ES5-ES6-ES7_class类
传统创建对象模板的方式
JavaScript 语言中,生成实例对象的传统方法是通过构造函数
//JavaScript 语言中,生成实例对象的传统方法是通过构造函数
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point.prototype.toString = function () {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
};
var p = new Point(1, 2);
console.log(p.toString()); //(1, 2)
ES6创建对象模板的方式Class
ES6 提供了更接近传统语言的写法,引入了 Class(类)这个概念,作为对象的模板。通过class关键字,可以定义类
基本上,ES6 的class可以看作只是一个语法糖,它的绝大部分功能,ES5 都可以做到,新的class写法只是让对象原型的写法更加清晰、更像面向对象编程的语法而已
ES6 的类,完全可以看作构造函数的另一种写法
//ES6 提供了更接近传统语言的写法,引入了 Class(类)这个概念,作为对象的模板。通过class关键字,可以定义类
class Point {
constructor(x, y) { //构造方法,而this关键字则代表实例对象
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
} //toString方法。注意,定义“类”的方法的时候,前面不需要加上function这个关键字,直接把函数定义放进去了就可以了。
// 另外,方法之间不需要逗号分隔,加了会报错
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
} const p = new Point(1,2); //类必须使用new调用,否则会报错。这是它跟普通构造函数的一个主要区别,后者不用new也可以执行
console.log(p.toString()); //(1, 2) console.log(typeof Point) //function,类的数据类型就是函数,类本身就指向构造函数
console.log(Point === Point.prototype.constructor) // true
constructor 方法
constructor方法是类的默认方法,通过new命令生成对象实例时,自动调用该方法。一个类必须有constructor方法,如果没有显式定义,一个空的constructor方法会被默认添加。
//定义了一个空的类Point,JavaScript 引擎会自动为它添加一个空的constructor方法
class Point {
} // 等同于
class Point {
constructor() {}
}
class Foo {
constructor() { //constructor方法默认返回实例对象(即this),完全可以指定返回另外一个对象
return Object.create(null); //constructor函数返回一个全新的对象,结果导致实例对象不是Foo类的实例
}
}
console.log(new Foo() instanceof Foo); // false
类的实例对象
根据类创建实例对象——类必须使用new调用,否则会报错。这是它跟普通构造函数的一个主要区别,后者不用new也可以执行
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
const p = new Point(1,2); //类必须使用new调用,否则会报错。这是它跟普通构造函数的一个主要区别,后者不用new也可以执行
