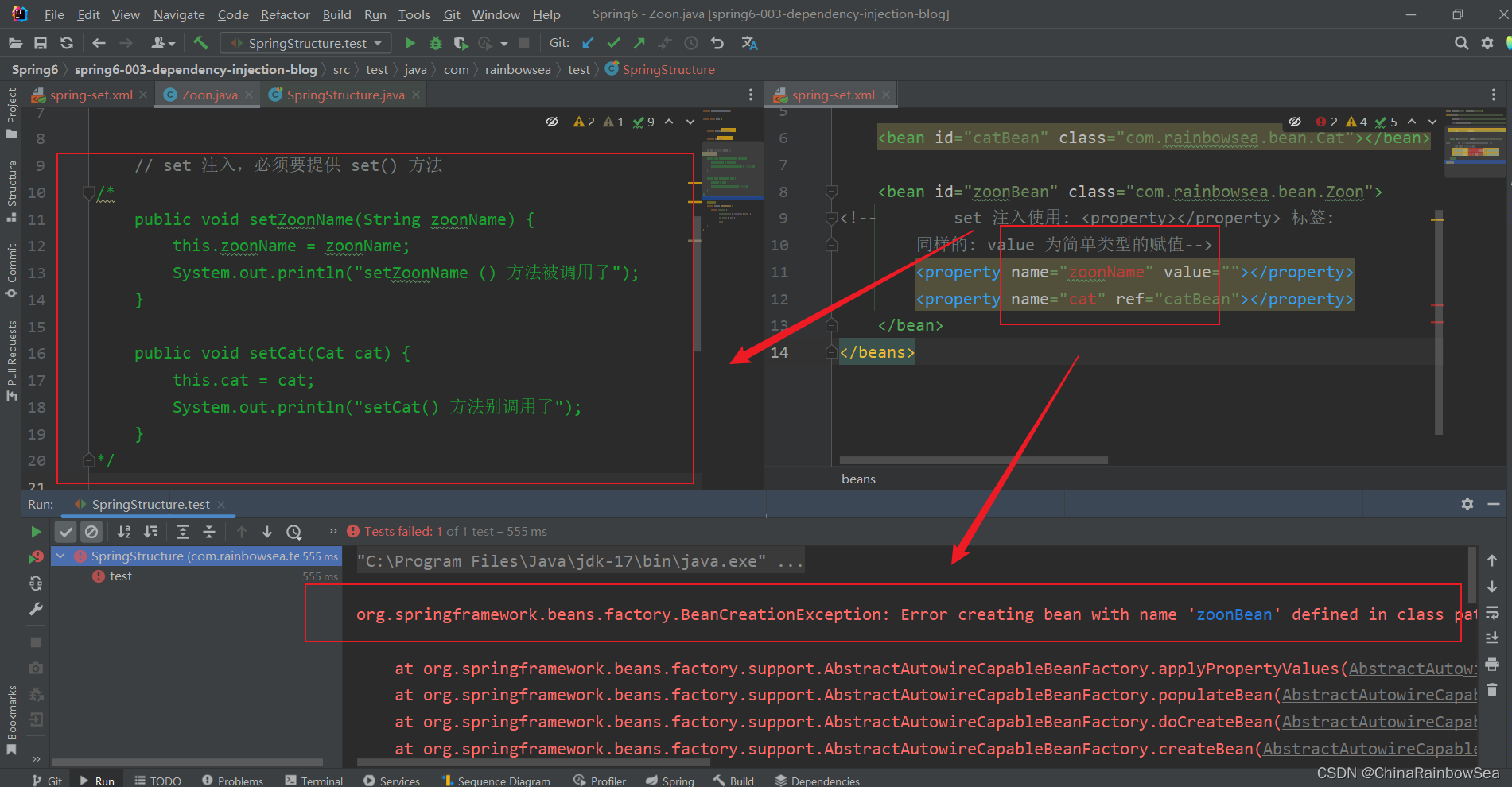
从结果上,我们可以看出:set 方法是必须 存在的。
set 注入的简单总结:
- 实现原理:
通过property标签获取到属性名:userDao:
通过性名推断出set方法名:setUserDao
通过反射机制调用setUserDao()方法给属性赋值
property标签的 name是属性名。
property标签的ref是要注入的bean对象的id。(通过ref属性来完成bean的装配,这是bean最简单的一种装配方式。装配指的是:创建系统组件之间关联的动作)
set注入的核心实现原理:通过反射机制调用set方法来给属性赋值,让两个对象之间产生关系。
2. set注入的各种方式详解
实际上在实际的开发过程中,我们使用的更多的是 set()方法的注入 。
2.1 set 注入外部Bean
外部Bean的特点: bean定义到外面,在property标签中使用ref 属性或是 value 属性进行注入。通常这种方式是常用。
格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!--如下:方式是 外部 bean 的注入的方式-->
<property name="zoonName" value=""></property>
<property name="cat" ref="catBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
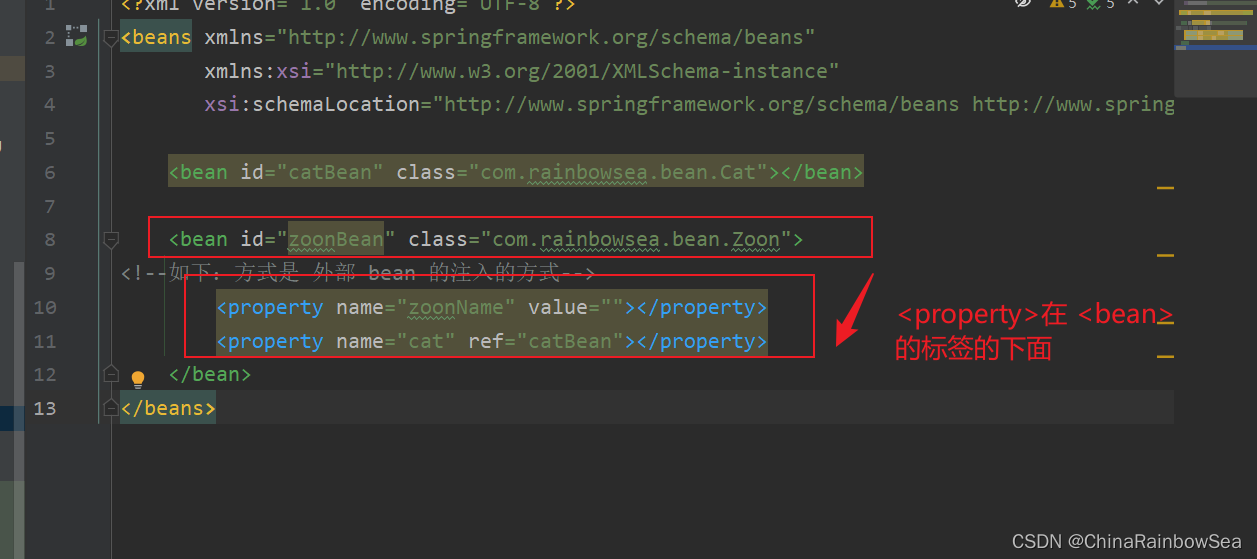
上面:我们测试用的 set 注入的方式:用的都是这种外部 Bean 的方式。
2.2 set 注入内部Bean
内部Bean的方式:在bean标签中嵌套bean标签:
具体格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!--如下:方式是 内部 bean 的注入的方式-->
<property name="cat" >
<!-- <property> 标签当中嵌入了 <bean>进行一个赋值-->
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat">
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
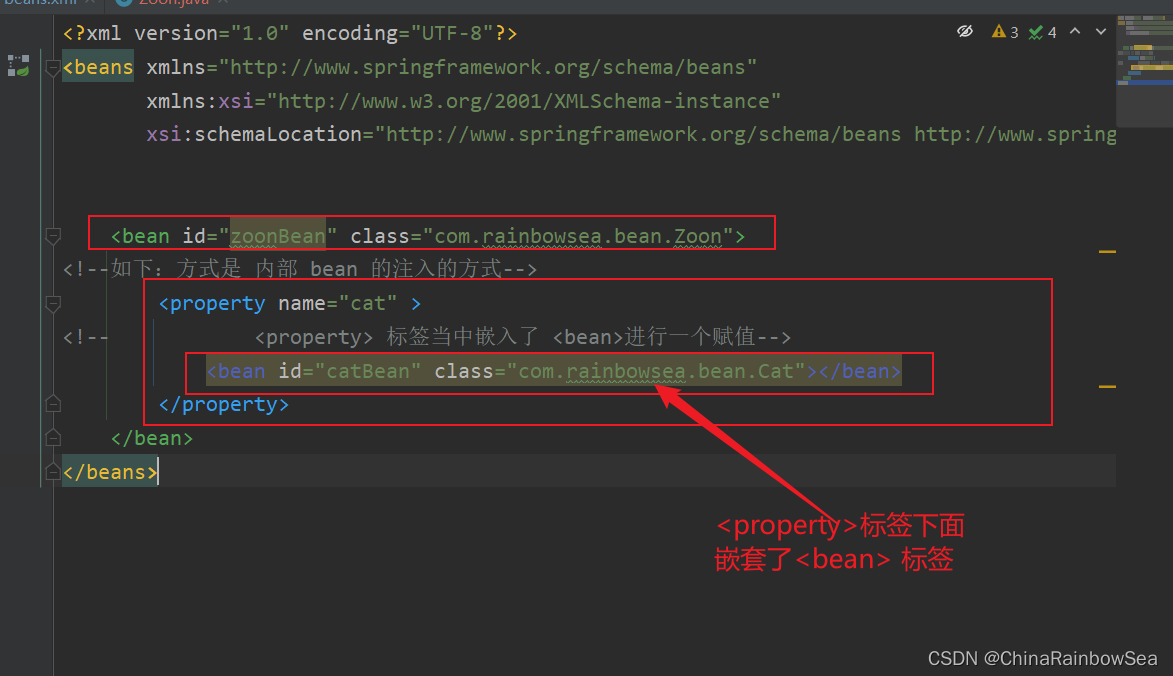
运行测试:
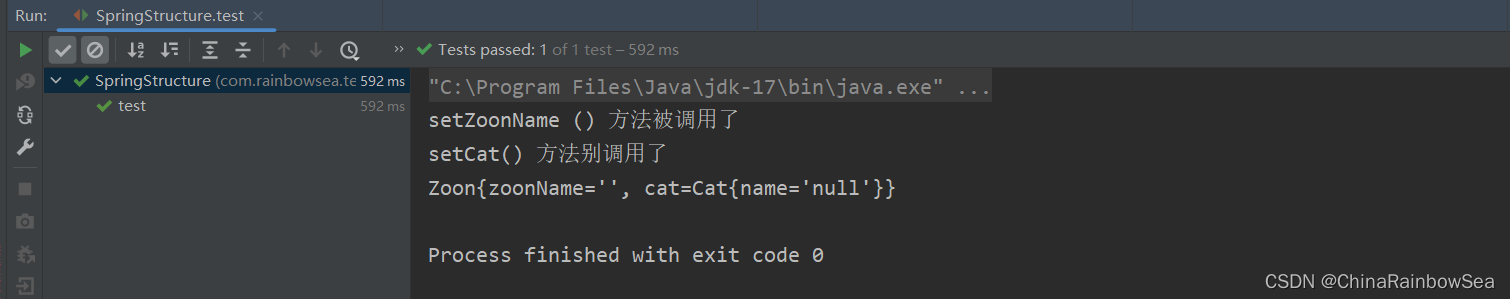
2.3 set 注入类型
2.3.1 set 注入简单类型
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Cat {
private int age;
private String name;
// set注入:底层反射调用 set 方法
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
格式:
在set 注入当中:简单类型的注使用 value 标签属性,进行一个属性的赋值操作
需要特别注意:如果给简单类型赋值,使用value属性或value标签。而不是ref。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
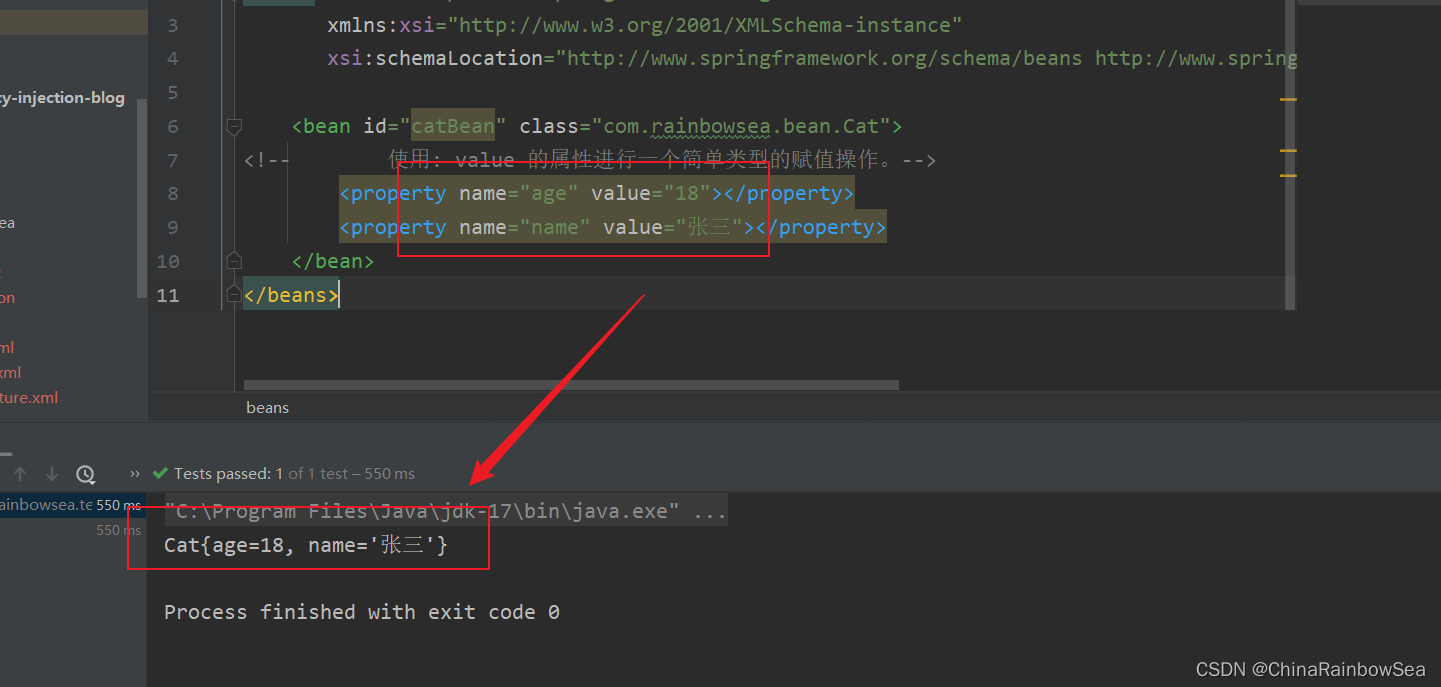
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat">
<!-- 使用: value 的属性进行一个简单类型的赋值操作。-->
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
Cat catBean = applicationContext.getBean("catBean", Cat.class);
System.out.println(catBean);
}
}
既然我们知道了:简单类型如何使用 set 注入了,那么我们就需要知道哪些是 简单类型了 ?
简单类型包括哪些呢?可以通过Spring的源码来分析一下:BeanUtils类
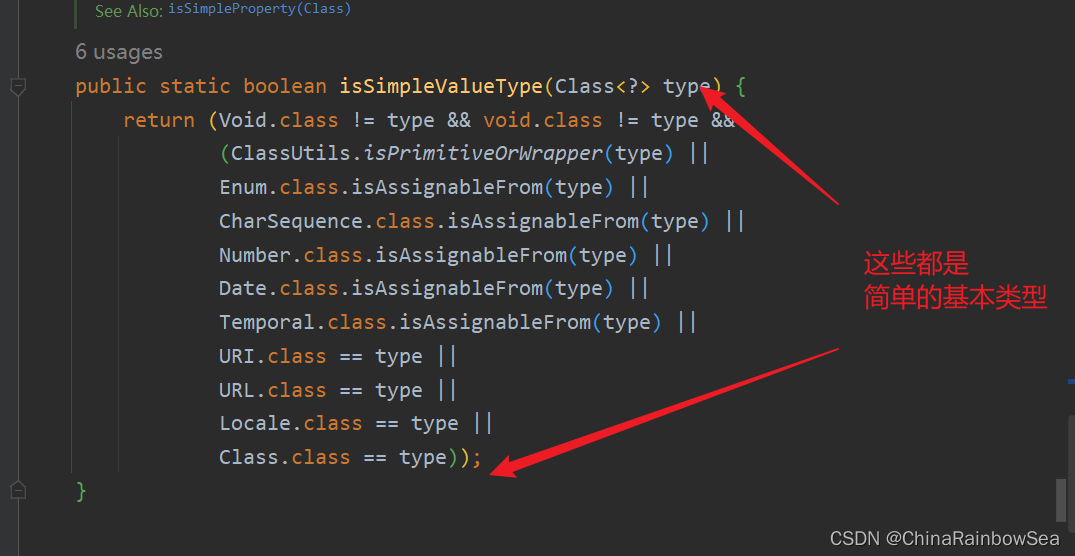
/**
* Check if the given type represents a "simple" value type: a primitive or
* primitive wrapper, an enum, a String or other CharSequence, a Number, a
* Date, a Temporal, a URI, a URL, a Locale, or a Class.
* <p>{@code Void} and {@code void} are not considered simple value types.
