HashMap的底层原理
简单说: 底层原理就是采用数组加链表:

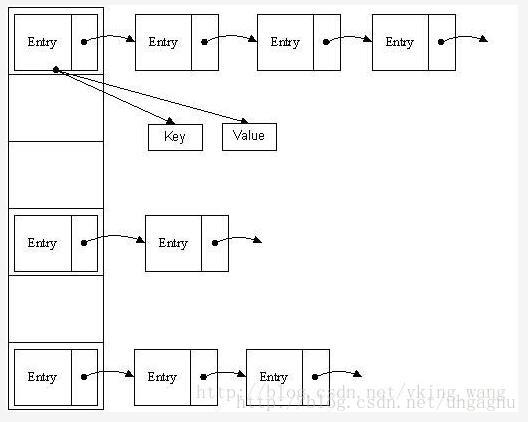
两张图片很清晰地表明存储结构:
既然是线性数组,为什么能随机存取?这里HashMap用了一个小算法,大致是这样实现:
// 存储时:
int hash = key.hashCode(); // 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
// 取值时:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
return Entry[index];
HashMap的底层原理的更多相关文章
- HashMap的底层原理(jdk1.7.0_79)
前言 在Java中我们最常用的集合类毫无疑问就是Map,其中HashMap作为Map最重要的实现类在我们代码中出现的评率也是很高的. 我们对HashMap最常用的操作就是put和get了,那么你知道它 ...
- 谈一下HashMap的底层原理是什么?
底层原理:Map + 无序 + 键唯一 + 哈希表 (数组+Entry)+ 存取值 1.HashMap是Map接口的实现类.实现HashMap对数据的操作,允许有一个null键,多个null值. Co ...
- HashMap的底层原理 cr:csdn:zhangshixi
1. HashMap概述: HashMap是基于哈希表的Map接口的非同步实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用null值和null键.此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变 ...
- 深度解析HashMap集合底层原理
目录 前置知识 ==和equals的区别 为什么要重写equals和HashCode 时间复杂度 (不带符号右移) >>> ^异或运算 &(与运算) 位移操作:1<&l ...
- 浅谈HashMap 的底层原理
本文整理自漫画:什么是HashMap? -小灰的文章 .已获得作者授权. HashMap 是一个用于存储Key-Value 键值对的集合,每一个键值对也叫做Entry.这些个Entry 分散存储在一个 ...
- HashMap 的底层原理
1. HashMap的数据结构 数据结构中有数组和链表来实现对数据的存储,但这两者基本上是两个极端. 数组 数组存储区间是连续的,占用内存严重,故空间复杂的很大.但数组的二分查找时间复杂度小,为O(1 ...
- 最简单的HashMap底层原理介绍
HashMap 底层原理 1.HashMap底层概述 2.JDK1.7实现方式 3.JDK1.8实现方式 4.关键名词 5.相关问题 1.HashMap底层概述 在JDK1.7中HashMap采用的 ...
- HashMap的底层实现原理
HashMap的底层实现原理1,属性static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;//1073741824(十进制)0100000000000000000 ...
- HashMap底层原理分析(put、get方法)
1.HashMap底层原理分析(put.get方法) HashMap底层是通过数组加链表的结构来实现的.HashMap通过计算key的hashCode来计算hash值,只要hashCode一样,那ha ...
随机推荐
- 利用MD5加密字符串
private static string MD5E(string temp) { MD5 md5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider(); byte[] source=Sy ...
- SQL Server 2008 R2 添加登录账户配置权限
一.新建登录名1. 在登录名右侧的文本框中输入新建的管理员账号名称:2. 一对单选按钮组中,选择Sql Server 身份验证,并输入登录密码:3. 勾选强制实施密码策略复选框:(密码策略一般是指加强 ...
- 远程块存储iSCSI
/* Border styles */ #table-2 thead, #table-2 tr { border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; bo ...
- cookie的设置和获取
// 创建cookiefunction setCookie(name, value, expires, path, domain, secure) { var cookieText = encodeU ...
- C#图解教程 第二十三章 预处理指令
预处理指令 什么是预处理指令基本规则#define和#undef指令条件编译条件编译结构诊断指令行号指令区域指令#pragma warning 指令 预处理指令 什么是预处理指令 源代码指定了程序的定 ...
- myeclipse 打开jsp文件出错
第一步:找到MyEclipse的安装路径:第二步:删除掉MyEclipse\configuration下名为:org.eclipse.update的文件夹:第三步:产出之后重启myeclipse,在打 ...
- gprecoverseg导致的元数据库问题致使数据库无法启动以及修复
一.现象描述 在一次执行gprecoverseg后发现数据库无法正常连接,现象如下: 执行gprecoverseg日志如下: gprecoverseg:mdw-:gpadmin-[INFO]:-Sta ...
- 谈谈MySQL的事务隔离级别
这篇文章能够阐述清楚跟数据库相关的四个概念:事务.数据库读现象.隔离级别.锁机制 一.事务 先来看下百度百科对数据库事务的定义: 作为单个逻辑单元执行一系列操作,要么完全执行,要么完全不执行.事务处理 ...
- 【BZOJ2160】拉拉队排练(回文树)
[BZOJ2160]拉拉队排练(回文树) 题面 BZOJ 题解 看着题目, 直接构建回文树 求出每个回文串的出现次数 直接按照长度\(sort\)一下就行了 然后快速幂算一下答案就出来了 这题貌似可以 ...
- [BZOJ2761] [JLOI2011] 不重复数字 (set)
Description 给出N个数,要求把其中重复的去掉,只保留第一次出现的数. 例如,给出的数为1 2 18 3 3 19 2 3 6 5 4,其中2和3有重复,去除后的结果为1 2 18 3 19 ...