console.log(p.toString()); //(1, 2)
实例对象属性与原型对象属性——实例的属性除非显式定义在其本身(即定义在this对象上),否则都是定义在原型上(即定义在class上)
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
const p = new Point(1,2);
console.log(p.toString()); //(1, 2)
//x和y都是实例对象point自身的属性(因为定义在this变量上)不是原型对象的,所以hasOwnProperty方法返回true
console.log(Point.hasOwnProperty('x')) // true
console.log(Point.hasOwnProperty('y'))// true
console.log(Point.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('y'))// false
//toString是原型对象的属性(因为定义在Point类上),不是实例对象的,所以hasOwnProperty方法返回false
console.log(Point.hasOwnProperty('toString')) // false
console.log(Point.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('toString')) // true
通过__proto__属性为‘类’添加方法
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
var p1 = new Point(2,3);
var p2 = new Point(3,2);
//p1和p2都是Point的实例,它们的原型都是Point.prototype,所以__proto__属性是相等的
console.log(p1.__proto__ === p2.__proto__) //true
//可以通过实例的__proto__属性为“类”添加方法
p1.__proto__.printName = function () {
return 'Oops'
};
console.log(p1.printName()) // "Oops"
console.log(p2.printName()) // "Oops"
var p3 = new Point(4,2);
console.log(p3.printName()) // "Oops"
//p1的原型上添加了一个printName方法,由于p1的原型就是p2的原型,因此p2也可以调用这个方法。
// 而且,此后新建的实例p3也可以调用这个方法。
// 这意味着,使用实例的__proto__属性改写原型,必须相当谨慎,不推荐使用,因为这会改变“类”的原始定义,影响到所有实例
立即执行的类的实例
let person = new class {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
sayName() {
console.log(this.name);
}
}('张三');
person.sayName(); // "张三"
使用表达式的形式定义类
const MyClass = class Me {
getClassName() {
return Me.name;
}
};
//使用表达式定义了一个类。需要注意的是,这个类的名字是MyClass而不是Me,Me只在 Class 的内部代码可用,指代当前类
const p = new MyClass();
console.log(p.getClassName()); //Me,Me只在 Class 内部有定义。