* @param type the type to check
* @return whether the given type represents a "simple" value type
* @see #isSimpleProperty(Class)
*/
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type ||
Class.class == type));
}
通过源码分析得知,简单类型包括:
- 基本数据类型
- 基本数据类型对应的包装类
- String或其他的CharSequence子类
- Number子类
- Date子类
- Enum子类
- URI
- URL
- Temporal子类
- Locale
- Class
- 另外还包括以上简单值类型对应的数组类型。
测试验证:
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
/**
* 枚举类
*/
public enum Season {
SPRING,SUMMER,AUTUMN,WINTER
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class SimpleValueType {
// 下面的都是简单的类型
private int age;
private Integer age2;
private boolean flag;
private Boolean flag2;
private char c;
private Character c2;
private Season season; // 枚举
private String username;
private Class clazz;
// set 注入必须要:设置 set() 方法
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setAge2(Integer age2) {
this.age2 = age2;
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public void setFlag2(Boolean flag2) {
this.flag2 = flag2;
}
public void setC(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void setC2(Character c2) {
this.c2 = c2;
}
public void setSeason(Season season) {
this.season = season;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
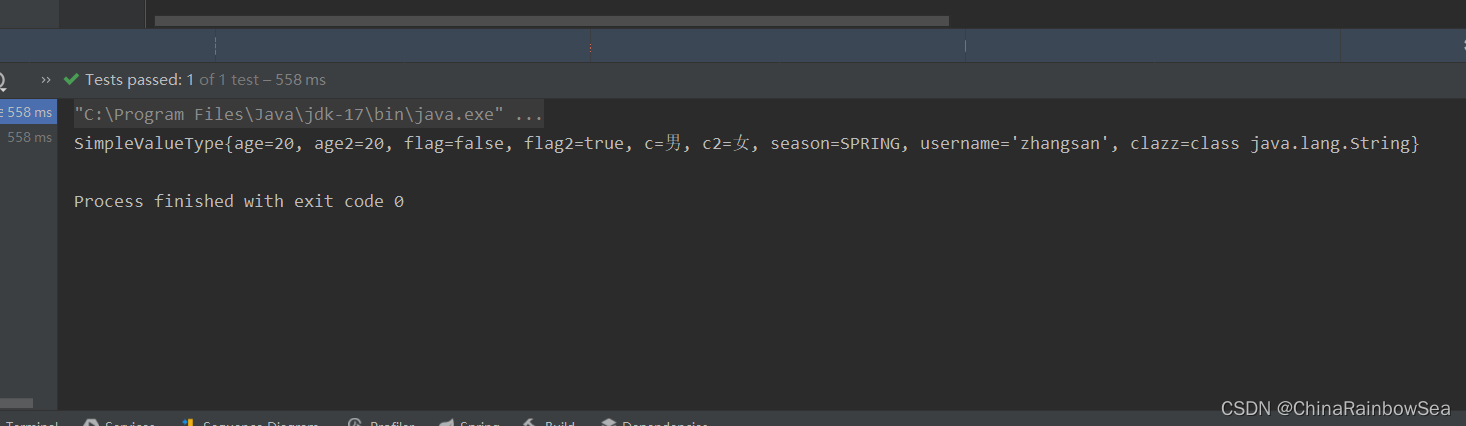
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SimpleValueType{" +
"age=" + age +
", age2=" + age2 +
", flag=" + flag +
", flag2=" + flag2 +
", c=" + c +
", c2=" + c2 +
", season=" + season +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", clazz=" + clazz +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="svt" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType">
<!-- 下面这种方式是外部的注入-->
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<property name="age2" value="20"></property>
<property name="username" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="season" value="SPRING"></property>
<property name="flag" value="false"></property>
<property name="flag2" value="true"></property>
<property name="c" value="男"></property>
<!-- 如果简单类型使用的是 ref 是会报错的, ref 注入的是 bean 类的信息-->
<property name="c2" value="女"></property>
<property name="clazz" value="java.lang.String"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
SimpleValueType svt = applicationContext.getBean("svt", SimpleValueType.class);
System.out.println(svt);
}
}
注意了: 特殊的日期时间进行一个特殊的赋值:
从上面的 BeanUtils 我们可以知道的的是 Date ,它是被Spring定义为了一个简单类型,来进行处理的。
但是,我们进行一个如下的测试:
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestDate {
private Date date;
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TestDate{" +
"date=" + date +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testDateBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate">
<property name="date" value="2023 -05-6"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
TestDate testDate = applicationContext.getBean("date", TestDate.class);
System.out.println(testDate);
}
}
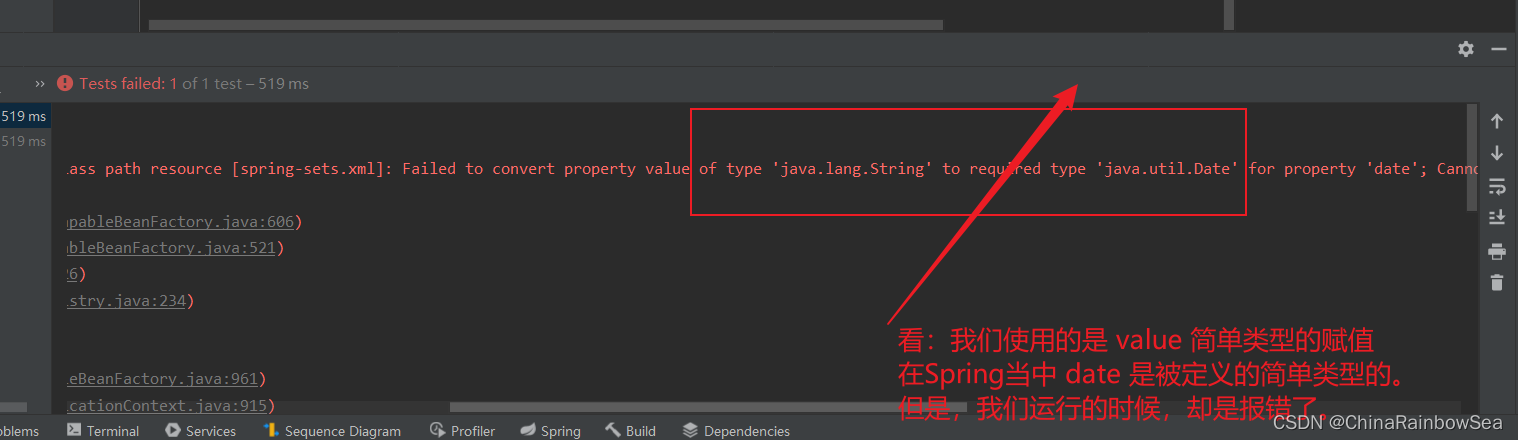
报错的原因是:
从报错的信息上,我们可以看到:
[
说:
'java.lang.String' to required type 'java.util.Date'说 这个 2023 -05-6 这个字符串,无法转换成 java.util.Date 类型。<property name="date" value="2023 -05-6"></property>如果你硬要把Date 当作简单类型的话,使用 value 赋值的话,这个日期字符串格式有要求的。所有的要求就是: new Date toString 打印显示的格式形式:Fri Jun 30 11:27:41 CST 2023。但是,我们在实际开发中,我们一般不会把 Date 当做简单类型,虽然是简单类型,但是我们一般采用的是ref 的Date 类型的属性赋值。
- 如果把Date当做简单类型的话,日期字符串格式不能随便写。格式必须符合Date的toString()方法格式。显然这就比较鸡肋了。如果我们提供一个这样的日期字符串:2010-10-11,在这里是无法赋值给Date类型的属性的。
- spring6之后,当注入的是URL,那么这个url字符串是会进行有效性检测的。如果是一个存在的url,那就没问题。如果不存在则报错。
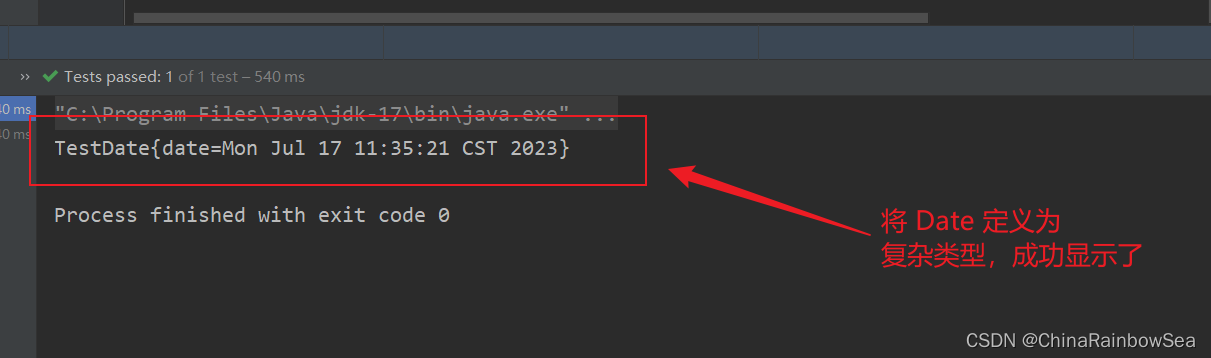
测试使用: 我们要求的格式: Fri Jun 30 11:27:41 CST 2023 进行一个 Date 的测试
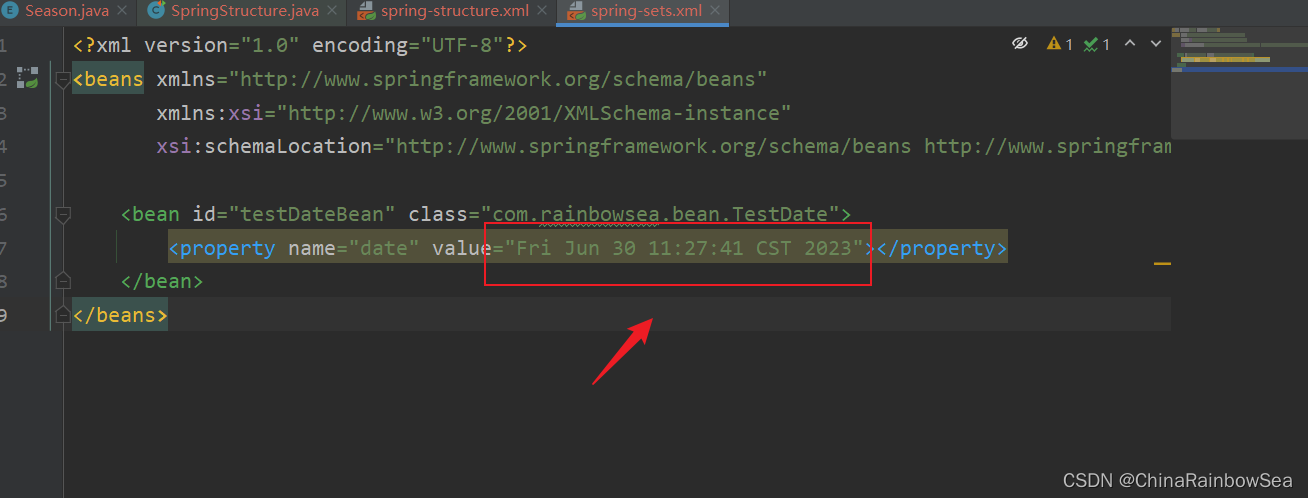
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testDateBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate">
<property name="date" value="Fri Jun 30 11:27:41 CST 2023"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
TestDate testDate = applicationContext.getBean("testDateBean", TestDate.class);
System.out.println(testDate);
}
}
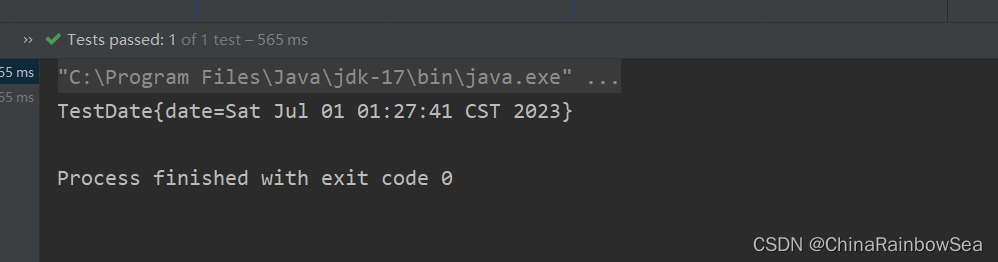
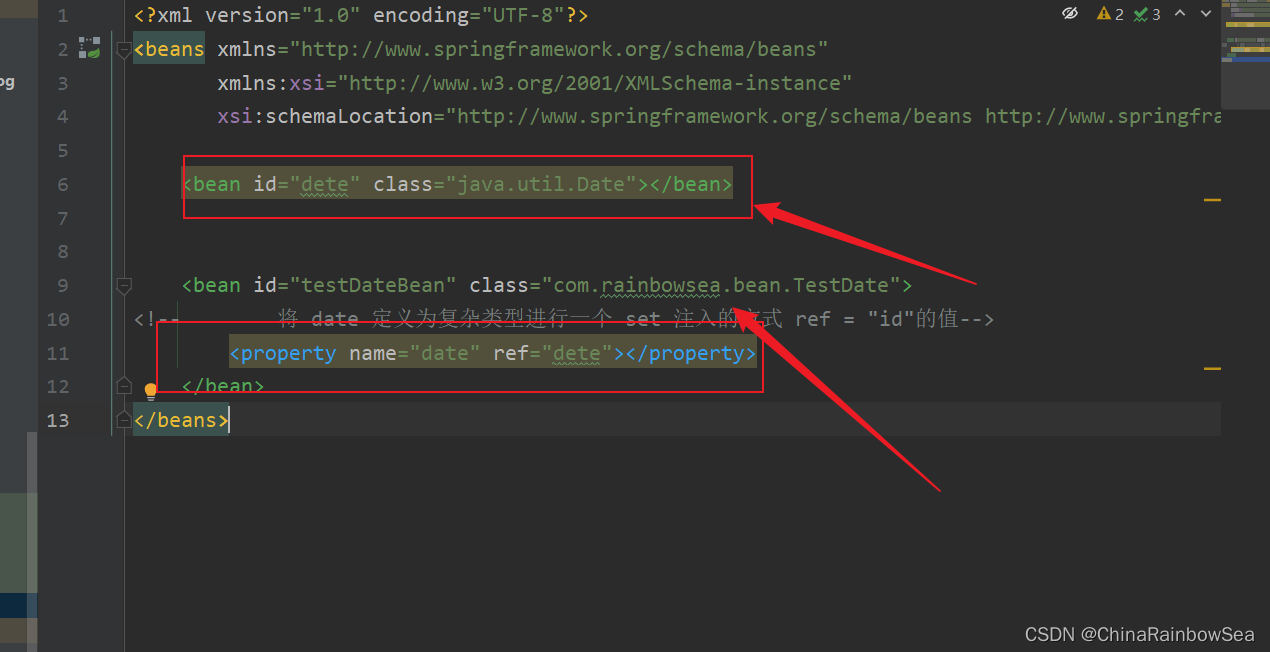
测试将 Date 当作为复杂类型进行一个set 注入的方式:测试
