Tensorflow模型加载与保存、Tensorboard简单使用
先上代码:
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Nov 14 20:34:00 2017 @author: HJL
""" # Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ============================================================================== """A deep MNIST classifier using convolutional layers. See extensive documentation at
https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/pros
"""
# Disable linter warnings to maintain consistency with tutorial.
# pylint: disable=invalid-name
# pylint: disable=g-bad-import-order import argparse
import sys
#import tempfile
import time
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import tensorflow as tf FLAGS = None def deepnn(x):
"""deepnn builds the graph for a deep net for classifying digits. Args:
x: an input tensor with the dimensions (N_examples, 784), where 784 is the
number of pixels in a standard MNIST image. Returns:
A tuple (y, keep_prob). y is a tensor of shape (N_examples, 10), with values
equal to the logits of classifying the digit into one of 10 classes (the
digits 0-9). keep_prob is a scalar placeholder for the probability of
dropout.
"""
# Reshape to use within a convolutional neural net.
# Last dimension is for "features" - there is only one here, since images are
# grayscale -- it would be 3 for an RGB image, 4 for RGBA, etc.
with tf.name_scope('reshape'):
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
tf.summary.image('input_image', x_image) # First convolutional layer - maps one grayscale image to 32 feature maps.
with tf.name_scope('conv1'):
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
tf.summary.histogram('W_conv1', W_conv1)
# Pooling layer - downsamples by 2X.
with tf.name_scope('pool1'):
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # Second convolutional layer -- maps 32 feature maps to 64.
with tf.name_scope('conv2'):
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) # Second pooling layer.
with tf.name_scope('pool2'):
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) # Fully connected layer 1 -- after 2 round of downsampling, our 28x28 image
# is down to 7x7x64 feature maps -- maps this to 1024 features.
with tf.name_scope('fc1'):
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) # Dropout - controls the complexity of the model, prevents co-adaptation of
# features.
with tf.name_scope('dropout'):
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) # Map the 1024 features to 10 classes, one for each digit
with tf.name_scope('fc2'):
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2
return y_conv, keep_prob def conv2d(x, W):
"""conv2d returns a 2d convolution layer with full stride."""