变量提升——类不存在变量提升(hoist), ES6 不会把类的声明提升到代码头部。这种规定的原因与下文要提到的继承有关,必须保证子类在父类之后定义
//Foo类使用在前,定义在后,这样会报错,
// 因为 ES6 不会把类的声明提升到代码头部。这种规定的原因与下文要提到的继承有关,必须保证子类在父类之后定
new Foo(); // ReferenceError: Foo is not defined
class Foo {}
私有方法
私有方法是常见需求,但 ES6 不提供,只能通过变通方法模拟实现
私有方法模拟实现方式一——在命名上加以区别,方法前面的下划线,表示这是一个只限于内部使用的私有方法。但是,这种命名是不保险的,在类的外部,还是可以调用到这个方法
class Widget {
foo (baz) { // 公有方法
this._bar(baz);
}
_bar(baz) { // 私有方法,_bar方法前面的下划线,表示这是一个只限于内部使用的私有方法
return this.snaf = baz;
}
}
const w = new Widget();
console.log(w._bar('fffffff')) //fffffff,这种命名是不保险的,在类的外部,还是可以调用到这个方法
私有方法模拟实现方式二————将私有方法移出模块,因为模块内部的所有方法都是对外可见的
class Widget {
foo (baz) {
bar.call(this, baz);
}
}
function bar(baz) {
return this.snaf = baz;
}
//foo是公有方法,内部调用了bar.call(this, baz)。这使得bar实际上成为了当前模块的私有方法
const w = new Widget();
console.log(w.foo('fffff'))
静态方法
静态方法在方法名前面添加一个叫static的修饰符来修饰,那么这个方法就是静态方法,可以直接通过类名来调用,不需要通过创建实例对象来调用
class Foo {
static classMethod () {
return 'hello static'
}
}
console.log(Foo.classMethod())// hello static
如果通过实例对象来调用静态方法会报错
class Foo {
static classMethod () {
return 'hello static'
}
}
var f = new Foo()
console.log(f.classMethod())//报错:f.classMethod is not a function
Class的继承
Class 可以通过extends关键字实现继承,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多。
子类必须在constructor方法中调用super方法,否则新建实例时会报错。这是因为子类没有自己的this对象,而是继承父类的this对象,然后对其进行加工。如果不调用super方法,子类就得不到this对象
ES6 的继承机制实质是先创造父类的实例对象this(所以必须先调用super方法),然后再用子类的构造函数修改this
如果子类没有定义constructor方法,这个方法会被默认添加,也就是说,不管有没有显式定义,任何一个子类都有constructor方法。
另一个需要注意的地方是,在子类的构造函数中,只有调用super之后,才可以使用this关键字,否则会报错。这是因为子类实例的构建,是基于对父类实例加工,只有super方法才能返回父类实例
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
//this.color = color; //在调用super之前,this是不存在的,所以会报错