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dete" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<bean id="testDateBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate">
<!-- 将 date 定义为复杂类型进行一个 set 注入的方式 ref = "id"的值-->
<property name="date" ref="dete"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
TestDate testDate = applicationContext.getBean("testDateBean", TestDate.class);
System.out.println(testDate);
}
}
经典案例:给数据源的属性注入值:
假设我们现在要自己手写一个数据源,我们都知道所有的数据源都要实现javax.sql.DataSource接口,并且数据源中应该有连接数据库的信息,例如:driver、url、username、password等。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
// set 注入必须提供 set () 方法
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
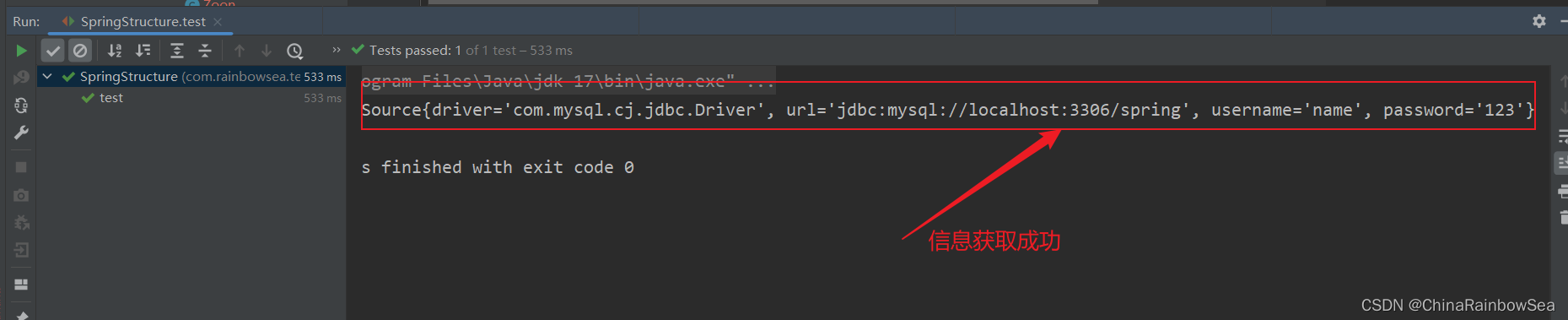
<bean id="data" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="name"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
MyDataSource data = applicationContext.getBean("data", MyDataSource.class);
System.out.println(data);
}
}
2.3.2 set 复杂类型注入的方式
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- ref 表示的是复杂类型,其中的值表示的是: 对应的复杂类型的id 值。-->
<property name="user" ref="userBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class People {
private User user;
private String name;
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"user=" + user +
'}';
}
}
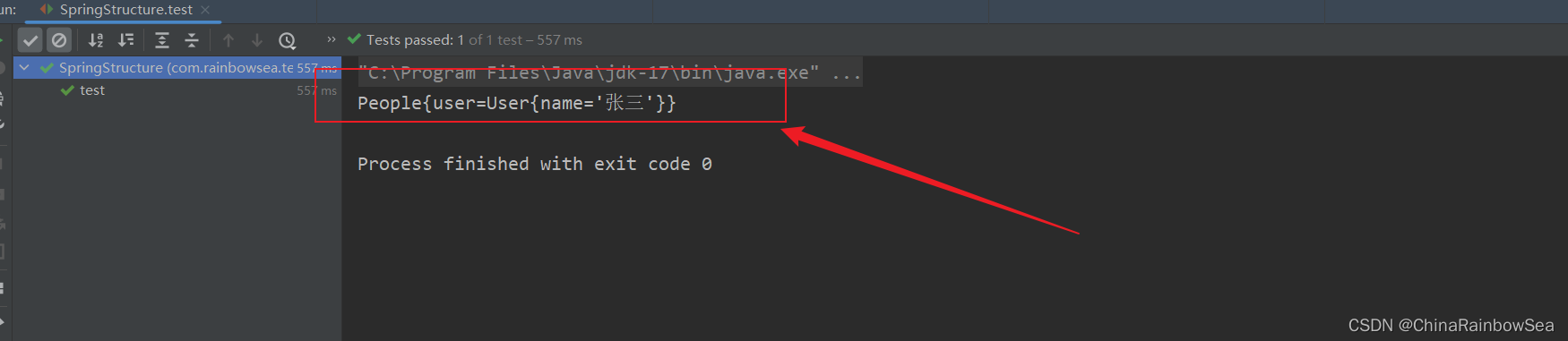
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- ref 表示的是复杂类型,其中的值表示的是: 对应的复杂类型的id 值。-->
<property name="user" ref="userBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
2.4 级联属性赋值
级联的要求:
- 对应级联的类下的属性的赋值,必须提供 get() 方法,因为级联的底层调用的就是 get() 方法。不然无法级联到。
- 注意:级联的上下放置的顺序,级联当中的使用的 id ,必须在级联之前先定义处理出来,不然同样无法级联到。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class People {
private User user;
private String name;
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 使用级联的话,必须提供其中的 get() 方法进行一个获取
// 级联的底层调用的就是 get()方法。
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"user=" + user +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
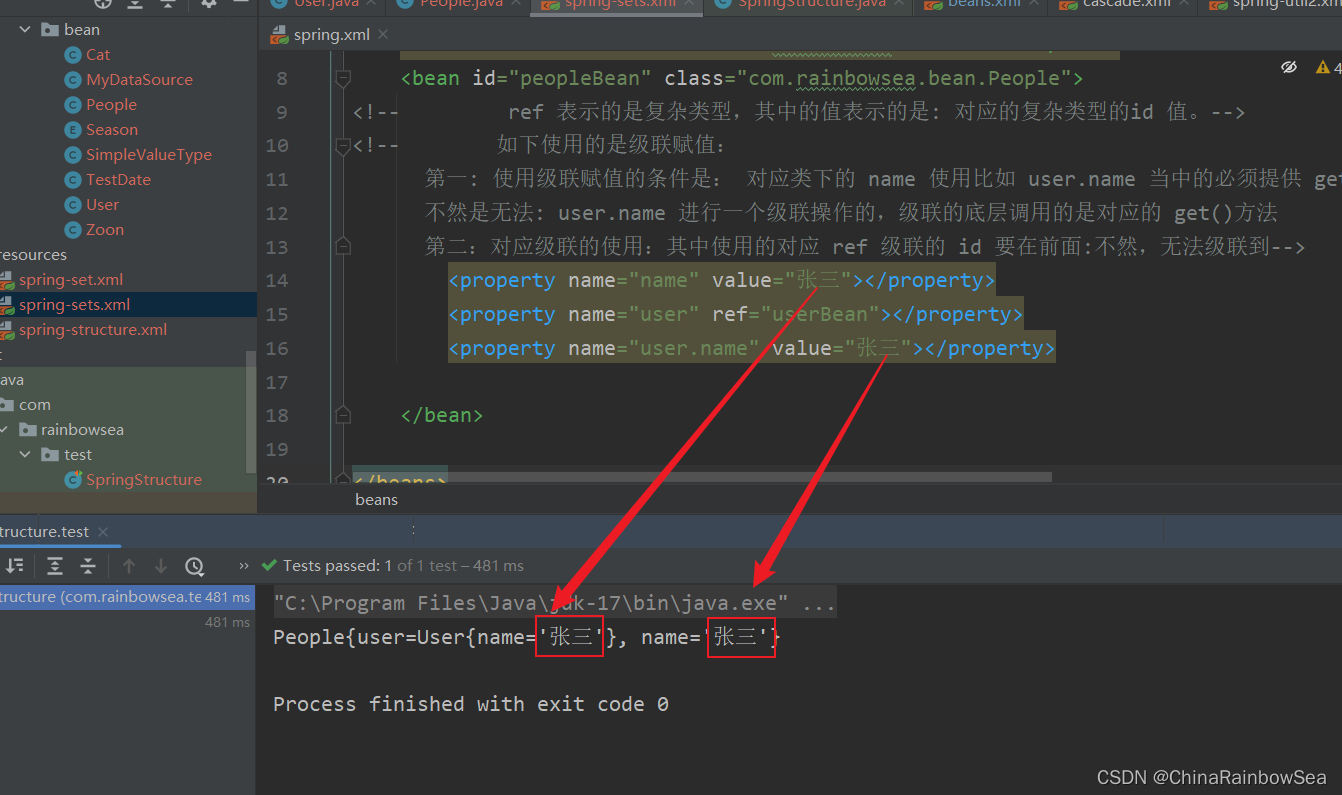
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- ref 表示的是复杂类型,其中的值表示的是: 对应的复杂类型的id 值。-->
<!-- 如下使用的是级联赋值:
第一: 使用级联赋值的条件是: 对应类下的 name 使用比如 user.name 当中的必须提供 get() 方法。
不然是无法: user.name 进行一个级联操作的,级联的底层调用的是对应的 get()方法
第二:对应级联的使用:其中使用的对应 ref 级联的 id 要在前面:不然,无法级联到-->
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
<property name="user" ref="userBean"></property>
<property name="user.name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
级联用的比较少,所以大家了解一下就好了。
2.5 set 注入数组类型
关于set 数组类型的注入的方式:
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- 数组的赋值使用: array 标签-->
<array>
<value></value>
<value></value>
<value></value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.5.1 当数组中的元素是简单类型
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class People {
private String[] name;
public void setName(String[] name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name=" + Arrays.toString(name) +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- 数组的赋值使用: array 标签-->
<array>
<!-- 简单类型使用: value-->
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- 数组的赋值使用: array 标签-->
<array>
<!-- 简单类型使用: value-->
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
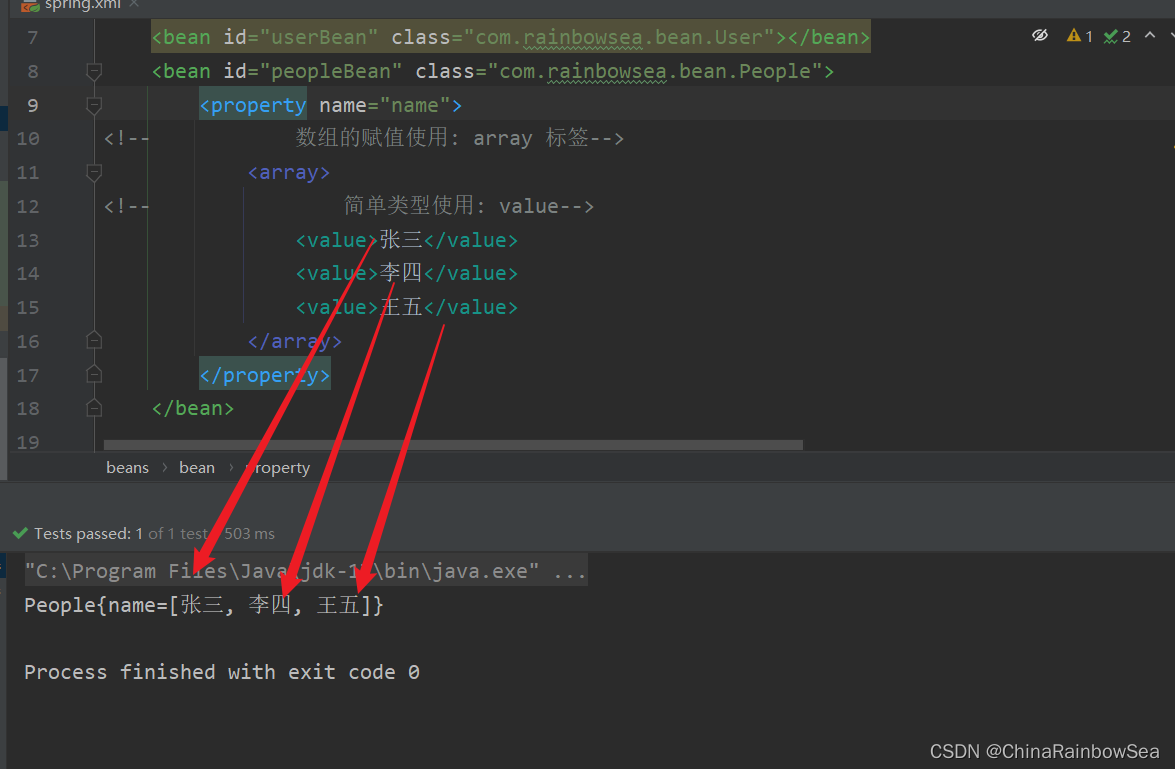
2.5.2 当数组中的元素是复杂类型
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="xxx1" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="xxx2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- 数组的赋值使用: array 标签-->
<array>
<!-- 复杂型使用: ref bean 是对应的id-->
<ref bean="xxx1"></ref>
<ref bean="xxx2"></ref>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
**举例: **
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class People {
private User[] users;
public void setUsers(User[] users) {
this.users = users;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"users=" + Arrays.toString(users) +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userBean2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- 数组的赋值使用: array 标签-->
<array>
<!-- 复杂类型使用: ref-->
<ref bean="userBean"></ref>
<ref bean="userBean2"></ref>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
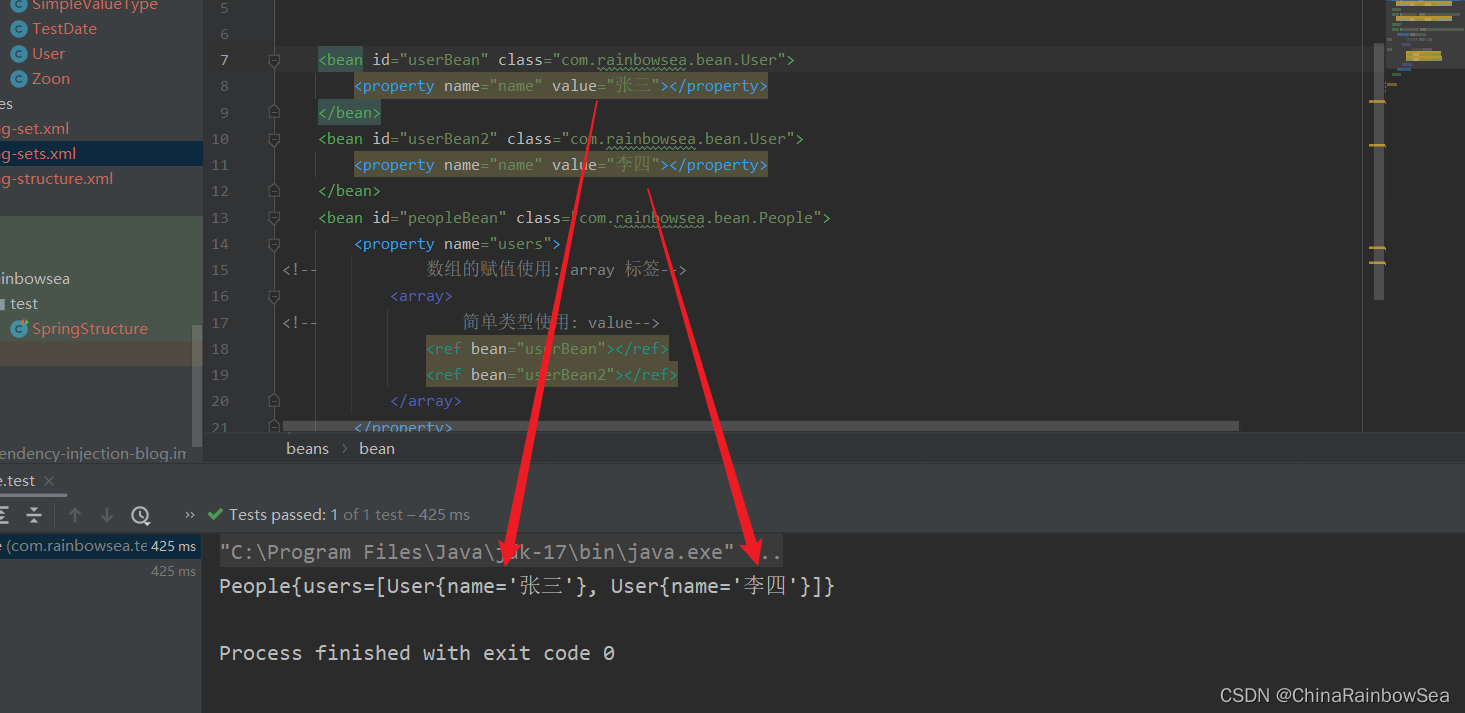
2.6 set注入List集合类型
List集合:有序可重复