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') def max_pool_2x2(x):
"""max_pool_2x2 downsamples a feature map by 2X."""
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') def weight_variable(shape):
"""weight_variable generates a weight variable of a given shape."""
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape):
"""bias_variable generates a bias variable of a given shape."""
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) def main(_):
# Import data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('./', one_hot=True) # Create the model
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # Define loss and optimizer
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # Build the graph for the deep net
y_conv, keep_prob = deepnn(x) with tf.name_scope('loss'):
cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_,
logits=y_conv)
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy) with tf.name_scope('adam_optimizer'):
#train_step = tf.train.AdadeltaOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
correct_prediction = tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct_prediction) graph_location = "./log/" #tempfile.mkdtemp()
print('Saving graph to: %s' % graph_location)
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(graph_location)
train_writer.add_graph(tf.get_default_graph())#保存默认的图 tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() with tf.Session() as sess:
#模型保存 step1
saver = tf.train.Saver()
checkpoint_dir="./"
#返回checkpoint文件中checkpoint的状态
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(checkpoint_dir)
#print(ckpt)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:#如果存在以前保存的模型
print('Restore the model from checkpoint %s' % ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
# Restores from checkpoint
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)#加载模型
start_step = int(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1])
else:#如果不存在之前保存的模型
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())#变量初始化
start_step = 0
print('start training from new state') for i in range(start_step,start_step+20000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i % 100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print('step %d, training accuracy %g' % (i, train_accuracy))
#step2 每隔一段时间 保存模型
saver.save(sess, './log/my_test_model',global_step=i) summary,_=sess.run([merged, train_step],feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
#time.sleep(0.5) print('test accuracy %g' % accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0})) if __name__ == '__main__':
#main() parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str,
default='./data/MNIST/',
help='Directory for storing input data')
FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed)
上述代码输出如下:
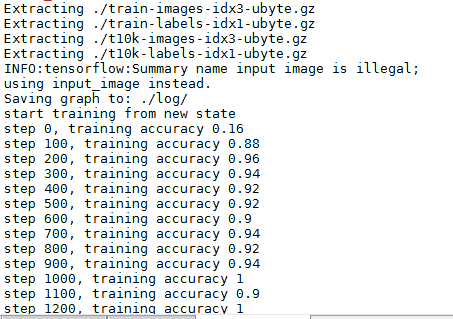
模型的加载与保存
模型的保存涉及到两个函数:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
和
saver.save(sess, './log/my_test_model',global_step=i)
即,先创建tf.train.Saver 对象,用于后续模型保存与加载,默认保存所有参数。saver.save用于将模型及参数保存到文件中,通过传递一个值给可选参数 global_step ,你可以编号checkpoint 名字。上述代码中每隔100步,将模型保存一次。保存结果如下(默认保存最新的5个模型):
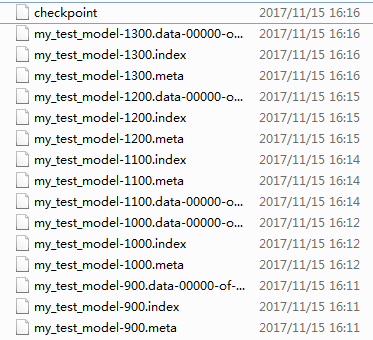
对于模型的加载,涉及如下函数:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
和
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
- sess: 用于恢复参数的Session
- save_path: 参数之前保存的路径
TensorBoard简单使用
涉及如下几个函数:
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(graph_location)
train_writer.add_graph(tf.get_default_graph()) ... tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)#
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
tf.summary.image('input_image', x_image)
tf.summary.histogram('W_conv1', W_conv1)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() ...
summary,_=sess.run([merged, train_step],feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
Summary:所有需要在TensorBoard上展示的统计结果。tf.name_scope():为Graph中的Tensor添加层级,TensorBoard会按照代码指定的层级进行展示,初始状态下只绘制最高层级的效果,点击后可展开层级看到下一层的细节。tf.summary.scalar():添加标量统计结果。tf.summary.histogram():添加任意shape的Tensor,统计这个Tensor的取值分布。tf.summary.merge_all():添加一个操作,代表执行所有summary操作,这样可以避免人工执行每一个summary op。tf.summary.FileWrite:用于将Summary写入磁盘,需要制定存储路径logdir,如果传递了Graph对象,则在Graph Visualization会显示Tensor Shape Information。执行summary op后,将返回结果传递给add_summary()方法即可。
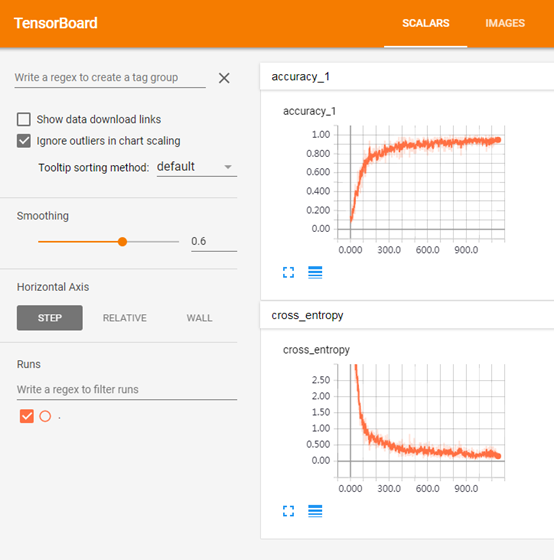
最后结果:
Scalar
(对应:
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
)
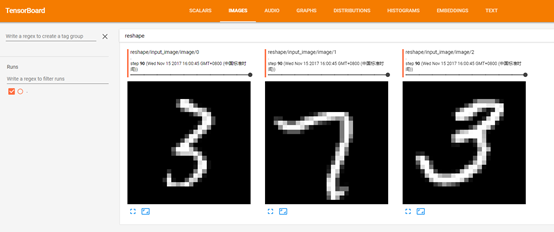
对应:
tf.summary.image('input_image', x_image)
对应:
train_writer.add_graph(tf.get_default_graph())
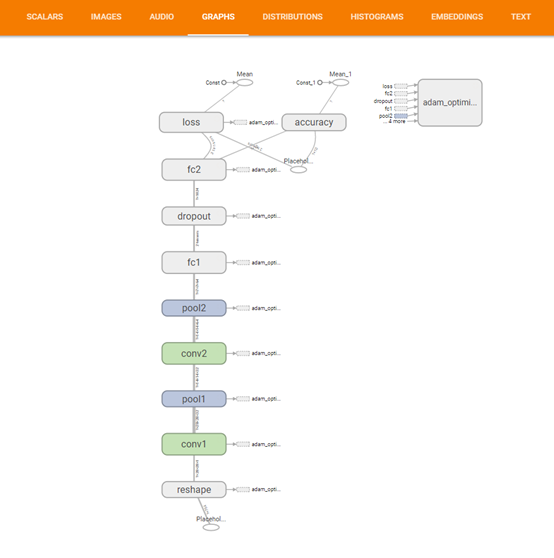
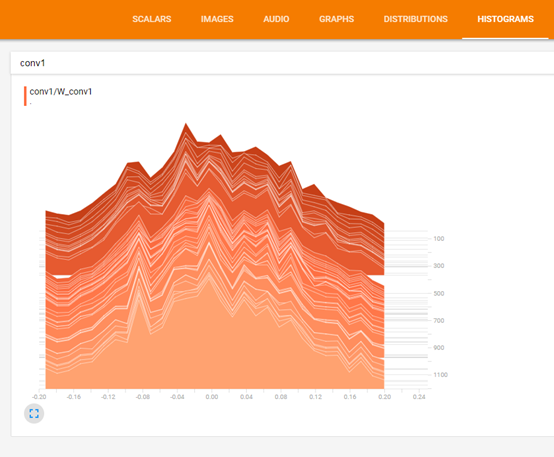
对应:
tf.summary.histogram('W_conv1', W_conv1)
Tensorflow模型加载与保存、Tensorboard简单使用的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow模型加载与保存
我们经常遇到训练时间很长,使用起来就是Weight和Bias.那么如何将训练和测试分开操作呢? TF给出了模型的加载与保存操作,看了网上都是很简单的使用了一下,这里给出一个神经网络的小程序去测试. 本 ...
- PyTorch模型加载与保存的最佳实践
一般来说PyTorch有两种保存和读取模型参数的方法.但这篇文章我记录了一种最佳实践,可以在加载模型时避免掉一些问题. 第一种方案是保存整个模型: 1 torch.save(model_object, ...
- tensorflow 模型加载(没有checkpoint文件或者说只加载其中一个模型)
1.如果有checkpoint文件的话,加载模型很简单: 第一步:都是加载图: with tf.Session() as sess: saver=tf.train.import_meta_graph( ...
- Tensorflow同时加载使用多个模型
在Tensorflow中,所有操作对象都包装到相应的Session中的,所以想要使用不同的模型就需要将这些模型加载到不同的Session中并在使用的时候申明是哪个Session,从而避免由于Sessi ...
- KnockoutJS 3.X API 第七章 其他技术(1) 加载和保存JSON数据
Knockout允许您实现复杂的客户端交互性,但几乎所有Web应用程序还需要与服务器交换数据,或至少将本地存储的数据序列化. 最方便的交换或存储数据的方式是JSON格式 - 大多数Ajax应用程序今天 ...