super(x, y); // 调用父类的constructor(x, y),
this.color = color;
}
toString() {
return this.color + ' ' + super.toString(); // 调用父类的toString()
}
}
const cp = new ColorPoint(1,2,'red');
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(ColorPoint)); //[Function: Point]
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(ColorPoint) === Point); //true
通过继承创建的实例对象所属的类的实例——实例对象cp同时是ColorPoint和Point两个类的实例
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
//this.color = color; //在调用super之前,this是不存在的,所以会报错
super(x, y); // 调用父类的constructor(x, y),
this.color = color;
}
toString() {
return this.color + ' ' + super.toString(); // 调用父类的toString()
}
}
const cp = new ColorPoint(1,2,'red');
console.log(cp instanceof Point); // true
console.log(cp instanceof ColorPoint); // true
Object.getPrototypeOf()——Object.getPrototypeOf方法可以用来从子类上获取父类,可以使用这个方法判断,一个类是否继承了另一个类
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
//this.color = color; //在调用super之前,this是不存在的,所以会报错
super(x, y); // 调用父类的constructor(x, y),
this.color = color;
}
toString() {
return this.color + ' ' + super.toString(); // 调用父类的toString()
}
}
const cp = new ColorPoint(1,2,'red');
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(ColorPoint)); //[Function: Point]
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(ColorPoint) === Point); //true
super关键字
super作为函数调用时,代表父类的构造函数。ES6 要求,子类的构造函数必须执行一次super函数
super虽然代表了父类的构造函数,但是返回的是子类的实例,即super内部的this指的是子类,因此super()在这里相当于父类.prototype.constructor.call(this)。
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
console.log(new.target.name);
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