2.6.1 set 注入 List集合简单类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- List 集合使用 <list> 标签进行注入,简单类型使用 <value> -->
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.List;
public class People {
private List<String> name;
public void setName(List<String> name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name=" + name +
'}';
}
}
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
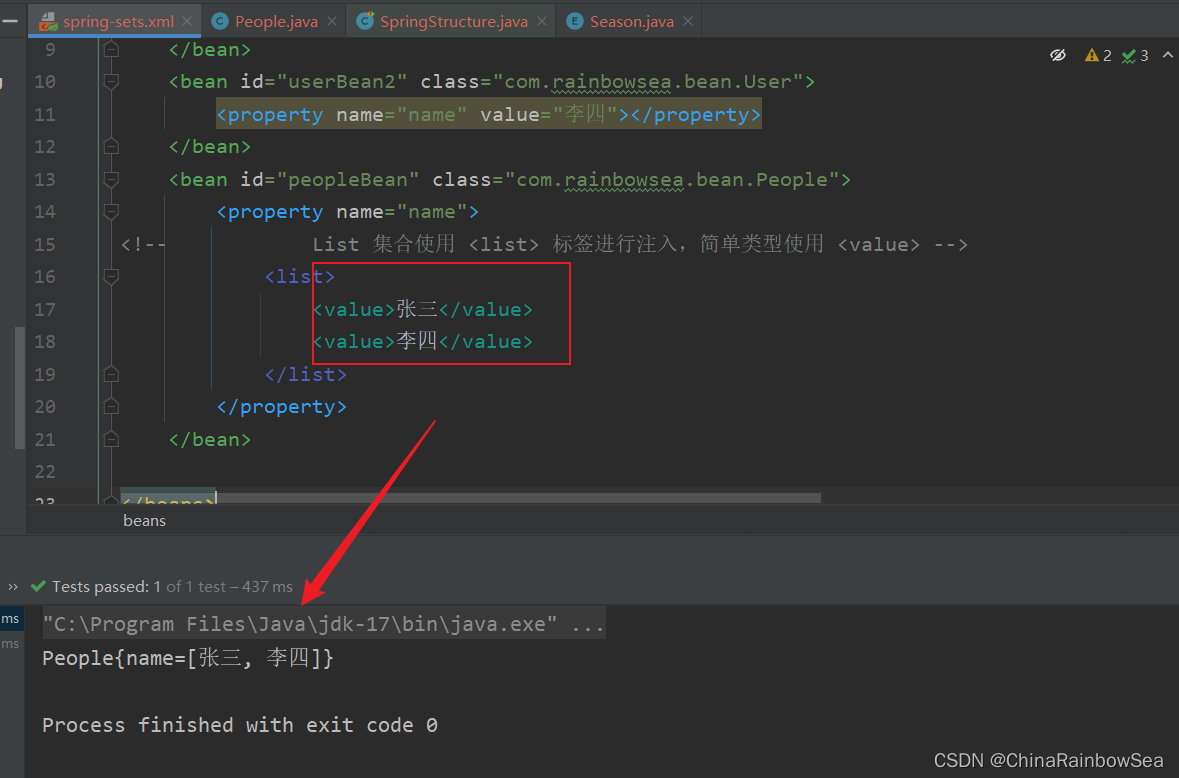
2.6.2 set 注入List集合复杂类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userBean2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- List 集合使用 <list> 标签进行注入,简单类型使用 <ref> bean=对应的Id -->
<list>
<ref bean="userBean"></ref>
<ref bean="userBean2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.List;
public class People {
private List<User> users;
public void setUsers(List<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"users=" + users +
'}';
}
}
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
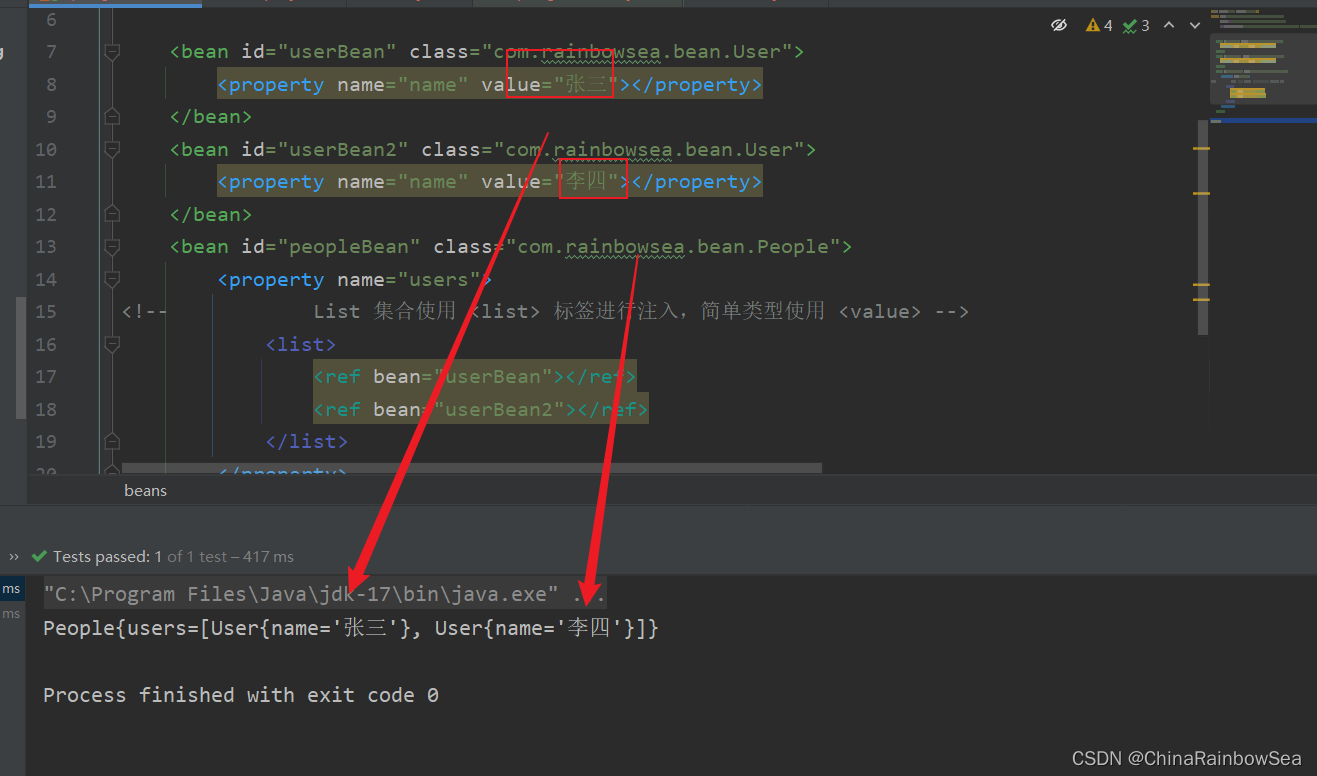
注意:注入List集合的时候使用list标签,如果List集合中是简单类型使用value标签,反之使用ref标签。
2.7 set注入Set集合类型
Set集合:无序不可重复
2.7.1 set 注入 Set集合简单类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="names">
<!-- set 集合使用 <set> 标签进行注入,复杂类型使用 <value> 进行 -->
<set>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Set;
public class People {
private Set<String> names;
public void setNames(Set<String> names) {
this.names = names;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
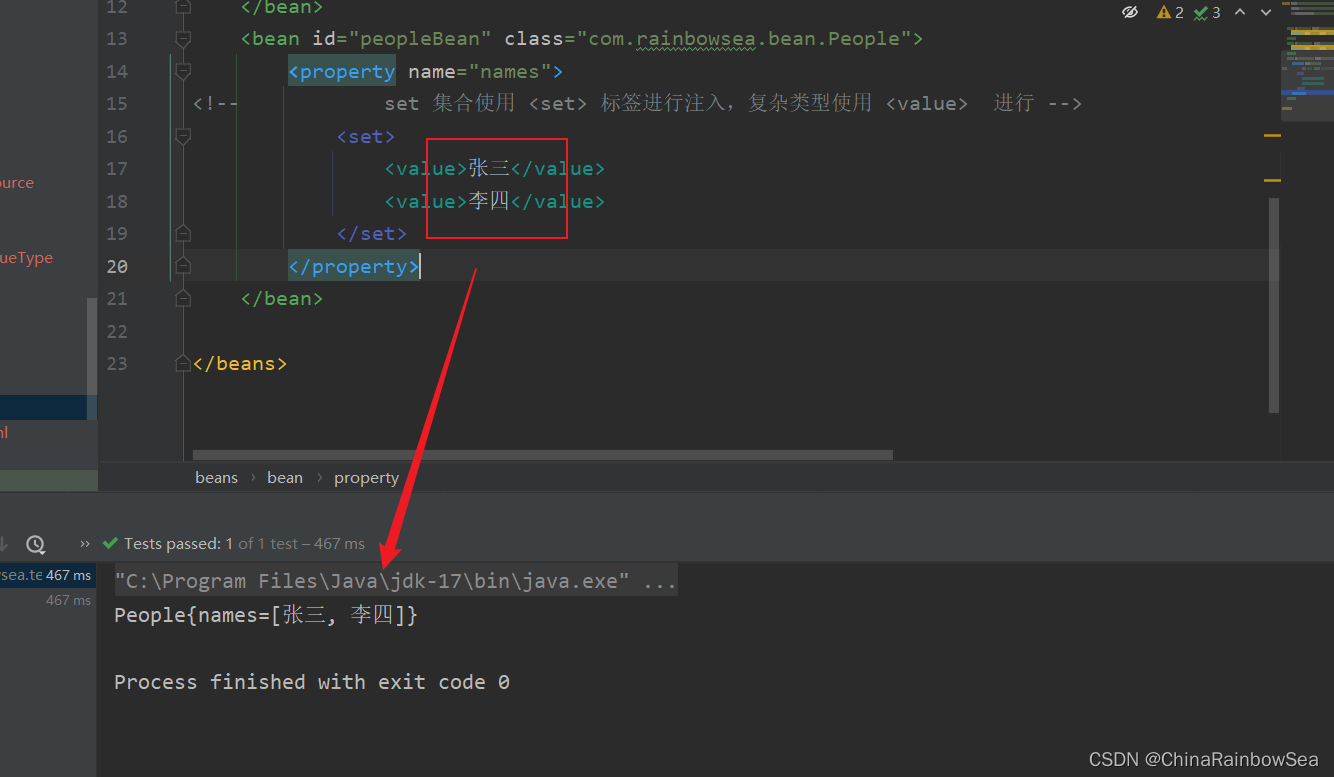
2.7.2 set 注入Set集合复杂类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userBean2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- set 集合使用 <set> 标签进行注入,复杂类型使用 <ref> bean 进行 -->
<set>
<ref bean="userBean"></ref>
<ref bean="userBean2"></ref>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Set;
public class People {
private Set<User> users;
public void setUsers(Set<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"users=" + users +
'}';
}
}
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
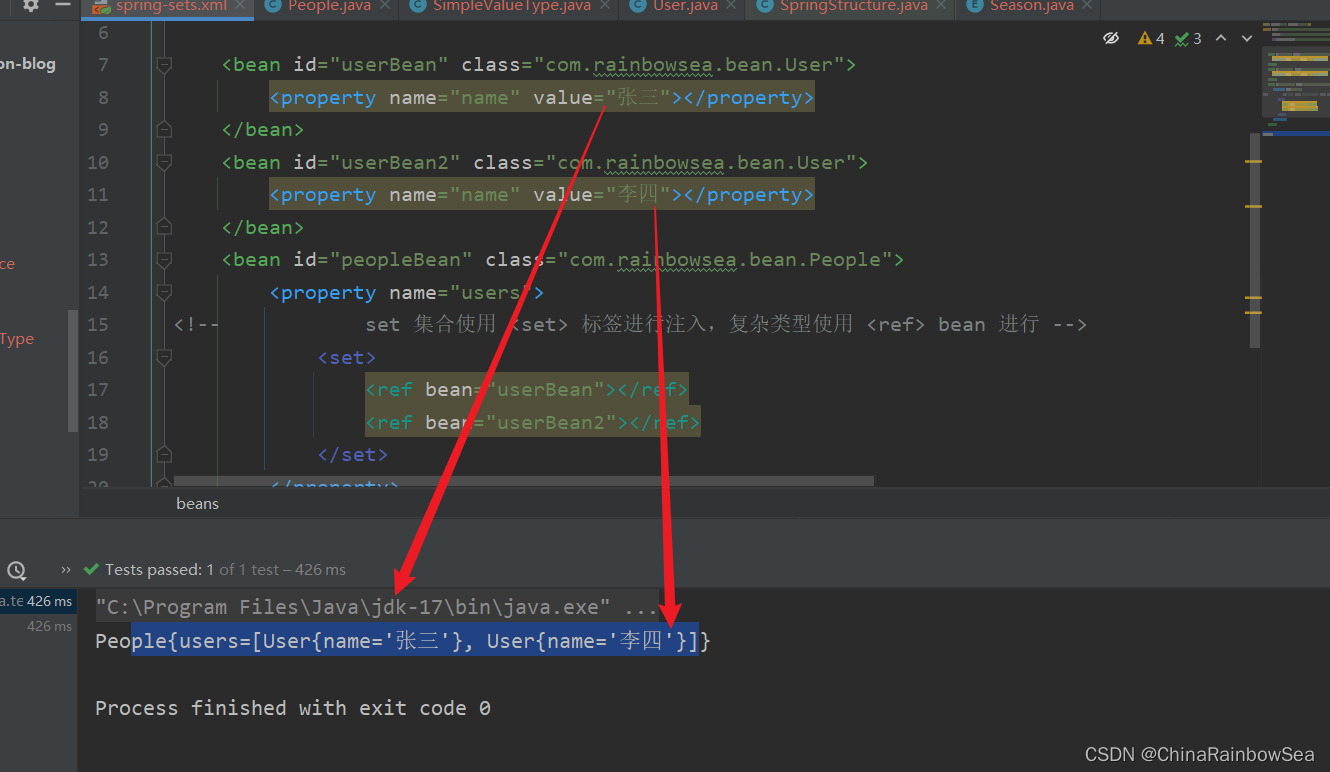
2.8 set注入Map集合
2.8.1 set 注入的Map集合简单类型
要点:
- 使用标签
- 如果key是简单类型,使用 key 属性,反之使用 key-ref 属性。
- 如果value是简单类型,使用 value 属性,反之使用 value-ref 属性。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="names">
<!-- map 集合使用 <map> 标签进行注入,复杂类型使用 <value> 进行 -->
<map>
<!--key 是简单类型使用 key属性-->
<!--value是简单类型,使用 value 属性-->
<entry key="1" value="北京大兴区"/>
<entry key="2" value="上海浦东区"/>
<entry key="3" value="深圳宝安区"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Map;
public class People {
private Map<Integer,String> names;
public void setNames(Map<Integer, String> names) {
this.names = names;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
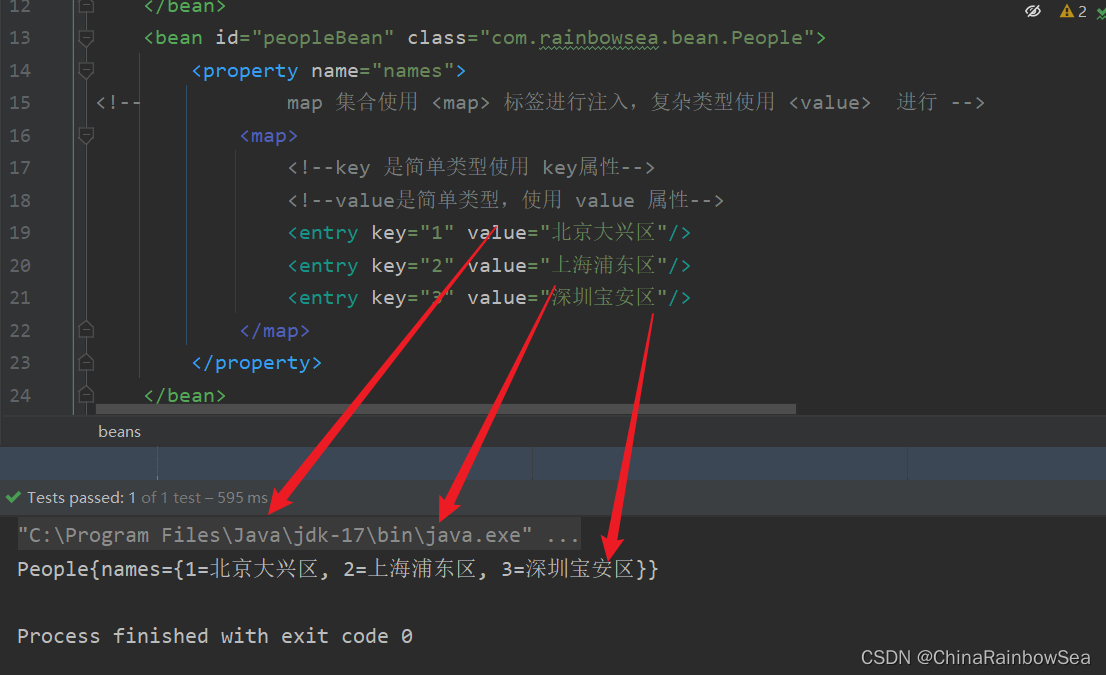
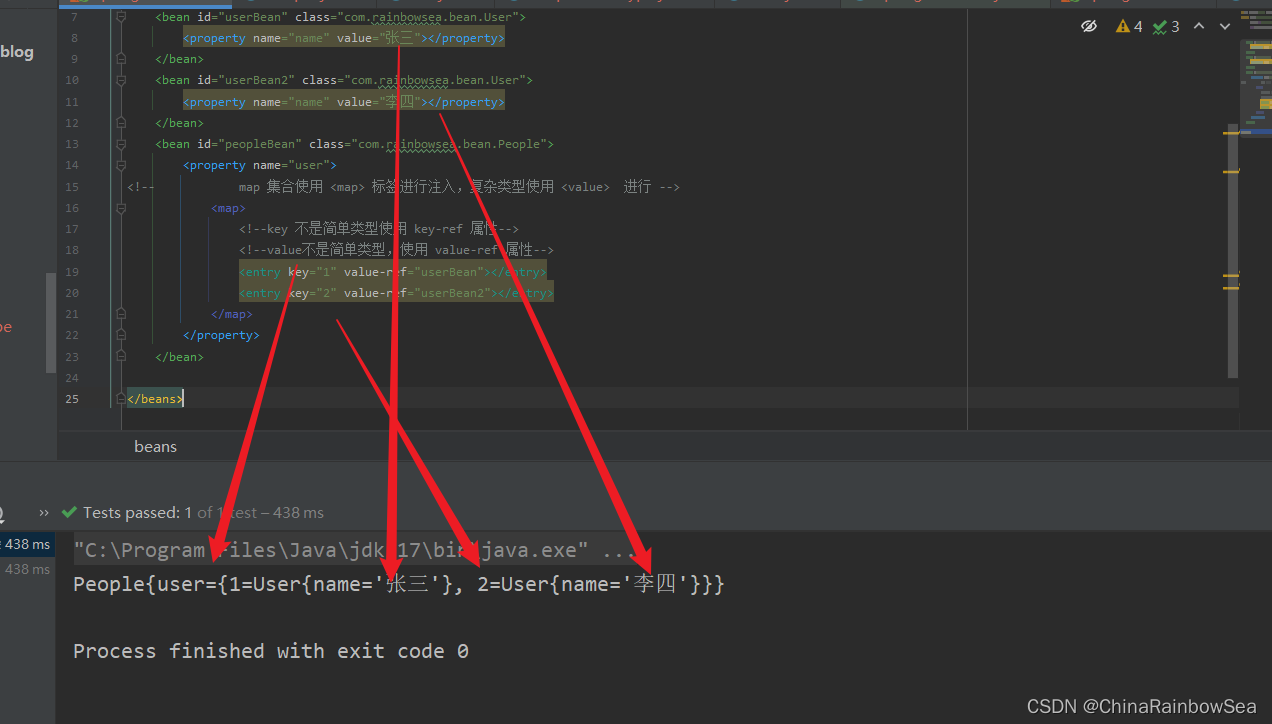
2.8.2 set 注入的Map集合的复杂类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userBean2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="user">
<!-- map 集合使用 <map> 标签进行注入,复杂类型使用 <value> 进行 -->
<map>
<!--key 不是简单类型使用 key-ref 属性-->
<!--value不是简单类型,使用 value-ref 属性-->
<entry key="1" value-ref="userBean"></entry>
<entry key="2" value-ref="userBean2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Map;
public class People {
private Map<Integer,User> user;
// set 注入,必须要有 set 方法
public void setUser(Map<Integer, User> user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"user=" + user +
'}';
}
}
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
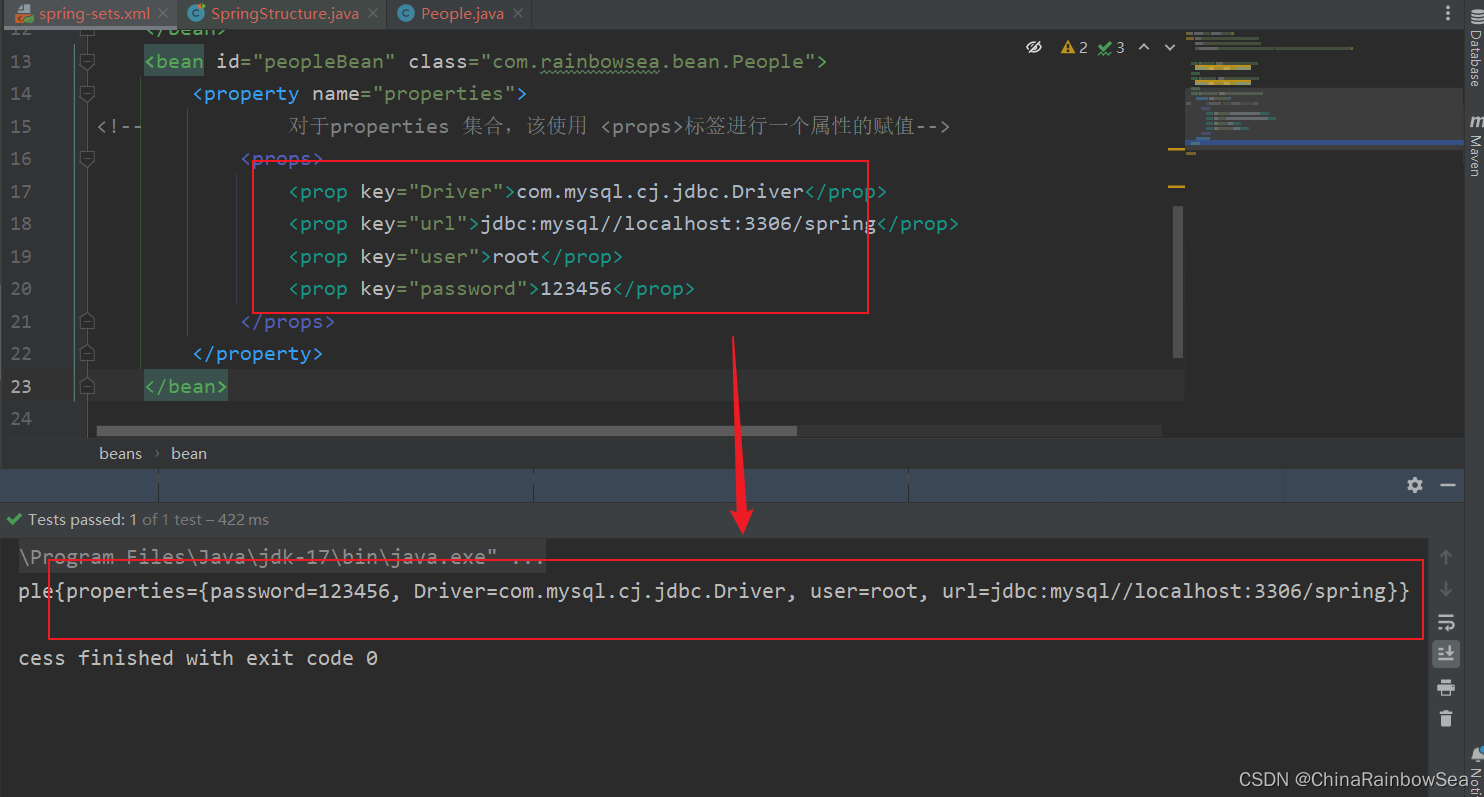
2.9 set注入Properties 特殊的 Map 集合
java.util.Properties继承java.util.Hashtable,所以Properties也是一个Map集合。
但是虽然 Properties 是一个 Map 集合,但是在 Spring当中,是无法使用 标签进行一个 set 注入的。
对于 properties 集合类型的,set 注入使用的是 p标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="properties">
<!-- 对于properties 集合,该使用 <props>标签进行一个属性的赋值-->
<props>
<prop key="Driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql//localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="user">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Properties;
public class People {
private Properties properties;
// set 注入必须提供 set 方法
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
2.10 set 注入 null 和空字符串的方式
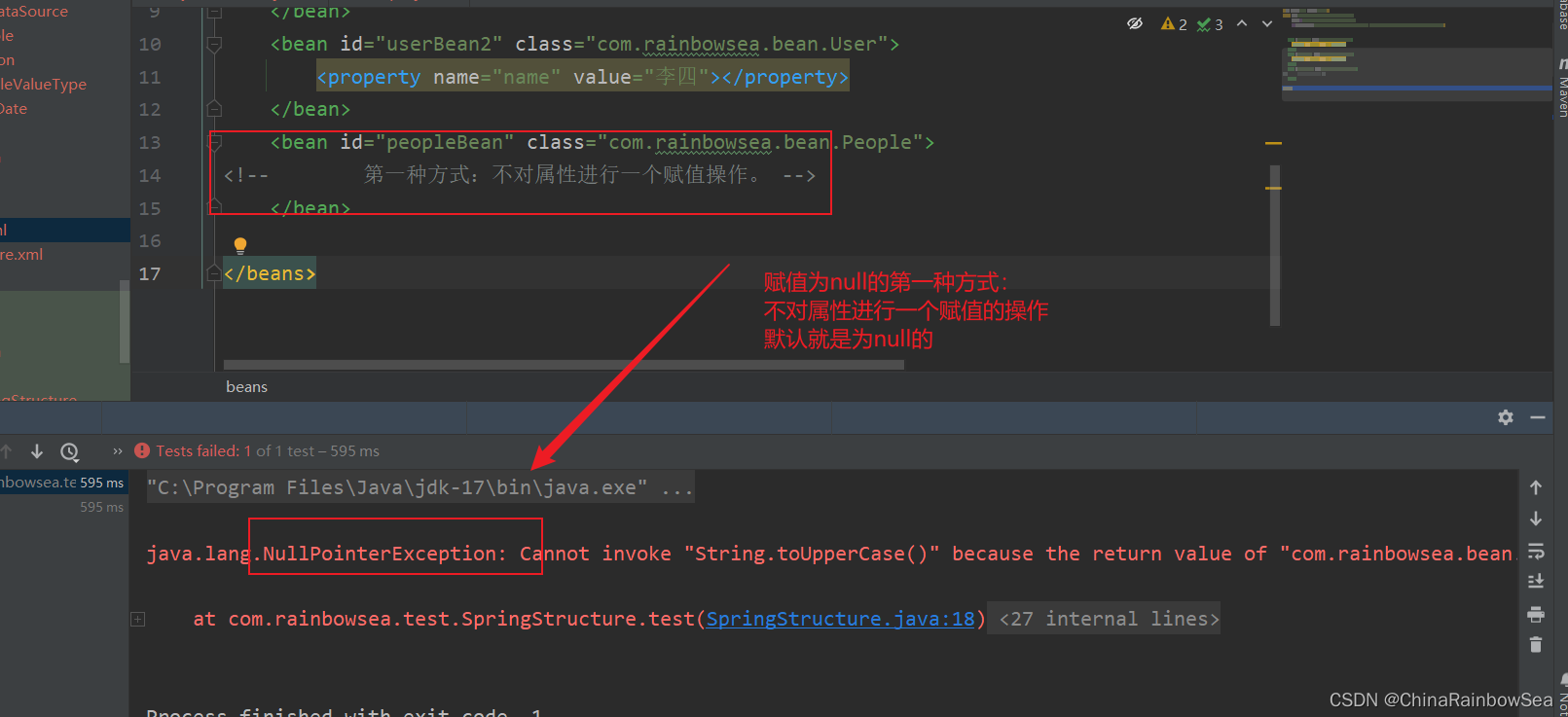
2.10.1 set 注入 null 值的方式
当我们想要对一个属性为一个 null 值的时候,我们应该怎么做呢?