- DirectX11 With Windows SDK--19 模型加载:obj格式的读取及使用二进制文件提升读取效率
前言 一个模型通常是由三个部分组成:网格.纹理.材质.在一开始的时候,我们是通过Geometry类来生成简单几何体的网格.但现在我们需要寻找合适的方式去表述一个复杂的网格,而且包含网格的文件类型多种多 ...
- OpenGL OBJ模型加载.
在我们前面绘制一个屋,我们可以看到,需要每个立方体一个一个的自己来推并且还要处理位置信息.代码量大并且要时间.现在我们通过加载模型文件的方法来生成模型文件,比较流行的3D模型文件有OBJ,FBX,da ...
- 从零开始openGL——三、模型加载及鼠标交互实现
前言 在上篇文章中,介绍了基本图形的绘制.这篇博客中将介绍模型的加载.绘制以及鼠标交互的实现. 模型加载 模型存储 要实现模型的读取.绘制,我们首先需要知道模型是如何存储在文件中的. 通常模型是由网格 ...
- 6.Knockout.Js(加载或保存JSON数据)
前言 Knockout可以实现很复杂的客户端交互,但是几乎所有的web应用程序都要和服务器端交换数据(至少为了本地存储需要序列化数据),交换数据最方便的就是使用JSON格式 – 大多数的Ajax应用程 ...
随机推荐
- SpringMvc的传递参数方式 -- url / requestMapping
在使用spring的项目中,前台传递参数到后台是经常遇到的事, 我们必须熟练掌握一些常用的参数传递方式和注解的使用,废话少说,直接上正文. 1. @requestMapping: 类级别和方法级别的注 ...
- Java后台模拟发送http的get和post请求,并测试
个人学习使用:谨慎参考 1 Client类 import com.thoughtworks.gauge.Step; import com.thoughtworks.gauge.Table; impor ...
- Spring Boot Junit单元测试
http://blog.csdn.net/catoop/article/details/50752964
- 【Python】 linux中python命令的命令行参数
Python命令行参数 原文地址:http://blog.163.com/weak_time/blog/static/25852809120169333247925/ Python的命令行参数,提供了 ...
- 【Python】 压缩文件处理 zipfile & tarfile
[zipfile] 虽然叫zipfile,但是除了zip之外,rar,war,jar这些压缩(或者打包)文件格式也都可以处理. zipfile模块常用的一些操作和方法: is_zipfile(file ...
- 一、Python安装与Pycharm使用入门
一.安装Python 1.Linux下安装 一般系统默认已安装2.6.6版本,升级成2.7版本, 但 2.6 不能删除,因为系统对它有依赖,epel源里最新的也是2.6版本,所以以源代码的方式安装2. ...
- Java注解(2)-注解处理器(运行时|RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
如果没有用来读取注解的工具,那注解将基本没有任何作用,它也不会比注释更有用.读取注解的工具叫作注解处理器.Java提供了两种方式来处理注解:第一种是利用运行时反射机制:另一种是使用Java提供的API ...
- C语言结构体作业
一.PTA实验作业 题目1:6-3 结构体数组中查找指定编号人员 1. 本题PTA提交列表 2. 设计思路 定义一个结构体指针*p for i=0 to i=7 如果std+i的编号与输入的编号一样 ...
- 一起happy--C++小组Alpha版本发布说明
1 功能介绍 该PC端APP,是一个同行者的信息搜索平台,旨在为喜欢游玩,但是身边同学朋友时间冲突,想找人结伴的年轻人提供一个检索平台,让他们尽量能够快速便捷的寻找合适同行者.该APP有登录.注册.主 ...
- Django 模版语法
一.简介 模版是纯文本文件.它可以产生任何基于文本的的格式(HTML,XML,CSV等等). 模版包括在使用时会被值替换掉的 变量,和控制模版逻辑的 标签. {% extends "base ...