//子类的构造函数之中的super(),代表调用父类的构造函数。这是必须的,否则 JavaScript 引擎会报错
super(x, y); // 调用父类的constructor(x, y),
this.color = color;
}
toString() {
//super(); //SyntaxError: 'super' keyword unexpected here
// 作为函数时,super()只能用在子类的构造函数之中,用在其他地方就会报错
return this.color + ' ' + super.toString(); // 调用父类的toString()
}
}
const cp = new ColorPoint(1,2,'red'); //ColorPoint,创建子类对象的时候,this指向的是子类
console.log(cp.toString()) // red (1, 2)
super作为对象时,在普通方法中,指向父类的原型对象;在静态方法中,指向父类
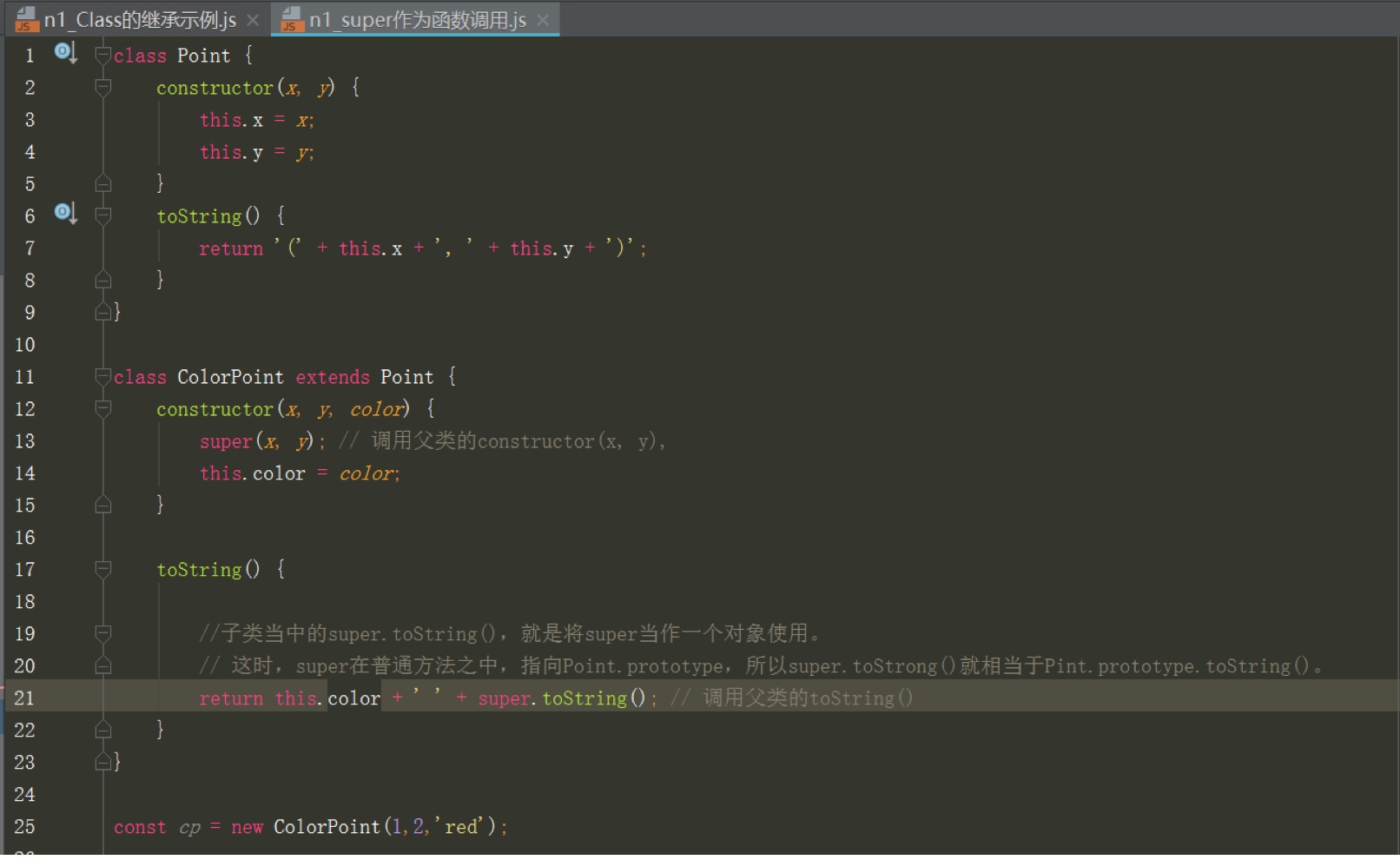
由于super指向父类的原型对象,所以定义在父类实例上的方法或属性,是无法通过super调用的
如果属性定义在父类的原型对象上,super就可以取到
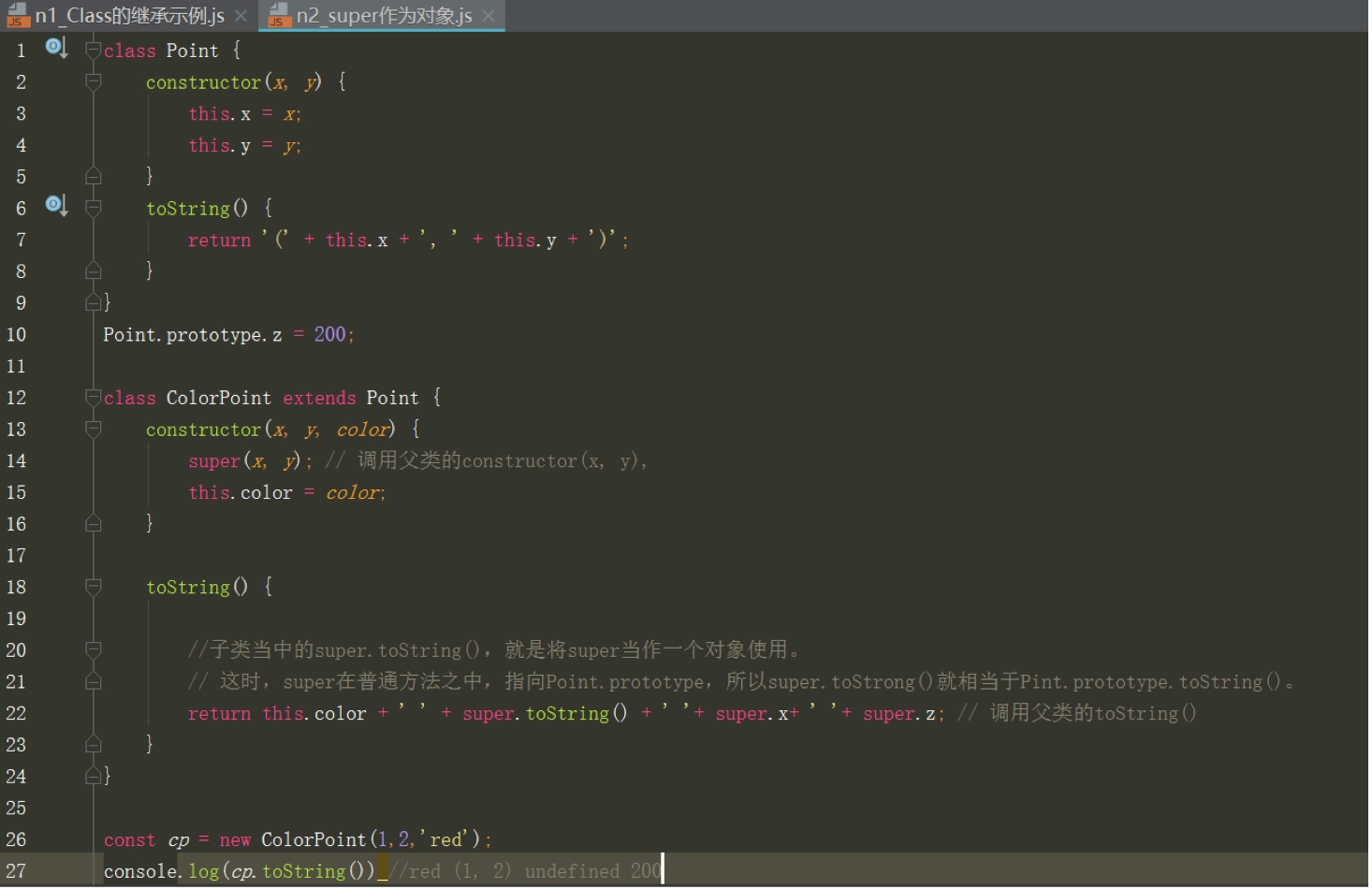
通过super调用父类的方法时,super会绑定子类的this
class Point {
constructor() {
this.x = 1;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ')';
}
}
Point.prototype.z = 200;
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor() {
super();
this.x = 3
}
toString() {
// 调用父类的toString(),通过super调用父类的方法时,super会绑定子类的this
return super.toString();
}
}
const cp = new ColorPoint();
console.log(cp.toString()) //(3)
ES5-ES6-ES7_class类的更多相关文章
- [js高手之路] es6系列教程 - new.target属性与es5改造es6的类语法
es5的构造函数前面如果不用new调用,this指向window,对象的属性就得不到值了,所以以前我们都要在构造函数中通过判断this是否使用了new关键字来确保普通的函数调用方式都能让对象复制到属性 ...
- Atitit js版本es5 es6新特性
Atitit js版本es5 es6新特性 Es5( es5 其实就是adobe action script的标准化)1 es6新特性1 Es5( es5 其实就是adobe action scrip ...
- 简述ES5 ES6
很久前的某一天,一位大神问我,你知道ES6相对于ES5有什么改进吗? 我一脸懵逼的反问,那个啥,啥是ES5.ES6啊. 不得不承认与大神之间的差距,回来深思了这个问题,结合以前的知识,算是有了点眉目. ...
- Es6 的类(class)
首先根据es5的类(原型对象)的基本点做参照. 序号 基本点 es5 >es6 1 实例属性(方法) √ √ 2 原型属性(方法) 或 公共属性(方法) √ √ 3 es5的私有变量 或 私有属 ...
- Atitit js es5 es6新特性 attilax总结
Atitit js es5 es6新特性 attilax总结 1.1. JavaScript发展时间轴:1 1.2. 以下是ES6排名前十的最佳特性列表(排名不分先后):1 1.3. Es6 支持情况 ...