有如下两种方式:
第一种方式:方式不给属性注入,属性的默认值就是为 null 的
测试:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- 第一种方式:不对属性进行一个赋值操作。 -->
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Properties;
public class People {
private String name;
// set 注入必须提供 set 方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 提供一个get 方法用于测试,是否为null的
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
运行测试
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
// 将小写字母转换为大写字母,如果name为空报 null 异常测试:
System.out.println(peopleBean.getName().toUpperCase());
}
}
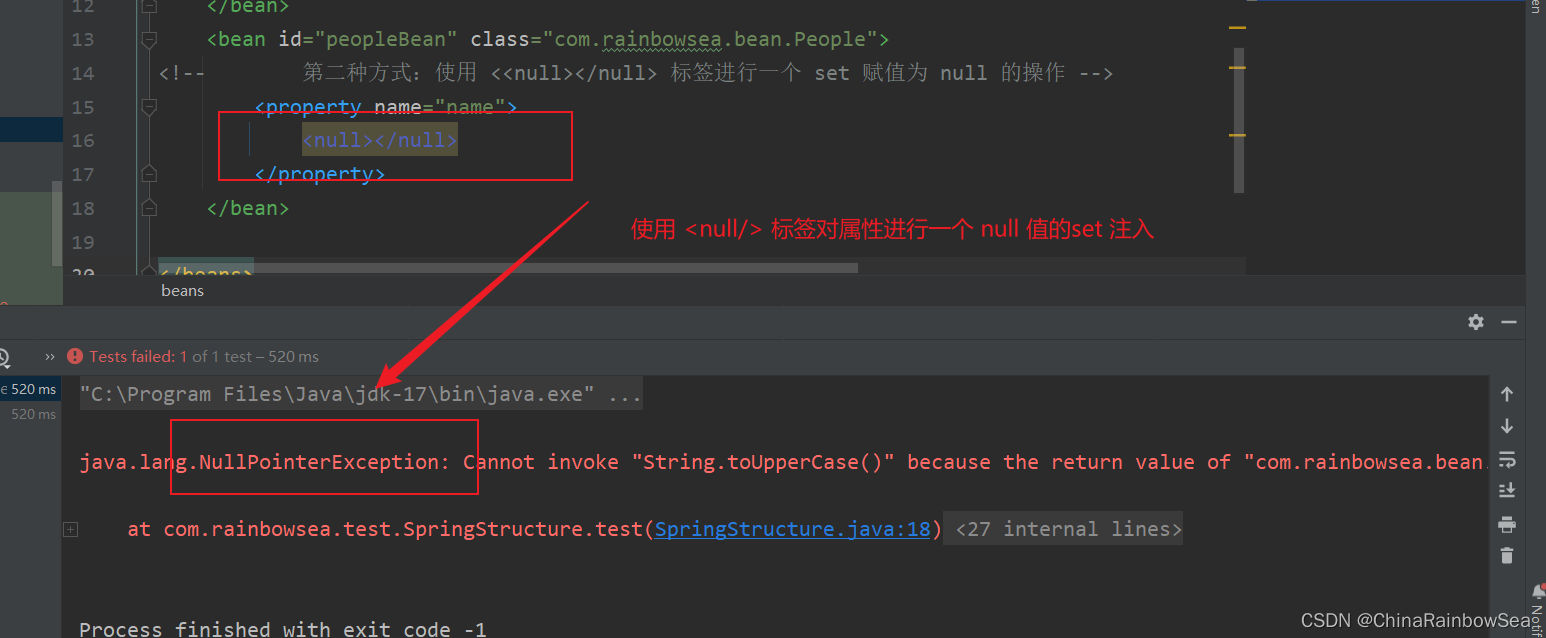
方式二:使用 <null></null> 的标签进行一个属性 set 注入赋值为 null 的操作
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- 第二种方式:使用 <<null></null> 标签进行一个 set 赋值为 null 的操作 -->
<property name="name">
<null></null>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
// 将小写字母转换为大写字母,如果name为空报 null 异常测试:
System.out.println(peopleBean.getName().toUpperCase());
}
}
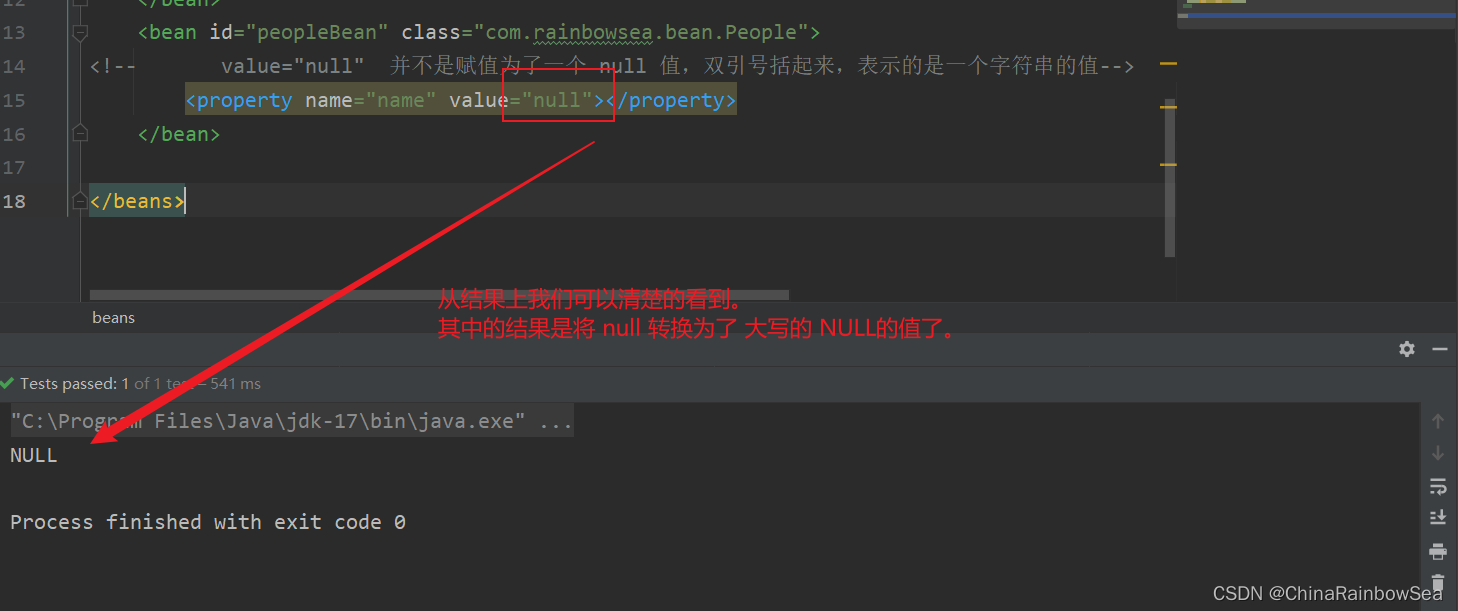
注意点:就是如果我们将 value = null ,set 注入的话,并不是将 value 的属性值,赋值为了null,而是赋值为了一个 null 的字符串而已。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- value="null" 并不是赋值为了一个 null 值,双引号括起来,表示的是一个字符串的值-->
<property name="name" value="null"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.10.2 set 注入空字符串值的方式
同样的,如果我们想要将一个属性的值,赋值为 空字符串 该怎么做呢?
**方式一:我们可以 value="" 的方式进行一个空字符串的赋值 **
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class People {
private String name;
// set 注入必须提供 set 方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- value="" 就是将值赋值为一个空字符串-->
<property name="name" value=""></property>
</bean>
</beans>
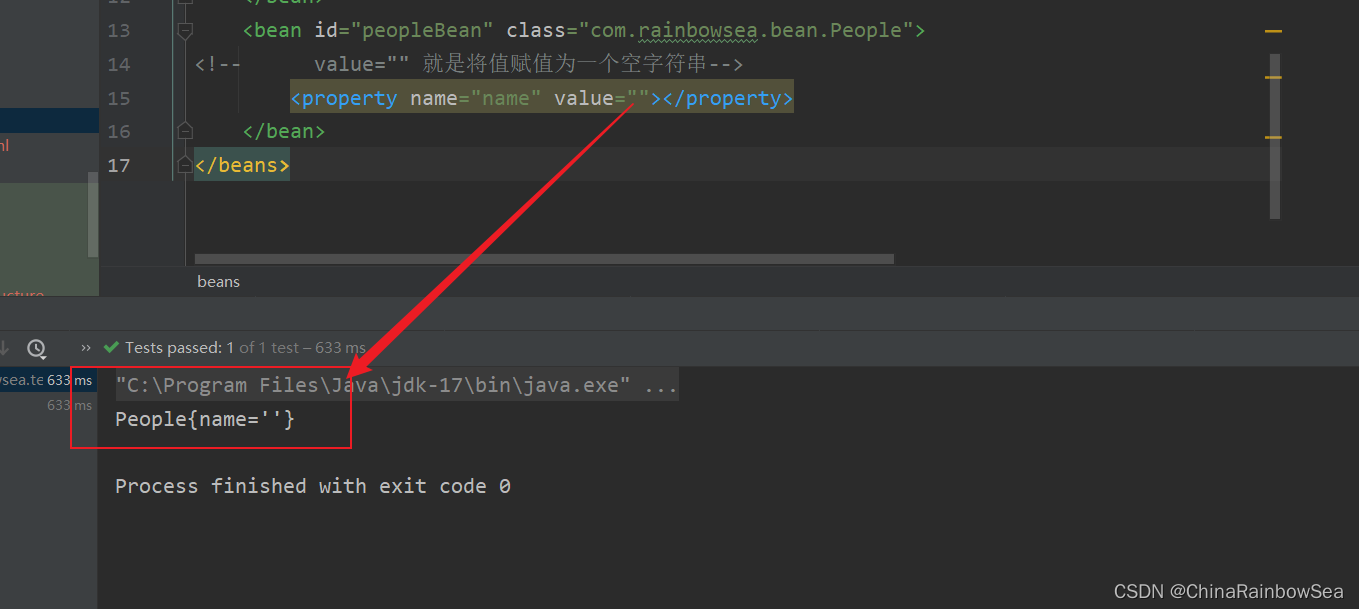
方式二: 使 <value/> 进行一个空字符串的 set 注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- value="" 就是将值赋值为一个空字符串-->
<property name="name">
<value></value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
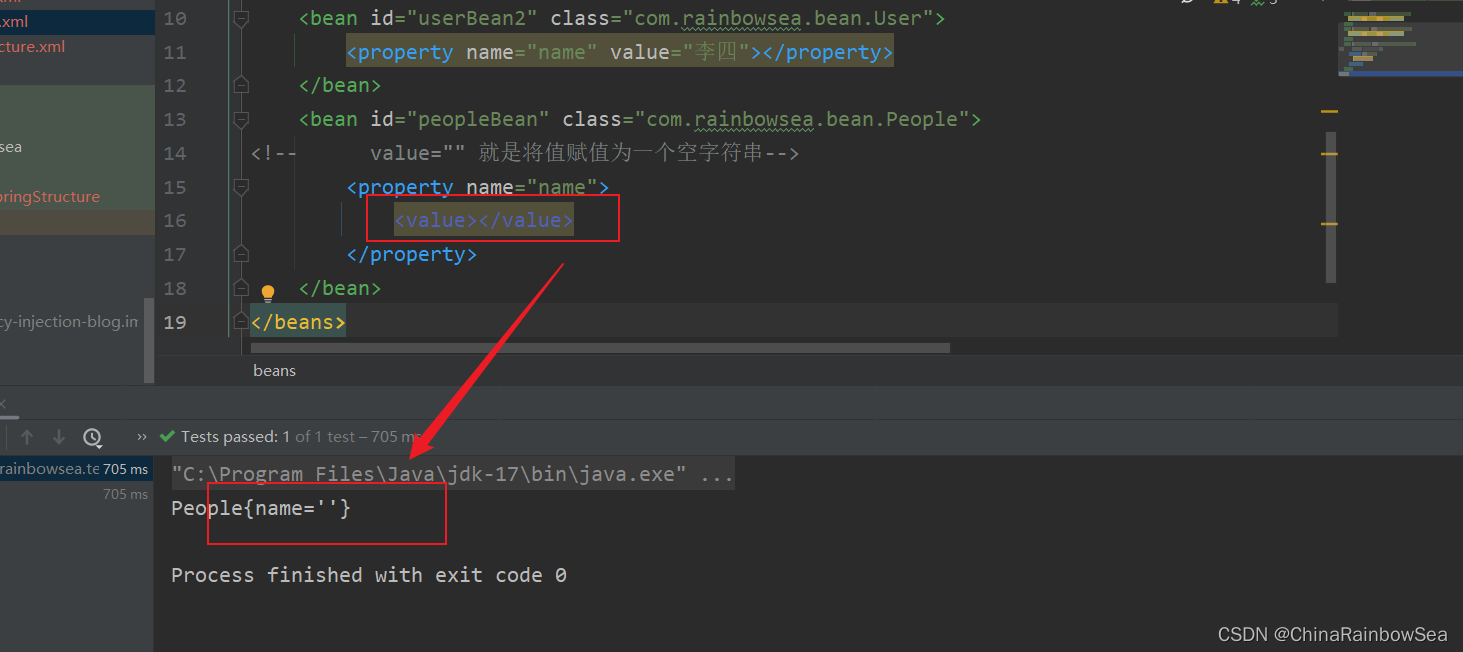
2.11 set 注入的属性值当中含有特殊符号,怎么处理
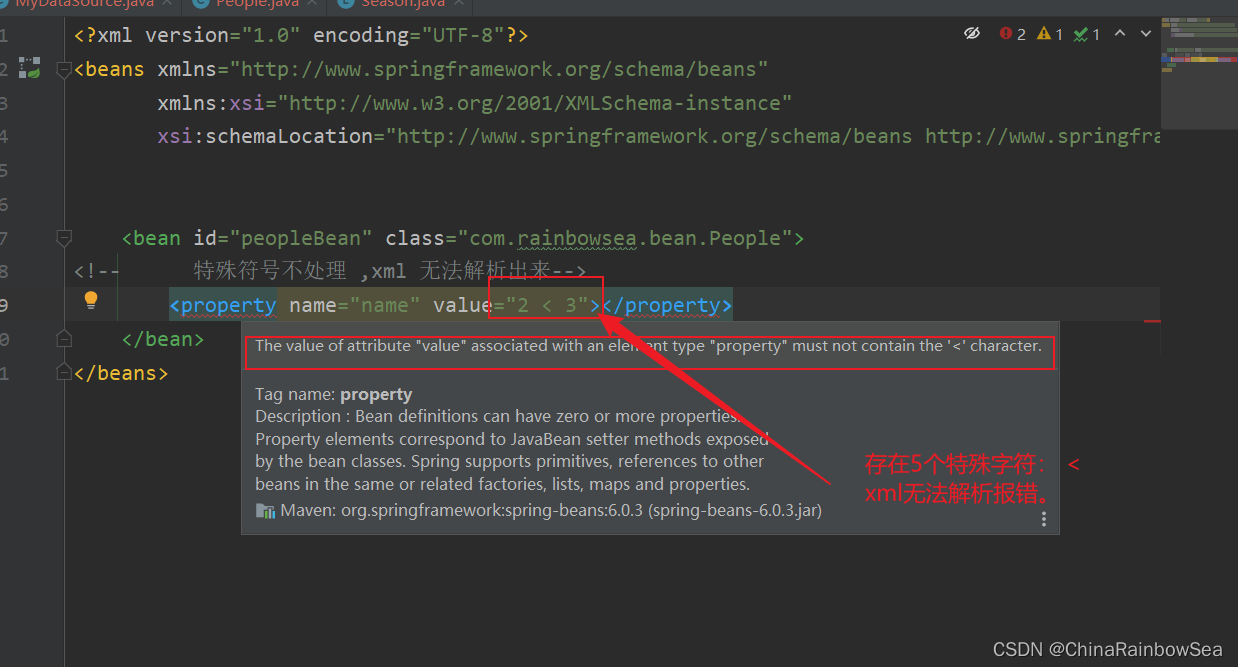
注意: 当我们在 xml 文件中出现了,特殊的字符串的时候,不然不进行一个特殊的处理的话,是会报错的。
XML 中有 5 个特殊字符,分别是:<、>、'、"、& 。以上这 5 个特殊符号在 xml 中会被特殊对待,会被当做xml语法的一部分进行解析,如果这些特殊符号直接出现注入的字符串当中,会报错的。具体体现如下:
The value of attribute "value" associated with an element type "property" must not contain the '<' character 翻译为: 与元素类型“property”关联的属性“value”的值不能包含“<”字符
解决方案包括两种:
- 第一种:特殊符号使用转义字符代替。
- 第二种:将含有特殊符号的字符串放到: 当中。因为放在CDATA区中的数据不会被XML文件解析器解析。
5个特殊字符对应的转义字符分别是:
需要注意的是: 其中转义字符当中是含有 ; 分号的,不可以省略掉的。这一点需要注意。
| 特殊字符 | 转义字符 |
|---|---|
| > | > |
| < | < |
| ' | ' |
| " | " |
| & | & |
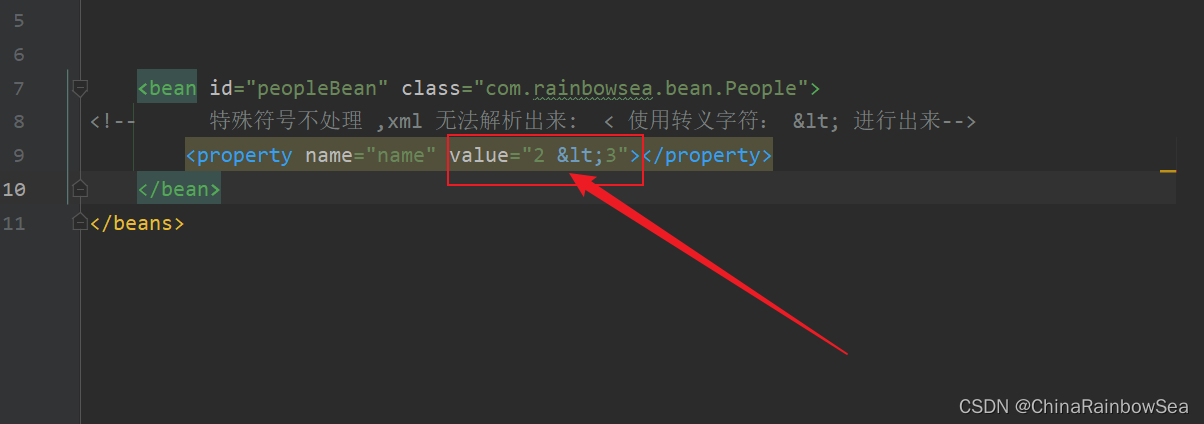
先使用转义字符来代替: 测试如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
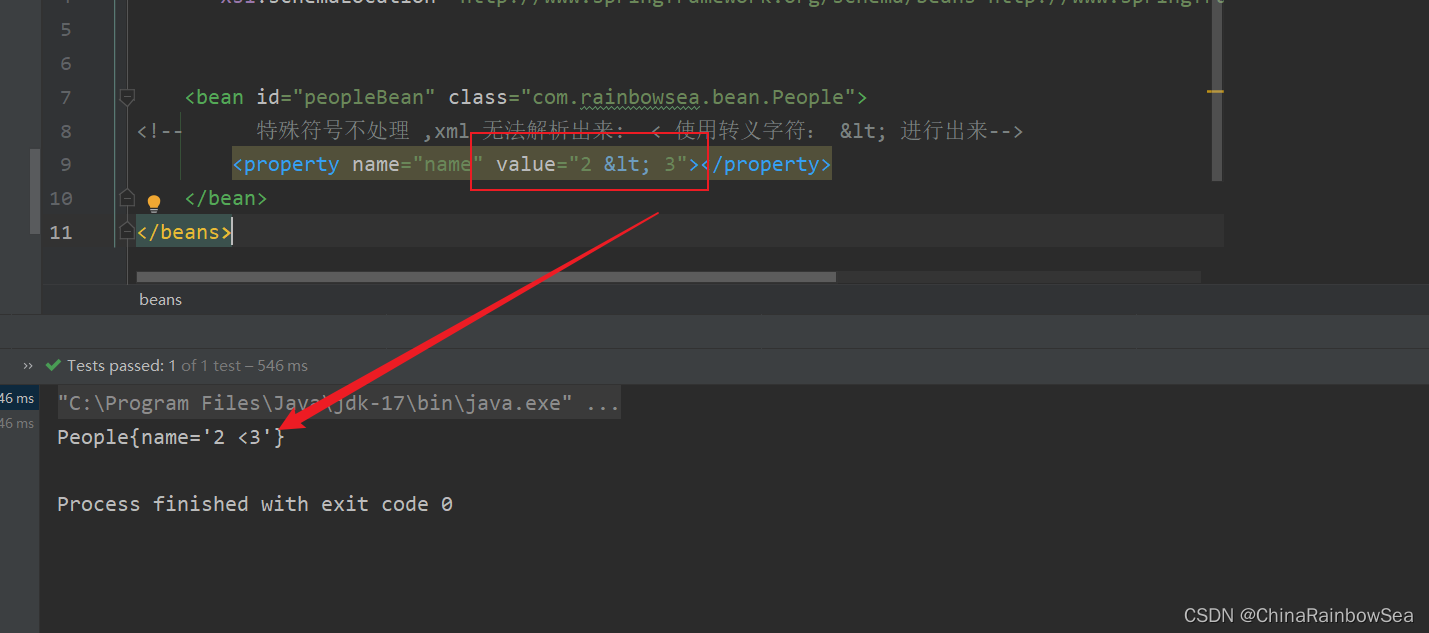
<!-- 特殊符号不处理 ,xml 无法解析出来: < 使用转义字符: < 进行出来-->
<property name="name" value="2 < 3"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
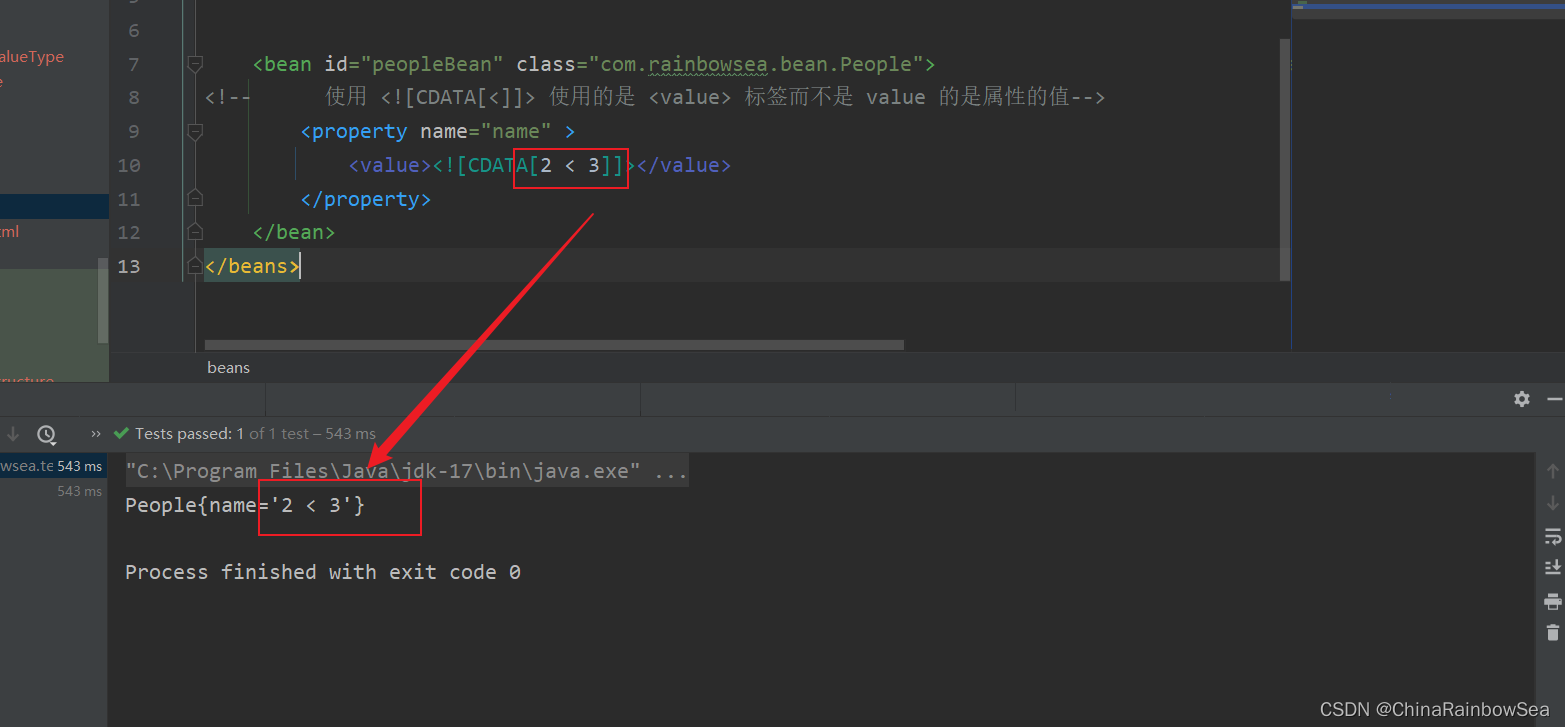
方式二:将含有特殊符号的字符串放到: 当中。因为放在CDATA区中的数据不会被XML文件解析器解析
格式:
<value><![CDATA[这里放特殊的字符]]></value>
比如:
<value><![CDATA[ 2 < 3 ]></value>
注意:使用CDATA时,不能使用value属性,只能使用value标签。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- 使用 <![CDATA[<]]> 使用的是 <value> 标签而不是 value 的是属性的值-->
<property name="name" >
<value><![CDATA[2 < 3]]></value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
3. 命名空间注入
从上面的案例实践中,我们可以知道的是,在 xml 中我们需要会存在编写一些重复性的信息。
这样导致的结果就是:导致我们的 xml 的代码量过长,以及冗余度过高,等等一些问题。
而解决这一类问题的话,我们可以使用一些命名空间注入 的方式,提高复用性,减少必要的冗余。
命名空间的目的:就是简化配置。
如下介绍了三个命名空间:
- P命名空间注入
- c命名空间注入
- util命名空间注入
上述的三种命名空间我们都会进行一个:不使用命名空间,和使用了命名空间后的一个效果的对比,这样可以更加明显的体现出命名空间的好处。
3.1 p命名空间注入
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class People {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean sex;
private Date date;
// set 注入必须提供 set 方法()
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
", date=" + date +
'}';
}
}
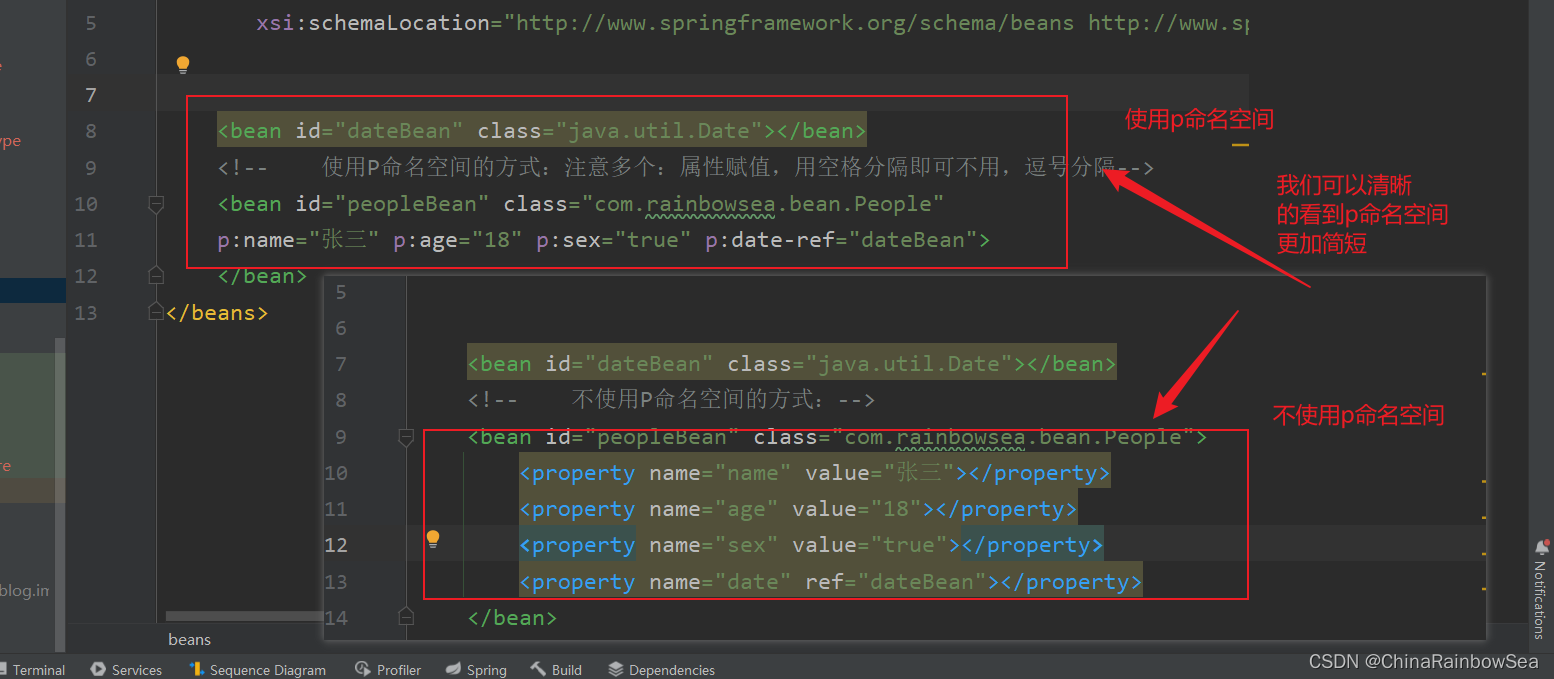
不使用p命名空间编写的 xml 配置信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dateBean" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!-- 不使用P命名空间的方式:-->
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="sex" value="true"></property>
<property name="date" ref="dateBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
使用 p命名空间进行一个 set 注入
目的:简化配置。
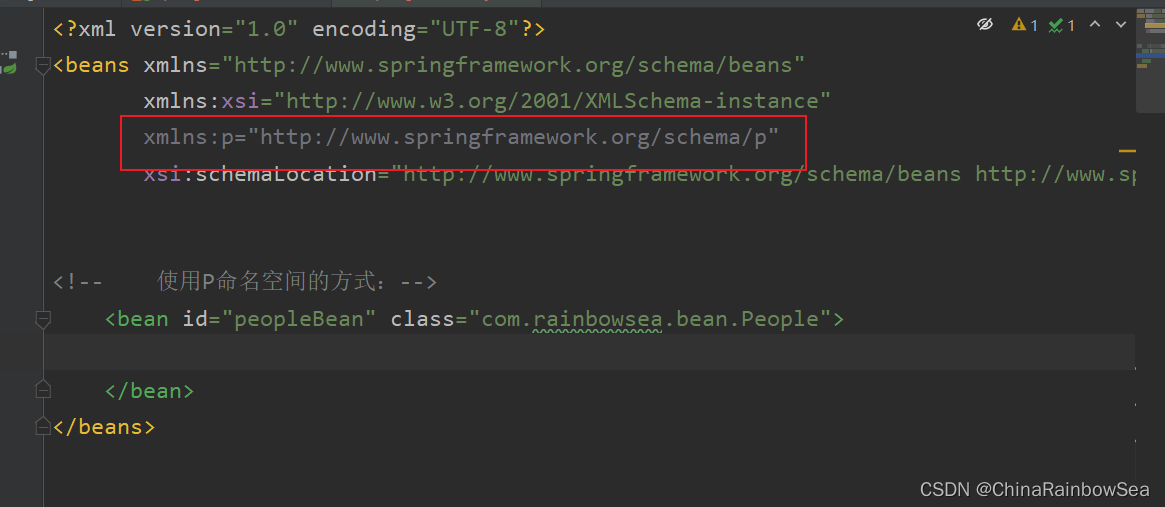
使用p命名空间注入的前提条件包括两个:
- 第一:在XML头部信息中添加p命名空间的配置信息:
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- 第二:p命名空间注入是基于setter方法的,所以需要对应的属性提供setter方法。
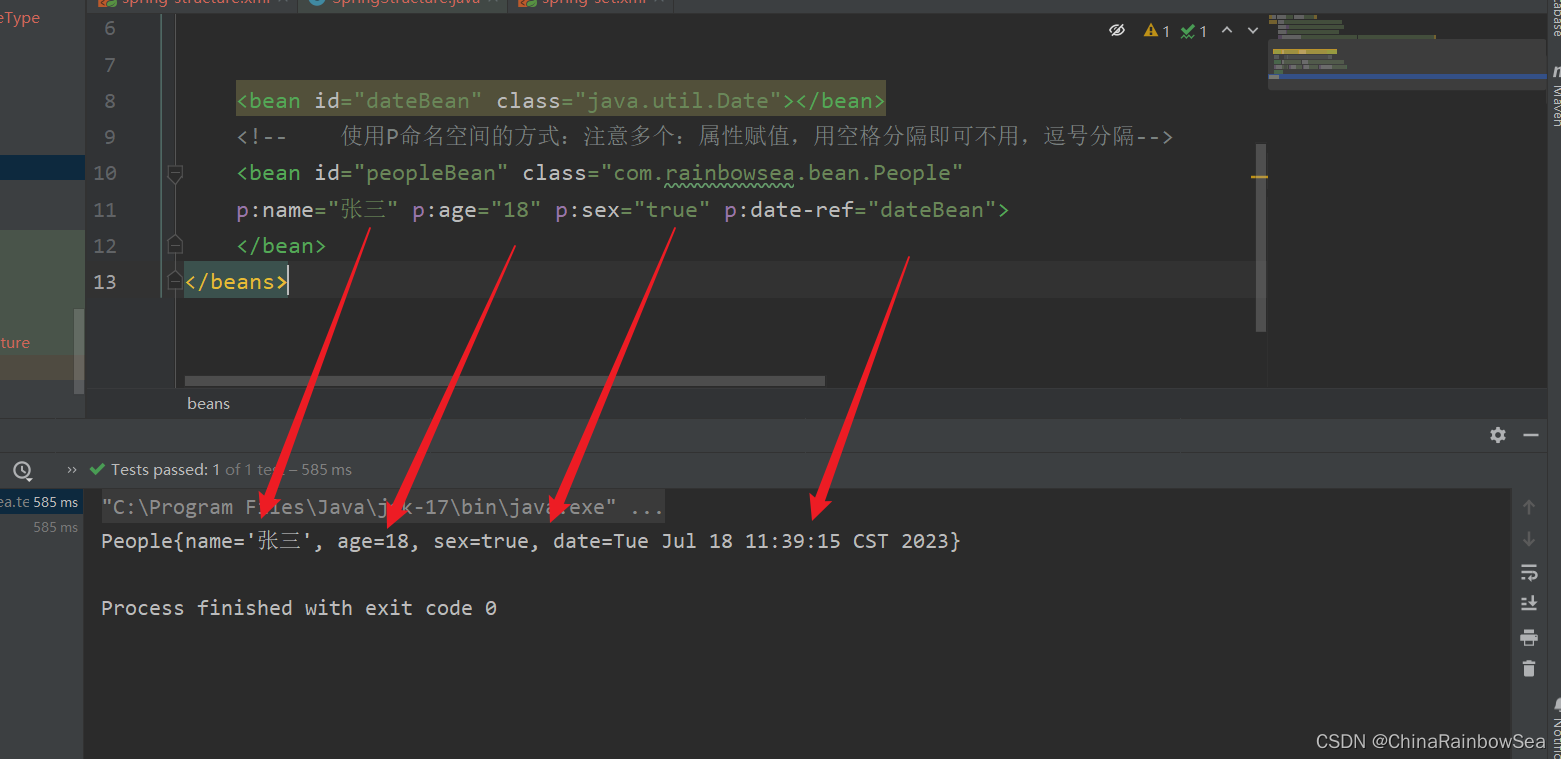
- 第三: 使用p命名空间格式如下: 需要注意的是:使用P命名空间的方式:注意多个:属性赋值,用空格分隔即可,不用逗号分隔,同时其中的 p 是小写的。
- 核心: p命名空间底层使用的还是 set 注入,所以还是必须要实现 set()方法的。
p:属性名 = "属性值"
p:birth-ref = 复杂类型
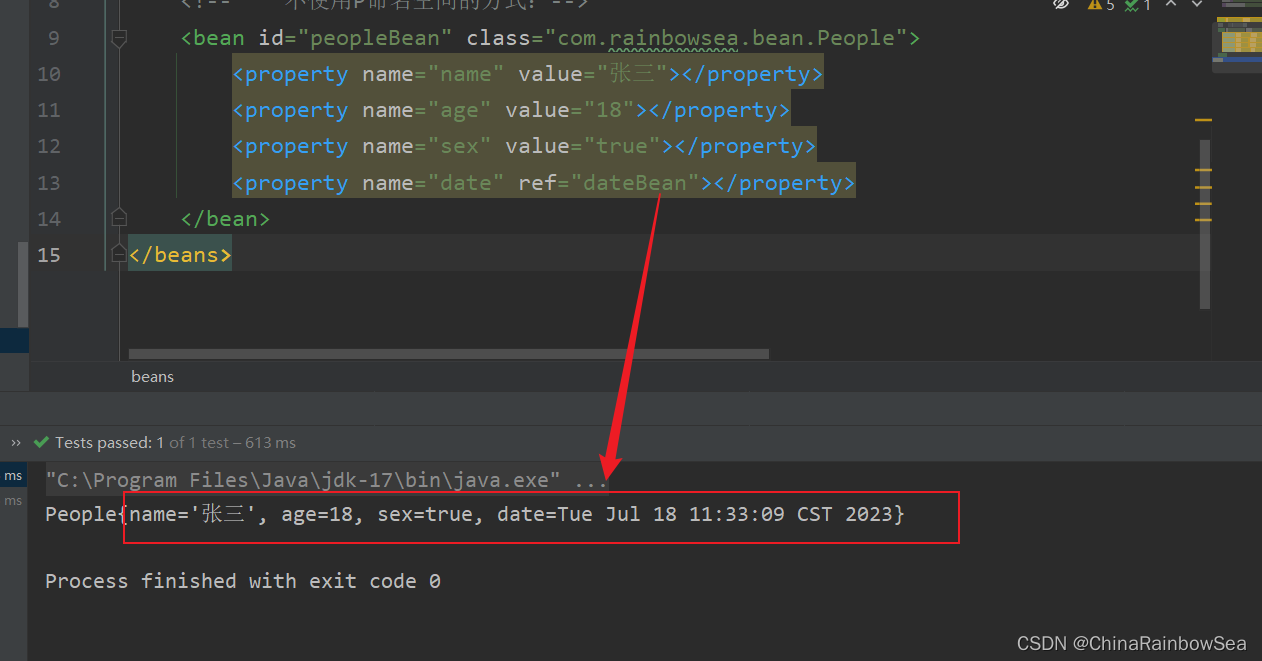
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dateBean" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!-- 使用P命名空间的方式:注意多个:属性赋值,用空格分隔即可不用,逗号分隔-->
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People"
p:name="张三" p:age="18" p:sex="true" p:date-ref="dateBean">
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
3.2 c命名空间注入
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class People {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean sex;
private Date date;
// c命名空间底层调用的是构造方法,所以必须实现对应的构造方法
public People(String name, int age, boolean sex, Date date) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.date = date;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
", date=" + date +
'}';
}
}
不使用c命名空间注入
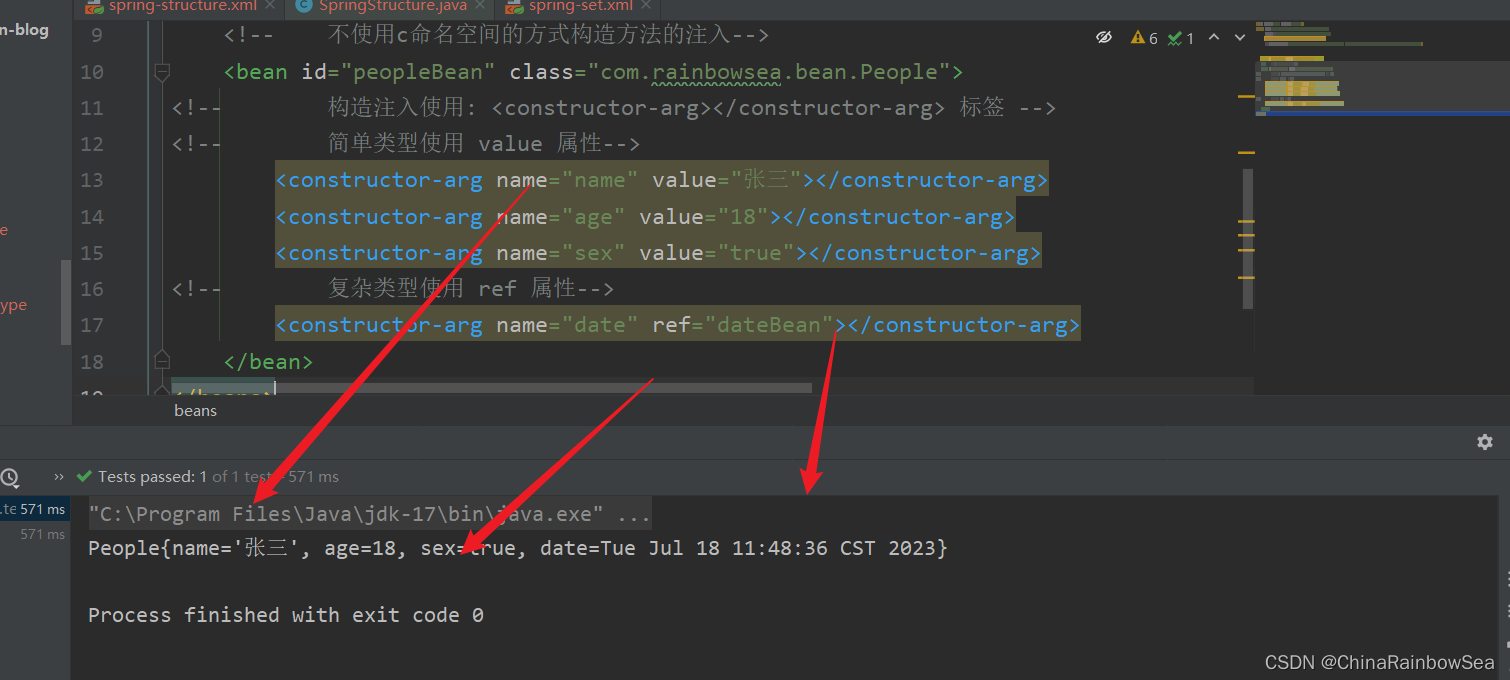
构造方法的set注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dateBean" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
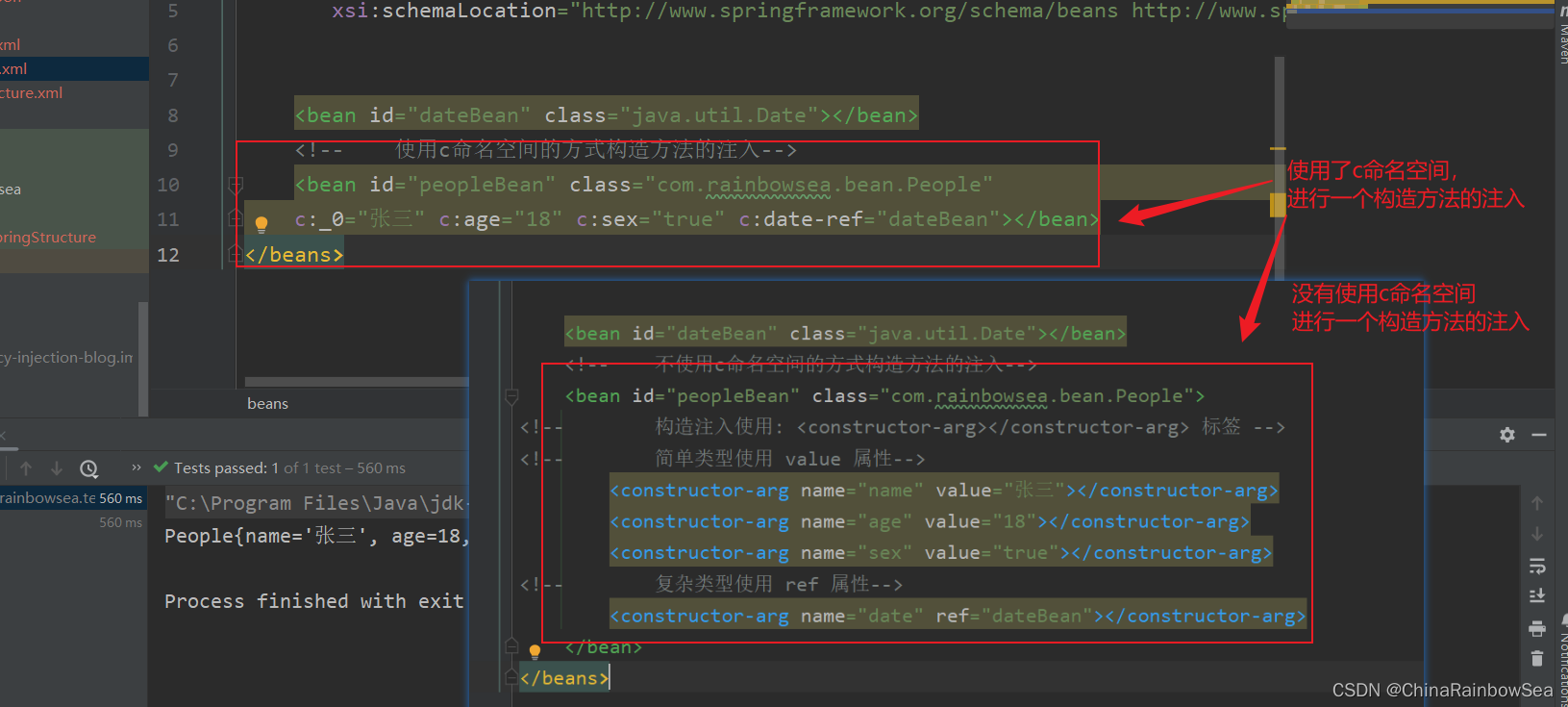
<!-- 不使用c命名空间的方式构造方法的注入-->
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- 构造注入使用: <constructor-arg></constructor-arg> 标签 -->
<!-- 简单类型使用 value 属性-->
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="sex" value="true"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 复杂类型使用 ref 属性-->
<constructor-arg name="date" ref="dateBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
使用 c命名空间进行一个构造方法的 set 注入
c命名空间是简化构造方法注入的。c命名空间底层调用的是构造方法进行一个属性的赋值。所以必须实现对应的构造方法。
使用c命名空间的两个前提条件:
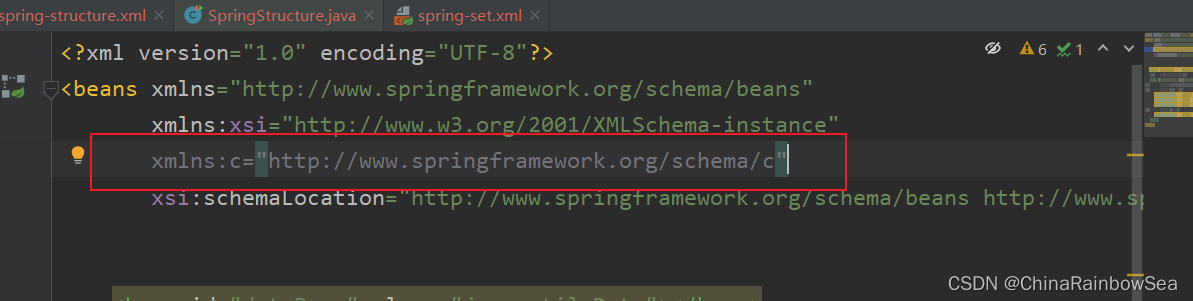
第一:需要在xml配置文件头部添加信息:xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
第二:需要提供构造方法。
第三:使用c命名空间:c命名空间两种格式对属性进行一个赋值c:_o 下标的方式,二 c:name 参数名的方式
注意:多个属性的赋值,使用空格 分隔,不要使用逗号分隔
格式如下:
c:_0 下标方式
c:name 参数名方式
复杂类型:在简单类型的后面加个-ref
c:name-ref