- ES6入门——类的概念
1.Class的基本用法 概述 JavaScript语言的传统方式是通过构造函数,定义并生成新对象.这种写法和传统的面向对象语言差异很大,下面是一个例子: function Point(x, y) { ...
- JavaScript es6 class类的理解。
本着互联网的分享精神,在本篇文章我将会把我对JavaScript es6 class类的理解分享给大家. JavaScript 类主要是 JavaScript 现有的基于原型的继承的语法糖. 类语法 ...
- 【转】React Native中ES5 ES6写法对照
很多React Native的初学者都被ES6的问题迷惑:各路大神都建议我们直接学习ES6的语法(class Foo extends React.Component),然而网上搜到的很多教程和例子都是 ...
- ES6 | class类的基本语法总结
类和模块的内部,默认就是严格模式,所以不需要使用use strict指定运行模式.只要你的代码写在类或模块之中,就只有严格模式可用. 考虑到未来所有的代码,其实都是运行在模块之中,所以 ES6 实际上 ...
- es6 --- class 类的继承使用
传统的javascript中只有对象,没有类的概念.它是基于原型的面向对象语言.原型对象特点就是将自身的属性共享给新对象.这样的写法相对于其它传统面向对象语言来讲,很有一种独树一帜的感脚!非常容易让人 ...
随机推荐
- JDBC&Hibernate
当数据库有大量用户来访问要采取什么技术解决 可以采用连接池: 什么是ORM 对象关系映射(Object Relational Mapping 简称ORM)是一种为了解决面向对象与面向关系数据库存在的互 ...
- MyBatis:事务回滚
事务的隔离级别:DEFAULT.READ_UNCOMMITED.READ_COMMITTED.REPEATABLE_READ.SERIALIZABLE 事务的传播行为:REQUIRED.SUPPORT ...
- java过滤器(简化认证)
最近在看过滤器,刚刚实现了过滤器的简化认证功能: 使用过滤器简化认证: 在Web应用程序中,过滤器的一个关键用例是保护应用程序不被未授权的用户访问.为跨国部件公司开发的客户支持应用程序使用了一种非常原 ...
- linux 单引号,双引号,反引号
单引号 目的: 为了保护文字不被转换.除了他本身. 就是说除去单引号外, 在单引号内的所有文字都是原样输出. 1. [root@jszwl161 SP49EP9]# echo '$*><! ...
- Android Navigation使用
简介 Navigation导航编辑器旨在简化Android开发中导航的实现,可以帮助我们很好的处理Activity和fragment之间通过FragmentTransaction交互的复杂性,也可以很 ...
- 三问助你Fundebug
译者按: Debug也要三省吾身! 原文: Three Questions About Each Bug You Find 译者: Fundebug 为了保证可读性,本文采用意译而非直译.另外,本文版 ...
- mysql date_format()函数
DATE_FORMAT(DATE,FORMAT)函数 占位符 说明 %a 缩写的星期几(Sun.....Sat) %b 缩写的月份(Jan.....Dec) %c 数字形式的月份(1.......1 ...
- hihoCoder编程练习赛49
题目1 : 相似颜色 时间限制:10000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 在CSS中我们可以用井号(#)加6位十六进制数表示一种颜色,例如#000000是黑色,#ff0000 ...
- IO学习一(File类)
File类 1.凡是与输入.输出相关的类.接口都定义在java.io包下 2.File有构造器来创建对象,此对象对应着一个文件或文件目录 支持文件类型:.txt .avi .doc .jpg .ppt ...
- 2018-11-23 手工翻译Vue.js源码:尝试重命名标识符与文本
续前文: 手工翻译Vue.js源码第一步:14个文件重命名 对core/instance/索引中的变量, 方法进行重命名如下(题图): import { 混入初始化 } from './初始化' im ...