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dateBean" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!-- 使用c命名空间的方式构造方法的注入-->
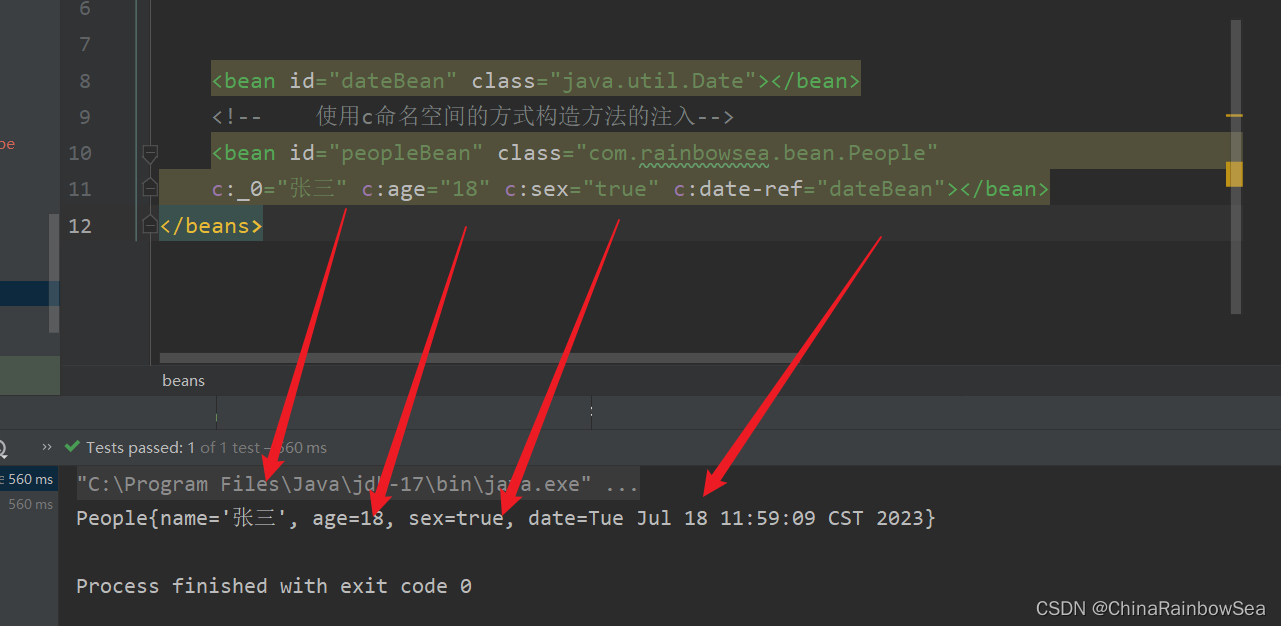
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People"
c:_0="张三" c:age="18" c:sex="true" c:date-ref="dateBean"></bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
3.3 util命名空间注入
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MyDataSource02 {
private Properties properties;
// set 注入必须提供 set方法
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource02{" +
"properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
不使用 util 命名空间的效果:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
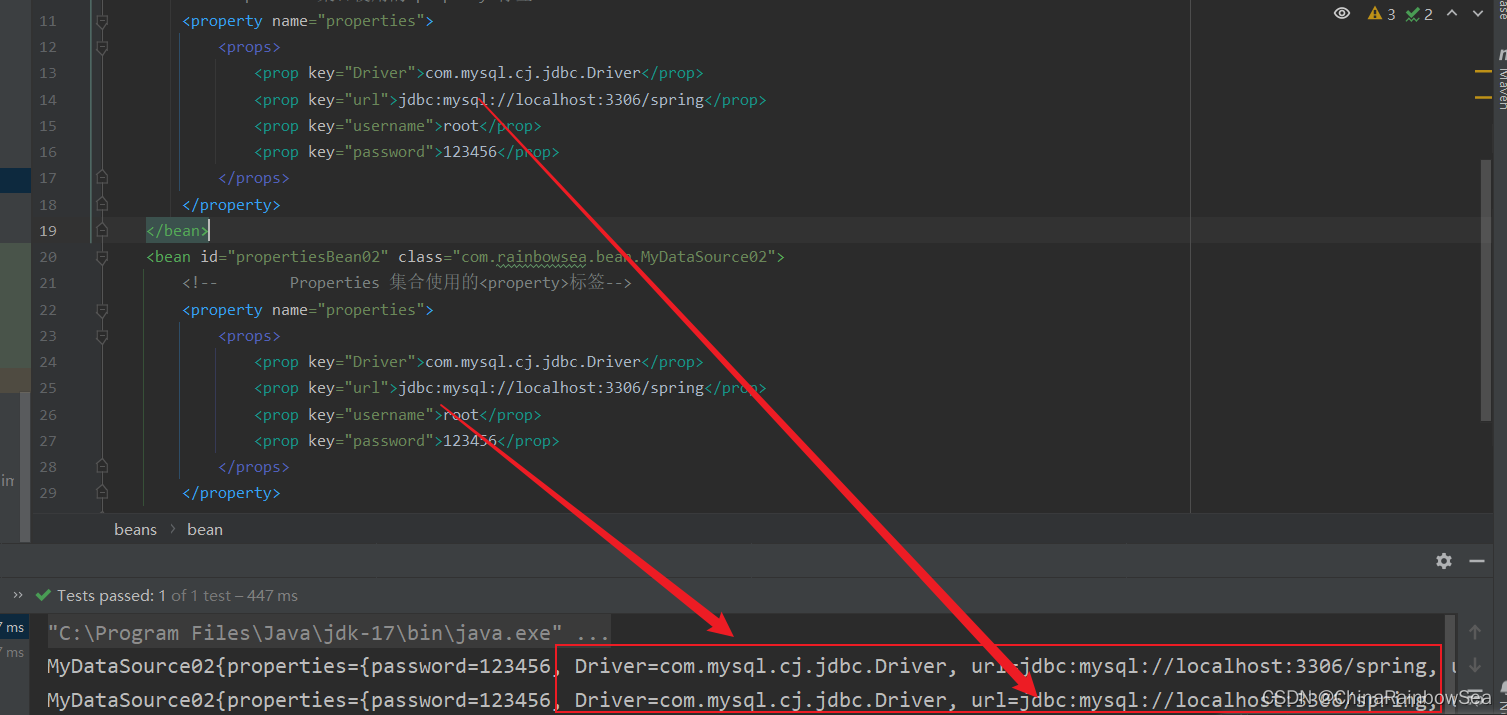
<bean id="propertiesBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource02">
<!-- Properties 集合使用的<property>标签-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="Driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="propertiesBean02" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource02">
<!-- Properties 集合使用的<property>标签-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="Driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行测试:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource02;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
MyDataSource02 propertiesBean = applicationContext.getBean("propertiesBean", MyDataSource02.class);
System.out.println(propertiesBean);
MyDataSource02 propertiesBean02 = applicationContext.getBean("propertiesBean02", MyDataSource02.class);
System.out.println(propertiesBean);
}
}
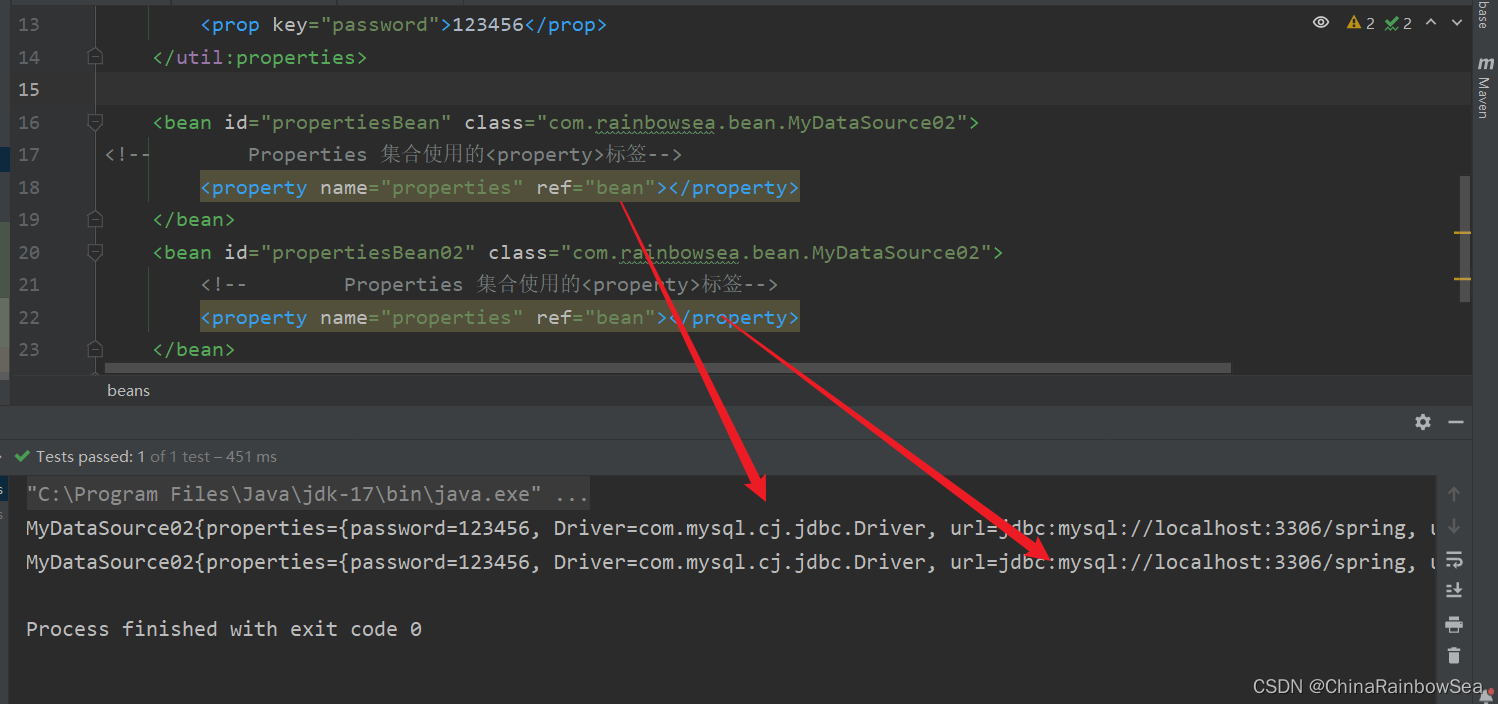
使用 util 命名空间的效果
使用util命名空间可以让配置复用。
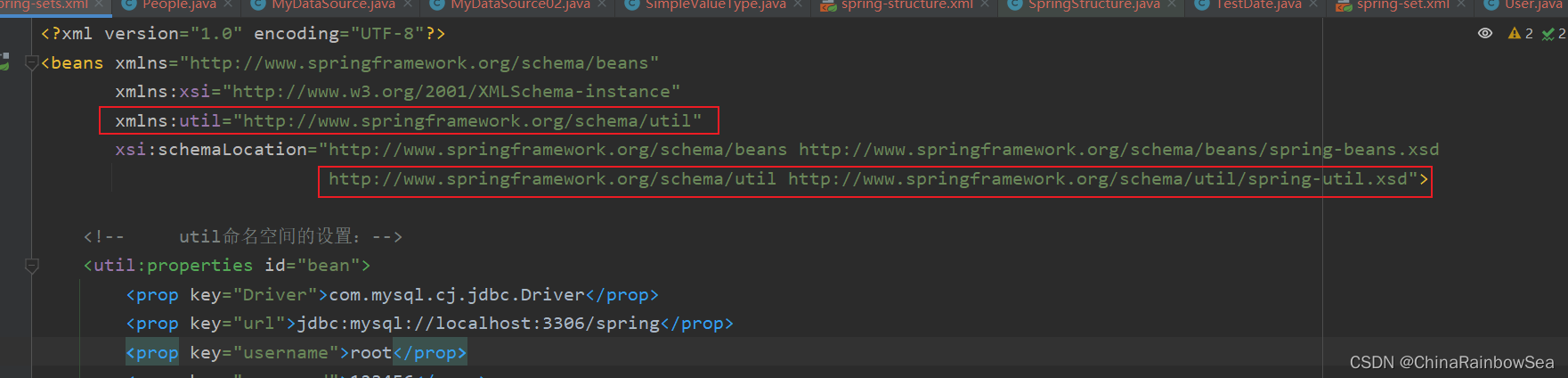
使用util命名空间的前提是:在spring配置文件头部添加配置信息。如下:
- 第一:在spring 当中的 xml 的配置文件的导入相关的命名空间:
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
具体的如下图所示:
- 第二: 使用 util 命名空间,格式首先需要定义好相对应的 util 的数据源信息。格式如下:使用的话,作为复杂类型进行一个 ref 处理。
<!-- util命名空间的设置:-->
<util:properties id="bean">
<prop key="Driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</util:properties>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-util.xsd">
<!-- util命名空间的设置:-->
<util:properties id="bean">
<prop key="Driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</util:properties>
<bean id="propertiesBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource02">
<!-- Properties 集合使用的<property>标签-->
<property name="properties" ref="bean"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="propertiesBean02" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource02">
<!-- Properties 集合使用的<property>标签-->
<property name="properties" ref="bean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource02;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
MyDataSource02 propertiesBean = applicationContext.getBean("propertiesBean", MyDataSource02.class);
System.out.println(propertiesBean);
MyDataSource02 propertiesBean02 = applicationContext.getBean("propertiesBean02", MyDataSource02.class);
System.out.println(propertiesBean);
}
}
4. 补充:Spring引入外部属性配置文件
我们都知道编写数据源的时候是需要连接数据库的信息。例如: Driver ,url ,username,password 等信息,这些休息可以单独写到一个属性配置文件中,这样用户修改起来会更加的方便。
Eg: 我们创建一个 jdbc.propertise 配置文件,让spring当中的xml 可以读取到其中的配置信息.
第一步:写一个数据源类,提供相关属性。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
// set 注入必须提供 set () 方法
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
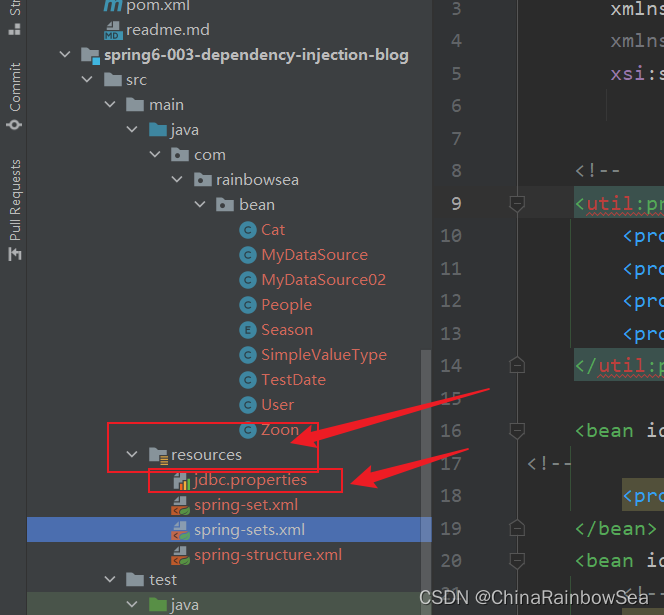
第二步:在类路径下新建jdbc.properties文件,并配置信息。
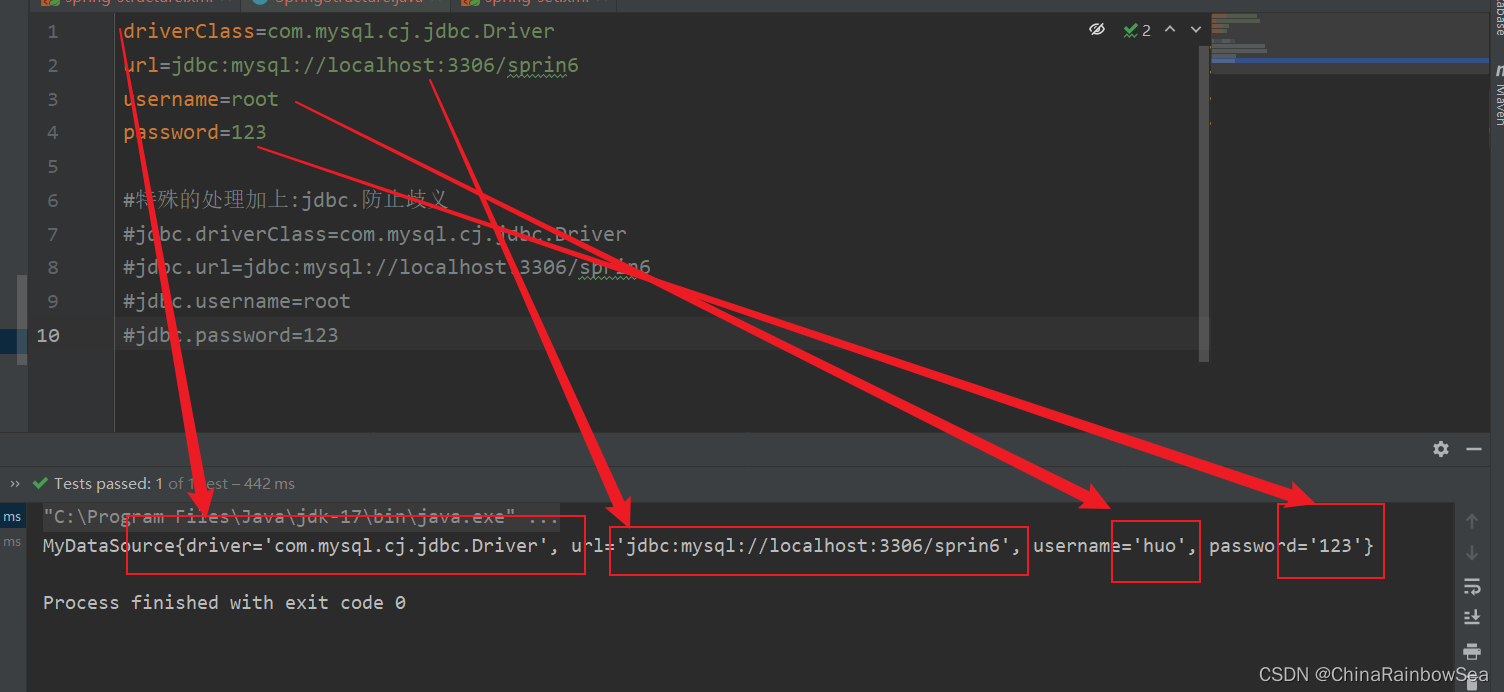
driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sprin6
username=root
password=123
#特殊的处理加上:jdbc.防止歧义
#jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sprin6
#jdbc.username=root
#jdbc.password=123
需要注意的是:我们需要该 jdbc.properties 文件创建到,其中的该 resources 当中去。
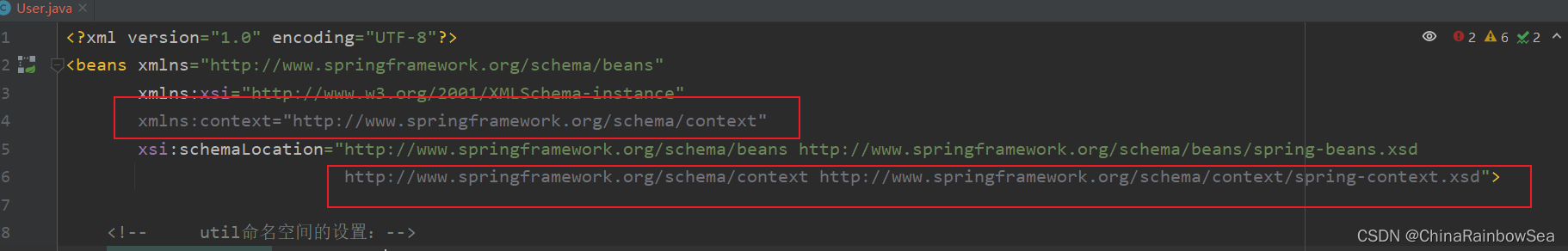
第三步:在spring配置文件中引入context命名空间。
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"
具体如下图所示:
第四步:在spring中配置使用jdbc.properties文件。
格式如下:
第三步: 使用标签context:property-placeholder 的Location属性来指定属性配置文件的路径:location默认类型的根路径下开始加载资源.
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
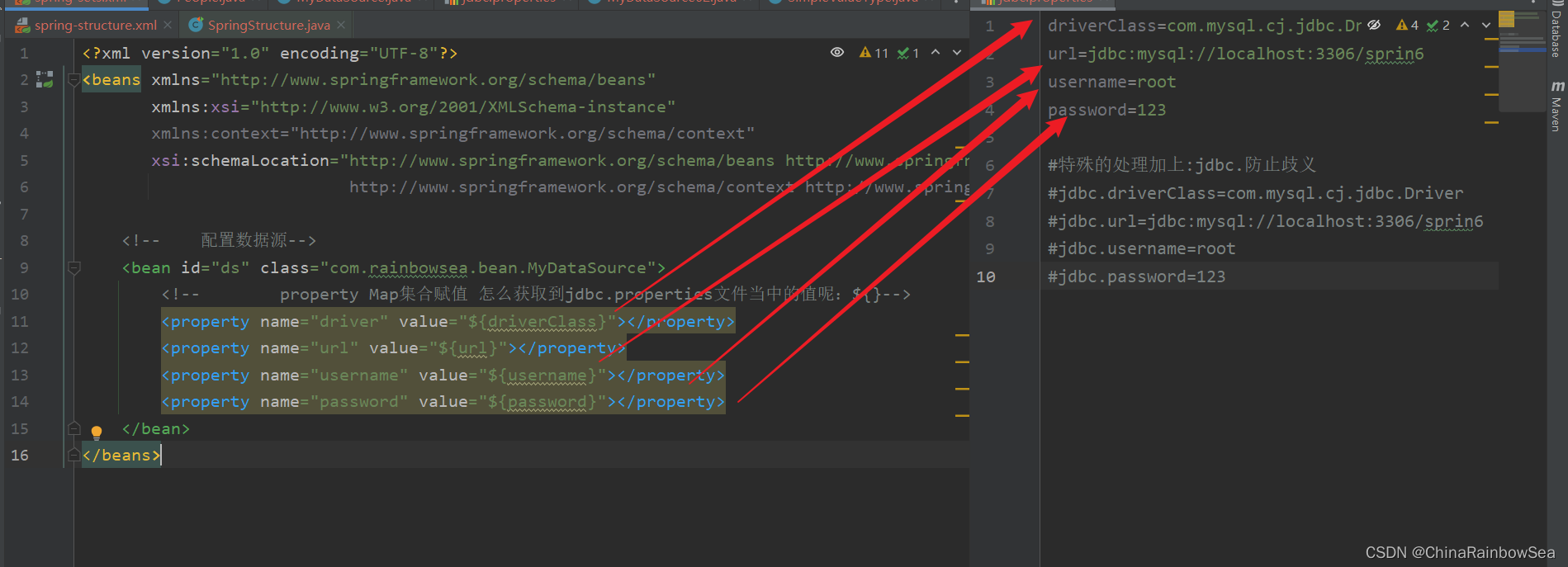
<!--在: xml 中使用 怎么获取到jdbc.properties文件当中的值呢:使用${} 其中的 ${放的是对应propertise 配置文件当中的 key 名}-->
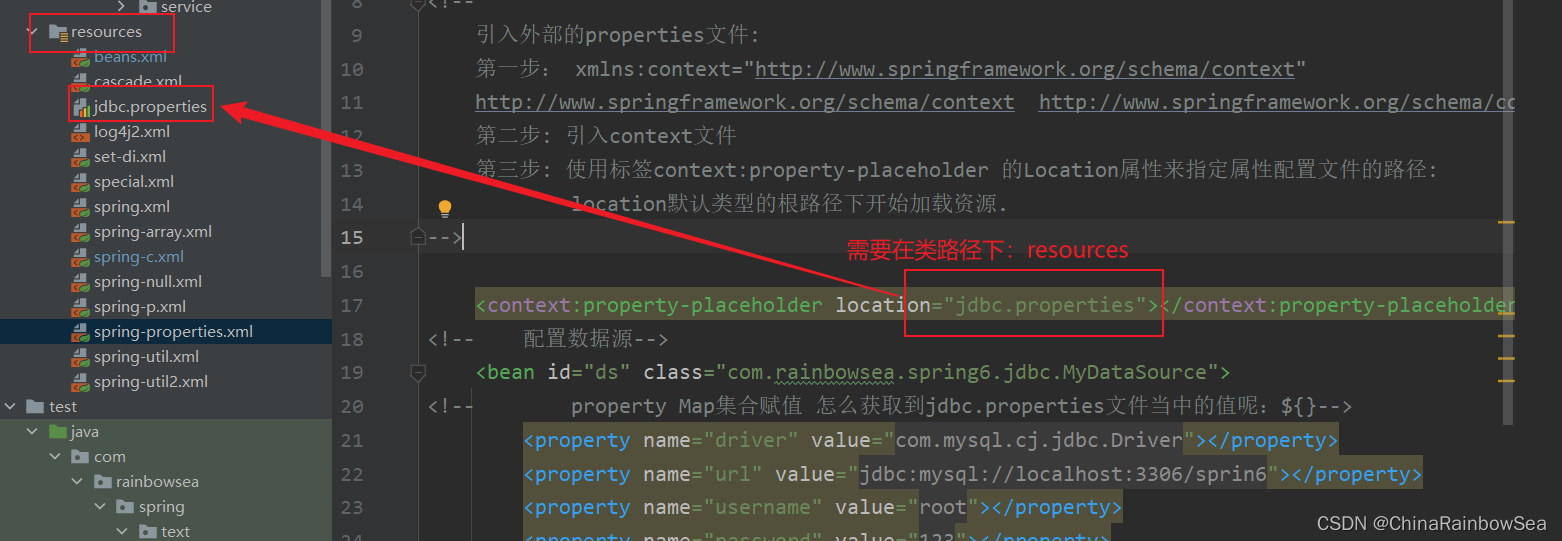
具体的如下图所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- xml 读取对应文件当中的 jdbc.properties 文件信息-->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 配置数据源-->
<bean id="ds" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource">
<!-- property Map集合赋值 怎么获取到jdbc.properties文件当中的值呢:${}-->
<property name="driver" value="${driverClass}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${password}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试程序:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 获取到对应的 spring6当中的xml的,容器对象
// 面向接口编程,左边为接口,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通过 id 获取到对应的类/class
MyDataSource ds = applicationContext.getBean("ds", MyDataSource.class);
System.out.println(ds);
}
}
5. 总结:
依赖注入:
依赖指的是对象和对象 之间的关联关系。
注入指的是一种数据传递行为,通过注入行为来让对象和对象产生关系。
依赖注入常见的实现方式包括两种:
第一种:set注入 : set 注入必须实现了其中类的 set () 方法不然,是实现 set 注入的。因为set 注入的底层调用的是 set () 方法
第二种: 构造注入: 构造注入必须实现了对应参数的构造方法,不然是无法实现构造注入的。因为构造注入的底层调用的是 对应的构造方法。
使用其中 set 注入的各种应用场景:
- 简单类型的set 注入使用 value 属性操作
- 复杂类型的 set 注入使用 ref 属性进行一个赋值操作
set 注入的各种类型的格式处理:
- 数组类型
- 集合类型: Set,List,Map, Properties 集合
set 注入当中 如何实现 null 指的赋值,以及空字符串 的赋值
在 xml 当中,五种特殊的字符串的处理的方式:XML 中有 5 个特殊字符,分别是:<、>、'、"、& 。以上这 5 个特殊符号在 xml 中会被特殊对待,会被当做xml语法的一部分进行解析,如果这些特殊符号直接出现注入的字符串当中,会报错的。
命名空间上的使用:简化配置信息: p命名空间,c命名空间,util 命名空间。
- p命名空间底层调用的还是 set () 方法
- c命名空间底层调用的是 构造方法
- util 命名空间进行一个配置信息的复用
Spring 当中的 xml 读取到外部的 properties 配置文件的信息的操作。
6. 最后:
“在这个最后的篇章中,我要表达我对每一位读者的感激之情。你们的关注和回复是我创作的动力源泉,我从你们身上吸取了无尽的灵感与勇气。我会将你们的鼓励留在心底,继续在其他的领域奋斗。感谢你们,我们总会在某个时刻再次相遇。”
Spring 的依赖注入的更多相关文章
- (spring-第3回【IoC基础篇】)spring的依赖注入-属性、构造函数、工厂方法等的注入(基于XML)
Spring要把xml配置中bean的属性实例化为具体的bean,"依赖注入"是关卡.所谓的"依赖注入",就是把应用程序对bean的属性依赖都注入到spring ...
- Spring的依赖注入(DI)三种方式
Spring依赖注入(DI)的三种方式,分别为: 1. 接口注入 2. Setter方法注入 3. 构造方法注入 下面介绍一下这三种依赖注入在Spring中是怎么样实现的. 首先我们需要以下几个 ...
- spring的依赖注入的最常见的两种方法
package com.lsz.spring.action; public class User { /** * set注入 */ private String username; public vo ...
- 一步一步深入spring(3)--spring的依赖注入方式
对于spring配置一个bean时,如果需要给该bean提供一些初始化参数,则需要通过依赖注入方式,所谓的依赖注入就是通过spring将bean所需要的一些参数传递到bean实例对象的过程,sprin ...
- spring的依赖注入是什么意思
最近学习spring框架,对依赖注入有些模糊,遂上网翻阅资料,做了下列总结,原博客为CSDN 南夏的 spring的依赖注入是什么意思,侵删! Spring 能有效地组织J2EE应用各层的对象.不管是 ...
- SpringBoot系列: 理解 Spring 的依赖注入(一)
==============================Spring 的依赖注入==============================对于 Spring 程序, Spring 框架为我们提供 ...
- Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--实例化容器常用方法
Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习---实例化容器常用方法 本篇学习实例化Spring.NET容器的俩种方式 1.通过XmlObjectFactory创建一个Spring.NET容器 IResour ...
- Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--简单对象注入
Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--简单对象注入 在前面的俩篇中讲解了依赖注入的概念以及Spring.NET框架的核心模块介绍,今天就要看看怎么来使用Spring.NET实现一个简单的对象注入 常 ...
- Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--简介
Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--Spring.NET简介 概述 Spring.NET是一个应用程序框架,其目的是协助开发人员创建企业级的.NET应用程序.它提供了很多方面的功能,比如依赖注入. ...
- Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--入门
Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--入门 在学些Spring.net框架之前,有必要先脑补一点知识,比如什么是依赖注入?IOC又是什么?控制反转又是什么意思?它们与Spring.net又有什么关系 ...
随机推荐
- 华为云新一代iPaaS全域融合集成平台全新升级
摘要:基于华为十多年的数字化转型实践,华为云通过组装式交付.数智驱动.DevOps.服务化架构.安全可信.韧性6大关键技术助力客户实现应用现代化和高质量增长,华为云新一代iPaaS全域融合集成平台RO ...
- 深入理解python虚拟机:调试器实现原理与源码分析
深入理解python虚拟机:调试器实现原理与源码分析 调试器是一个编程语言非常重要的部分,调试器是一种用于诊断和修复代码错误(或称为 bug)的工具,它允许开发者在程序执行时逐步查看和分析代码的状态和 ...
- Vue的生命周期的详解
Vue的生命周期 Vue的生命周期是每个使用Vue框架的前端人员都需要掌握的知识,以此作为记录. Vue的生命周期就是vue实例从创建到销毁的全过程,也就是new Vue() 开始就是vue生 ...
- [C++核心编程] 4.3、类和对象-C++对象模型和this指针
文章目录 4.3 C++对象模型和this指针 4.3.1 成员变量和成员函数分开存储 4.3.2 this指针概念 4.3.3 空指针访问成员函数 4.3.4 const修饰成员函数 4.3 C++ ...
- Sementic Kernel 案例之网梯科技在线教育
2023年4月25日,微软公布了2023年第一季度财报,营收528亿美元, 微软CEO纳德称,「世界上最先进的AI模型与世界上最通用的用户界面--自然语言--相结合,开创了一个新的计算时代.」该公司有 ...
- Flutter 如何将代码显示到界面上
前言 如何优雅的将项目中的代码,亦或是你的demo代码展示到界面上?本文对使用简单.便于维护且通用的解决方案,进行相关的对比和探究 为了节省大家的时间,把最终解决方案的相关接入和用法写在前面 预览代码 ...
- map和multimap
map相对于set区别,map具有键值和实值,所有元素根据键值自动排序,pair的第一个值被称为键值key,pair的第二个值被称为实值value.map也是以红黑树为底层实现机制,根据key进行排序 ...
- Golang常用语法糖
1.名字由来 语法糖(Syntactic sugar)的概念是由英国计算机科学家彼得·兰丁提出的,用于表示编程语言中的某种类型的语法,这些语法不会影响功能,但使用起来却很方便.语法糖,也称糖语法,这些 ...
- Prompt learning 教学[技巧篇]:通过增加示例、引导词、特殊符号指令等方式让chatgpt输出更好的答案
Prompt learning 教学[技巧篇]:通过增加示例.引导词.特殊符号指令等方式让chatgpt输出更好的答案 技巧1:To Do and Not To Do 在问答场景里,为了让 AI 回答 ...
- Redis内存兜底策略——内存淘汰及回收机制
Redis内存兜底策略--内存淘汰及回收机制 Redis内存淘汰及回收策略都是Redis内存优化兜底的策略,那它们是如何进行兜底的呢?先来说明一下什么是内存淘汰和内存回收策略: Redis内存淘汰:当 ...